Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit One BC. What is Civilization?
|
|
|
- Rosaline Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit One BC What is Civilization?
2
3 * In the Beginning. In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. 2 Now the earth was formless and empty, darkness was over the surface of the deep, and the Spirit of God was hovering over the waters. 3 And God said, Let there be light, and there was light. 4 God saw that the light was good, and he separated the light from the darkness. 5 God called the light day, and the darkness he called night. And there was evening, and there was morning the first day. 6 And God said, Let there be a vault between the waters to separate water from water. 7 So God made the vault and separated the water under the vault from the water above it. And it was so. 8 God called the vault sky. And there was evening, and there was morning the second day. 9 And God said, Let the water under the sky be gathered to one place, and let dry ground appear. And it was so. 10 God called the dry ground land, and the gathered waters he called seas. And God saw that it was good. 11 Then God said, Let the land produce vegetation: seed-bearing plants and trees on the land that bear fruit with seed in it, according to their various kinds. And it was so. 12 The land produced vegetation: plants bearing seed according to their kinds and trees bearing fruit with seed in it according to their kinds. And God saw that it was good. 13 And there was evening, and there was morning the third day. 14 And God said, Let there be lights in the vault of the sky to separate the day from the night, and let them serve as signs to mark sacred times, and days and years, 15 and let them be lights in the vault of the sky to give light on the earth. And it was so. 16 God made two great lights the greater light to govern the day and the lesser light to govern the night. He also made the stars. 17 God set them in the vault of the sky to give light on the earth, 18 to govern the day and the night, and to separate light from darkness. And God saw that it was good. 19 And there was evening, and there was morning the fourth day. 20 And God said, Let the water teem with living creatures, and let birds fly above the earth across the vault of the sky. 21 So God created the great creatures of the sea and every living thing with which the water teems and that moves about in it, according to their kinds, and every winged bird according to its kind. And God saw that it was good. 22 God blessed them and said, Be fruitful and increase in number and fill the water in the seas, and let the birds increase on the earth. 23 And there was evening, and there was morning the fifth day. 24 And God said, Let the land produce living creatures according to their kinds: the livestock, the creatures that move along the ground, and the wild animals, each according to its kind. And it was so. 25 God made the wild animals according to their kinds, the livestock according to their kinds, and all the creatures that move along the ground according to their kinds. And God saw that it was good. 26 Then God said, Let us make mankind in our image, in our likeness, so that they may rule over the fish in the sea and the birds in the sky, over the livestock and all the wild animals, [a] and over all the creatures that move along the ground.
4 * The preponderance of evidence The evidence supporting evolution includes: Fossil finds that looked for changes in cranial size, distinct changes in canine teeth, and the shape of the pelvis Changes in cranial size indicate growth, and roundness of the brain, which demonstrate development into the large, rounded brain of modern humans, and reduce brow ridges evident in other apes Changes in canine teeth from long and sharp to more squared off demonstrate a change from ancestral ape to modern man, and most likely came about as a change in sexual dimorphism that allowed for men to engage in less regular fighting over mating rights Other changes in sexual dimoprhism include hidden year long estrus in females and no visible signs of fertility, and size difference between males and females.
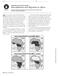
5 * The preponderance of evidence The evidence supporting evolution includes: Fossil finds that looked for changes in cranial size, distinct changes in canine teeth, and the shape of the pelvis Pelvis shape difference between ape and man would be wider pelvises in females to allow for human birth with the larger human head, and a tilting of the pelvis that would indicate bipedalism Other changes in the fossil record that indicate lineage include an increased importance on vision rather than smell indicated by larger ocular orbits; a smaller gut indicated by less of a barrel shape in the rib cage; development of a chin (only found in Homo sapiens) that enabled modern humans to make minute movements of the jaw and lips that aided in the facilitation of speech, as well did the development of a descended larynx. And several other features. Ape Skeletons
6 * The preponderance of evidence The evidence supporting evolution includes: DNA evidence of mutation and similarity between apes and man DNA investigation began with the study of blood serum albumin in apes, chimpanzees and humans. These tests indicated that immunology reactions to various factors showed a great deal of similarity between the three, indicating relationship. The strength of each reaction could be expressed by the difference in the number of amino acids, known as immunological difference. By comparing these difference with the evidence in the fossil record they could estimate when the changes had occurred and therefore determine when we had separated from both apes and chimpanzees
7 * The preponderance of evidence The evidence supporting evolution includes: DNA evidence of mutation and similarity between apes and man The difference in amino acids remained constant, particularly in DNA, and using a molecular clock method that determined at what temperature DNA would fall apart, one could determine approximately when one set of DNA had departed from another set. It could not give an exact age, only a time frame of separation (these separated 20,000 years from each other) and therefore require collaborating evidence in the fossil record to determine dates.
8 The earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Ardipithecus ramidus, supposed to have lived roughly 4.4 million years ago. They stood roughly 4 feet tall, and most likely resided in a forest like environment.
9 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus anamensis, supposed to have lived roughly 3.9 million years ago. While it showed advanced bipedal features, its skull still resembled that of the great apes
10 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus afarensis, supposed to have lived roughly 3.5 million years ago. It was between 3 6 and 5 tall and fully bipedal The most famous fossil find of early hominids is Lucy, who fell into this family
11 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus africanus, supposed to have lived roughly 3 million years ago. It was between 3 6 and 5 tall and fully bipedal Compared afarensis, africanus was slightly larger in body size. Its brain size was also slightly larger, ranging up to 500 cc, but still not advanced enough for speech. This hominid was a herbivore and ate tough, hard to chew, plants. The shape of the jaw was now like the human.
12 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus aethiopicus, supposed to have lived roughly 2 million years ago. This hominid ate a rough and hard to chew diet. He had huge molars and jaws and a large sagittal crest. A sagittal crest is a bony ridge on the skull extending from the forehead to the back of the head. Massive chewing muscles were anchored to this crest. Brain sizes were still about 500cc, with no indication of speech functions.
13 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus robustus, supposed to have lived roughly 1.75 million years ago. It had a body similar to that of africanus, but a larger and more massive skull and teeth. Its huge face was flat and with no forehead. It had large brow ridges and a sagittal crest. Brain size was up to 525cc with no indication of speech capability.
14 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the Australopithecus boisei, supposed to have lived roughly 1.1 million years ago. It was quite similar to robustus, but with an even more massive face. It had huge molars, the larger measuring 0.9 inches across. The brain size was about the same as robustus. Some authorities believe that robustus and boisei are variants of the same species.
15 The next earliest hominid (great ape) discovered is the beginning of that race of creatures who are closest to man, and not ape, and thus whose genus name begins with the descriptor of Homo, which is Greek for man. This is Homo Habilis. Homo Habilis (Greek for Handy Man ) was called this because tools were found with his fossil remains. This species existed between 2.4 and 1.5 million years ago. The brain size in earlier fossil specimens was about 500cc but rose to 800cc toward the end of the species life period. The species brain shape shows evidence that some speech had developed. Habilis was about 5' tall and weighed about 100 pounds. Some scientists believe that habilis is not a separate species and should be carried either as a later Australopithecine or an early Homo erectus. It is possible that early examples are in one species group and later examples in the other.
16 The next earliest Homo Genus discovered was Homo Erectus (Greek for upright man.) He lived between 1.8 million and 300,000 years ago. It was a successful species for a million and a half years. Early examples had a 900cc brain size on the average. The brain grew steadily during its reign. Toward the end its brain was almost the same size as modern man, at about 1200cc. The species definitely had speech. Erectus developed tools, weapons and fire and learned to cook his food. He traveled out of Africa into China and Southeast Asia and developed clothing for northern climates. He turned to hunting for his food. Only his head and face differed from modern man. Like Habilis, the face had massive jaws with huge molars, no chin, thick brow ridges, and a long low skull. Though proportioned the same, he was sturdier in build and much stronger than the modern human.
17 The next earliest Homo Genus discovered was Homo Heidelbergensis(Greek for man from Heidelberg.) He provided the bridge between erectus and Homo Sapiens during the period 200,000 to 500,000 years ago. Many skulls have been found with features intermediate between the two. Brain averaged about 1200cc and speech was indicated. Skulls are more rounded and with smaller features. Molars and brow ridges are smaller. The skeleton shows a stronger build than modern human but was well proportioned. * Homo Heidelbergensis has variously been known as Cro- Magnon Man, and Java man, and Peking Man as his remains have been discovered throughout Europe, Asia, and the southeast Asian islands, particularly Indonesia.
18 The next earliest Homo Genus discovered was Homo Nenandertalensis(Greek for man from Neandertal.) He lived in Europe and the Mideast between 150,000 and 35,000 years ago. Neandertals coexisted with Heidelbergensis, and early Sapiens. It is not known whether he was of the same species and disappeared into the Sapiens gene pool or he may have been crowded out of existence (killed off) by the Sapiens. recent DNA studies have indicated that the Neandertal was an entirely different species and did not merge into the Sapiens gene pool. Though within the last year scientists mapping the Neandertal genome have claimed that they did interbreed with non African Sapiens, and so a portion of their genome survives in modern humans. Brain sizes averaged larger than modern man at about 1450cc but the head was shaped differently, being longer and lower than modern man. His nose was large and was different from modern man in structure. He was a massive man at about 5'6" tall with an extremely heavy skeleton that showed attachments for massive muscles. He was far stronger than modern man. His jaw was massive and he had a receding forehead, like erectus.
19
20 Us. Homo Sapiens Sapiens, or in Latin, Wise Man.
21 The most widely accepted theory on the dispersal of Homo Sapiens throughout the world is known as the Out of Africa Theory The Out of Africa theory states that a small group of modern humans migrated out of Africa and into the Middle East, and that their descendants went on to populate the Earth Thus, modern humans evolved in Africa, around 150,000 to 200,000 years ago, and migrated from there around 60,000 to 125,000 years ago This theory was first proposed by Charles Darwin in his book The Descent of Man, however it was only speculation with no other evidence except guesses based on bone structure and other physical similarities between archaeological finds Beginning in the 1980 s however, DNA evidence has arisen that supports this theory above all others
22 DNA evidence supporting Out of Africa Mitochondrial DNA Mitochondrial DNA is found in the mitochondria (the powerhouse) of cells, and is inherited directly from the mother Because this DNA sits outside of the nucleus, it has a tendency to mutate much quicker than other DNA strands (approximately once every 3,500 years), and so mutations can be plotted over short spans of time By comparing human mitochondrial DNA to Chimpanzees, it can be observed that there is much less diversity between the two, and thus we are the younger of the two species. Then, assuming that Homo Erectus and Neandertals are extinct, we can chart difference in human mitochondrial DNA to arrive at the conclusion that there was one lucky woman who was the matrilineal ancestor of us all
23 DNA evidence supporting Out of Africa Mitochondrial DNA Each significant mutation found in specific groups, is known as a Haplogroup. So, for example a group that settled in China would carry a different mutation than a group that settled in Europe, or would not carry a later mutation that Europeans do Using these methods, author Brian Sykes has narrowed down the matrilineal descendant of Europe into 7 to 12 women, based on geographic origin, in his book The Seven Daughters of Eve
24 DNA evidence supporting Out of Africa Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup U (Ursula) is said to be the mother of groups of people from India to the Caucus mountains in Russia Haplogroup X (Xenia) is said to be the mother of a small portion of humans in Europe with no distinct geographic location, but pockets ranging from the Druze community in Israel, to the Shetland and Orkney Islands of Scotland. It is also very heavy in Native Americans. Haplogroup H (Helena) is said to be the mother of South Western Europe showing particularly in populations of south western France, Spain and Portugal
25 DNA evidence supporting Out of Africa Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup V (Velda) is said to be the mother of groups of people from northern Scandinavia and southern Spain Haplogroup T (Tara) is said to be the mother of groups of people from northern Italy to the eastern Baltic Sea Haplogroup K (Katherine) is said to be the mother of groups of people from Belgium, Austria and Georgia Haplogroup J (Jasmine) shows up in 2 to 12% of all Europeans from Ireland to Italy
26 DNA evidence supporting Out of Africa Y Chromosome DNA Y Chromosomal DNA is found in the sex determinant cells of males, and is inherited directly from the father to the son Y Chromosomal Adam probably lived approximately 142,000 years ago in central to west Africa The Y Chromosome has still not been fully documented, and so depending on it to trace human migration is much less sure than mitochondrial DNA traces, but what we have so far does seem to match up with migration patterns learned from matrilineal descendant
The Genus Homo Overview
 The Genus Homo Overview There are five subspecies of hominids in the genus Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, Homo sapiens neanderthalenis and Homo sapiens sapiens. Between 2.5 and 2 million
The Genus Homo Overview There are five subspecies of hominids in the genus Homo: Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, Homo sapiens neanderthalenis and Homo sapiens sapiens. Between 2.5 and 2 million
Omo- oldest known AMH found at Omo site in Ethiopia date ~ 195,000ya. Same morphology as noted above.
 Test 3 Study Guide ANATOMICALLY MODERN HUMANS- earliest fossils found in Africa dated to about 200,000 years ago, well-rounded rear of skull (no occipital bun), high skull (doesn t slope), small brow ridges
Test 3 Study Guide ANATOMICALLY MODERN HUMANS- earliest fossils found in Africa dated to about 200,000 years ago, well-rounded rear of skull (no occipital bun), high skull (doesn t slope), small brow ridges
Chapter 2: Early Hominids
 Chapter 2: Early Hominids 2.1 Introduction (p.13) o Hominids: prehistoric humans o Paleoanthropologists: specialize in studying the earliest hominids (paleo means ancient ) o (1974) Donald Johanson, an
Chapter 2: Early Hominids 2.1 Introduction (p.13) o Hominids: prehistoric humans o Paleoanthropologists: specialize in studying the earliest hominids (paleo means ancient ) o (1974) Donald Johanson, an
Who s Who on the Family Tree
 Name Time Period Characteristics: Skull: Brain: Physical size and type: Walked upright: Environment type: Social interaction: Technology: Diet: Australopithecus afarensis Meaning: 'Southern Ape of Afar'
Name Time Period Characteristics: Skull: Brain: Physical size and type: Walked upright: Environment type: Social interaction: Technology: Diet: Australopithecus afarensis Meaning: 'Southern Ape of Afar'
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago
 The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
KEY. Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People
 KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
PLANET OF THE APES. Can you imagine a world like this? Can you imagine a world like this?
 P a l e o l I t h I c P e o p l e s PLANET OF THE APES While humans are the only ones still alive today, there were once many different hominin (formerly called hominid) species living in our world. In
P a l e o l I t h I c P e o p l e s PLANET OF THE APES While humans are the only ones still alive today, there were once many different hominin (formerly called hominid) species living in our world. In
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
Evolutionary Microbiology. Chapter 12. Human Apex of All Life?
 Evolutionary Microbiology Chapter 12. Human Apex of All Life? Jong-Soon Choi Chungnam National Univ. GRAST University of Science and Technology Korea Basic Science Institute 247 Human vs. Human Being Human
Evolutionary Microbiology Chapter 12. Human Apex of All Life? Jong-Soon Choi Chungnam National Univ. GRAST University of Science and Technology Korea Basic Science Institute 247 Human vs. Human Being Human
Do Now. Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper
 Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
People of the Old Stone Age
 1 People of the Old Stone Age Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period Notebook Number 2 Neanderthal People Learned Basic Skills Imagine, if you can, a muscular group of people
1 People of the Old Stone Age Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period Notebook Number 2 Neanderthal People Learned Basic Skills Imagine, if you can, a muscular group of people
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
How Did We Get Here?
 How Did We Get Here? Where did humans come from? How did we get to where we are now? Where are we going in the future? Studying the migration patterns of humans gives us a glimpse of the development of
How Did We Get Here? Where did humans come from? How did we get to where we are now? Where are we going in the future? Studying the migration patterns of humans gives us a glimpse of the development of
Early Hominids CHAPTER. 2.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 4 Humans living 2 million years ago shaped stone and animal bones into simple tools. Early Hominids 2.1 Introduction In Chapter 1, you explored cave paintings made by prehistoric humans. Scientists
CHAPTER 4 Humans living 2 million years ago shaped stone and animal bones into simple tools. Early Hominids 2.1 Introduction In Chapter 1, you explored cave paintings made by prehistoric humans. Scientists
Chapter 2 Section 1. Paleolithic Age
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
the scientific name for us as a species Homo sapiens
 Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age. Making A Connection
 Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Chapter 2 Early Hominids. What capabilities helped hominids survive?
 2.1. Introduction Chapter 2 Early Hominids What capabilities helped hominids survive? Scientist Donald Johanson displays the partial skeleton, nicknamed Lucy, that he discovered in Africa in 1974. Prehistoric
2.1. Introduction Chapter 2 Early Hominids What capabilities helped hominids survive? Scientist Donald Johanson displays the partial skeleton, nicknamed Lucy, that he discovered in Africa in 1974. Prehistoric
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
Chapter 2. Early Hominids
 Chapter 2 Early Hominids Chapter 2 Early Hominids What capabilities helped hominids survive? 2.1 Introduction Prehistoric humans left clues about their lives in cave paintings. Scientists call these prehistoric
Chapter 2 Early Hominids Chapter 2 Early Hominids What capabilities helped hominids survive? 2.1 Introduction Prehistoric humans left clues about their lives in cave paintings. Scientists call these prehistoric
Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution. Lecture 17 & 18: Homo sapiens. Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier
 Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 17 & 18: Homo sapiens Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier While Neanderthals were evolving in Europe, hominins in Africa were becoming more like us 300-200 kya, fragmentary
Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 17 & 18: Homo sapiens Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier While Neanderthals were evolving in Europe, hominins in Africa were becoming more like us 300-200 kya, fragmentary
Chapter 2. Early Hominids. EQ: What capabilities helped hominids survive?
 2.1 Introduction Chapter 2 Early Hominids EQ: What capabilities helped hominids survive? Prehistoric humans left clues about their lives in cave paintings. Scientists call these prehistoric humans hominids.
2.1 Introduction Chapter 2 Early Hominids EQ: What capabilities helped hominids survive? Prehistoric humans left clues about their lives in cave paintings. Scientists call these prehistoric humans hominids.
The historical context
 The historical context What were our ancestors like? How did they live? How do we know about them, and how reliable is our information? New finds and methods of investigation have recently given us more
The historical context What were our ancestors like? How did they live? How do we know about them, and how reliable is our information? New finds and methods of investigation have recently given us more
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
WHI.02: Early Humans In this space, you will create a visual representation of what you have learned in the notes that follow on pages 9-15. You will be graded on your use of space, color and perceived
Early Humans Day 2. Enter Silently Begin Do Now Write HW in planner
 Early Humans Day 2 Enter Silently Begin Do Now Write HW in planner Continents/Oceans? Artifacts and Fossils Most of what we know about the earliest humans comes from the things they left behind. Archaeologists
Early Humans Day 2 Enter Silently Begin Do Now Write HW in planner Continents/Oceans? Artifacts and Fossils Most of what we know about the earliest humans comes from the things they left behind. Archaeologists
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Chapter 1. The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C.
 Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS 1. MODERN HUMANS
 THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS Modern Humans The Advent of Behavioral Modernity Advances in Technology Glacial Retreat Cave Art The Settling of Australia Settling the Americas The Peopling of the
THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS Modern Humans The Advent of Behavioral Modernity Advances in Technology Glacial Retreat Cave Art The Settling of Australia Settling the Americas The Peopling of the
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
PREHISTORY THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND
 TASK 1: How do you understand the term Prehistory? What does the prefix pre- mean? When does history start then? THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND There are three theories explaining the origins of life
TASK 1: How do you understand the term Prehistory? What does the prefix pre- mean? When does history start then? THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND There are three theories explaining the origins of life
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
CHAPTER 11. The Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans
 CHAPTER 11 The Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans Chapter Outline Approaches to Understanding Modern Human Origins The Earliest Discoveries of Modern Humans Something New and Different: The Little People
CHAPTER 11 The Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans Chapter Outline Approaches to Understanding Modern Human Origins The Earliest Discoveries of Modern Humans Something New and Different: The Little People
Historians, archeologists and anthropologists
 Historians, archeologists and anthropologists What s the difference? Searching for our Human Ancestors Information taken from Echoes of the Past Senior Author: Garfield Newman McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited,
Historians, archeologists and anthropologists What s the difference? Searching for our Human Ancestors Information taken from Echoes of the Past Senior Author: Garfield Newman McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited,
Chauvet Cave v=79luyqwznh4. Sunday, May 15, 2011
 Chauvet Cave http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=79luyqwznh4 1 2 Last time... What happened in human evolution after 25,000 years ago? How did humans change in the last 25,000 years? Anatomically? Behaviorally?
Chauvet Cave http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=79luyqwznh4 1 2 Last time... What happened in human evolution after 25,000 years ago? How did humans change in the last 25,000 years? Anatomically? Behaviorally?
Prehistoric Technology
 Prehistoric Technology Human History Prehistory generally associated with artifacts 2 million years ago to 5,000 years ago History generally associated with the emergence of written records 5,000 years
Prehistoric Technology Human History Prehistory generally associated with artifacts 2 million years ago to 5,000 years ago History generally associated with the emergence of written records 5,000 years
Lecture 0. Prehistory before civilization
 Lecture 0. Prehistory before civilization Before we ask when did mathematics begin, we may ask the following questions: When did our ancestors begin to have geometric ideas (e.g. painting in caves)? When
Lecture 0. Prehistory before civilization Before we ask when did mathematics begin, we may ask the following questions: When did our ancestors begin to have geometric ideas (e.g. painting in caves)? When
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Prehistory Evolution of Man. AP World History Chapter 1a
 Prehistory Evolution of Man AP World History Chapter 1a Development of Hominids Animals adapt themselves to environment Hominids adapt environment to themselves Use of tools Language Complex cooperative
Prehistory Evolution of Man AP World History Chapter 1a Development of Hominids Animals adapt themselves to environment Hominids adapt environment to themselves Use of tools Language Complex cooperative
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Today in Astronomy 106: apes to modern humans
 Today in Astronomy 106: apes to modern humans Meet the hominids. Brains, diet and toolmaking: going where natural selection fears to tread. Genetic diversity in Africa, the Saharan bottleneck, and the
Today in Astronomy 106: apes to modern humans Meet the hominids. Brains, diet and toolmaking: going where natural selection fears to tread. Genetic diversity in Africa, the Saharan bottleneck, and the
Chapter 1 Notes 9/15/2015 HUMAN BEGINNINGS
 Chapter 1 Notes HUMAN BEGINNINGS Score Discussion Notes 4.0 Student has mastered the learning goal and can fully explain and apply information from the agricultural revolution. 3.0 Student can summarize
Chapter 1 Notes HUMAN BEGINNINGS Score Discussion Notes 4.0 Student has mastered the learning goal and can fully explain and apply information from the agricultural revolution. 3.0 Student can summarize
China Before it was China. September 10, 2013
 China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
Traditions and Encounters A Global Perspective on the Past
 PowerPoint Presentation Materials For Instructor s Online Learning Center Traditions and Encounters A Global Perspective on the Past 5th Edition Jerry H. Bentley Herbert F. Ziegler PowerPoint Presentations
PowerPoint Presentation Materials For Instructor s Online Learning Center Traditions and Encounters A Global Perspective on the Past 5th Edition Jerry H. Bentley Herbert F. Ziegler PowerPoint Presentations
Scientific Change. Course Director: Course website: SC/NATS York University Faculty of Science and Engineering Division of Natural Science
 Scientific Change SC/NATS 1730.06 York University Faculty of Science and Engineering Division of Natural Science SC/NATS 1730, I Course Director: Professor Byron Wall Office: Room 218, Norman Bethune College
Scientific Change SC/NATS 1730.06 York University Faculty of Science and Engineering Division of Natural Science SC/NATS 1730, I Course Director: Professor Byron Wall Office: Room 218, Norman Bethune College
The Pleistocene Epoch 1
 The Pleistocene Epoch 1 Tuesday - Recall the big deal about the hominins Hominins - groups us and our bipedal ape-like ancestors Four evolutionary trends ~ 7 mya divergence from apes Adopted the following
The Pleistocene Epoch 1 Tuesday - Recall the big deal about the hominins Hominins - groups us and our bipedal ape-like ancestors Four evolutionary trends ~ 7 mya divergence from apes Adopted the following
Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society
 1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell
 World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
AP World History-Exam #1
 AP World History-Exam #1 Section 1 of this examination contains 35 multiple-choice questions. Therefore, please be careful to fill in only the ovals that are preceded by numbers 1 through 35 on your answer
AP World History-Exam #1 Section 1 of this examination contains 35 multiple-choice questions. Therefore, please be careful to fill in only the ovals that are preceded by numbers 1 through 35 on your answer
Graphic Organizer. Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter.
 Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history
 Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history So how do we form a realistic idea about humans at the Dawn of Time? With information provided by: ARCHEOLOGISTS:
Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history So how do we form a realistic idea about humans at the Dawn of Time? With information provided by: ARCHEOLOGISTS:
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
Ch 11 Modern Homo sapiens
 Ch 11 Modern Homo sapiens 1 Summary Final redtape Modern human morphology Origins and dispersal Important fossil finds Modern human/upper paleolithic culture 2 Modern humans - morphology and overview Anatomically
Ch 11 Modern Homo sapiens 1 Summary Final redtape Modern human morphology Origins and dispersal Important fossil finds Modern human/upper paleolithic culture 2 Modern humans - morphology and overview Anatomically
Vocabulary Builder. netw rks. A. Content Vocabulary. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution
 Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1
 Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
PRIMITIVE ARCHITECTURE
 What is architecture? Architecture is the way through which humans create a shelter to make their life secure and comfortable; but architecture it is also a form of communication, is the physical representation
What is architecture? Architecture is the way through which humans create a shelter to make their life secure and comfortable; but architecture it is also a form of communication, is the physical representation
TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE
 TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE Tool use did not begin with humans, but can be found among even the earliest hominin species. The primary material used for creating tools was stone, which is why the earliest period
TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE Tool use did not begin with humans, but can be found among even the earliest hominin species. The primary material used for creating tools was stone, which is why the earliest period
Before reading. Archaeology. Preparation task. Magazine Archaeology. Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise.
 Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Need: Scantron 882-E (big one) and note paper for short answer questions. Topics: End of chapter 8, chapter 9, chapters 10, a little of chapter 11
 Class updates Quiz 2 - This Wednesday, May 16 Need: Scantron 882-E (big one) and note paper for short answer questions Topics: End of chapter 8, chapter 9, chapters 10, a little of chapter 11 Short answer
Class updates Quiz 2 - This Wednesday, May 16 Need: Scantron 882-E (big one) and note paper for short answer questions Topics: End of chapter 8, chapter 9, chapters 10, a little of chapter 11 Short answer
THE HUMAN LINEAGE: Features and bilingual activities.
 THE HUMAN LINEAGE: Features and bilingual activities. Australopithecus. - 1-5 million years ago - Lived in Africa - Similar to chimpanzees - Walked on two feets - They used bones and branches Homo Habilis.
THE HUMAN LINEAGE: Features and bilingual activities. Australopithecus. - 1-5 million years ago - Lived in Africa - Similar to chimpanzees - Walked on two feets - They used bones and branches Homo Habilis.
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 25 Modern Homo sapiens Copyright Bruce Owen 2011 This semester I have not discussed the interesting
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 25 Modern Homo sapiens Copyright Bruce Owen 2011 This semester I have not discussed the interesting side branch of the Neanderthals in Europe please review
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 25 Modern Homo sapiens Copyright Bruce Owen 2011 This semester I have not discussed the interesting side branch of the Neanderthals in Europe please review
Early Man. Paleolithic and Neolithic Era
 Early Man Paleolithic and Neolithic Era Early Humans in the Paleolithic & Neolithic Ages Archaeology is the study of the ancient and recent human past through material remains. It is a subfield of anthropology,
Early Man Paleolithic and Neolithic Era Early Humans in the Paleolithic & Neolithic Ages Archaeology is the study of the ancient and recent human past through material remains. It is a subfield of anthropology,
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Water, Life, Humans, and Civilization. The First Organisms. Two energy sources: photoautotrophs. The First Organisms
 Water, Life, Humans, and Civilization The First Organisms Must survive in low-oxygen environments Could not eat other organisms for food Assemble complex carbon compounds from simple Carbon compounds (CO
Water, Life, Humans, and Civilization The First Organisms Must survive in low-oxygen environments Could not eat other organisms for food Assemble complex carbon compounds from simple Carbon compounds (CO
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Evolution. by Dana Visalli. Skull shapes & sizes: Chimpanzee, Australopithecus, Homo habilis, H. erectus, H. neanderthalensis, H.
 Human Evolution by Dana Visalli Skull shapes & sizes: Chimpanzee, Australopithecus, Homo habilis, H. erectus, H. neanderthalensis, H. sapiens This brief rendition of the story of human evolution attempts
Human Evolution by Dana Visalli Skull shapes & sizes: Chimpanzee, Australopithecus, Homo habilis, H. erectus, H. neanderthalensis, H. sapiens This brief rendition of the story of human evolution attempts
Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures
 Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures Objective: I will be able to describe the growth of Native American cultures (Paleo, Archaic, Woodland, and Mississippian) prior to European contact. B.C.-A.D. or B.C.E.-C.E.?????
Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures Objective: I will be able to describe the growth of Native American cultures (Paleo, Archaic, Woodland, and Mississippian) prior to European contact. B.C.-A.D. or B.C.E.-C.E.?????
The First Americans. Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples. All images found in this PPT were found at Google.
 The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies?
 How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
Outline. Early Modern Humans. Moderns invade Eurasia. Acheulean hand axe ( mya) Oldowan tools mya
 Outline Early Modern Humans Alan R. Rogers February 7, 2018 Archaeology and paleontology Expansion out of Africa Paleolithic Eurasia Mesolithic Eurasia 1 / 71 2 / 71 Moderns invade Eurasia Oldowan tools
Outline Early Modern Humans Alan R. Rogers February 7, 2018 Archaeology and paleontology Expansion out of Africa Paleolithic Eurasia Mesolithic Eurasia 1 / 71 2 / 71 Moderns invade Eurasia Oldowan tools
What Happened to the Neanderthals?
 What Happened to the Neanderthals? July 21, 2012 Chipwalter http://www.allthingshuman.net/what-happened-to-the-neanderthals/ It s one of the great mysteries of human evolution the disappearance of the
What Happened to the Neanderthals? July 21, 2012 Chipwalter http://www.allthingshuman.net/what-happened-to-the-neanderthals/ It s one of the great mysteries of human evolution the disappearance of the
Neanderthal or Neandertal?
 Prehistoric Times Food, Clothing, and Shelter Could you survive in the wild? TV shows like Gilligan s Island and Survivor and books and movies like Lord of the Flies ask this question. Small groups of
Prehistoric Times Food, Clothing, and Shelter Could you survive in the wild? TV shows like Gilligan s Island and Survivor and books and movies like Lord of the Flies ask this question. Small groups of
Stone Age & Archaeology. Unit Review
 Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
The Woolly Mammoth. Edward I. Maxwell
 The Woolly Mammoth The Woolly Mammoth Edward I. Maxwell The closest relative of the woolly mammoth is the Asian elephant. The main difference between the two is that the mammoth had an incredible coat
The Woolly Mammoth The Woolly Mammoth Edward I. Maxwell The closest relative of the woolly mammoth is the Asian elephant. The main difference between the two is that the mammoth had an incredible coat
+ Notes and Study Guide / Pre-Civilization and Simple Machines
 Vocabulary: + Notes and Study Guide / Pre-Civilization and Simple Machines A.D. Anno Domini or The year of our lord (referring to Jesus Christ) B.C. Before Christ B.C.E. Before the Common Era = B.C. (Not
Vocabulary: + Notes and Study Guide / Pre-Civilization and Simple Machines A.D. Anno Domini or The year of our lord (referring to Jesus Christ) B.C. Before Christ B.C.E. Before the Common Era = B.C. (Not
Die-off of large animals in many parts of the world about 15,000 10,000 B.C.E., caused by climate change and perhaps human hunting.
 Chapter 1 1. Select the word or phrase from the section that best matches the definition or example Die-off of large animals in many parts of the world about 15,000 10,000 B.C.E., caused by climate change
Chapter 1 1. Select the word or phrase from the section that best matches the definition or example Die-off of large animals in many parts of the world about 15,000 10,000 B.C.E., caused by climate change
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1
 THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Discovered: Oldest Writing in the New World
 Discovered: Oldest Writing in the New World The Cascajal block, found in Veracruz, Mexico, shows an example of ancient writing. Photograph by Michael D. Coe Catherine Clarke Fox Anthropologists study people
Discovered: Oldest Writing in the New World The Cascajal block, found in Veracruz, Mexico, shows an example of ancient writing. Photograph by Michael D. Coe Catherine Clarke Fox Anthropologists study people
166 Part Five: The Age of Humanity
 166 Part Five: The Age of Humanity et al. 1987). After analyzing mtdna samples from 147 different people from five geographic regions, Wilson and his team concluded that all humans living today are descended
166 Part Five: The Age of Humanity et al. 1987). After analyzing mtdna samples from 147 different people from five geographic regions, Wilson and his team concluded that all humans living today are descended
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C.
 CHAPTER The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Essential Question Where did early human beings originate and what were some of their technological and artistic achievements? What You Will Learn
CHAPTER The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Essential Question Where did early human beings originate and what were some of their technological and artistic achievements? What You Will Learn
EL SEGUNDO MIDDLE SCHOOL UNIT 1: EARLY HUMANS. Individuals and Societies Year 1
 EL SEGUNDO MIDDLE SCHOOL UNIT 1: EARLY HUMANS Individuals and Societies Year 1 CHAPTER 1 INVESTIGATING THE PAST Essential Question: How do social scientists interpret the past? Setting The Stage Our study
EL SEGUNDO MIDDLE SCHOOL UNIT 1: EARLY HUMANS Individuals and Societies Year 1 CHAPTER 1 INVESTIGATING THE PAST Essential Question: How do social scientists interpret the past? Setting The Stage Our study
PISA Style Scientific Literacy Question
 PISA Style Scientific Literacy Question The dodo was a large bird, roughly the size of a swan. It has been described as heavily built or even fat. It was flightless, but is believed to have been able to
PISA Style Scientific Literacy Question The dodo was a large bird, roughly the size of a swan. It has been described as heavily built or even fat. It was flightless, but is believed to have been able to
For Review Only. Contents. The World in the Year Columbus and His Big Plan The Big Voyage Land!... 12
 Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Class:... School:.. Teacher:..
 Contents: 1.- Prehistory: definition 2.- Stone Age 2.1.- Paleolithic Age 2.2.- Neolithic Age 3.- Human evolution: Australopithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus Neanderthals Homo sapiens sapiens Full name:..
Contents: 1.- Prehistory: definition 2.- Stone Age 2.1.- Paleolithic Age 2.2.- Neolithic Age 3.- Human evolution: Australopithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus Neanderthals Homo sapiens sapiens Full name:..
150,000 BCE Our mother Eve These beings may seem primitive and remote. But all our family trees have their roots in these
 1 In the beginning Humble beginnings. Life stirs in the mud pools and blossoms into fish, reptiles and finally mammals. Then humans take the stage and start to colonize the planet. IN the beginning there
1 In the beginning Humble beginnings. Life stirs in the mud pools and blossoms into fish, reptiles and finally mammals. Then humans take the stage and start to colonize the planet. IN the beginning there
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Unit 3. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C.
 Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
UNIT 5: THE STONE AGE
 UNIT 5: THE STONE AGE What is the origin of human beings? What is Prehistory? How many stages are there in Prehistory? What was life like in the Palaeolithic Age? What was life like in the Neolithic Age?
UNIT 5: THE STONE AGE What is the origin of human beings? What is Prehistory? How many stages are there in Prehistory? What was life like in the Palaeolithic Age? What was life like in the Neolithic Age?
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta
 Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK
 Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
