Agriculture. Agriculture. Population. The Basis of Civilization
|
|
|
- Ralf Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Agriculture The Basis of Civilization 1 Developed separately in three different parts of the world South-west Asia (Middle East) China Mesoamerica A major alteration of the ecosystem. Could provide much greater quantities of food. Made civilization possible. Agriculture 2 Population 10,000 years ago the human population was about 4 million; 5,000 years ago it was maybe 5 million. Then with agriculture, it began to double every millennium to reach 50 million by 1000 BCE. Then it grew to 100 million by 500 BCE. Then 200 million by 200 CE. 3
2 Irreversible Process The Agricultural Revolution: A transition from hunting and gathering that took place over thousands of years. Impossible to reverse. Much larger population could not be fed. All of the methods of agriculture were in use (somewhere) before 10,000 BCE. The revolution is the intensification of these methods. 4 Why was Agriculture Adopted? Agriculture was not easier than hunting & gathering. Much more effort was involved in clearing land, sowing, tending, and harvesting, and looking after domesticated animals. Food grown was not clearly more nutritious. Wild grains were often much more nutritious than cultivated ones. No greater security was guaranteed. Now humans had to depend on a small range of plants & animals. What it does is provide more food from less land. 5 Land Required to Feed One Person By hunting and gathering, 10 km 2 By dry farming (farming without irrigation), 0.5 km 2 By wet farming (farming with irrigation), 0.1 km H-G Dry Wet Land 6
3 Old Views: Farming was obviously better: The advantages of agriculture were so obvious that as soon as it was discovered, all hunting and gathering ceased. Climate change forced the change to agriculture: But climates had changed before without a change in hunting and gathering. Moreover, the climate changes in SW Asia, China, and Mesoamerica would have been very different from each other. 7 Best Explanation: Increasing population pressure. Efforts made by hunting and gathering groups to limit population were not always successful. Usual solution: Excess population migrated. Eventually all suitable areas were occupied. World population of 4 million reached 10,000 years ago was perhaps the maximum sustainable on hunting and gathering. Once people turned to agriculture to get enough food, there was a surplus, the population continued to rise, and then there was no turning back. 8 Different Developments Each major area of the world where agriculture developed independently did it differently. With profound consequences for world history. Consider each in turn: 1. South-West Asia Beginning in the Middle East. More specifically in the Fertile Crescent. 2. China Beginning in the northern plains. 3. Mesoamerica Earliest evidence from Mexico. 9
4 The first area to transform to agriculture. The so called fertile crescent. A region corresponding to parts of present day Iraq, Iran, Israel, Palestine, Syria, Egypt, and south Anatolia (part of Turkey). South-West Asia 10 Wild Plants Available The region was rich in naturally occurring wild, edible plants. Hunters and gatherers had lived there for thousands of years, subsisting on some of the wild plants available. Wild progenitors of domesticated crops include: Wheat: from emmer and einkorn. Emmer: limited distribution. Einkorn in Anatolia. Barley: from a wild form of itself. Wild barley is widely distributed. Legumes, wild forms exist of: lentils, chickpeas, peas. Chickpeas in Anatolia. 11 Cultivation Wheat, the main crop, began as an edible wild grass, emmer, with seeds light enough to spread on their own in the wind and therefore self-cultivate. Emmer could be cultivated, however. Eventually a mutation arose, bread wheat,, with seeds so heavy that it had to be cultivated (but was much more nutritious). Emmer Bread wheat 12
5 Domestication of Wild Plants Emmer and wild barley are easily cultivated. Modern wheats,, peas, and lentils stem from only a very limited part of the wild stock. Domestication of plants only began because a small number of groups of people were forced to exploit less favourable resources. Early cultivated plants were well adapted to growing in disturbed and open sites, had relatively big seeds, germinated easily, grew quickly, and survived dry summers. Harvesting would naturally select seeds with less effective dispersal mechanisms (heavier seeds). 13 Domestication of Wild Animals First was the dog. Aborigines of Australia and New Guinea domesticaled dogs, perhaps before anyone else. Mainly for companionship and possible protection. Sheep were first domestication for economic reasons. Probably done before the domestication of crops. Sheep don t t compete directly with humans for food. They convert otherwise unusable grasses into meat. Goats and cattle do the same. Pigs do compete with humans and were not domesticated until 6500 BCE at the earliest. 14 When food production could support a larger, permanent population in a single area, towns emerged. By 6500 BC, Jericho, a walled town of ten acres, had developed. Towns 15
6 Basis of Settled Life Pottery was invented about 6000 BC. All the major crops and domesticated animals were fixed. No new ones for thousands of years. This was the basis of the spread of agriculture elsewhere. This way of life was based on growing wheat and barley and keeping herds of sheep, goats and later cattle. All the crops (except a type of einkorn) used in Europe came from South West Asia. Also the animals came from the same region. 16 Spread of Agriculture into Europe Movement of agriculture into central and NW Europe took another 3 millennia after its spread to Greece, because of different climate and soils. Elsewhere hunting and gathering continued. 17 Farming Techniques Swidden system slash and burn This was the basic system for clearing land and assuring fertile soil. It involved clearing climax temperate forests with stone axes and burning. Crops were planted in ash-enriched soil until yields began to fall. Then a new area was cleared and the abandoned area was allowed to revert to grass, awaiting further clearance decades later. 18
7 European Crops Different crops were grown in a northern climate: Oats and rye. Mediterranean areas grew crops such as: Olives, figs, grapes. Of these, only grapes moved north. 19 Later Domesticated Animals The dromedary and the camel were domesticated between BC. 20 Later Domesticated Animals, 2 The horse, was domesticated shortly after 3000 BC. The horse revolutionized warfare. For thousands of years the Near East, China, India, and Europe were heavily influenced by waves of invading nomadic horsemen (e.g. Huns and Mongols) descending on settled societies. 21
8 This was the second area to develop agriculture. China 22 China Originally farming was established in the semi-arid loess plains of the north. Loess is a wind-borne soil of fine particles, easily worked. Soils were thick and had high mineral content. Most rain falls in the summer, making cultivation possible. Crops: Millet food for the masses. Rice (grown as a dry crop) food for the elite. Later rice was adapted to grow further south in wet paddy fields. 23 Main Difference of Chinese Agriculture In the other two regions, a balanced diet was based on a starchy cereal and legumes. In China, until soybeans were cultivated about 1100 BC, the diet was based on seed crops only. 24
9 Mesoamerica Encompassing Guatemala, Belize, some of Honduras, San Salvador, and Mexico. The last area to develop agriculture independently. Evidence comes from highland Mexico, where climate is dry enough to preserve plant remains. 25 Mesoamerica Until 6000 BC, all groups in the area were still hunting and gathering. They hunted rabbit and deer, and harvested nuts, beans, wild grasses, early maize, and squashes. First steps were small garden plots to grow previously wild plants. 30 plants grown for food, dyes, medicines, and containers (gourds). These included chili peppers, tomatoes, avocados, papaya, guava, 5 kinds of squash, gourds, and beans. Pumpkins were originally grown for their seeds until cultivation changed their bitter flesh into a sweet variety. 26 Why was Development Delayed? Lack of suitable animals for domestication. No sheep, goats, or cattle. Hunting animals remained a vital activity. Maize was originally a very small grain. No bigger than a human thumb. For at least 2000 years maize was chewed rather than ground. 27
10 The Development of Maize It is difficult to cross maize with other wild grasses. Not until 2000 BCE were bigger varieties developed. Maize cob sizes at roughly thousandyear intervals starting in 5000 BCE. 28 Why was Development Delayed, contd. For a long time, it was more economical to gather food than to grow it in Mesoamerica. Only around 2000 BC was productivity great enough to support village life. Hence complex societies began to develop 4000 years later in the new world. When Europeans arrived in XVI they found a society comparable to Mesopotamia in 2000 BCE. 29 Importance of Agriculture Agriculture was the most fundamental change in human history. Settled societies for the first time. No longer egalitarian. Specialization within society. Emergence of elites: religious, political, military. The state had the power to direct society. Root cause: Ownership of food. Concept of property. 30
11 Though agriculture takes a greater effort, the output of food is much higher, leading to a surplus. A surplus can be used to support individuals not engaged in food production. The Surplus Ancient Egyptian surplus grain being collected and stored in large urns. From a tomb mural. 31 The Surplus as the Key to Civilization Human history since agriculture has been about the acquisition and distribution of surplus food and its uses. Rising populations placed greater strain on food production. This required a form of government that could support infrastructure for more intensive farming. 32 Infrastructure Example of infrastructure:. Irrigation. Pictured are shadoofs devices to lift water from a river to an irrigation trench. A carving from Nineveh. 33
12 Social Hierarchies The priest class were at top of the elite. They controlled production and distribution to the entire community. 34 The Centre of Urban Life: The Temple Uruk in Mesopotamia. The temple was 225 feet long, 200 feet wide, 40 feet high. Regularly rebuilt, it required huge amounts of labour. The ruins of the Ziggurat, or Temple, at Uruk. 35 Uruk By 3500 BC Uruk was a substantial center with only small settlements around it. By 3000 it had a population of 50,000, and settlements around had fallen from 146 to
13 Sumer By 3000 BCE southern Mesopotamia had become the land of Sumer. Sumer was dominated by 8 cities. 37 Organization of Sumerian Society Organization in cities was largely concerned with managing the food supply: Transportation, storage, re-allocation. The advance of society depended on greater surpluses. More surpluses allowed more people to work outside farming. 38 Organization of Sumerian Society, 2 Concept of property: Who owned the land, the food, the draught animals were now questions that arose. In early settlements, the temple seemed to own everything. E.g. in the temple at Shuruppak,, the temple records accounted for 9,660 donkeys. 39
14 Organization of Sumerian Society, 3 Class structure emerged, in ascending order: Slaves Peasants Craftsmen Administrative, religious & military elite 40 Organization of Sumerian Society, 4 Rivalry led to military conflict. The new importance of warfare and defense led to greater internal control. By 2500 BCE, land was owned by private individuals with large estates. Later, in the Babylonian empire (1800 BCE), there were legally separate classes of nobles, commoners, and slaves. 41 Technological Advances Smelting of copper by 6000 BCE. 42
15 Technological advances, 2 Wheel used for making pottery 4500 BCE. 43 Technological advances, 3 Wheel adapted for vehicles. All these advances required specialists who had to be fed by others. 44 Needed to keep accounts in the temples. First baked tablets with a fully developed script from Uruk. 85% of the 4000 tablets deal with economic matters. Illustrates overwhelming importance of centralized accounts. Writing 45
16 The Nile valley took over the agricultural system of the Near East and adapted it. This area had been occupied for 20,000 years before by hunting and gathering groups. Agriculture based on sheep, cattle and emmer was well established for hundreds of years before farmers moved into the Nile valley. Egypt 46 The annual flood came at right time of year. It was an easier environment than Mesopotamia. Hence large cities did not emerge (less need for management). Two great cities were Memphis and Karnak- Luxor. They were local markets and residences of officials rather than populous cities. Gift of the Nile 47 Indus Valley Settled by farmers moving east from SW Asia about 3500 BCE. Highly stratified society emerged to manage the food surplus. 48
17 Slower process than in Mesopotamia,. Egypt and the Indus valley. Due perhaps to slow development of irrigation system. China A Seed Drill. In China hundreds of years before being introduced in the West. 49 Japan Developed very late in world terms. Dependent on developments in China. Began farming about 1400 BC. Scope of farming limited because ¾ of land unsuitable. Swidden system. Kept population low. Fish a major part of diet. Only when rice became the main basis of subsistence was there substantially higher food production. 50 Americas Settled communities did not emerge until 2000 BCE, due to difficulties in developing better maize. Lacked animals for domestication. Wheel not developed because no animals to pull carts. 51
18 Americas, 2 When better maize developed and food production soared (and population too) large ceremonial centers developed (in Mexico). Required vast amount of human labour. Huge increase in social complexity and organization in the Classic period from AD (when length of corn cob doubled). 52 Americas, 3 Centre was Teotihuacan. In the valley of Mexico, the population 100,000. Had enormous pyramids & plazas. An immense central power and a rigidly organized society. Empire collapsed about 700 AD. Replaced by the military empire of the Toltecs.. And then by the Aztecs, capital in Tenochtitlan (Mexico City). 53 Hawaii These islands were settled comparatively late, so their societies were at a comparatively earlier stage when first visited by Europeans. First settled about 500 AD by Polynesians. Probably no more than 50 original settlers. Brought with them the social structure of Polynesia: hereditary chiefs, religious rituals. This changed as population rose. 54
19 Hawaii, 2 By 1100 all the islands were settled. Villages existed and almost all were on the coasts. The population was about 20,000. Society was still simple and unstratified. Then a rapid rise in the population and expansion of settlement inland occurred. 55 Hawaii, 3 By 1400, all available land had been taken up. This produced major social problems. Previously conflicts were averted by younger sons of chiefs splitting off and setting up their own groups in another location. This was no longer possible. Revolts resulted. These conflicts were cxacerbated by crop failures as more and more marginal land had to be used. Population rose to 300,000 by end of the 18 th century. 56 Hawaiian Solution to Population Problem Individual chiefdoms replaced by a single ruler on each island. These big chiefs drew away from rest of society (married only into families of other chiefs). Enforced tribute to themselves (rather than to the gods). Took over commonly held land. Turned the peasants into tenants. Growing inter-island island warfare until 1795, when islands were conquered and united under a single ruler. Not long afterwards the society began to disintegrate with arrival al of Europeans. 57
20 Same story all over the world Surplus food fed religious and political elite and craftsmen. Redistribution of surplus required extensive control mechanisms. Led to powerful central institutions. Became self-reinforcing as elites grabbed more and more power. Imposed discipline with enforced labour for social projects and then in armies. Egalitarian societies replaced by class structures and huge differences in wealth. 58 Two Great Consequences of Agriculture for Society Civilization Art, architecture Writing, culture in general Philosophy and scientific knowledge All the great achievements Coercion Dictatorships Warfare Forced labour 59
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS. What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things?
 WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies?
 How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT
 GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers. Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming
 Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
The Civilizations of America
 The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations B.C.
 Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations
 Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C
 UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
Mesopotamian History. Chapter 2 Art History. Roxanna Ford 2014
 Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Before Contact with Europeans
 Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies
 Name: Date: Period: Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies Directions : Answer the questions using evidence from the documents provided. Historical Context The Neolithic revolution states
Name: Date: Period: Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies Directions : Answer the questions using evidence from the documents provided. Historical Context The Neolithic revolution states
The earliest written language. BCE The years before the year 0. The worship and belief in many gods. The land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
 Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent BC
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
ADVANCED CITIES: The people who established the world's first civilization around 4000 B.C. in southern Mesopotamia were known as the Sumerians.
 ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
Amazing Mesopotamia. Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography
 Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Unit 3. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C.
 Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia Between Rivers Iraq today Mesopotamia 1 Mesopotamia w Tigris & Euphrates River Valley w Fertile Crescent w 25 miles to 250 miles apart w Flood rich soil for agriculture
Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia Between Rivers Iraq today Mesopotamia 1 Mesopotamia w Tigris & Euphrates River Valley w Fertile Crescent w 25 miles to 250 miles apart w Flood rich soil for agriculture
Early Civilizations of Middle America. Chapter 2, Section 1
 Early Civilizations of Middle America Chapter 2, Section 1 The Mayas and the Aztecs Map pg. 39 What color represents the Mayas? The Aztecs? What are the current day locations? Were the two civilizations
Early Civilizations of Middle America Chapter 2, Section 1 The Mayas and the Aztecs Map pg. 39 What color represents the Mayas? The Aztecs? What are the current day locations? Were the two civilizations
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest
 Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
ANT 202 Wednesday November 19, 2014
 ANT 202 Wednesday November 19, 2014 XII. Civilization A. Basic Concepts B. Theories C. Old World 1. Mesopotamia 2. Egypt D. New World 1. Yucatan a. Formative/Preclassic f. Mississippian A.D. 1000-1500
ANT 202 Wednesday November 19, 2014 XII. Civilization A. Basic Concepts B. Theories C. Old World 1. Mesopotamia 2. Egypt D. New World 1. Yucatan a. Formative/Preclassic f. Mississippian A.D. 1000-1500
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Between what two rivers is Mesopotamia located? What river is associated with Egypt? Why do you think early man settled around rivers?
 Between what two rivers is Mesopotamia located? What river is associated with Egypt? Why do you think early man settled around rivers? World History 1 Mr. Driskell Farmers need their villages near water
Between what two rivers is Mesopotamia located? What river is associated with Egypt? Why do you think early man settled around rivers? World History 1 Mr. Driskell Farmers need their villages near water
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations
 CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
China in the Beginning
 China in the Beginning The fertile river valleys of China allowed villages and towns to flourish along their banks. The most important rivers were the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers which supported agricultural
China in the Beginning The fertile river valleys of China allowed villages and towns to flourish along their banks. The most important rivers were the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers which supported agricultural
The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two AB The code consisted of over 200 acts and their required
The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two AB The code consisted of over 200 acts and their required
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America?
 2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago
 The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers
 Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia. Miss Genovese
 Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Geography of the Fertile Crescent
 Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
Chapter 1. The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C.
 Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
SC06SS Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago?
 PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
How do you explain the distribution of wealth and power in the world today? The Incan Empire
 Goals: Be able to answer Why did Pizarro win the battle of Cajamarca? How can we explain the origins of agriculture? Why did Mediterranean climates facilitate crop domestication? Why did Eurasia have more
Goals: Be able to answer Why did Pizarro win the battle of Cajamarca? How can we explain the origins of agriculture? Why did Mediterranean climates facilitate crop domestication? Why did Eurasia have more
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
North American Native Americans
 North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
GRAINS AND LEGUMES OF THE WORLD
 GRAINS AND LEGUMES OF THE WORLD By: Grains 1. Grains are the seeds or fruits of plants from the grass family, including barley, corn, oats, rice, and wheat. 2. Early agriculture arose with the cultivation
GRAINS AND LEGUMES OF THE WORLD By: Grains 1. Grains are the seeds or fruits of plants from the grass family, including barley, corn, oats, rice, and wheat. 2. Early agriculture arose with the cultivation
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources
 Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta
 Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
MAYANS. The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE.
 MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Ancient Civilizations
 Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Fertile Crescent Empires
 Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The Fertile Crescent and the Promised Land
 Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Social Studies Homework: None. Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad?
 Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
Grade 6 Chapter 6 Social Studies Notes
 Grade 6 Chapter 6 Social Studies Notes Lesson 1 1. The geography of the Americas gave rise to complex cultures. a. They came from northern Asia and followed game across a land bridge to what is now called
Grade 6 Chapter 6 Social Studies Notes Lesson 1 1. The geography of the Americas gave rise to complex cultures. a. They came from northern Asia and followed game across a land bridge to what is now called
5/21/14 CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO
 CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS AP World History PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting
CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS AP World History PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting
UNIT 3 ANCIENT AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS
 Beginnings ANCIENT AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS UNIT 3 Early + Middle Stone Age Late Stone Age in West Africa (15,000 500BC) Development of Agriculture in Ancient Africa Iron Age in Africa Bantu MigraMons Early
Beginnings ANCIENT AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS UNIT 3 Early + Middle Stone Age Late Stone Age in West Africa (15,000 500BC) Development of Agriculture in Ancient Africa Iron Age in Africa Bantu MigraMons Early
NAME DATE CLASS. Paleolithic Europe and the Near East. Willendorf GREECE. Crete Cyprus EGYPT
 NAM DAT CLASS Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers SSNTIAL QUSTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUSTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during
NAM DAT CLASS Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers SSNTIAL QUSTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUSTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during
List any questions that you have pertaining about the Economics Unit we just finished.
 Unit 2: Native American Cultures Do now Beringia Native American Cultures Exit slip The Arrival of Men (worksheet) I can explain the Beringia Land Theory. American Heritage: Native Americans 21:52 By:
Unit 2: Native American Cultures Do now Beringia Native American Cultures Exit slip The Arrival of Men (worksheet) I can explain the Beringia Land Theory. American Heritage: Native Americans 21:52 By:
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell
 World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
How was life along the Yellow River both similar and different from life along the Nile River?
 As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
Vocabulary Builder. netw rks. A. Content Vocabulary. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution
 Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
ANCIENT THE CHINESE STATE
 THE ANCIENT CHINESE STATE CHINESE NEOLITHIC 8000-4500 BC CHINESE NEOLITHIC Village farmers (millet & rice). Distinct difference between northern and southern Neolithic traditions - specifically in the
THE ANCIENT CHINESE STATE CHINESE NEOLITHIC 8000-4500 BC CHINESE NEOLITHIC Village farmers (millet & rice). Distinct difference between northern and southern Neolithic traditions - specifically in the
Chapter 1: From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River-Valley Civilizations, BCE
 Guided Reading 1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, To 600 BCE Name: Period: Chapter 1: From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River-Valley Civilizations, 8000-1500 BCE The principle
Guided Reading 1: Technological and Environmental Transformations, To 600 BCE Name: Period: Chapter 1: From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River-Valley Civilizations, 8000-1500 BCE The principle
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera. 1.) Define: bipedalism, primary source and Paleolithic Age.
 Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
It was during the Neolithic age that farmers emerged and changed the way people lived. This can be seen in Catalhoyuk.
 Mesopotamia The Worlds first cities began as farming villages in the Middle East. As they grew they began to trade with each other. Trade, like farming, became a very important source of wealth. Catalhoyuk
Mesopotamia The Worlds first cities began as farming villages in the Middle East. As they grew they began to trade with each other. Trade, like farming, became a very important source of wealth. Catalhoyuk
1. Introduction enabled
 1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
Seventh Grade Social Studies: Early World History Unit 3: Early Civilizations and the Emergence of Pastoral Peoples ( B.C.E.
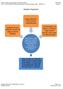 Graphic Organizer Between 4000 and 1000 BCE, larger groups of people began living together in one place in more complex societies with social hierarchies. This was the beginning of civilization. Michigan
Graphic Organizer Between 4000 and 1000 BCE, larger groups of people began living together in one place in more complex societies with social hierarchies. This was the beginning of civilization. Michigan
Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S. By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala
 Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala Geography by: Mia Ayala Here are some facts about Ancient Mesopotamia's geography. Mesopotamia is known as the "fertile crescent"
Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala Geography by: Mia Ayala Here are some facts about Ancient Mesopotamia's geography. Mesopotamia is known as the "fertile crescent"
Unit 1 Packet. c BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1
 Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
WESTERN HEMISPHERE CIVILIZATIONS. Isolation from Eastern Hemisphere
 THE AMERICAS WESTERN HEMISPHERE CIVILIZATIONS Isolation from Eastern Hemisphere c. 250 CE c. 900 CE Heirs of Olmecs Ceremonial center at Kaminaljuyu (held a relationship with Teotihuacan) Large cities
THE AMERICAS WESTERN HEMISPHERE CIVILIZATIONS Isolation from Eastern Hemisphere c. 250 CE c. 900 CE Heirs of Olmecs Ceremonial center at Kaminaljuyu (held a relationship with Teotihuacan) Large cities
Government city-states
 Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
China Before it was China. September 10, 2013
 China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
