|
|
|
- Bennett Thomas Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kingdoms of Africa
2
3
4
5
6 Bantu Migrations The most prominent event in Sub-Saharan Africa during ancient times were the migrations of the Bantu-speaking peoples and the establishment of agricultural societies in regions where Bantu speakers settled. Just as Sudanic agriculture spread to the Nile and provided an economic foundation for the development of many African societies, it also spread to most other regions of Africa south of the Sahara and supported the emergence of distinct tropical agricultural societies.
7 The Bantu Located initially in the lower Niger Valleys, the Bantu began to migrate from West Africa spreading their language, knowledge of iron production, and their experience with settled tropical agriculture. Between 500 B.C.E. to 500 C.E., this migration would move Bantu innovations and inherited innovations throughout central Africa and onto to southern Africa.
8 Geographic Considerations North- Mediterranean- access to trade- coastal mountains- land for agriculture East- Rift Valley- some mountains- Indian Ocean West- grasslands and some rainforest along the Niger river Central - equatorial- Congo-only real rainforest South- high plateau- temperate climate-savanna
9 African Kingdoms 800 C.E C.E.
10 African Kingdoms Ghana Mali Songhay Great Zimbabwe 11th -15th C.E. Swahili coast 12th -15th C.E. Many of the dates for these kingdoms are still debated
11 GHANA
12
13 Ghana Empire The Ghana Empire or Wagadou Empire (existed c ) was located in what is now southeastern Mauritania, Western Mali, and Eastern Senegal It is believed to be the first of many empires that would rise in that part of Africa. It first began in the eighth century, when a dramatic shift in the economy of the Sahel area south of the Sahara allowed more centralized states to form. The introduction of the camel, which preceded Arabs and Islam by several centuries, brought about a gradual revolution in trade, and for the first time, the extensive gold, ivory, and salt resources of the region could be sent north and east to population centers in North Africa, the Middle East and Europe in exchange for manufactured goods.
14 Ghana Empire The empire owed much of its prosperity to trans-saharan trade and a strategic location near the gold and salt mines. Both gold and salt seemed to be the dominant sources of revenue, exchanged for various products such as textiles, ornaments and cloth, among other materials. Many of the hand-crafted leather goods found in old Morocco also had their origins in the empire. The main centre of trade was Koumbi Saleh.
15
16
17 Ghana s Economy & Decline The taxation system imposed by the king (or 'Ghana') required that both importers and exporters pay a percentage fee, not in currency, but in the product itself. Tax was also extended to the goldmines. In addition to the exerted influence of the king onto local regions, tribute was also received from various tributary states and chiefdoms to the empire's peripheral. The empire began struggling after reaching its apex in the early 11th century. By 1059, the population density around the empire's leading cities was seriously overtaxing the region. The Sahara desert was expanding southward, threatening food supplies. While imported food was sufficient to support the population when income from trade was high, when trade faltered, this system also broke down.
18
19 Mali
20
21 Mali Empire The Mali Empire or Manding Empire or Manden Kurufa was a medieval West African state of the Mandinka from c to c The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa I. The Mali Empire had many profound cultural influences on West Africa allowing the spread of its language, laws and customs along the Niger River.
22 Mali Empire The Mali Empire flourished because of trade above all else. It contained three immense gold mines within its borders unlike the Ghana Empire, which was only a transit point for gold. The empire taxed every ounce of gold or salt that entered its borders. By the beginning of the 14th century, Mali was the source of almost half the Old World's gold exported from mines in Bambuk, Boure and Galam.
23
24
25
26
27
28 Songhay
29
30 Songhay Empire The Songhai Empire, also known as the Songhay Empire was a pre-colonial African state centered in eastern Mali. From the early 15th to the late 16th Century, Songhai was one of the largest African empires in history. Its capital was the city of Gao, where a small Songhai state had existed since the 9th Century. Its base of power was on the bend of the Niger River in present-day Niger and Burkina Faso.
31 Songhai Empire
32 Songhay Economy The Songhai economy was based on a traditional caste system. The clan a person belonged to ultimately decided their occupation. The most common castes were metalworkers, fishermen, and carpenters. Lower caste participants consisted of mostly non-farm working slaves, who at times were provided special privileges and held high positions in society. At the top were nobleman and direct descendants of the original Songhai people, followed by freemen and traders. At the bottom were war captives and slaves obligated to labor, especially in farming. Dogons, Tuareg, and others
33
34
35
36
37 Songhay Society Upper classes in society converted to Islam while lower classes often continued to follow traditional religions. Sermons emphasized obedience to the king. Timbuktu was the educational capital. Sonni Ali established a system of government under the royal court, later to be expanded by Askia Muhammad, which appointed governors and mayors to preside over local tributary states, situated around the Niger valley. Local chiefs were still granted authority over their respective domains as long as they did not undermine Songhai policy.
38 Decline Following Dauoud's death, a civil war of succession weakened the Empire, leading Morocco Sultan Ahmad I al-mansur Saadi to dispatch an invasion force under the eunuch Judar Pasha. Judar Pasha was a Spaniard by birth, but had been captured as an infant and educated at the Moroccan court. After a cross-saharan march, Judar's forces razed the salt mines at Taghaza and moved on Gao; when Askia Ishaq II (r ) met Judar at the 1591 Battle of Tondibi, Songhai forces were routed by a cattle stampede triggered by the Moroccans' gunpowder weapons despite vastly superior numbers. Judar proceeded to sack Gao, Timbuktu, and Djenné, destroying the Songhai as a regional power. Governing so vast an empire proved too much for the Moroccans, and they soon relinquished control of the region, letting it splinter into dozens of smaller kingdoms.
39 Djenne
40 Great Zimbabwe
41 Great Zimbabwe
42 Lost Kingdom Great Zimbabwe, or "house of stone", is the name given to hundreds of great stone ruins spread out over a 500 km² (200 sq mile) area within the modern day country of Zimbabwe, which itself is named after the ruins. The exact origin of the word Zimbabwe is not known.
43 Great Zimbabwe Built consistently throughout the period from the 11th century to the 15th century, the ruins at Great Zimbabwe are some of the oldest and largest structures located in Southern Africa. At its peak, estimates are that the ruins of Great Zimbabwe had as many as 18,000 inhabitants. The ruins that survive are built entirely of stone. The ruins span 1,800 acres (7 km²) and cover a radius of 100 to 200 miles (160 to 320 km).
44 Great Zimbabwe It is believed Great Zimbabwe located south of the Zambezi River was where much of Africa s gold was mined. At its peak in about 1400, the city which occupied 193 acres may have had 18,000 inhabitants. Between 1250 and 1450, local African craftsmen built stone structures for Great Zimbabwe s rulers, priests, and wealthy citizens.
45 Great Zimbabwe The largest structure served as a king s court. Mixed farming and cattle-herding was Great Zimbabwe s economic base. Long distance trade mostly in gold Ecological crisis caused from overgrazing and the destruction of forests may have led to their decline.
46 Great Zimbabwe While there is little known about Great Zimbabwe, its size and influence on the region is just recently being rediscovered. European disbelief in a Bantu-speaking empire is still under debate in some academic circles. The European belief that Africans were not capable of such an advanced kingdom fueled the speculation of the kingdom as a lost kingdom of some White nation perhaps the Queen of Sheba.
47 Swahili Coast
48 Swahili coast 1800 miles long Diffusion from Indian, Arab, Chinese, and others Islam perhaps most enduring
49 Swahili Coast While the Swahili Coast had kingdoms, it was not controled by just one kingdom. The region was a center hub of trade and commerce in east Africa. The introduction of various traditions such as Islam helped to shape the character of the Swahili Coast.
50 Swahili Coast While trans-saharan caravan traffic linked west Africa to the larger trading world, merchant mariners sailing in the sea lanes of the Indian Ocean formed a similar service for coastal east Africa or the Swahili Coast. Swahili is an Arabic term meaning coasters. The Swahili dominated the east African coast from Mogadishu in ht north to Kilwa, the Comoro Islands, and Sofala in the south.
51 Swahili Coast By the tenth century, Swahili society attracted increasing attention from Islamic merchants. From the interior regions of east Africa, the Swahili obtained gold, slaves, ivory, and exotic local products. In exchange, the Swahili city-states received pottery, glass, and textiles that the Muslim merchants brought from Persia, India, and China.
52 Swahili City-States By the 11th and 12th Century, trade had brought tremendous wealth to coastal east Africa. Mogadishu, Lamu, Malindi, Mombasa, Zanzibar, Kilwa, Mozambique, and Sofala were some of the trade centers that eventually developed into powerful city-states governed by a king who supervised trade and organized public life in the region. Wood structures to Coral and stone based structures
53 East African Kingdoms Recent archaeological discoveries are reshaping our picture of east African society. Racism and ethnic identification has helped to shape these previous conceptions of the Bantu-speaking peoples of this region. Like elsewhere, Islam laid a cultural foundation in East Africa but this cultural foundation was atop previous indigenous cultures.
54 African Society Africa is a land of tremendous diversity. The continent supported a wide array of societies and economies: mobile bands of hunting and gathering peoples, fishing peoples, nomadic herders, subsistence farmers, to city-based societies that drew their livelihoods from mining, manufacturing, and trade. In kingdoms, empires, and city-states, African peoples developed complex societies with clearly defined classes: ruling elites, military nobles, administrative officials, religious authorities, wealthy merchants, artisans, business entrepreneurs, common people, peasants, and slaves.
55 African Society These societies resembled those found in other settled, agricultural lands of Eurasia organized by powerful states. In the small states and kin-based societies of sub-saharan Africa, social structures were different. Kinship, sex and gender expectations, and age groupings were the principal considerations that determined social position.
56 Kinship Groups Extended families and clans served as the main foundation of social and economic organization in small-scale agricultural societies. Private owned property did not exist; common lands Gender roles and expectations were different than in other lands Creator god and lesser gods and spirits to the arrival of Christianity and Islam
57 Conclusions States and societies of sub-saharan Africa differed considerably from those in other parts of the eastern hemisphere. Agricultural based kin groups rather than state structures Interaction with other groups forged large city-states and imperial empires Gold, salt, ivory, and slaves from Africa became mainstays in other regions By 1500 C.E. African traditions and Islamic influences had combined to fashion a series of powerful, productive, and distinctive societies in sub-saharan Africa.
58 African Kingdoms Ghana Mali Songhay Great Zimbabwe 11th -15th C.E. Swahili coast 12th -15th C.E. Many of the dates for these kingdoms are still debated
59 Kingdoms of Africa
Originally created by Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Originally created by Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY A Satellite View Great Rift Valley 3,000 miles long Africa: Tropic of Cancer 20 N The Tropical Continent Equator 0 Tropic of Capricorn
Originally created by Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY A Satellite View Great Rift Valley 3,000 miles long Africa: Tropic of Cancer 20 N The Tropical Continent Equator 0 Tropic of Capricorn
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai
 Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai.SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. 1. Describe the development and decline of the Sudanic kingdoms (Ghana, Mali,
Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai.SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. 1. Describe the development and decline of the Sudanic kingdoms (Ghana, Mali,
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD.
 SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
Journal Journal A. Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire?
 Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
African Kingdoms and Salt
 African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
Journal What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa
 Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
AFRICA. Human Geography
 AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
Chapter Summary. Section 2: Kingdoms of West Africa. Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa
 Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief.
 GHANA Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief. By the 700s, Ghana was a kingdom, and its rulers were growing
GHANA Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief. By the 700s, Ghana was a kingdom, and its rulers were growing
Review Questions 1. How did the Bantu migrations affect existing cultures?
 Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
9/21/14. Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda. Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram. Take notes on Songhai
 Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions
 Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700
 African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700 Setting the Stage Africa spreads across the equator. It includes a broad range of Earth s environments-from coastal plains to mountains. Some parts of Africa suffer
African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700 Setting the Stage Africa spreads across the equator. It includes a broad range of Earth s environments-from coastal plains to mountains. Some parts of Africa suffer
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
African History. Return
 Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Note Taking Study Guide EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA
 SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Packet 7. Movement of People and Goods
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Contents. List of Acknowledgements. Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3
 Contents List List of Acknowledgements Preface xii xv xxii xxiv Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3 Chapter 1 prehistory of Africa 9 Human evolution 9 Homo sapiens, the
Contents List List of Acknowledgements Preface xii xv xxii xxiv Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3 Chapter 1 prehistory of Africa 9 Human evolution 9 Homo sapiens, the
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1
 Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Post Classical Civs. F Block - Humanities
 Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes
 Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES
 WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES DATE: AIM: Students will be able to compare and contrast the three major trading empires in Ancient West Africa. DO NOW: A Voice from the Past Pliny, a scholar and naturalist,
WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES DATE: AIM: Students will be able to compare and contrast the three major trading empires in Ancient West Africa. DO NOW: A Voice from the Past Pliny, a scholar and naturalist,
List of Illustrations
 List of Maps p. xii List of Illustrations p. xv Acknowledgements p. xxii Preface p. xxiv Introduction p. 1 Historiography p. 1 Geography, climate and vegetation p. 3 Early prehistory of Africa p. 9 Human
List of Maps p. xii List of Illustrations p. xv Acknowledgements p. xxii Preface p. xxiv Introduction p. 1 Historiography p. 1 Geography, climate and vegetation p. 3 Early prehistory of Africa p. 9 Human
Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries
 Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries Grade Level: Grades 6-12 National World History Standards: Era Four: Standard 5A The student understands state-building in...
Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries Grade Level: Grades 6-12 National World History Standards: Era Four: Standard 5A The student understands state-building in...
The Earliest Americans. Chapter 1 Section 1
 The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
Medieval Adventures. Travel Brochure. 9/27/2017 Medieval Africa Time Travel Guide - Diego Soto - Google Docs
 Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013
 History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
AP World History
 AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition
 Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition Chapter 8 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Copyright 2013 by Bedford/St. Martin s I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition Chapter 8 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Copyright 2013 by Bedford/St. Martin s I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
 1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia
![[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia](/thumbs/89/98244476.jpg) [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
Golden kingdoms of Africa *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
such as Great Zimbabwe, to get these items. The merchant would then wait for the next monsoon season to bring them back to Asia.
 These notes go over the geography of Africa and the development of some early civilizations in Africa. You may need to research some of this information on the internet. After you have read these notes,
These notes go over the geography of Africa and the development of some early civilizations in Africa. You may need to research some of this information on the internet. After you have read these notes,
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
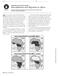 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
West Africa. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg
 West Africa https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg Geography Africa is located in the middle of the globe and is the second largest of the seven continents.
West Africa https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg Geography Africa is located in the middle of the globe and is the second largest of the seven continents.
Geography & Early Civilizations in Africa
 MR. Cegielski Geography & Early Civilizations in Africa Preview Starting Points Map: Environments of Africa The Geography of Africa Early African Societies Africa s Iron Age Map: Bantu Migrations Three
MR. Cegielski Geography & Early Civilizations in Africa Preview Starting Points Map: Environments of Africa The Geography of Africa Early African Societies Africa s Iron Age Map: Bantu Migrations Three
African Cultural Characteristics
 African Societies African Cultural Characteristics Certain common features Show an underlying cultural unity Some scholars have called Africanity One common cultural feature Concept of kingship Kings ritually
African Societies African Cultural Characteristics Certain common features Show an underlying cultural unity Some scholars have called Africanity One common cultural feature Concept of kingship Kings ritually
Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes
 Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Before Contact with Europeans
 Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Early and. Medieval African Kingdoms. Timeline Cards
 Early and Medieval African Kingdoms Timeline Cards ISBN: 978-1-68380-138-2 Subject Matter Expert David Owusu-Ansah, PhD, Department of History, James Madison University Illustration and Photo Credits Title
Early and Medieval African Kingdoms Timeline Cards ISBN: 978-1-68380-138-2 Subject Matter Expert David Owusu-Ansah, PhD, Department of History, James Madison University Illustration and Photo Credits Title
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
CHINESE EMPIRE. AP World History Notes Chapter 4
 CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
China in the Beginning
 China in the Beginning The fertile river valleys of China allowed villages and towns to flourish along their banks. The most important rivers were the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers which supported agricultural
China in the Beginning The fertile river valleys of China allowed villages and towns to flourish along their banks. The most important rivers were the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers which supported agricultural
The Civilizations of America
 The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
Economy The Inca government also controlled the economy. Instead of paying taxes, Incas had to pay their government in labor (usually several weeks pe
 Government The Inca were ruled by one person. He was known as the Sapa Inca. The Sapa Inca was considered to be a descendant of the sun god. He owned all land and made all laws. He was responsible for
Government The Inca were ruled by one person. He was known as the Sapa Inca. The Sapa Inca was considered to be a descendant of the sun god. He owned all land and made all laws. He was responsible for
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
Bellringer T1D6. How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed?
 Bellringer T1D6 How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed? U.S. History Ch. 2.1 A Changing World Main Questions: How new tech made longer sea voyages possible. How great civilizations
Bellringer T1D6 How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed? U.S. History Ch. 2.1 A Changing World Main Questions: How new tech made longer sea voyages possible. How great civilizations
Commerce and Culture
 Commerce and Culture 500 1500 CHAPTER OVERVIEW PERIOD 3: REGIONAL AND INTERREGIONAL INTERACTIONS, CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES To consider the significance of trade in human history To explore the interconnections
Commerce and Culture 500 1500 CHAPTER OVERVIEW PERIOD 3: REGIONAL AND INTERREGIONAL INTERACTIONS, CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES To consider the significance of trade in human history To explore the interconnections
9 HOW DID CHANGE ACCELERATE?
 9 HOW DID CHANGE ACCELERATE? Transcript: Part 1 In the last 500 years our world has been utterly transformed. At the heart of those transformations was a sharp increase in human control over the resources
9 HOW DID CHANGE ACCELERATE? Transcript: Part 1 In the last 500 years our world has been utterly transformed. At the heart of those transformations was a sharp increase in human control over the resources
Unit 9- Medieval Europe. Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review. Name:
 1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
MAYANS. The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE.
 MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
The Han Dynasty. By Kevin Meyer, Avery Weber, Hayden Weis, Zach Rademacher, Phillip Petersen, and Jason Johnson.
 The Han Dynasty By Kevin Meyer, Avery Weber, Hayden Weis, Zach Rademacher, Phillip Petersen, and Jason Johnson. Origins of the Dynasty The Han Dynasty became known in 206 BCE and the first emperor came
The Han Dynasty By Kevin Meyer, Avery Weber, Hayden Weis, Zach Rademacher, Phillip Petersen, and Jason Johnson. Origins of the Dynasty The Han Dynasty became known in 206 BCE and the first emperor came
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar
 Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development The land of China A glance on Chinese history Chinese
Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development The land of China A glance on Chinese history Chinese
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
Holt African American History Chapter 1
 Beginnings in Africa Section 1 Human Origins and Early Civilizations Section 2 Great Empires of West Africa Section 3 Kingdoms of East and South Africa Section 1: Human Origins and Early Civilizations
Beginnings in Africa Section 1 Human Origins and Early Civilizations Section 2 Great Empires of West Africa Section 3 Kingdoms of East and South Africa Section 1: Human Origins and Early Civilizations
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
FACULTY OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS THE ECONOMY OF MALI EMPIRE BABA OSMAN BUKARI 12/7/2016. Lecturer: PROF.
 FACULTY OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS THE ECONOMY OF MALI EMPIRE BABA OSMAN BUKARI 12/7/2016 Lecturer: PROF. MURAT ALI YULEK 2680 words 1 1 Number of words excluding tables and footnootes
FACULTY OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS THE ECONOMY OF MALI EMPIRE BABA OSMAN BUKARI 12/7/2016 Lecturer: PROF. MURAT ALI YULEK 2680 words 1 1 Number of words excluding tables and footnootes
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties
 Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America.
 The Earliest Americans The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America. Main Ideas Climate changes allowed Paleo-Indians to begin the first migration to the Americas.
The Earliest Americans The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America. Main Ideas Climate changes allowed Paleo-Indians to begin the first migration to the Americas.
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The medieval empire of Ghana included several large cities, such as Walata, the remains of which can be seen today.
 13.1 Introduction The early West African societies of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai all created empires that gained much of their wealth from trade. In this chapter, you will learn more about the role of trade
13.1 Introduction The early West African societies of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai all created empires that gained much of their wealth from trade. In this chapter, you will learn more about the role of trade
Indian Ocean. Routes from India to the Arabian Peninsula and Africa
 Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE. AP World History Notes Time Period:
 CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
Nomads. First inhabitants. years ago. source the Wooly. arrived about 22,000. Nomadic moving from place to following a food.
 Section 1 Nomads First inhabitants arrived about 22,000 years ago Nomadic moving from place to following a food source the Wooly Mammoth Provided Basic Needs -Food -Shelter -Clothing Ice Age Ended around
Section 1 Nomads First inhabitants arrived about 22,000 years ago Nomadic moving from place to following a food source the Wooly Mammoth Provided Basic Needs -Food -Shelter -Clothing Ice Age Ended around
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
China (religion) Evidence: China (trade)
 CCOT China (religion): Between 600 CE and 1500 CE, Tang China attempted to eradicate Buddhism for its high acceptance in 840 until the Yuan Empire demoted Confucianism in 1200s, which was followed by a
CCOT China (religion): Between 600 CE and 1500 CE, Tang China attempted to eradicate Buddhism for its high acceptance in 840 until the Yuan Empire demoted Confucianism in 1200s, which was followed by a
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century. By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham
 Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America?
 2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
Peoples and Civilizations of the Americas
 Peoples and Civilizations of the Americas 600-1500 Teotihuacan Teotihuacan was a large Mesoamerican city at the height of its power in 450 600 c.e. The city had a population of 125,000 to 200,000 inhabitants
Peoples and Civilizations of the Americas 600-1500 Teotihuacan Teotihuacan was a large Mesoamerican city at the height of its power in 450 600 c.e. The city had a population of 125,000 to 200,000 inhabitants
Chapter 6: The First Chinese Empires, 221 B.C. A.D Lesson 3: The Han Dynasty
 Chapter 6: The First Chinese Empires, 221 B.C. A.D. 220 Lesson 3: The Han Dynasty World History Bell Ringer #27 10-24-17 1. In 1974, farmers digging a well about 35 miles east of Xi an discovered A. A
Chapter 6: The First Chinese Empires, 221 B.C. A.D. 220 Lesson 3: The Han Dynasty World History Bell Ringer #27 10-24-17 1. In 1974, farmers digging a well about 35 miles east of Xi an discovered A. A
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
In addition to salt list two other products a North African trader might bring to trade in West Africa.
 List three things that show the power of the ruler. In addition to salt list two other products a might bring to trade in West Africa. List five products the people of the southern forest areas brought
List three things that show the power of the ruler. In addition to salt list two other products a might bring to trade in West Africa. List five products the people of the southern forest areas brought
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
Government city-states
 Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
