10/18/2017. Chapter 14. Europe and the World: New Encounters, Chapter Timeline
|
|
|
- Theodore Beasley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 Europe and the World: New Encounters, Chapter Timeline p434 A 1536 Mercator projection map showing the route of Ferdinand Magellan s first circumnavigation of the world Desire for wealth was the main motivation of the early explorers, though spreading Christianity was also an important factor. Portugal under Prince Henry the Navigator initiated the first voyages in the early fifteenth century; Spain s explorations began at the century s end. 1
2 On the Brink of a New World The Motives for Expansion Fantastic lands The Travels of John Mandeville (14th century) Economic motives Access to the East The Polos Religious Zeal (Catholic Missionaries) The Means for Expansion Maps Ptolemy s Geography (1477, available in print) Ships and sailing Navigational aids and enhanced knowledge Ptolemy s World Map p406 New Horizons: The Portuguese and Spanish Empires The Development of a Portuguese Maritime Empire Prince Henry the Navigator ( ) The Portuguese in India Bartholomeu Dias and Vasco da Gama Viceroys Alfonso d Albuquerque (c ) Commercial military bases In search of spices Reasons for Portuguese Success Guns and seamanship 2
3 Discoveries and Possessions in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries Spices and World Trade Discoveries and Possessions in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries. Desire for wealth was the main motivation of the early explorers, though spreading Christianity was also an important factor. Portugal under Prince Henry the Navigator initiated the first voyages in the early fifteenth century. Spain s explorations began at the century s end. p409 Spices and World Trade 3
4 Spices and World Trade p409 Voyages to the New World The Voyages of Christopher Columbus ( ) Spanish financing to sail west to reach Asia Reached the Bahamas (Oct. 12, 1492) Additional voyages (1493, 1498, and 1502) New Voyages John Cabot (New England) Pedro Cabral (Brazil) Amerigo Vespucci (Writer) Vasco Nunez de Balboa (Pacific Ocean) Ferdinand Magellan ( ) Circumnavigation of World Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)(Spain/Portugal) Christopher Columbus Columbus was an Italian explorer who worked for the queen of Spain. He has become a symbol for two entirely different perspectives. To some, he was a great and heroic explorer who discovered the New World; to others, especially in Latin America, he was responsible for beginning a process of invasion that led to the destruction of an entire way of life. Because Columbus was never painted during his lifetime, the numerous portraits of him are more fanciful than accurate. The portrait shown here was probably done by the Italian painter Ridolfo Ghirlandaio. 4
5 The Spanish Empire in the New World The Role of the Conquistadors Early Civilizations in Mesoamerica The Maya The Aztecs Spanish Conquest of the Aztec Empire Hernan Cortés ( ) Moctezuma (Montezuma) The Inca The leadership and conquests of Pachakuti Administration, buildings, and roads The Spanish Empire in the New World Spanish Conquest of the Inca Empire Francisco Pizarro (c ) The devastations of smallpox and Spanish weapons Administration of the Spanish Empire Encomienda and impact Viceroys and audiencias The church Disease in the New World Sweeping epidemics of Old World disease High mortality rates and labor shortages The Maya p412 5
6 The Aztecs p412 Aztec Victims of Smallpox The indigenous populations of the New World had no immunities to the diseases of the Old World, such as smallpox. By 1520, smallpox had spread throughout the Caribbean and Mesoamerica. This sixteenth-century drawing by a Franciscan friar portrays Native Americans afflicted with smallpox. The pustules that often covered the body are clearly depicted. The figure at the lower right twists in agony, reflecting the immense pain experienced by those who contracted the disease. p412 The Inca p414 6
7 CHRONOLOGY The Portuguese and Spanish Empires in the Sixteenth Century p414 New Rivals on the World Stage Africa: the Slave Trade Origins of the slave trade Cane sugar, plantations, and slavery Growth of the slave trade Triangular trade Up to 10,000,000 African slaves taken to the Americas between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries High death rate during the Middle Passage Conduct of the slave trade Prisoners of war Depopulation of African kingdoms Role of African middle men Effects of slave trade Limited criticism of slavery Triangular Trade Route in the Atlantic Economy As the trade in slaves grew, it became part of the triangular trade route that characterized the Atlantic economy. It involving the exchange of goods and slaves between the western coast of Europe. The slave depots on the African coast, and the ports of North and South America. 7
8 The Sale of Slaves In the eighteenth century, the slave trade was a highly profitable commercial enterprise. This painting shows a Western slave merchant negotiating with a local African leader over slaves at Gore e, Senegal, in West Africa in the late eighteenth century. p419 The West in Southeast Asia European and Native Rivals Portugal The limits of empire Spain The importance of the Philippines The Dutch and the English Dutch consolidation of economic, political, and military control The strength of mainland kingdoms in Burma (Myanmar), Thailand, and Vietnam Southeast Asia, c p420 8
9 Europe in Asia Batavia - Java As Europeans began to move into parts of Asia, they reproduced many of the physical surroundings of their homeland in the port cities they built there. This a seventeenth-century view of Batavia, which the Dutch built as their headquarters on the northern coast of Java in p420 Amsterdam, The Netherlands Amsterdam had become the financial/commercial capital of Europe. It was also the chief port for the ships of the Dutch East India Company, which brought the spices of the East to Europe. p420 The French and British in India The Mughal Empire The Impact of the Western Powers The decline of Portugal s dominance The increasing presence of the English Dutch and French competition Sir Robert Clive and the expansion of the East India Company The Black Hole of Calcutta Battle of Plassey (1757) Forced withdrawal of the French 9
10 The Mughal Empire p422 China China & Japan The Ming and Qing dynasties Dynastic shift (1644) and the greatness of Manchu China Western inroads Imperial decline and European pressures Qing attempts to control trade Japan Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu ( ) Opening to the West Initial traders and missionaries welcomed Reactions against Westerners Expulsion of missionaries and merchants The Qing Empire p423 10
11 The Portuguese Arriving at Nagasaki Portuguese traders landed accidentally in Japan in In a few years, they arrived regularly, taking part in a regional trade network involving Japan, China, and Southeast Asia. In these panels, done in black lacquer and gold leaf, we see a late-sixteenthcentury Japanese interpretation of the first Portuguese landing at Nagasaki. The West Indies The Americas The British and French sugar factories British North America The Dutch and the New Netherlands The English Jamestown (1607) Control of the eastern seaboard The thirteen colonies and their roles French North America Rivalries with Britain in Canada and Latin America The West Indies p425 11
12 A Sugar Mill in the West Indies Cane sugar was one of the most valuable products produced in the West Indies. By 1700, sugar was replacing honey as a sweetener for increasing numbers of Europeans. This seventeenth-century French illustration shows the operation of a sugar mill in the French West Indies. p425 CHRONOLOGY New Rivals on the World Stage p426 The Impact of European Expansion The Conquered Diverse effects Devastating effects to local populations in America and Africa Less impact in Asia Creation of a multiracial society in Latin America Ecology: livestock and crops Catholic Missionaries Conversion of native populations Hospitals, orphanages, and schools The Jesuits in Asia Conversions in China Japan 12
13 The Impact of European Expansion The Conquerors Opportunities for men and women Economic effects Gold, silver, and a price revolution Plants and animals: the Columbian Exchange Impact on European lifestyle Chocolate, coffee, and tea Deepening European rivalries New views of the world Gerardus Mercator ( ) and his map Psychological impact The Jesuit missionary Father Gabriel (Jeremy Irons) with the Guaraní Indians of Paraguay before their slaughter by Portuguese troops p429 The Columbian Exchange In addition to their diseases, which killed vast numbers of indigenous inhabitants of the Americas, Europeans transplanted many of their crops and domestic animals to the New World. Europeans also imported plants from the New World that improved food production and nutrition in Europe. 13
14 A Seventeenth-Century World Map p431 This beautiful world map was prepared in 1630 by Henricus Hondius. The four portraits are of Caesar, the Roman statesman; Ptolemy, the second century astronomer; Mercator, the Flemish cartographer whose map projection Hondius followed; and Hondius himself. By comparing this map with the map created by Ptolemy on page 406, one can see how much Europeans had learned about the shape of the world by the seventeenth century. Toward a World Economy Economic Conditions in the Sixteenth Century The causes and consequences of inflation The Growth of Commercial Capitalism Joint-stock trading companies New economic institutions The Bank of Amsterdam (1609) Amsterdam Bourse (Exchange) Continuing dependence on agriculture 14
15 Toward a World Economy Mercantilism Chief beliefs and practices Total volume of trade unchangeable Importance of bullion and favorable balance of trade State intervention Overseas Trade and Colonies: Movement toward Globalization The value of transoceanic trade Intra-European trade Trade patterns interlocked Europe, Africa, the East, and the Americas 15
Chapter 14. Europe and the World: New Encounters,
 Chapter 14 Europe and the World: New Encounters, 1500-1800 Chapter Timeline p434 A 1536 Mercator projection map showing the route of Ferdinand Magellan s first circumnavigation of the world Desire for
Chapter 14 Europe and the World: New Encounters, 1500-1800 Chapter Timeline p434 A 1536 Mercator projection map showing the route of Ferdinand Magellan s first circumnavigation of the world Desire for
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Renaissance Economics. The Age of Discovery
 Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Exploration & Colonization. Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School
 Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe.
 I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration
 The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Bartholomeu Dias. Cape of Good Hope 1487
 Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
Age of Discovery. SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
 Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1
 Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Chapter Two. When Worlds Collide
 Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
The Age of Exploration ( )
 The Age of Exploration (1450-1700) "Long live the high and mighty sovereigns of Castile! Thus in their names do I take possession of these seas and regions; and if any other prince, whether Christian or
The Age of Exploration (1450-1700) "Long live the high and mighty sovereigns of Castile! Thus in their names do I take possession of these seas and regions; and if any other prince, whether Christian or
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Empires of the Early Modern Era. The Emergence of a New World Order
 Empires of the Early Modern Era The Emergence of a New World Order 1450-1750 Agenda Mongol Essay wrap-up Aztec vs Inca Essay? European Empires discussion Learning Targets Explain what s new about the empires
Empires of the Early Modern Era The Emergence of a New World Order 1450-1750 Agenda Mongol Essay wrap-up Aztec vs Inca Essay? European Empires discussion Learning Targets Explain what s new about the empires
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA
 SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s
 European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 407 413 EXPLORATION AND EXPANSION KEY TERMS conquistadors Spanish conquerors of the Americas (page 412) colony a settlement of people living in a new territory,
Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 407 413 EXPLORATION AND EXPANSION KEY TERMS conquistadors Spanish conquerors of the Americas (page 412) colony a settlement of people living in a new territory,
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY ( )
 THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL. AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS
 CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2.
AP U.S. History 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2.
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
Chapter 23. Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections
 Chapter 23 Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections 1 Portuguese Exploration Originally for fishing Land hunger Discovery of Azores, Madeiras Islands Acquisition of land to plant sugarcane 2 The
Chapter 23 Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections 1 Portuguese Exploration Originally for fishing Land hunger Discovery of Azores, Madeiras Islands Acquisition of land to plant sugarcane 2 The
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter One: The Meeting of Cultures
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
Alfanso de Albuqurque. Amerigo Vespucci. Aztecs. Bartholomeu Dias. Bartolomé de las Casas. Batavia. Black Hole of Calcutta.
 Alfanso de Albuqurque Amerigo Vespucci (c. 1462-1515) after seeing the need for a land base in the area to help cut off spices to Muslim rulers in Egypt and the Ottoman Empire, he set up port facilities
Alfanso de Albuqurque Amerigo Vespucci (c. 1462-1515) after seeing the need for a land base in the area to help cut off spices to Muslim rulers in Egypt and the Ottoman Empire, he set up port facilities
Columbus was thrilled. In a later letter, he wrote, I write this to tell you how in thirty-three
 Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Age of Discovery The New World. The New World II. Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Cantino World Map, 1502
 Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Age of Discovery 1450-1550 Cantino World Map, 1502 Allegorical engraving showing Vespucci "disembarking in the New World." The background shows the often-illustrated cannibal
Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Age of Discovery 1450-1550 Cantino World Map, 1502 Allegorical engraving showing Vespucci "disembarking in the New World." The background shows the often-illustrated cannibal
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Age of Exploration. Use the text to answer each question below.
 Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? Age of Exploration and Trade Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Spain Builds an Empire
 Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02)
 American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration. Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture
 Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia
 Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia Min Shu Waseda University 2017/11/6 1 Outline of the Lecture A brief history of colonialism in East Asia Participating in East Asian trade networks Spice
Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia Min Shu Waseda University 2017/11/6 1 Outline of the Lecture A brief history of colonialism in East Asia Participating in East Asian trade networks Spice
Exploration + Isolation. Ch
 Exploration + Isolation Ch 19 1400-1800 Europeans Explore the East Crusades in the Middle East beginning in 1100s 1275, Marco Polo travels to China But until the 1400s, Europeans didn t have the interest
Exploration + Isolation Ch 19 1400-1800 Europeans Explore the East Crusades in the Middle East beginning in 1100s 1275, Marco Polo travels to China But until the 1400s, Europeans didn t have the interest
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Global Empires of the 1500s
 Global Empires of the 1500s In World History, we will spend a lot of time talking about Europe. This is strange because in 1500s, Europe isn t the center of world. At all! They are not powerful! They are
Global Empires of the 1500s In World History, we will spend a lot of time talking about Europe. This is strange because in 1500s, Europe isn t the center of world. At all! They are not powerful! They are
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST
 WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
Vocabulary. Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming notes. Jump to first page
 Vocabulary Conquistador Royal Fifth Francisco Pizarro Monopoly Hacienda Social class Treaty Hernan Cortes Debt peonage Mestizo Peninsular (Montezuma) Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming
Vocabulary Conquistador Royal Fifth Francisco Pizarro Monopoly Hacienda Social class Treaty Hernan Cortes Debt peonage Mestizo Peninsular (Montezuma) Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE. AP World History Notes Time Period:
 CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
DISEASE PLANTS ANIMAL. Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes
 ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
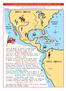 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Conquest in the Americas. World History
 Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
First Visitors From Europe
 THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century. By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham
 Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory
 Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Mexican History and Systems of Empire
 Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
Additional Explorations:
 In The Beginning: Prince Henry The Navigator set up a school to teach geography, science and math so that Portugal could train sailors to find a water route to Asia. In 1486 Bartolomeu Dias became the
In The Beginning: Prince Henry The Navigator set up a school to teach geography, science and math so that Portugal could train sailors to find a water route to Asia. In 1486 Bartolomeu Dias became the
Chapter Three Contact and Conflict
 Chapter Three Contact and Conflict History Reconsidered The view that lands were discovered my Europeans and not people living in these areas were the ones who encountered Euros is common The World in
Chapter Three Contact and Conflict History Reconsidered The view that lands were discovered my Europeans and not people living in these areas were the ones who encountered Euros is common The World in
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013
 History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
Setting the Stage. Europe Enters the Modern Age. European Exploration and Land Claims,
 fe 1 I.* \>> Setting the Stage o Europe Enters the Modern Age In the last unit, you learned about the Renaissance and the Reformation. In this unit, you'll learn about Europe during the early modern age.this
fe 1 I.* \>> Setting the Stage o Europe Enters the Modern Age In the last unit, you learned about the Renaissance and the Reformation. In this unit, you'll learn about Europe during the early modern age.this
World History II. Robert Taggart
 World History II Robert Taggart Table of Contents To the Student.............................................. v Unit 1: A Rebirth in Europe Lesson 1: The Renaissance....................................
World History II Robert Taggart Table of Contents To the Student.............................................. v Unit 1: A Rebirth in Europe Lesson 1: The Renaissance....................................
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Chapter 16: The First Global Age ( ) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in
 Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
Exploration and Conquest of the New World
 Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet
 Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
