Unit #2- Classical Period. Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 BCE to c. 600 CE
|
|
|
- Shawn Harrington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit #2- Classical Period Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 BCE to c. 600 CE
2 Period #2: 600 BCE to 600 CE Large empires appear in Eurasia & Americas These empires would grow in this time period They developed powerful armies and governments Eventually they would have difficulty holding their empires together Long-distance trade routes developed in this time period In your exam preparation always know trade routes, migrations, and empire expansions/collapses
3 Key Concepts in this time period Key Concept 2.1 The Development and Codification of Religious and Cultural Traditions Key Concept 2.2 The Development of States and Empires Key Concept 2.3 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange
4 Important defining dates for this time period c.600 BCE to c.600 CE c.800 BCE: the rise of Greek city-states c.320 BCE: the rise of the Mauryan dynasty c.250 CE: beginning of Mesoamerican Classical Era
5 Civilizations of Influence c.600 BCE to c.600 CE Southwest Asia: Hellenism & Parthian West Africa: none East Africa: Bantus North Africa: Hellenism Mediterranean: Greek, Roman South Asia: Mauryan & Gupta East Asia: Qin & Han Central Asia: Persian Americas: Mayan, Teotihuacan, & Moche
6 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Phoenician city-states and their colonies around the Mediterranean (c c.200 BCE)
7 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Greek city-states and their colonies around the Mediterranean (c.600-c.330 BCE)
8 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Alexander s Hellenistic empires (c.330-c.30 BCE)
9 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE East Asia Qin Dynasty (c.220 BCE-c.206 BCE)
10 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE East Asia Han Dynasty (c.206 BCE-c.220 CE)
11 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE South Asia Mauryan Empire (c.321 BCE-c.185 CE)
12 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE South Asia Gupta Empire (c.320 CE- c.550 CE)
13 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Roman Republic (c.500-c.30 BCE)
14 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Roman Empire (c.30 BCE-c.476 CE)
15 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mediterranean Byzantine Empire (c.476 CE-c.1453 CE)
16 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Southwest Asia Persian (Achaemenid) Empire (c.550 BCE-c.330 BCE)
17 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Southwest Asia Parthian Empire (c.250 BCE-c.220 BCE)
18 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mesoamerica Teotihuacan city-state (c c.700 CE)
19 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Mesoamerica Mayan city-states (c c.900 CE)
20 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Andean South America Chavin (c.900 BCE - c.250 BCE)
21 New Empires 600 BCE to 600 CE Andean South America Moche Empire (c c. 800 CE)
22 Looking Back at 8000 BCE to 600 BCE Development of Agriculture & Early Agricultural Communities ( c.8000 BCE to c.3500 BCE) Earliest Civilizations (c.3500 BCE to c.600 BCE) Ancient Mesopotamia Babylonians, Hittites, Assyrians, & New Babylonians Ancient Egypt Egypt & Kush Indus Valley Ancient China Shang Meso and South America Olmec & Chavin
23 How do the new civilizations in Period #2 differ from Period #1? New civilizations differed from previous period Size and political strength new systems of government, larger states, expansive territory Think of Roman Empire & Gupta Empires Han in China not much larger, but had more centralized control More complex cultures great world religions develop: Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, & Christianity; Confucianism emerges in China More numerous and better written records all developed sophisticated forms of writing & some with simplified alphabets; literacy increased
24 How do the new civilizations in Period #2 differ from Period #1? New civilizations differed from previous period More complex long-distance trade trade routes connect the civilizations by land (Silk Road trade) and by sea (Indian Ocean trade) These trade routes increased prosperity of empires and spread ideas, belief systems, and material goods More contacts between nomads & sedentary people core areas came in contact with periphery areas Central Asian nomads became major facilitators of trade along the Silk Road Some nomads became settled in key Silk Road trade cities
25 How do the new civilizations in Period #2 differ from Period #1? New civilizations differed from previous period More direct influence on modern civilizations many modern practices and belief systems can be traced to this era than the era before Think of impact of the belief systems that came from this era on today s world Law heritage today is from the Roman law system, not Hammurabi s Code of early Mesopotamia
26 Belief Systems to Come from this Era Judaism (Monotheism) Hebrew Bible written c.1000 BCE; modern version c.500 BCE Zoroastrianism From Zoroaster born 7 th century BCE & recorded in 3 rd century BCE Christianity 30 CE Missionary works of Paul accounts for 10% of Roman Empire was Christian by 4 th century CE Hinduism Doctrines come from Vedas Foundation developed during 500 BCE and 300 CE
27 Belief Systems to Come from this Era Buddhism Began sometime between the 6 th & 4 th centuries BCE with Siddhartha Gautama Ashoka spread Buddhism 263 BCE in Mauryan Empire Confucianism BCE Lasting impact on Chinese society Daoism Laozi 6 th century BCE
28 Don t Forget Animism & Shamanism Outside of core classical civilization animism and shamanism remained popular Animism belief that the natural world has powers Shamanism belief that human spirit guides (shamans) are contacts between this world and the spirit world In this era much of Africa, Andean region, & some parts of East Asia As religion or culture spread remember the term syncretism or the amalgamation of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought.
29 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE) Think about trade in general Climate and topography determine what can be grown and what raw materials are available Merchants have incentives to trade when high profit exists Today we think about goods and food as primary trade items, but then the preservation of food was the high priority: SALT Some traveled from Southwest Asia and Central Africa to get salt Afro-Eurasia trade network allowed wealthy Romans to buy silk made in China The trade network was one of multiple transactions; silk, tea, spices, or salt was relayed from town to town until it reached its final destination
30 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Silk Road
31 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Silk Road
32 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Silk Road Silk Road For centuries, only China was able to produce silk Other items traded From East Asia to points west Horses, spices, furs, ivory perfumes, lacquered boxes, furniture, rice, wool, tea, and porcelain From South Asia to points east and west Cotton, spices, & sandalwood From Central Asia to points east, west, and south Horses, camels, dates, fruit, and almonds From points west (Black Sea & Mediterranean regions) to east and south Glass, gold, furs, amber, cattle, olives, oil, perfumes
33 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Silk Road Silk Road Exchange of grains across Eurasia due to Silk Road changed farming techniques; crops grew in new regions Qanat system, underground irrigation, in arid regions allowed new crops for regions previously devoid of crops Merchants and missionaries on Silk Road introduced Buddhism, which impacted East and Southeast Asia When Han Empire collapsed many Chinese converted to Buddhism
34 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Silk Road Silk Road Disease was transported along Silk Road Bubonic plague frequently crossed Afro-Eurasia Bubonic plague perhaps contributed to fall of Han Dynasty Tea and horse caravan roads extended from southern China to South Asia Ancient Tea Route was a trade link from Yunnan, one of the first tea-producing regions: to Bengal via Burma; to Tibet; and to central China via Sichuan Province
35 Ancient Tea Route was a trade link from Yunnan, one of the first tea-producing regions: to Bengal via Burma; to Tibet; and to central China via Sichuan Province
36 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Sahara Caravan Routes Sahara Caravan Routes Commerce across North Africa Along the Mediterranean coast were coastal cities and ports, rich in vegetation & resources Commodities like dates, cotton, dyes, cloth, leather goods, and glass were supplied from these city ports South of the rim of Mediterranean Africa is the Sahara Desert. Merchants carries out gold, salt, ivory, animal hides & slaves connecting it to the Silk Road network
37 Sahara Caravan Routes c.600 BCE-c.600 CE
38 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- Sahara Caravan Routes Sahara Caravan Routes Introduction of the camel Around the change from BCE to CE the camel was introduced as a way to transport goods This led to an increase in trade between West Africa and Southwest Asia
39 Trade During the Classical Era (600 BCE to 600 CE)- North-South Eurasian routes Silk Roads ran east and west for the most part Connected to the east/west Silk Roads were more networks of trade running north and south These linked Central Asia to South and Southwest Asia Along these routes merchants carried: From South Asia: cotton, spices, & rice From Southeast Asia: spices To and from Central Asia: horses and textiles These routes connected edges of the Baltic Sea in Europe, involving Russia and the Black Sea trade Constantinople-key center linked these routes
40 Sea Networks of Africa, Europe, and Asia Developed Extensive Trade Networks by Sea Indian Ocean Trading Network This was the largest trading network in the world until Europeans began crossing the Atlantic in the late 1400s Indian Ocean connected Southeast Asia and China to Africa, the Middle East and South Asia Indian Ocean major conduit for the spread of Buddhism from South Asia to Southeast Asia in the next era c.600 to c.1450 Many items carried on Silk Road also exchanged in Indian Ocean: silk, cotton, rice, spices, horses, gold, porcelain, & people
41 Sea Networks of Africa, Europe, and Asia Developed Extensive Trade Networks by Sea Indian Ocean Trading Network This network was all dependent on successful navigation of ocean currents and wind Monsoon winds blow along the East African coast toward South Asia in the summer and down the East African coast in the winter Merchants planned their shipments accordingly Highly active trading routes for all these regions East Asia, South Asia, East African Swahilis, Arabs from Southwest Asia, Malays from Southeast Asia, Turks, Greeks, & Russians
42
43
44 Arab merchants used the dhows and a triangular lateen sail to follow the winds
45 Mediterranean & Black Sea Trading Areas Mediterranean Sea network was vast and long-lasting Started with the Egyptians and Phoenicians followed by the Greeks, Romans, & Byzantines Items traded in the Mediterranean world olives, pottery, glass, woodwork, leather, & wool textiles Out of Africa gold, ivory, salt, copper, and slaves During 1 st century CE Christianity was carried to western Europe and Africa on foot, but especially by boats that carried cargo Black Sea Through the Black Sea merchants carried goods from the Silk roads, Mediterranean and Russia
46 Mediterranean Sea Trade During Roman Empire
47 Mediterranean & Black Sea Trade
48 Exchanging Goods in the Americas Americas exchanged goods, but on a much smaller scale than Afro-Eurasia (Why?) Fewer people in the Americas of an estimated 250 million people on the earth in 1 st century, only 12 million lived in the Americas Wheel not developed the Americas until 15 th century CE (few large domesticated animals in Americas) Llama and alpaca used as pack animals in Andes & dogs pulled sheds in other parts of America Trade from South America to Central and North America difficult because of narrow Isthmus of Panama
49 Exchanging Goods in the Americas Some evidence of exchange in the Amerces with plants, tobacco, corn, and manufactured goods such as pottery, jewelry (made with gold, turquoise, or turtle shells) and clothing made from animal skins American corn first developed in Mesoamerica and it then spreads to regions north and south along trade connections Largest areas of trade in the Americas was with the Maya and Teotihuacan in Mesoamerica and with the Moche in the Andes
50 Important Migrations c.600 BCE to c.600 CE Central Asia into Europe (Huns) Attila the Hun (c CE)
51 Important Migrations c.600 BCE to c.600 CE Germanic peoples within Europe (e.g., Goths and Vandals)
52 Important Migrations c.600 BCE to c.600 CE Continued Bantu Migration Bantu people today make up about 2/3 of Africa Bantu people known as a language group
53 Bantu people known as a language group
54 Bantu Language Most widely spoken is Swahili spoken on east coast of Africa 50 million speakers of Swahili today Remember that the lingua franca is an Arabic Swahili
55 History of Bantu Migration Bantu migrated from Congo or Niger Basin This migration is one of largest in history of humans Today China s interior to exterior largest Migration took place around 1500 BCE and continued to 1800 CE
56 History of Bantu Migration No clear reason why it took place Overpopulation? Search of fertile land? Internal conflicts? External conflicts?
57 History of Bantu Migration Three phases of Bantu Migration BCE to 1000 CE East & southward CE to 1600s CE Bantu speaking state formations Great Zimbabwe th & 19 th centuries 1. Zulu state formed
58 Effects of Bantu Migration Development of novel methods of agriculture and metalworking Bantu speakers adopted livestock husbandry and passed this on to others Spread and interchange of diverse cultures
59 Key Terms & Concepts c.600 BCE to c.600 CE Classical Era Maurya/Gupta Empires Hinduism Bantu Migrations Buddhism Silk Roads Confucianism Indian Ocean Trade Christianity Fall of Classical Empires Han Empire Mandate of Heaven Chinese Examination System Mediterranean Civilizations Hellenism
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD.
 SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE)
 AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
Sea Road: Indian Ocean. By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton
 Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
PACKET D. Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade. 9 Topic Workshop #26. Module
 PACKET D Module 9 Topic Workshop #26 Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade PERIOD 3 KEY CONCEPT 3.1 Expansion and Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks KEY CONCEPT 3.1 A deepening
PACKET D Module 9 Topic Workshop #26 Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade PERIOD 3 KEY CONCEPT 3.1 Expansion and Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks KEY CONCEPT 3.1 A deepening
AP World History
 AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Student s Name: Subject: Social Studies
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SOL Narrative Review. with questions
 SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera. 1.) Define: bipedalism, primary source and Paleolithic Age.
 Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes
 Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia
 1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
8 HOW DID THE WORLD ZONES CONNECT?
 8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
Indian Ocean. Routes from India to the Arabian Peninsula and Africa
 Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
World History 3219 January 2017
 World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 1 Packet. c BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1
 Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
Review Questions 1. How did the Bantu migrations affect existing cultures?
 Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
How, when, and where did we become human?
 How, when, and where did we become human? Meet our closest ancestor, Homo erectus. Homo erectus was one of the hominid groups that was developing increasingly large brains in both Africa and Asia between
How, when, and where did we become human? Meet our closest ancestor, Homo erectus. Homo erectus was one of the hominid groups that was developing increasingly large brains in both Africa and Asia between
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
10/30/15. Big Era Four. Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE. Welcome to Big Era Four!
 Big Era Four Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE 1 Welcome to Big Era Four! 2 1 Let s focus on two key developments of this era. Population Growth Expanding Networks of Exchange
Big Era Four Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE 1 Welcome to Big Era Four! 2 1 Let s focus on two key developments of this era. Population Growth Expanding Networks of Exchange
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations
 CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
Tuesday, February 7, 17 THE SILK ROAD
 THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
AFRICA. Human Geography
 AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Where is our stuff made?
 Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
Big Era Four. Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE
 Big Era Four Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE Welcome to Big Era Four! 1200 BCE 500 CE 1 CE Big Era 4 10,000 BCE 2000 CE Big Era 3 1200 BCE 500 CE Big Era 4 Let s focus on two
Big Era Four Expanding Networks of Exchange and Encounter 1200 BCE 500 CE Welcome to Big Era Four! 1200 BCE 500 CE 1 CE Big Era 4 10,000 BCE 2000 CE Big Era 3 1200 BCE 500 CE Big Era 4 Let s focus on two
" "' Beginnings to 600 BCE. ! z. c,,
 Beginnings to 6 BCE Preparing for the AP World History exam does not mean you have to know all history "from the dawn of time" until the present. Instead, the exam focuses on important developments over
Beginnings to 6 BCE Preparing for the AP World History exam does not mean you have to know all history "from the dawn of time" until the present. Instead, the exam focuses on important developments over
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
The Qin and Han Dynasties
 The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS
 YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Packet 7. Movement of People and Goods
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Commerce and Culture
 Commerce and Culture 500 1500 CHAPTER OVERVIEW PERIOD 3: REGIONAL AND INTERREGIONAL INTERACTIONS, CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES To consider the significance of trade in human history To explore the interconnections
Commerce and Culture 500 1500 CHAPTER OVERVIEW PERIOD 3: REGIONAL AND INTERREGIONAL INTERACTIONS, CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES To consider the significance of trade in human history To explore the interconnections
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
The Civilizations of America
 The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition
 Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition Chapter 8 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Copyright 2013 by Bedford/St. Martin s I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Second Edition Chapter 8 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Copyright 2013 by Bedford/St. Martin s I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
Trade Creates Links. 430 Unit 3
 Trade Creates Links A trade network exists when a group of people or countries buys from or sells to each other on a regular basis. Historically, trade networks arose as merchants traded local products
Trade Creates Links A trade network exists when a group of people or countries buys from or sells to each other on a regular basis. Historically, trade networks arose as merchants traded local products
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties
 Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Ancient Chinese Dynasties BCE Shang Zhou
 Ancient Chinese Dynasties 1700 221 BCE Shang Zhou Shang Dynasty 1766-1050 BCE Important Because: First Chinese Dynasty historians have evidence of Called the Yellow River Civilization Bronze Civilization
Ancient Chinese Dynasties 1700 221 BCE Shang Zhou Shang Dynasty 1766-1050 BCE Important Because: First Chinese Dynasty historians have evidence of Called the Yellow River Civilization Bronze Civilization
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers. Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
SC06SS Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago?
 PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
*China s physical geography helped keep China economically and culturally isolated throughout its early dynasties *Its mountains and deserts
 Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES
 NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
Note Taking Study Guide EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA
 SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
 1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Chapter Summary. Section 2: Kingdoms of West Africa. Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa
 Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Unit 9- Medieval Europe. Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review. Name:
 1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
Fertile Crescent Empires
 Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
07 Commerce and Culture,
 07 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Introduction Modern highways are being built across Africa and Asia. part of modern process of globalization but also evoke older patterns of global commerce The roots
07 Commerce and Culture, 500 1500 Introduction Modern highways are being built across Africa and Asia. part of modern process of globalization but also evoke older patterns of global commerce The roots
The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River)
 Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods. Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick
 Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
RULING A LARGE EMPIRE
 RULING A LARGE EMPIRE The First Empire Builder: In 2,300B.C., Sargon, the ruler or Akkad, invaded and conquered the city-state of Sumer. He thus created the very first empire in known history when he spread
RULING A LARGE EMPIRE The First Empire Builder: In 2,300B.C., Sargon, the ruler or Akkad, invaded and conquered the city-state of Sumer. He thus created the very first empire in known history when he spread
The Earliest Americans. Chapter 1 Section 1
 The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources
 Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
China Before it was China. September 10, 2013
 China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia
![[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia](/thumbs/89/98244476.jpg) [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: Subject: Social Studies. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Revision Sheet: Social Studies Grade 9B 1. Trade in the Ancient World. - Trade is simply the exchange
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Revision Sheet: Social Studies Grade 9B 1. Trade in the Ancient World. - Trade is simply the exchange
Text One. The Silk Road
 Text One The Silk Road The Silk Road was an extensive network of overland trade routes across the Asian continent. They connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North
Text One The Silk Road The Silk Road was an extensive network of overland trade routes across the Asian continent. They connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North
CHINESE EMPIRE. AP World History Notes Chapter 4
 CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Growth of International Trade CE
 Growth of International Trade 1000-1500 CE OBJECTIVES Interconnectedness of global trade pre-1450 Trade links from Greenland to Western Europe Western and Eastern Europe to Muslim World Muslim world to
Growth of International Trade 1000-1500 CE OBJECTIVES Interconnectedness of global trade pre-1450 Trade links from Greenland to Western Europe Western and Eastern Europe to Muslim World Muslim world to
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
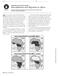 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
