1 African Beginnings
|
|
|
- Jocelin Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Section Step-by-Step Instruction Objectives Social Studies 1. Examine the ways in which the survival skills of early Africans changed over time. 2. Find out about early civilizations that arose along the Nile River. 3. Learn about the Bantu migrations. Reading/Language Arts Learn how to set a purpose for reading to establish a focus. Prepare to Read Build Background Knowledge Tell students that they will learn about Africa s first peoples in this section. Explain that archaeologists study artifacts to learn about ancient people. Ask students to suppose that a thousand years from now, archaeologists are studying your classroom. Challenge students to speculate on what the scientists might learn about them by studying various items such as pencils, a computer, and desks. Set a Purpose for Reading Preview the Objectives. Read each statement in the Reading Readiness Guide aloud. Ask students to mark the statements true or false. Have students discuss the statements in pairs or groups of four, then mark their worksheets again. Use the Numbered Heads participation strategy (TE, p. T36) to call on students to share their group s perspectives. Africa Teaching Resources, Reading Readiness Guide, p Africa Section Prepare to Read 1 African Beginnings Objectives In this section you will 1. Examine the ways in which the survival skills of early Africans changed over time. 2. Find out about early civilizations that arose along the Nile River. 3. Learn about the Bantu migrations. Taking Notes As you read, look for details about Africa s first people. Copy the chart below, and use it to record your findings. Survival Skills Early Africans Nile Civilizations Bantu Migrations Target Reading Skill Set a Purpose for Reading When you set a purpose for reading, you give yourself a focus. Before you read this section, look at the headings and illustrations to see what the section is about. Then set a purpose for reading this section. Your purpose might be to learn about the people who lived in Africa long ago. Finally, read to meet your purpose. Key Terms domesticate (duh MES tih kayt) v. to adapt wild plants or animals and breed them for human use civilization (sih vuh luh ZAY shun) n. a society that has cities, a central government, and social classes and that usually has writing, art, and architecture migrate (MY grayt) v. to move from one place to settle in another ethnic group (ETH nik groop) n. a group of people who share the same ancestors, culture, language, or religion Today, the dry sands and rocks of the Sahara cover most of North Africa. But 10,000 years ago, this large area held enough water to support many people and animals. Scientists think Africa s first farmers lived in the Sahara. Ancient paintings on cliffs and cave walls tell their story. The history of humans in Africa goes back even further in time than the history of farmers in the Sahara. Scientists believe that our early human ancestors lived in East Africa at least 2 million years ago. Today, scientists study the stone tools and bones that these ancestors left behind. By doing so, they learn about the ways our early human ancestors found to survive. Ancient cave painting from Namibia Vocabulary Builder Preview Key Terms Pronounce each key term, then ask the students to say the word with you. Provide a simple explanation such as, Dogs are domesticated animals that were tamed thousands of years ago and today are mainly pets. Target Reading Skill Set a Purpose for Reading Point out the Target Reading Skill. Tell students that setting a purpose for reading will help them to focus on important information as they read. Model the skill by setting a purpose for reading the Civilizations on the Nile subsection on p. 39. Explain that you will read the subheads and study the photos to help you set your purpose. (Possible purpose: I will learn about the people who lived in Egypt and Nubia.) Give students Preview and Set a Purpose. Have them complete the activity in groups. Africa Teaching Resources, Preview and Set a Purpose, p Africa
2 Changing Survival Skills What skills did our early human ancestors need to survive? Like people today, they needed to find food, water, and shelter to live. Survival skills changed and developed over the course of many thousands of years. Hunting and Gathering Our early human ancestors were hunter-gatherers. A hunter-gatherer is someone who hunts animals and gathers food in the wild to survive. Hunter-gatherers hunted animals to use the meat for food and the hides and fur for clothing and shelter. They ate foods such as fruits, nuts, and roots. They made tools out of wood, animal bones, and eventually stone. The first use of stone tools marks the beginning of a time period scientists call the Stone Age. The stone tools made by our early human ancestors worked very well. The scientist Louis Leakey found some of the first evidence of human ancestors in East Africa. He also taught himself how to make and use their tools. Using a two-inch, 25,000-year-old stone knife, Leakey could skin and cut up a gazelle in just 20 minutes. Studying Early Human Ancestors This stone tool (above) was made by one of our early human ancestors. For more than 30 years, Louis Leakey studied finds like this one at Olduvai Gorge (left) in Tanzania. His family (below) also studied them. Analyze Images Do you find it easy or hard to tell this stone tool from an ordinary stone? Instruct Changing Survival Skills Guided Instruction Vocabulary Builder Clarify the high-use word adapt before reading. Read Changing Survival Skills using the Oral Cloze strategy (TE, p. T33). Ask students to list the ways in which early Africans made use of the animals they hunted. (They ate their meat, used their hides and fur for clothing and shelter, and used their bones to make tools.) Discuss how the survival skills of early Africans changed over time. (They first made tools out of wood and bones, but later learned how to make better tools out of stone. Early Africans also found new ways to get food. Hunter-gatherers began farming. Their farming techniques improved over time. Domesticating plants and animals allowed them to grow better crops and create enough food to sustain settlements.) Chapter 2 Section 1 37 Vocabulary Builder Use the information below to teach students this section s high-use words. High-Use Word adapt, p. 38 conquer, p. 39 distinct, p. 41 Definition and Sample Sentence v. to make fit for a specific or new use Cheryl adapted her speech to suit her audience. v. to take control by force The emperor conquered the lands surrounding his kingdom. adj. separate; not the same I smelled the distinct aroma of fresh-baked apple pie when I walked into the bakery. Answer Analyze Images Answers will vary, but students may say that they find the stone tool difficult to distinguish from an ordinary stone. Chapter 2 Section 1 37
3 Target Reading Skill Set a Purpose As a follow up, ask students to answer the Target Reading Skill question in the Student Edition. (Possible purpose: I will learn about how survival skills changed over time in Africa. If the text did not help students accomplish their purpose, help them set a new one.) Guided Instruction (continued) Discuss the ways in which the early Africans domesticated plants and animals. (They threw away the seeds from weak plants and saved seeds from stronger ones. They tamed wild animals and then bred them.) Remind students that food surpluses allowed some early Africans to do other kinds of work. Ask What other kinds of work might have been needed in a new settlement? (Possible answers: builders to create homes, toolmakers to make farming tools) Independent Practice Ask students to create the Taking Notes graphic organizer on a blank piece of paper. Then have them fill in the Survival Skills segment of the chart with the information they have just learned. Briefly model how to identify which details to record. Monitor Progress As students fill in their organizers, circulate and make sure individuals are choosing the correct details. Provide assistance as needed. Set a Purpose What purpose did you set for the section? Has the text you have read so far helped you toward achieving this purpose? If not, set a new purpose for the rest of the section. African Farmers Today In African communities that practice agriculture today, women play a variety of roles. Here, Central African women carry firewood to their homes. Predict What activities are essential to a successful agricultural community? Farming and Herding Between 10,000 and 6,000 years ago, some hunter-gatherers began to farm and to herd animals. As you read earlier, farming in Africa probably began in North Africa, when the area that is now the Sahara offered more water than is available there today. The first farmers probably planted wild grains such as barley. At first, gatherers just protected the areas where these grains grew best. Then they began to save some seeds to plant for the next year s crop. Later, people began to domesticate plants, or adapt them for their own use. They threw away seeds from weaker plants and saved seeds from stronger ones. People also domesticated certain wild animals by taming and breeding them. Early Settlements Domesticating plants and animals meant people could have better control over their food supply. They did not have to travel to places where grains were already growing. Instead, they planted the crops they wanted. As a result, they could settle in one place. Most early farmers settled on fertile land near a water supply. Some communities produced a food surplus, or more than what was needed. Surpluses allowed some people in the community to do work other than farming. What was the Stone Age? 38 Africa Answers Predict domestication of plants and animals, planting and harvesting of crops, and irrigation The Stone Age was the period of time that began with the first use of stone tools. 38 Africa For Less Proficient Readers L1 Have students read the section as they listen to the recorded version on the Student Edition on Audio CD. Check for comprehension by pausing the CD and asking students to share their answers to the Reading Checks. Chapter 2, Section 1, Student Edition on Audio CD For Special Needs Students L1 Have students work with more able partners to create a flow chart that shows how early Africans survival skills changed over time. Display the Flow Chart Transparency and model how to fill in the first box. Africa Transparencies, Transparency B5: Flow Chart
4 Civilizations on the Nile Over a period of hundreds of thousands of years, some Stone Age groups became civilizations. A civilization is a society with cities, a government, and social classes. A social class is a group that is made up of people with similar backgrounds, wealth, and ways of living. Social classes form when people do different jobs. The types of jobs people do determine whether they are rich, poor, or in the middle. Civilizations also usually have architecture, writing, and art. A few thousand years ago, two important African civilizations Egypt and Nubia arose along the Nile River. Egypt Each summer, the Nile River used to flood its banks. The flooding waters would cover the ground with a layer of fertile silt that was ideal for farming because it enriched the soil. Around 5000 B.C., people began farming along the river s banks. They settled in scattered villages. Over many years, these villages grew into the civilization of ancient Egypt. Ancient Egypt was ruled by kings and queens. The kings of Egypt were called pharaohs (FEHR ohz). The people believed that their pharaohs were also gods. When kings and queens died, they were buried in tombs. Some of the tombs were built as large pyramids. People painted murals and picture-writing symbols called hieroglyphs (HY ur oh glifs) on the inner walls of the tombs. The ancient Egyptians became skilled in papermaking, architecture, medicine, and astronomy. Nubia In about 6000 B.C., settled hunting and fishing communities began to arise along the Nile south of Egypt. About 1,000 years later, these communities began farming. This area was called Nubia. Scientists believe the formation of Nubian kingdoms may have started around 3100 B.C. One of the greatest Nubian kingdoms was centered in the city of Napata. Around 724 B.C., the Nubians of Napata conquered Egypt. Nubians ruled Egypt for about 60 years. A later Nubian kingdom was based farther south, in the city of Meroë (MEHR oh ee). Meroë began to weaken in the A.D. 200s. It was finally conquered in A.D. 350 by invading forces from the Ethiopian kingdom of Aksum (AHK soom). What are social classes, and how are they formed? Leftover From Ancient Times The Nubian mural (top) was painted inside a tomb more than 3,000 years ago. The pair of Egyptian leather sandals (above), which are similar to the ones shown in the mural, are more than 5,000 years old. Infer What kind of information can objects like these teach us about ancient civilizations? Civilizations on the Nile Guided Instruction Vocabulary Builder Clarify the high-use word conquer before reading. Read Civilizations on the Nile with students. As they read, circulate and make sure individuals can answer the Reading Check question. Discuss the elements that characterize a civilization. (A civilization is a society with cities, a government, and different social classes that form when people do a variety of different jobs. Civilizations also have writing, architecture, and art.) Help students compare and contrast ancient Egypt and Nubia. (Both arose along the Nile, and farming was important to both. The Nubian civilization started earlier than the Egyptian.) Then ask Why do you think the banks of the Nile were a good place to start a civilization? (The banks of the Nile were fertile and good for farming. A regular food supply is needed to sustain a civilization.) Independent Practice Ask students to fill in the Nile Civilizations box of the graphic organizer with the information they have just learned. Monitor Progress As students fill in the graphic organizer, circulate and make sure individuals are choosing the correct details. Provide assistance as needed. Chapter 2 Section 1 39 For English Language Learners Pair students with native speakers to review the use of pronouns throughout this section. Encourage students to discuss the section together, using pronouns to replace some words and phrases, for example, they or them for human ancestors, kings and queens; he or him for Louis Leakey; it for the Nile River. Also ask students to explore the use of some and others as pronoun references for people. Answers Infer Objects like those pictured allow us to learn more about the daily lives of people in ancient civilizations. Social classes are groups made up of people with similar backgrounds, wealth, and ways of living. They are formed when people in a civilization do a variety of jobs. Chapter 2 Section 1 39
5 Equator Lake Victoria C OCEAN Lake Nyasa Ri E W 2 S Ask students Why do you think the Bantu language became dominant in places where Bantu-speaking people were not the native peoples? (Possible answer: They had so many skills to teach the native peoples that it became important for native peoples to learn the Bantu language in order to advance their civilizations.) ver 2 S S Tropic of Caprico pricorn rn Tropic of Ca I N D I A N KEY Or an ge Rive r O C E A N 0 miles 2000 B.C. A.D. 1 A.D. 1 A.D E 1,000 0 kilometers 1,000 Lambert Azimuthal Equal Area 4 E The Bantu Migrations About 4,000 years ago, people in Africa began one of the largest migrations that has ever taken place. To migrate is to move from one place to resettle in another. Around that time, a group of people who spoke Bantu (BAN too) languages began to migrate out of the region that today forms the border between Nigeria and Cameroon. Monitor Progress Show Section Reading Support Transparency AF 36 and ask students to check their graphic organizers individually. Why Migrate? No one knows for certain why the migrations began. Some experts believe that a new ability to grow certain crops in the tropical rain forest made the migrations possible. For example, yams and oil palms became a larger part of people s diet. Then increased food supplies may have led to overpopulation, or overcrowding of people living in one area. As a result, Bantu-speaking farmers migrated, perhaps looking for new land to farm. Over hundreds of years, settlements of Bantu speakers spread across Central and Southern Africa. Africa Transparencies, Section Reading Support Transparency AF 36 Tell students to fill in the last column of their Reading Readiness Guides. Africa Teaching Resources, Reading Readiness Guide, p Africa Answers Skills Mini Lesson Identify in north central Africa near what is today Nigeria and Cameroon Analyze Information Lake Tanganyika Students may practice their map skills by using the interactive online version of this map. 40 Africa Lake Tanganyika AT L A N T I C N Ask students to complete their charts with the information they have just learned. Equator Use Web Code lap-5211 for step-by-step map skills practice. Independent Practice ver Discuss the chain of events that some people believe led to the Bantu migrations. (Some experts believe that the ability to grow crops in the tropical rainforest led to an abundance of food, such as yams. The abundance of food may have led to overpopulation. This led the Bantu-speaking people to move to other regions to find new land to farm.) A F R I C A Ri Bantu homeland, about 2000 B.C. ezi Read about the spread of Bantu-speaking people in The Bantu Migrations. R Zam b migrations were some of the largest movements of people in history. As a result, millions of Africans today speak Bantu languages. Identify Where did the Bantu migrations begin? Analyze Information Notice that the arrows on the map change color to show time passing. Which place did the migrations reach first, Lake Tanganyika or the Orange River? er iv Vocabulary Builder Clarify the high-use academic word distinct before reading. 4 E 2 E N er ig Movement The Bantu go Guided Instruction Routes of the Bantu Migrations on The Bantu Migrations Using Special Purpose Maps 1. Teach the skill by telling students that route maps show a route, or path, from one place to another. They also include other elements common to most maps, such as a compass rose and a scale. Review the purpose of each one. 2. Help students practice the skill by looking at the map on this page to determine in what direction the Bantu traveled. 3. Have students apply the skill by determining how far the Bantu traveled south and southeast from 2000 B.C. to A.D. 1.
6
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
Graphic Organizer. Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter.
 Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago
 The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
Vocabulary Builder. netw rks. A. Content Vocabulary. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution
 Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell
 World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
Bell Ringer: August (), 2017
 Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK
 Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Ancient Civilizations
 Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest
 Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Chapter 2 Section 1. Paleolithic Age
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society
 1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
KEY. Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People
 KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers ANSWER KEY How did the development of agriculture change daily life in the Neolithic Age? P R E V I E W In the boxes below, create a two-part cartoon strip that shows
From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers ANSWER KEY How did the development of agriculture change daily life in the Neolithic Age? P R E V I E W In the boxes below, create a two-part cartoon strip that shows
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
earliest recorded history to today. writing art artifacts Centuries-old written records reveal a long-lasting civilization in
 Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT
 GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 10: THE FIRST SETTLERS
 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 10: THE FIRST SETTLERS WHAT IS PREHISTORY? Prehistory is the first period of history. It began about 2.5 million years ago when the first humans appeared.
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 10: THE FIRST SETTLERS WHAT IS PREHISTORY? Prehistory is the first period of history. It began about 2.5 million years ago when the first humans appeared.
Stone Age & Archaeology. Unit Review
 Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1
 Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Guided Reading. netw rks. The Maya. The Americas. Lesson 2 Life in the Americas ESSENTIAL QUESTION. Identifying Answer these questions about the Maya.
 Guided Reading Lesson 2 Life in the Americas ESSENTIAL QUESTION What makes a culture unique? The Maya Identifying Answer these questions about the Maya. 1. Where was the Maya civilization located? 2. From
Guided Reading Lesson 2 Life in the Americas ESSENTIAL QUESTION What makes a culture unique? The Maya Identifying Answer these questions about the Maya. 1. Where was the Maya civilization located? 2. From
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations
 Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
North American Native Americans
 North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO
 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO PREHISTORY Prehistory is the oldest and longest period of our past. It began when human beings first appeared on
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UNIT 19: LEARNING FROM THE HISTORY: LIFE THOUSANDS YEARS AGO PREHISTORY Prehistory is the oldest and longest period of our past. It began when human beings first appeared on
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age. Making A Connection
 Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
The First Americans. Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples. All images found in this PPT were found at Google.
 The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
African History. Return
 Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Chapter 1. The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C.
 Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera. 1.) Define: bipedalism, primary source and Paleolithic Age.
 Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes
 Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
Big Green Lessons Germination: Kindergarten-2 nd Grade
 Big Green Lessons Germination: Kindergarten-2 nd Grade Lesson Outcomes In this lesson, students will identify that seeds germinate and grow into plants. A seed is made up of different parts (cotyledon,
Big Green Lessons Germination: Kindergarten-2 nd Grade Lesson Outcomes In this lesson, students will identify that seeds germinate and grow into plants. A seed is made up of different parts (cotyledon,
1. Introduction enabled
 1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
Unit 3. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C.
 Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Note Taking Study Guide EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA
 SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
Famous Things ESL lesson plans from ESL-Images.com
 PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. Do you live in a wine producing country? 2. Do you think that red wine and white wine are produced in the same way? 3. When do you think people first started to make wine? 4. Which
PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. Do you live in a wine producing country? 2. Do you think that red wine and white wine are produced in the same way? 3. When do you think people first started to make wine? 4. Which
Mesopotamia LESSON. rivers for trade. civilization ancient city-state empire justice fertile irrigation conquer code punishment.
 LESSON 4 civilization ancient city-state empire justice You ve learned about how agriculture led to the first villages. Now read this selection to find out how the first villages grew into larger cities.
LESSON 4 civilization ancient city-state empire justice You ve learned about how agriculture led to the first villages. Now read this selection to find out how the first villages grew into larger cities.
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
How was life along the Yellow River both similar and different from life along the Nile River?
 As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta
 Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
First Humans of Utah NOTES #1
 First Humans of Utah NOTES #1 History History is the study of the past. It deals with written records or accounts. PREHISTORIC: Term used referring to people who lived before white explorers and missionaries
First Humans of Utah NOTES #1 History History is the study of the past. It deals with written records or accounts. PREHISTORIC: Term used referring to people who lived before white explorers and missionaries
Do Now. Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper
 Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C
 UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers
 Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming
 Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
the scientific name for us as a species Homo sapiens
 Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
NAME DATE CLASS. Paleolithic Europe and the Near East. Willendorf GREECE. Crete Cyprus EGYPT
 NAM DAT CLASS Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers SSNTIAL QUSTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUSTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during
NAM DAT CLASS Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers SSNTIAL QUSTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUSTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during
NAME DATE CLASS. Paleolithic Sites in Europe and Southwest Asia GREECE. Crete EGYPT
 Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during the
Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during the
Golden kingdoms of Africa *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1
 Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Section 2 Standards-Based Instruction
 Section 2 Ghana H-SS 7.4.2 Analyze the importance of family, labor specialization, and regional commerce in the development of states and cities in West Africa. E-LA Reading 6.2.2 Analyze text that uses
Section 2 Ghana H-SS 7.4.2 Analyze the importance of family, labor specialization, and regional commerce in the development of states and cities in West Africa. E-LA Reading 6.2.2 Analyze text that uses
Georgia. The Land And Its Early People. and the American Experience Chapter 3: Study Presentation
 Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples? Section 1: How
Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples? Section 1: How
Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period
 Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period Unit 2 - Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Overview: During this unit, students will explore how Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Kush
Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period Unit 2 - Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Overview: During this unit, students will explore how Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Kush
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
Social Studies Homework: None. Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad?
 Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
Early Native Americans of Florida
 Lesson 4 Early Native Americans of Florida Essential Question How does location affect culture? What do you think? The geography and environment of Florida that you have learned about in this unit greatly
Lesson 4 Early Native Americans of Florida Essential Question How does location affect culture? What do you think? The geography and environment of Florida that you have learned about in this unit greatly
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
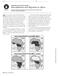 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
Ag in the Classroom Going Local
 Ag in the Classroom Going Local Post Office Box 27766 Raleigh, NC 27611 (919) 719-7282 Oh, Say Can You Seed Bean Dissection - 1 st Grade Purpose Students will identify the parts of a seed and explore the
Ag in the Classroom Going Local Post Office Box 27766 Raleigh, NC 27611 (919) 719-7282 Oh, Say Can You Seed Bean Dissection - 1 st Grade Purpose Students will identify the parts of a seed and explore the
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Before reading. Archaeology. Preparation task. Magazine Archaeology. Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise.
 Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia. Miss Genovese
 Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Historical Society SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS kshs.org
 Historical Society 6425 SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS 66615 785-272-8681 kshs.org 2014 Student Journal The Archaeology of Early Agriculture in Kansas Cali Letts Mary J. Adair Virginia A. Wulfkuhle Robert Hoard
Historical Society 6425 SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS 66615 785-272-8681 kshs.org 2014 Student Journal The Archaeology of Early Agriculture in Kansas Cali Letts Mary J. Adair Virginia A. Wulfkuhle Robert Hoard
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies?
 How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS. What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things?
 WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
