How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt?
|
|
|
- Philippa Hines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Nile & Ancient Egypt ICER How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? A wall painting from the tomb of Sennefer, mayor of Thebes and Overseer of the Royal Gardens during the reign of Amenhotep II, BCE. Overview: Ancient Egyptian society Jasted almost 3,000 years. It began with the unification of Egypt under the first pharaoh in 2920 BCE and ended when the Romans conquered the kingdom in 30 BCE. Of special interest to us is the mighty Nile, the longest river in the world, which flowed through this rich and vibrant civilization. This ICER explores the importance of the Nile to the people of Ancient Egypt. The Documents: Document A: Ancient Egypt (map) Document B: The Nile River Flood Cycle (chart) Document C: Transport on the Nile (image) Document D: Field of Reeds (tomb painting) Document E: Hymn to the Nile What does analyze mean? READ everything! F: Background Essay and Map Review for Quiz
2 Background Essay How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? In today's society, it is easy to forget the importance of rivers. Ours is a world of highways and ai rp orts, of supennarkets and shopping malls. When we travel or want food, we don't think "river." When we bathe or get thirsty, we think shower or bottled water. This has not always been the case. In fact, four of the world's most important ancient cultures are known by historians as the "river civilizations." These were Mesopotamia on the Tigris-Euphrates River, China on the Yangtze ("yang-see"), India on the Indus, and Egypt on the Nile. They are called the river civilizations because of the powerful influence a large river system had on the lives of the people. And nowhere was this more true than in the ancient kingdom of Egypt. Perhaps the most stunning fact about Egypt is its age. The first pharaoh began his rule in 2920 BCE, nearly 5,000 years ago. From this early beginning, Egypt has been a land of contrasts, a place of hot, sunny days and cold nights, of crop-laden fields and empty desert. In its early days, Egypt was two distinct kingdoms. To the south was Upper Egypt, where the Nile flows north out of the mountains. To the north was Lower Egypt where the river spreads into a delta before emptying into the Mediterranean. Egyptians also spoke of the "Black Land" and the "Red Land." The Black Land hugged the Nile. The Red Land was the desert just beyond. The Black Land represented life. The Red Land meant danger. For Egyptians, the Nile literally meant the difference between life and death. The source of the Nile was a mystery to the ancient Egyptians. Now we know that one branch, called the Blue Nile, begins in Lake Tana in the highlands of Ethiopia. The other main branch, the White Nile, begins with the waters that flow into and then out of Lake Victoria in Kenya. Every year, when heavy rains fall in central Africa, the tributaries of the Blue and White Nile grow full and flow into the main river. The mother Nile, its waters replenished, then flows north and into Egypt. There, the water spills over its banks and covers the low-lying flood plain. For thousands of years, this flooding cycle has provided a seasonal rhythm for the Egyptian people. The flooding cycle detennined the planting season for farmers. Their main crops were barley and emmer wheat for making bread and beer. People paid their taxes in wheat, and wheat was a main export. Fanners also grew flax for producing fine linen, and harvested papyrus from the marshy areas along the river and in the delta. Irrigation channels from the Nile flowed to smaller gardens where fanners grew vegetables such as onions, beans, and cucumbers. Date, fig, and pomegranate trees were tended along the river. While fruits, grains, and vegetables might sound like the makings of a healthful diet, one ingredient of Egyptian meals was definitely not good: desert sand. Sand was everywhere, easily settling into the dough for flat bread, a basic food eaten by everyone. Once the ever-present sand ground down a person's teeth, infection and pain set in. Thus, dental disease became a common medical problem in Ancient Egypt. Let's time-travel to this fertile yet hostile land where life revolved around the ebb and flow of a single waterway. On the following pages are five documents that provide a glimpse of Egyptian life thousands of years ago. As you read the documents, think about how the Nile gave rise to a civilization that, all this time later, continues to fascinate. Then answer the question: How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt?
3 Document A Source: Map created from various sources. Egypt around 1500 BCE Western Desert eakhetaten Eastern Desert Valley of the Kings. ' lllebes UPPER EGYPT Edfu w+e NUBIA 0 SO ID0111Ut1 0 SO 100 kltomotm D Fertile Nile V,dlq, Important scl11cmcntlcity
4 Document A Analysis: 1. Why is the delta region to the north called "Lower Egypt" and the southern region called "Upper Egypt" Due to the Nile current - it flows North to the Mediterranean Sea. (Think Upper is the beginning of the Nile, and Lower is the end of the Nile.) 2. What makes the Nile River Valley attractive for settlement? Fresh water and fertile soil (silt) for farming and livestock. Protection from the deserts. Access to trade using the Nile and seas. Geography EQ: How does geography (the Nile River) influence the way people live, move, and define regions? LIVE: water for survival, fish, sewage system, mud for bricks for homes, water for crop irrigation MOVE: boats - water highway for trade and travel DEFINE REGIONS: Upper and Lower Egypt based on the current of the Nile, desert = Red Lamd / silt (fertile soil) = Black Land
5 Document B Source: Chart adapted from Katherine Hinds, Life in Ancient Egypt: The Countryside, Marshall Cavendish Benchmark, The Nile River Flood Cycle Akhet (flood season) Mid-June to mid-october Fields in the Nile floodplain covered in water and fertilized by a new batch of silt. Time when many farmers worked off their public-labor tax, doing jobs like canal repair or quarrying. Peret (planting & growing season) Mid-October to mid-february Waters receded but Nile high enough to fill irrigation canals; crops planted and tended. Shemu (harvest season) Mid-February to mid-june Crops in the Lower Nile harvested and sent to market. Note: Average rainfall, historically and today, has remained about the same. The Nile delta receives about four inches per year. The Nile Valley south of Cairo and Giza receives less than one inch. In comparison, Atlanta, Georgia, gets about 50 inches of rain annually and Phoenix, Arizona, about eight inches. Document B Analysis: 1. How did Egypt's geography affect their farming methods and daily life? The Nile seasons told farmers what jobs to do during that part of the year - planting, harvesting, or working for the pharaoh on building projects. It affected every day life because it could bring surplus and happiness or destruction, flooding, and starvation. 2. The population of Egypt was probably about one million, 95% were farmers. According to the chart, when were farmers busiest? When would this large work force of farmers be available to work on government projects, like building palaces and tombs? Farmers were busiest during Shemu or harvest. They had time to work for the pharaoh during the flood season or Akhet. Geography EQ: How does geography (the Nile River) influence the way people live, move, and define regions? LIVE: jobs/work, flooding, rainfall, irrigation, food, etc. MOVE: DEFINE REGIONS:
6 DocumentC Source: Illustration by Oliver Frey in Living in Ancient Egypt, Norman Bancroft Hunl, editor, Thalamus Publlshlng, Note: The Nile River flows south to north against a prevailing northerly wind. In ancient times, boats traveling upstream against the Nile current used a sail or rowers or both. Boats traveling down stream to the north often just floated with the help of steering oars. The Nile current was about four knots (4 mph) during flood season. lt slowed to a sluggish one knot (1 mph) during the rest of the year. Document C Analysis: 1. What technology did ancient Egyptians use to help them move on the Nile? boats/barges 2. How can you travel in both directions on the Nile? with the current to the North or downstream, and with a sail and the wind upstream 3. What role do you think trade played in Egyptian civilization? provided money and contact with other cultures Geography EQ: How does geography (the Nile River) influence the way people live, move, and define regions? LIVE: wealth from trade, need to know how to swim MOVE: transport stone for building and goods for trade, general travel and trade DEFINE REGIONS:
7 Document D Source: Painting from the tomb of a tradesman named Sennedjem, who lived sometime between 1307 and 1196 BCE. Note: Heaven in Ancient Egypt was a paradise called the Field of Reeds, shown in this tomb painting. Those whose heart had the correct weight at death could, after a long journey, live in the Field of Reeds forever. The Field of Reeds was believed to be somewhere in the east, near the rising sun. Top: The sun god, Ra, traveling across the sky in his boat. Baboons are shown worshipping Ra. Bottom panels: Date palms and ornamental plants Border and Channels: The Nile River and irrigation canals Middle panels: Harvesting emmer wheat; harvesting flax to weave into linen cloth
8 Document D Analysis: 1. The middle panels of this tomb painting show the deceased man and his wife engaged in various activities. What are they doing? making wheat and clothes from the crops they harvested 2. What would disappear from this picture of paradise if the Nile weren't present? EVERYTHING in their afterlife! Also, the sun god Ra would not be able to move the sun around or transport things in the Land of the Dead. Geography EQ: How does geography (the Nile River) influence the way people live, move, and define regions? LIVE: it influenced their religion and afterlife as well MOVE: DEFINE REGIONS:
9 Document E Source: From the song "Hymn to the Nile; circa 2100 BCE. Hail to you, oh Nile, spring from the ground, come to keep the land alive... who floods the fields that Ra [the sun god] has created to make all the animals live... who produces barley and makes wheat grow, that the temples might be in festival. If he is sluggish, noses suffocate, everyone is impoverished... If he rises, the land is in exultation, and everyone is in joy. II I II I 11 Document E Analysis: 1. What is a hymn? song of praise, usually to a god (religious) 2. According to the "Hymn to the Nile," why do the Egyptian people praise the river? Because of all the blessing it provides them with - food, water for animals, festivals, etc. Geography EQ: How does geography (the Nile River) influence the way people live, move, and define regions? LIVE: influenced their religion and gods - prayed to the Nile god and thought it was that important MOVE: DEFINE REGIONS:
10
11 Name: Date: Period # History: Period # English: World History 7 Geography EQ/TDA Writing Prompt: EGYPT QUESTION: How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? Your response should follow ICER format. Criteria Answer 1: LIVED, MOVED, OR DEFINED REGIONS Citation Explanation Answer 2: LIVED, MOVED, OR DEFINED REGIONS A clear and detailed explanation that supports the answer is provided; the explanation is on topic and is at least 2-3 sentences in length. The answer is strong and clearly explains how geography influences the way people live. Evidence that strongly supports the answer is and is cited correctly is provided. An explanation that somewhat supports the answer is provided. Explanation is somewhat detailed and meets minimum requirements. The answer is strong and clearly explains how geography influences the way people move. The answer is somewhat strong and/or somewhat explains how geography influences the way people live. Evidence that somewhat clearly supports the answer and/or is not correctly cited is provided. An explanation that does not clearly or effectively support the answer and/or does not meet the minimum requirement is provided. The answer is somewhat strong and/or somewhat explains how geography influences the way people move. An answer was not referenced, and/or barely explains how geography influences the way people live. Evidence is not provided, or the evidence provided is does not make an accurate connection with the answer. An explanation is not provided, or the explanation provided is off topic and does not make an accurate connection with the answer. An answer was not referenced, and/or barely explains how geography influences the way people move. Citation Evidence that strongly supports the answer is and is cited correctly is provided. Evidence that somewhat clearly supports the answer and/or is not correctly cited is provided. An explanation that does not clearly or effectively support the answer and/or does not meet the minimum requirement is provided. Evidence is not provided, or the evidence provided is does not make an accurate connection with the answer. An explanation is not provided, or the explanation provided is off topic and does not make an accurate connection with the answer. Explanation A clear and detailed explanation that supports the answer is provided; the explanation is on topic and is at least 2-3 sentences in length. An explanation that somewhat supports the answer is provided. Explanation is somewhat detailed and meets minimum requirements. Comments /20
12 What type of writing is this? TDA (text dependent analysis) Where can you find ideas/notes to help you? HERE! all the documents you analyzed What is the question I need to answer in writing? How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? What civilization should my explanations refer to? Egypt OUTLINE the information you could use here. Thesis:The Nile River influenced the way people and in ancient Egypt. LIVE Answer: Document I will use to support my answer: Explanation: MOVE Answer: Document I will use to support my answer: Explanation: DEFINE REGIONS Answer: Document I will use to support my answer: Explanation:
13 Name: Date: Period # History: Period # English: World History 7 Prompt / Question ICER Essay Graphic Organizer for an Essay with Two Examples 1. Answer the question (*re-state entire question!!!!!) 2. Pick two points for thesis (main topics your essay will cover) Point 1 Point 2 Combine step 3 and step 4 to create your thesis. *Remember to include the article title AND author!* Thesis = Answer + Two Points Introductory Paragraph 3. Thesis (1 sentence) Write a broad (general) statement about the topic of the essay. Do NOT include the same words from your thesis! 4. Broad statement (1 sentence) REMEMBER When you write your introductory paragraph, the order of the sentences is: 1 st : Broad statement 2 nd : Thesis
14 I Introduce (Transition + Topic sentence for point 1) ICER Body Paragraph 1 C Cite (A quote from the text that supports point 1) E Explain (In AT LEAST 3 SENTENCES, explain how/why the quote you just gave supports the answer) R Re-state (Transition + Wrapup the paragraph)
15 I Introduce (Transition + Topic sentence for point 2) ICER Body Paragraph 2 C Cite (A quote from the text that supports point 2) E Explain (In AT LEAST 3 SENTENCES, explain how/why the quote you just gave supports the answer) R Re-state (Transition + Wrapup the paragraph)
16 SENTENCE 1: Transition + Re-state thesis Concluding Paragraph SENTENCE 2: Re-state main points SENTENCE 3+ Memorable end
How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt?
 The Nile & Ancient Egypt ICER How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? A wall painting from the tomb of Sennefer, mayor of Thebes and Overseer of the Royal Gardens during the reign of Amenhotep
The Nile & Ancient Egypt ICER How did the Nile River influence life in ancient Egypt? A wall painting from the tomb of Sennefer, mayor of Thebes and Overseer of the Royal Gardens during the reign of Amenhotep
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest
 Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Chapter 4 Section 1- Egypt Under the Pharaohs. Titles Notes QCIPL. - The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles)
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL I) The Nile River Valley A) The World s Longest River The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles) it flows from the south in modern
Chapter 4 Section 1 Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL I) The Nile River Valley A) The World s Longest River The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles) it flows from the south in modern
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers. Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
The earliest written language. BCE The years before the year 0. The worship and belief in many gods. The land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
 Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Chapter 4 Ancient Egypt
 Chapter 4 Ancient Egypt People settled in Nile River Valley of Egypt around 3200 B.C. Water, fertile land and geography allowed the Egyptians to become rich, powerful, and unified. Egypt is referred to
Chapter 4 Ancient Egypt People settled in Nile River Valley of Egypt around 3200 B.C. Water, fertile land and geography allowed the Egyptians to become rich, powerful, and unified. Egypt is referred to
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT
 GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
How was life along the Yellow River both similar and different from life along the Nile River?
 As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
City-States in Mesopotamia
 Name CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more
Name CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia
 Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia Imaginealifedirectlydefinedbyroughlyathirdofayearofrainandflooding.Thepeopleof ancientmesopotamia,egypt,andthekingdomofkushalllivedthatlife:theireconomies, power,andsimplesurvivaldependedontheseasonsoftheriversthatranthrougheach
Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia Imaginealifedirectlydefinedbyroughlyathirdofayearofrainandflooding.Thepeopleof ancientmesopotamia,egypt,andthekingdomofkushalllivedthatlife:theireconomies, power,andsimplesurvivaldependedontheseasonsoftheriversthatranthrougheach
City-States in Mesopotamia
 CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more about
CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more about
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia. Miss Genovese
 Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
Mesopotamia. The Worlds First Civilization
 Mesopotamia The Worlds First Civilization What is a civilization? Civilizations (SIHvuhluhZAY shuhns) are complex societies. They have cities, organized governments, art, religion, class divisions, and
Mesopotamia The Worlds First Civilization What is a civilization? Civilizations (SIHvuhluhZAY shuhns) are complex societies. They have cities, organized governments, art, religion, class divisions, and
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO
 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO PREHISTORY Prehistory is the oldest and longest period of our past. It began when human beings first appeared on
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO PREHISTORY Prehistory is the oldest and longest period of our past. It began when human beings first appeared on
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming
 Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Economy The Inca government also controlled the economy. Instead of paying taxes, Incas had to pay their government in labor (usually several weeks pe
 Government The Inca were ruled by one person. He was known as the Sapa Inca. The Sapa Inca was considered to be a descendant of the sun god. He owned all land and made all laws. He was responsible for
Government The Inca were ruled by one person. He was known as the Sapa Inca. The Sapa Inca was considered to be a descendant of the sun god. He owned all land and made all laws. He was responsible for
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers
 Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Assessment: China Develops a New Economy
 Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Period Date. Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new ways.
 Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S. By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala
 Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala Geography by: Mia Ayala Here are some facts about Ancient Mesopotamia's geography. Mesopotamia is known as the "fertile crescent"
Ancient Mesopotamia G.R.A. P.E.S By: Austin Lee, Amber Nguyen, and Mia Ayala Geography by: Mia Ayala Here are some facts about Ancient Mesopotamia's geography. Mesopotamia is known as the "fertile crescent"
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere
 Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Located in what is now partly Syria and Iraq
 The Fertile Crescent A plain with rich topsoil carried down the Tigris and Euphrates River valleys with the spring floods. Bordered by the Zagros Mountains to the East, and the Syrian and Arabian Deserts
The Fertile Crescent A plain with rich topsoil carried down the Tigris and Euphrates River valleys with the spring floods. Bordered by the Zagros Mountains to the East, and the Syrian and Arabian Deserts
SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES
 NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Famous Things ESL lesson plans from ESL-Images.com
 PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. Do you live in a wine producing country? 2. Do you think that red wine and white wine are produced in the same way? 3. When do you think people first started to make wine? 4. Which
PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. Do you live in a wine producing country? 2. Do you think that red wine and white wine are produced in the same way? 3. When do you think people first started to make wine? 4. Which
Early Civilizations of Middle America. Chapter 2, Section 1
 Early Civilizations of Middle America Chapter 2, Section 1 The Mayas and the Aztecs Map pg. 39 What color represents the Mayas? The Aztecs? What are the current day locations? Were the two civilizations
Early Civilizations of Middle America Chapter 2, Section 1 The Mayas and the Aztecs Map pg. 39 What color represents the Mayas? The Aztecs? What are the current day locations? Were the two civilizations
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C
 UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
Geography of the Fertile Crescent
 Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
ADVANCED CITIES: The people who established the world's first civilization around 4000 B.C. in southern Mesopotamia were known as the Sumerians.
 ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST!
 Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST! 1. How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? Flood Control Built levees and storage basin to
Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST! 1. How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? Flood Control Built levees and storage basin to
Basic parts of a friendly letter: Heading, greeting, body, closing, and signature
 Name Grading Criteria Basic parts of a friendly letter: Heading, greeting, body, closing, and signature (10 points) Ideas: 1. Why should your family give you more resources to explore the area and civilization?
Name Grading Criteria Basic parts of a friendly letter: Heading, greeting, body, closing, and signature (10 points) Ideas: 1. Why should your family give you more resources to explore the area and civilization?
The Fertile Crescent and the Promised Land
 Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Government city-states
 Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
Mesopotamia LESSON. rivers for trade. civilization ancient city-state empire justice fertile irrigation conquer code punishment.
 LESSON 4 civilization ancient city-state empire justice You ve learned about how agriculture led to the first villages. Now read this selection to find out how the first villages grew into larger cities.
LESSON 4 civilization ancient city-state empire justice You ve learned about how agriculture led to the first villages. Now read this selection to find out how the first villages grew into larger cities.
African History. Return
 Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent BC
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Homework. Bring Something from your everyday life Ex. Picture, favorite toy, clothing item
 Homework Bring Something from your everyday life Ex. Picture, favorite toy, clothing item Heritage Studies 6 Lesson 1 Mesopotamia Days of Abraham Discovering the Past Locating Mesopotamia The Days of Abraham
Homework Bring Something from your everyday life Ex. Picture, favorite toy, clothing item Heritage Studies 6 Lesson 1 Mesopotamia Days of Abraham Discovering the Past Locating Mesopotamia The Days of Abraham
earliest recorded history to today. writing art artifacts Centuries-old written records reveal a long-lasting civilization in
 Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Bread Baking Now and Then By ReadWorks
 Bread Baking Now and Then Bread Baking Now and Then By ReadWorks Did you know that bread is one of the earliest human inventions? Bread is a food made of flour and water. Other ingredients and shape can
Bread Baking Now and Then Bread Baking Now and Then By ReadWorks Did you know that bread is one of the earliest human inventions? Bread is a food made of flour and water. Other ingredients and shape can
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
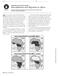 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
 http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/mr-educator-a-social-studies-professional Instructions: 1.) This activity can be completed in a variety of ways depending on the grade level or the level at which
http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/mr-educator-a-social-studies-professional Instructions: 1.) This activity can be completed in a variety of ways depending on the grade level or the level at which
Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society
 1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
The Civilizations of America
 The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Mesopotamian History. Chapter 2 Art History. Roxanna Ford 2014
 Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
It was during the Neolithic age that farmers emerged and changed the way people lived. This can be seen in Catalhoyuk.
 Mesopotamia The Worlds first cities began as farming villages in the Middle East. As they grew they began to trade with each other. Trade, like farming, became a very important source of wealth. Catalhoyuk
Mesopotamia The Worlds first cities began as farming villages in the Middle East. As they grew they began to trade with each other. Trade, like farming, became a very important source of wealth. Catalhoyuk
 Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Name Period. Maya, Aztec & Inca Civilizations Latin America Notes. The Maya
 Name Period Maya, Aztec & Inca Civilizations Latin America Notes Class Objective: The Maya From. is known as the of Mayan civilization. Mayan Geography Central America: Rugged terrain, hilly Tropical Climate
Name Period Maya, Aztec & Inca Civilizations Latin America Notes Class Objective: The Maya From. is known as the of Mayan civilization. Mayan Geography Central America: Rugged terrain, hilly Tropical Climate
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Amazing Mesopotamia. Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography
 Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Were the Aztecs really that brutal? Basic Introduction to the Aztecs. The Aztecs
 Basic Introduction to the Aztecs The Aztecs Were the Aztecs really that brutal? found their city. Who were they? The Aztecs were a very successful ancient civilisation who lived in what is now central
Basic Introduction to the Aztecs The Aztecs Were the Aztecs really that brutal? found their city. Who were they? The Aztecs were a very successful ancient civilisation who lived in what is now central
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
Ancient China History Flow Chart
 R78 L85 Ancient China History Flow Chart First Civ. of China- Xia (Shyah) or Shang Dynasty? Pgs 280-283 Zhou Dynasty- Longest dynasty Pgs 283-285 Warring States- Chinese Philosophy develop Qin (Chin) Dynasty
R78 L85 Ancient China History Flow Chart First Civ. of China- Xia (Shyah) or Shang Dynasty? Pgs 280-283 Zhou Dynasty- Longest dynasty Pgs 283-285 Warring States- Chinese Philosophy develop Qin (Chin) Dynasty
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
Ancient Egypt Social Class and Daily Life
 Ancient Egypt Social Class and Daily Life Ancient Egyptian Social Class A Social Class refers to a group of people who have similar wealth and income, education, or types of jobs. Ancient Egyptian Social
Ancient Egypt Social Class and Daily Life Ancient Egyptian Social Class A Social Class refers to a group of people who have similar wealth and income, education, or types of jobs. Ancient Egyptian Social
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Mesopotamia ancient civilization river Afterlife Ur ancient city in Mesopotamia India Hittites-empire used iron weapons
 What do you suppose life was like five thousand years ago in the first river valley civilizations for everyday people? Below is a list of terms associated with that time period. We are going to examine
What do you suppose life was like five thousand years ago in the first river valley civilizations for everyday people? Below is a list of terms associated with that time period. We are going to examine
Made in Mesopotamia. HistoriCool Resources
 MADE IN MESOPOTAMIA Made in Mesopotamia Mesopotamia. The name sounds a bit like an alternative rock band, or a fungal infection cream. But it s neither! Mesopotamia, meaning land between rivers in Ancient
MADE IN MESOPOTAMIA Made in Mesopotamia Mesopotamia. The name sounds a bit like an alternative rock band, or a fungal infection cream. But it s neither! Mesopotamia, meaning land between rivers in Ancient
1 African Beginnings
 1 Section Step-by-Step Instruction Objectives Social Studies 1. Examine the ways in which the survival skills of early Africans changed over time. 2. Find out about early civilizations that arose along
1 Section Step-by-Step Instruction Objectives Social Studies 1. Examine the ways in which the survival skills of early Africans changed over time. 2. Find out about early civilizations that arose along
China Before it was China. September 10, 2013
 China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions
 Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
The Qin and Han Dynasties
 The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations
 Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
Before reading. Archaeology. Preparation task. Magazine Archaeology. Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise.
 Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
SOL Narrative Review. with questions
 SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
*China s physical geography helped keep China economically and culturally isolated throughout its early dynasties *Its mountains and deserts
 Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
