UHC31X Produce fermented dough and batter products
|
|
|
- Dennis Maximilian Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UHC31X Produce fermented dough and batter Unit reference number: L/507/5545 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing, cooking and finishing fermented dough and batter for service. Learners will investigate the different types of fermented dough and batter and how to produce and finish the using traditional methods, culinary science and contemporary styles. They will be able to identify faults in as well as correct and rectify them. They will learn how to use professional practices to control time and temperature, and to finish fermented dough and batter in a variety of ways whilst following food safety guidelines. Finally learners will produce and finish a range of fermented dough and batter using the skills they have developed and they will finish the to a professional standard. Learning outcomes On completion of this unit learners will: LO1 Know how to produce and cook fermented dough and batter LO2 Know how to finish fermented dough and batter LO3 Be able to prepare, cook and finish fermented dough and batter Version 7 1
2 Assessment requirements Learners must produce a portfolio of evidence which includes: 1. Service portfolio 2. Summative practical assessment 1. Service portfolio Learners must produce a service portfolio. At a minimum the service portfolio for this unit must include, producing and finishing covering all of the following: Prepared and cooked a minimum of 6 types of fermented dough and batter - White bread - Wholegrain bread - Sour dough - Flavoured breads - Baguettes - Focaccia - Ciabatta - Laminated dough goods - Brioche - Savarin - Rye breads - Seasonal doughs - Blinis Used a minimum of 6 finishing techniques - Glazing - Dipping - Dusting/dredging - Crème Chantilly - Crème patisserie - Jam - Fruits/fruit purée - Chocolate - Marzipan - Herbs - Spices - Garlic Evidence from the practical assessment must also be presented in the service portfolio. The service portfolio must be completed prior to learners undertaking the practical assessment. 2
3 2. Summative practical assessment Learners must carry out a complete assessment which will be observed and marked by centre assessors. The practical assessment must take place in a real or realistic working environment and at a minimum the practical assessment for this unit must cover: Producing a fermented dough or batter product Finishing a fermented dough or batter product Recorded professional discussion can also be used as an assessment method attached to the practical assessment and is particularly useful for gathering evidence for criteria related to evaluation and reflection. Professional discussions should be planned and recorded. 3
4 Unit content LO1 Know how to produce and cook fermented dough and batter Identify a range of fermented dough and batter : Fermented dough - Traditional, such as white and wholemeal loaves and rolls, sandwich loaf, split tin, farmhouse, batch loaf, plait, Coburg, cob, bloomer, Vienna, cottage - Ethnic and speciality breads such as pitta, naan, chapattis, paratas and roti, ciabatta, focaccia flavourings such as herbs, garlic, sun-dried tomatoes or olives are frequently added. Baguette, soda bread, rye breads, cholla, bagels, wraps or flour tortillas - Exotic, contemporary breads that have additions such as sun-dried tomatoes, basil, garlic, olives and onions and other herbs and flavours - Artisan breads made by highly trained bakers using traditional slower methods - Gluten free bread using gluten free flour Batter - Savarins, babas, brioche, blinis Identify the tools and equipment used when producing fermented dough and batter : Proofing drawer, bowls, spoons, whisks, mixers, sieves, scales, tins, moulds, knives, ovens Describe the range of ingredients used in the production of fermented dough and batter : Flour wheat is grown in many parts of the world. However flour made from `hard` wheats such as those produced in North America are higher in protein/gluten. Hard and soft wheats in milling terms are equivalent to strong and weak flours in baking. Wheat flour is the key ingredient in most bread. Flour quality is particularly important in bread making as the quality of the flour will have a significant impact on the finished product. When flour is moistened and stirred, beaten or kneaded, gluten develops to give dough `stretch`. The elastic framework of gluten holds the gas produced by the fermentation action of yeast Yeast yeast requires moisture, food and warmth for growth. When these requirements are satisfied, the yeast grows. Its function in bread making is to produce carbon dioxide gas to enable the dough to rise, expand the dough s cellular network to form bread crumb and give bread its characteristic flavour and aroma Salt salt is an essential ingredient in bread. It is used in very small amounts to give bread flavour. It also helps to strengthen the gluten and help fermentation to produce bread of good volume and texture Water water is used to produce the dough. It is important that the correct quantity of water is used when making bread because it affects the dispersal of the other ingredients Other Ingredients - Fat non-hydrogenated vegetable fat is used in very small quantities, this helps to keep the bread soft over life - Flour Treatment Agents ascorbic acid (E300 otherwise known as Vitamin C) is the most commonly used flour treatment agent in bread making. It is used to strengthen the dough and has a beneficial effect on the volume, crumb structure and softness of the bread 4
5 - Emulsifiers All emulsifiers are based on vegetable oils, they are used to provide dough stability in addition to improving loaf volume and crumb structure, and in maintaining softness - Enzymes enzymes may be added to the bread dough to supplement the enzymes naturally present in the flour and minimise variations caused by environmental factors such as climate and soil quality. Enzymes are destroyed by heat, they are therefore regarded as processing aids and, in accordance with current EU legislation, are not required to be labelled in the list of ingredients - Preservatives preservatives, such as acetic acid (vinegar), are often used in commercial baking to ensure the freshness of the product - Soya flour soya flour is milled from un-cooked soya beans, it works with the oxygen in the air to strengthen the dough, to provide support and structure to the loaf during baking. It also helps provide a creamy, bready flavour Explain how fermented dough is produced: Scaling all ingredients must be weighed accurately. Special care should be taken when measuring spices and other ingredients used in small quantities. This is very important with salt which affects the rate of fermentation Mixing mixing has three main purposes - to combine ingredients into a uniform, smooth dough, to distribute the yeast evenly throughout the dough, to develop the gluten. There are three mixing methods used for yeast doughs - the straight dough method, the modified straight dough method, and the sponge method Fermentation fermentation (first rising or first proofing) is the process when the yeast acts on the sugar and starches in the dough to produce carbon dioxide and alcohol. The dough should be placed in a greased container large enough to allow for expansion. The container should be covered and the dough left to rise in a warm, draught-free place (80 F). Fermentation is complete when the dough has doubled in size. This process may be slowed down by putting it in the refrigerator overnight. The dough must then come back to room temperature before continuing the process. If the dough rises too quickly before you have the time to finish it, you can simply punch the dough down and allow it to ferment again. The dough can rise several times. Gluten becomes smoother and more elastic during fermentation, so it can stretch and hold more gas. Dough that is under - fermented will not develop the proper volume and the texture will be poor. A dough that ferments too long or at too high a temperature will become sticky, slightly sour, and be hard to work with. Yeast action continues until the cells are killed when the temperature reaches 140 F in the oven Punching a method of deflating the dough that expels the carbon dioxide, redistributes the yeast for further growth, relaxes the gluten, and equalises the temperature throughout the dough. Pull the dough on all sides, fold it over the centre, and press down. Then turn the dough upside down in the container Scaling (measuring) scaling is simply dividing or measuring the dough into pieces of the same weight. This should be done quickly so the dough doesn t over-ferment or develop a dry exterior crust. A bench knife or knife should be used. NEVER pull or tear the dough into separate portions Rounding after scaling, the pieces of dough should be shaped into smooth round balls. Rounding simplifies the shaping process, and helps retain gases produced by the yeast Benching (relaxing) the rounded portions of dough are covered and allowed to relax for 10 to 20 minutes. This relaxes the gluten and makes the shaping of the dough easier Panning (shaping) shaping into rolls, loaves, or desired shapes and placed in pans or on baking sheets. All gases should be expelled during panning. Bubbles left in the dough will result in large air holes in the baked product. Seams should be centre bottom of each piece Proofing (rising) and proofing (second fermentation, second rising) proofing is a continuation of the process of yeast fermentation. This increases the volume of the 5
6 shaped dough. The best conditions for proofing are 90 F and 85% humidity. The dough should again double in volume. To test touch lightly, if the dough springs back slowly it is done. If it is still firm and elastic, it needs more proofing. If the dent remains or dough deflates, the dough is over-proofed. Under-proofing results in poor volume and dense texture. Over-proofing results in coarse texture and loss of flavour. French bread is usually given a long proof to create its characteristic open texture. The strong gluten can withstand the extra stretching of long proofing. Rich doughs are slightly under-proofed, because their weaker gluten will not withstand too much stretching Baking important things happen during this process. Oven spring is the rapid rise in the oven due to the production and expansion of trapped gases as a result of the oven s heat. The yeast is very active at first, but stops acting when the temperature reaches 140 F. Then coagulation of proteins and gelatinisation of starches occurs, so the dough holds shape and finally browning occurs Oven temperatures and baking times when the correct temperature is used, the process works so that the inside of the dough becomes completely baked while the crust achieves the desired colour at the same time. Larger pieces are baked at a lower temperature for a longer time than smaller rolls. Rich, sweet doughs are baked at a lower temperature because their fat, sugar and milk content make them brown faster. French breads are generally made with no sugar and a long fermentation, so they require a very high temperature to achieve the desired crust. Golden brown crust and a hollow sound when loaves are tapped with the knuckle are a good indication that the bread is cooked Cooling after baking, bread must be removed from the pans and placed on a rack to cool. This allows the excess moisture and alcohol that was created during fermentation to escape. Smaller rolls may be left on their baking sheet Storing bread served within 8 hours can be left on the rack. For longer storage wrap cooled bread, label and date Identify appropriate flavour combinations for fermented dough and batter : Sea salt, herbs, garlic, olives, sun-dried tomatoes, walnut, sugar, jam, cream, vanilla, fruits Explain how to control time, temperature and environment to achieve desired outcome when producing fermented dough and batter : Professional practices and remaining organised Keeping ingredients at correct temperature Working with dough at correct temperature Proving in correct atmosphere Explain the effect of preparation and cooking methods on the end product: Achieving a quality end product Following recipes and recipe specifications Referring to specification photographs Correct colour Correct consistency Correct texture Correct flavour Correct portion size State quality checks to be made during production of fermented dough and batter : Appearance Fermentation 6
7 Proofing correctly Consistency Aroma Portions Degree of cooking Identify potential faults for a range of fermented dough and batter : Insufficient yeast Tough and closed crumb texture High crust Pale crust Insufficient salt and sugar Dry Under-proofed or over-proofed Degree of cooking Describe procedures for correcting faults with : Reshaping and remoulding Discarding not meeting quality requirements Adding ingredients Seeking advice from appropriate person 7
8 LO2 Know how to finish fermented dough and batter Explain the finishing techniques for fermented dough and batter : Traditional, classical and modern skills and techniques glazing, brushing, dipping, dusting, spreading, glazing Culinary science fondant, apricot glaze Contemporary styles moulding, shaping, decorating Describe fillings, glazes, creams and icings for fermented dough and batter : Glazes, cream, crème Chantilly, crème patisserie, jams, fruits, fruit purées, chocolate, marzipan, herbs, spices, garlic Explain how to store fermented dough and batter : Room temperature, cool, dry, humidity control, dough with high-risk foods refrigerated, bags, wrappers, wrapped in paper, freezing, avoiding cross-contamination Explain the ingredients that may cause allergic reactions: Flours, gluten, nuts, dairy, eggs 8
9 LO3 Be able to prepare, cook and finish fermented dough and batter Comply with uniform and personal appearance standards: Wear the correct uniform to comply with health and safety, food safety, personal protective equipment (PPE) regulations. The uniform must be clean, hair must be tied back and put under a hat or hair net, beards or facial hair must be covered with a net and a clean apron must be used to prevent cross-contamination. Nails must be short, clean and unpolished. To prevent cross-contamination, no jewellery should be worn; lost jewellery will contaminate food items. Strong smelling perfume or body spray should be avoided as this will affect the flavour of delicate food items Comply with food safety and food hygiene regulations: Make sure food is safe to eat, make sure you don t add, remove or treat food in a way that makes it harmful to eat; make sure the food is the same quality that you say it is, make sure you don t mislead people by the way food is labelled, advertised or marketed, keep records on where you got food from and show this information on demand known as traceability, withdraw unsafe food and complete an incident report, tell people why food has been withdrawn or recalled e.g. a leaflet or poster, display your food hygiene rating (if you sell food direct to the public) Food additives only use an approved additive, only use it if it is approved for use in that food, the food additive doesn t exceed the maximum permitted level Materials and packaging that can be reasonably expected to come into contact with food are called food contact materials. These can include packaging, food processing equipment, cookware, work surfaces Make sure food contact materials do not transfer anything to food they touch Make sure food contact materials do not change the food they touch When inspected, be able to show where the food contact materials came from To keep food safe from bacteria, you should follow HAACP. Bacteria that cause serious health problems are - E.coli O157 and campylobacter - Salmonella, especially with the storage and handling of eggs Apply hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP): To avoid hazards. This keeps your food safe from biological, chemical and physical safety hazards Follow mise en place work plan: Plan work to timescales and follow work plan to ensure mise en place is prepared on time and correctly and the work plan should be realistic and adjusted when necessary. Work plans help to ensure that food items and dishes are ready for service Work with accuracy (reduced waste, maximum yield) Work with speed Work with proficiency Produce fermented and batter in line with product requirements: Produce for example, scaling, mixing, fermentation, punching, rounding, benching, planning, proofing Use the correct cooking methods for the dish requirements Cook the at the correct temperatures Cook the using the correct timings 9
10 Finish fermented dough and batter to meet dish requirements: Use correct fillings, glazes, creams and icings appropriate to the product, for example a savarin will be soaked in a flavoured syrup after cooking, filled with cream and then glazed with a simple jam and water glaze Use the correct finishing and decorating techniques appropriate for the. for example a focaccia can be finished with a generous drizzle of olive oil, a sprinkle of sea salt and a couple of rosemary sprigs Implement correct storage procedures: - Date, labelling, covered, correct position, stock rotation Review the finished fermented dough and batter identifying strengths and areas for improvement: Taste, texture, appearance, flavour combinations Appropriate selection of - Preparation methods - Finishing methods Recommendations for improvements - To preparation, cooking and finishing the dish - To the finished dish (texture, appearance, flavour combination) - To their own performance during the practical session 10
11 Employability skills to be demonstrated throughout the practical assessment Communication: With the head chef during service With other sections during service Talking to the head chef and other sections to coordinate finishing dishes to arrive at the pass on time Commercial and environmental awareness: Eco-friendly and cost-efficient use of resources (cleaning and consumables), disposal of waste, using less expensive ingredients, locally sourced 11
12 Assessment criteria In order to pass this unit, learners must achieve all pass criteria. The pass criteria relate to the proficient demonstration of skills and knowledge. Learning outcome The learner must: LO1 Know how to produce and cook fermented dough and batter LO2 Know how to finish fermented dough and batter Pass The learner can: P1 Identify a range of fermented dough and batter P2 Identify the tools and equipment used when producing fermented dough and batter P3 Describe the range of ingredients used in the production of fermented dough and batter P4 Explain how fermented dough is produced P5 Identify appropriate flavour combinations for fermented dough and batter P6 Explain how to control time, temperature and environment to achieve desired outcome when producing fermented dough and batter P7 Explain the effect of preparation and cooking methods on the end product P8 State quality checks to be made during production of fermented dough and batter P9 Identify potential faults for a range of fermented dough and batter P10 Describe procedures for correcting faults with P11 Explain the finishing techniques for fermented dough and batter P12 Describe fillings, glazes, creams and icings for fermented dough and batter P13 Explain how to store fermented dough and batter P14 Explain the ingredients that may cause allergic reactions LO3 Be able to prepare, cook and finish fermented dough and batter P15 Comply with uniform and personal appearance standards P16 Comply with food safety and food hygiene standards P17 Apply hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) P18 Follow mise en place work plan P19 Produce fermented dough and batter in line with dish requirements P20 Finish fermented dough and batter to meet dish requirements P21 Review the finished fermented dough and batter identifying strengths and areas for improvement 12
13 Assessment guidance Assessors must use the amplified assessment guidance in this section to judge whether assessment criteria have been achieved in the practical assessment. P15 Comply with uniform and personal appearance standards Learners must be professionally presented for practical sessions. They need to wear the correct uniform and PPE. The uniform must be clean. Hair must be tied back and under their hat and beard nets must be worn if appropriate. The learner must have minimum make up, no jewellery, no strong smelling perfume/body spray and short, clean unpainted nails. P16 Comply with food safety and food hygiene standards Learners must show that they can work within the current food safety regulations throughout the assessment. Their methods and behaviour must minimise the risk of crosscontamination and follow routines to avoid potentially severe health hazards. P17 Apply hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) Learners must follow the HACCP procedures throughout the practical assessment. P18 Follow mise en place work plan Learners must be able to follow their work plan which needs to include the resources needed, the required ingredients to cook and finish the dish and tasks with time allocations. The work plan must be realistic and the learner needs to follow the plan during mise en place. At a pass level the plan may need to be adjusted during the mise en place or the plan may in general lack detail. P19 Produce fermented dough and batter in line with dish requirements Learners must be able to show they have the skills to produce fermented dough and batter to the dish specifications and requirements. The cooking method(s) for the chosen items must be in line with the dish requirements, for example the oven must be at the correct temperature and item cooked for the correct amount of time, so the meet the requirements. Fermented dough and batter will not be over-cooked or undercooked or over-proofed or under-proofed and the texture of the finished will be in line with the dish requirements. P20 Finish fermented dough and batter to meet dish requirements Learners must use the correct finishing techniques for the chosen fermented dough and batter product. The product produced must be appropriately finished for example a focaccia will be finished with a generous drizzle of olive oil a sprinkle of flaky sea salt and a couple of rosemary sprigs (leaves stripped and finely chopped). The finished will be stored using the correct procedures for storage for the item produced. P21 Review the finished fermented dough and batter identifying strengths and areas for improvement Both the assessor and learners review finished. Learners to identify the main strengths of the and these are in line with the assessor s feedback. Through the evaluation process learners can recognise the areas for improvement based on taste, flavour balance, flavour combinations and the overall look of the dish. 13
14 Resources The special resources required for this unit are access to a real or realistic working environment which supports the provision of producing fermented dough and batter. Recommended books: Professional Patisseries for Level 2 and 3 Professional Chefs; Chris Baker, Mick Burke, Neil Rippington Hodder Education ISBN Delivery guidance Teachers are encouraged to use innovative, practical and engaging delivery methods to enhance the learning experience. Learners may benefit from: Meaningful employer engagement so they relate what is being learned to the real world of work and understand commercial competence and the use of, tools and equipment Work experience within a commercial professional kitchen or catering organisation so they can practise to hone their skills in a real environment Using interactive information and technology systems and hardware so they can learn about concepts and theories, research current trends, research product knowledge and produce visual aids Links with other units This unit is closely linked with the following units: UHC11M Food safety for catering Food safety must be embedded into every practical session and learners must be able to apply the theory of food safety to every day practices in the kitchen. UHC93M Planning for preparing, cooking and finishing dishes Planning is the key to success therefore learners will be required to create and follow a mise en place time plan for their practical assessments as included in this unit s specification. A mise en place work plan should be used for every practical session and learners should be able to implement and follow their mise en place work plan for the practical session. 14
UHC17X Produce petit fours
 UHC17X Produce petit fours Unit reference number: F/507/5512 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 60 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in the
UHC17X Produce petit fours Unit reference number: F/507/5512 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 60 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in the
UHC31M Produce fermented dough and batter products
 UHC31M Produce fermented dough and batter products Unit reference number: J/507/5544 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding
UHC31M Produce fermented dough and batter products Unit reference number: J/507/5544 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding
UV31191 Produce fermented dough and batter products
 Produce fermented dough and batter products The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing, cooking and finishing fermented dough and batter products
Produce fermented dough and batter products The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing, cooking and finishing fermented dough and batter products
UV21116 Produce fermented dough products
 Produce fermented dough products The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing, cooking and finishing fermented dough products for service in restaurants
Produce fermented dough products The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing, cooking and finishing fermented dough products for service in restaurants
UHC72M Working with chocolate
 UHC72M Working with chocolate Unit reference number: K/615/0908 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills
UHC72M Working with chocolate Unit reference number: K/615/0908 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills
Assessment Record. Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts UHC26X. Learner name: Learner number: R/507/5529. UHC26X_v3
 Assessment Record UHC26X Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts Learner name: R/507/5529 Learner number: UHC26X_v3 Service portfolio Learners must: Produce a service portfolio that includes evidence of
Assessment Record UHC26X Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts Learner name: R/507/5529 Learner number: UHC26X_v3 Service portfolio Learners must: Produce a service portfolio that includes evidence of
Artisan baking, bread and fermented
 UHC71M Artisan baking, bread and fermented dough H/615/0907 UHC71M_v1 Portfolio Learners must: Produce a portfolio that includes evidence of practical assessments carried out with proficiency. The portfolio
UHC71M Artisan baking, bread and fermented dough H/615/0907 UHC71M_v1 Portfolio Learners must: Produce a portfolio that includes evidence of practical assessments carried out with proficiency. The portfolio
UHC71M Artisan baking, bread and fermented dough
 UHC71M Artisan baking, bread and fermented dough Unit reference number: H/615/0907 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 80 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding
UHC71M Artisan baking, bread and fermented dough Unit reference number: H/615/0907 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 80 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding
UV21081 Produce biscuit, cake and sponge products
 Produce biscuit, cake and sponge products The aim of this unit is to prepare you for the production of biscuits, cakes and sponges. Baked items require particular skills and you will develop these throughout
Produce biscuit, cake and sponge products The aim of this unit is to prepare you for the production of biscuits, cakes and sponges. Baked items require particular skills and you will develop these throughout
COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS
 Name: Due Date: COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics Description: Students further their skills in the handling of yeast dough through the preparation of a variety of yeast
Name: Due Date: COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics Description: Students further their skills in the handling of yeast dough through the preparation of a variety of yeast
UV31179 Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts
 Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts The aim of this unit is to provide you with the opportunity to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in producing hot, cold and frozen desserts.
Produce hot, cold and frozen desserts The aim of this unit is to provide you with the opportunity to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in producing hot, cold and frozen desserts.
SITHCCC019 Produce cakes, pastries and breads
 Element 1. Select ingredients. 2. Select, prepare and use equipment. 3. Portion and prepare ingredients. 4. Cook cakes, pastries, breads. Performance Criteria SITHCCC019 Produce cakes, 1.1.Confirm food
Element 1. Select ingredients. 2. Select, prepare and use equipment. 3. Portion and prepare ingredients. 4. Cook cakes, pastries, breads. Performance Criteria SITHCCC019 Produce cakes, 1.1.Confirm food
On successful completion of this unit a learner will: 1 Understand the use of equipment and methods for creative patisserie work
 Unit 29: Creative Patisserie Unit code: F/601/1769 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 30 Aim This unit will enable learners to gain understanding of equipment and methods for creative patisserie work and develop
Unit 29: Creative Patisserie Unit code: F/601/1769 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 30 Aim This unit will enable learners to gain understanding of equipment and methods for creative patisserie work and develop
Yeast Breads. Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore!
 Yeast Breads Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore! Terminology Kneading: Process in which dough develops gluten to give the dough shape and structure. Gluten Protein that forms when flour and
Yeast Breads Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore! Terminology Kneading: Process in which dough develops gluten to give the dough shape and structure. Gluten Protein that forms when flour and
UV31168 Advanced skills and techniques in producing meat dishes
 Advanced skills and techniques in producing meat dishes The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in producing meat dishes. The unit builds on existing skills
Advanced skills and techniques in producing meat dishes The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in producing meat dishes. The unit builds on existing skills
Fairfield Public Schools Family Consumer Sciences Curriculum Food Service 30
 Fairfield Public Schools Family Consumer Sciences Curriculum Food Service 30 Food Service 30 BOE Approved 05/09/2017 1 Food Service 30 Food Service 30 Students will continue to participate in the school
Fairfield Public Schools Family Consumer Sciences Curriculum Food Service 30 Food Service 30 BOE Approved 05/09/2017 1 Food Service 30 Food Service 30 Students will continue to participate in the school
A d v a n c e d B a k i n g a n d P a s t r i e s ( 1 2 D )
 8 9 9 8 A d v a n c e d B a k i n g a n d P a s t r i e s ( 1 2 D ) 40S/40E/40M A Baking and Pastry Arts Course 8 9 9 8 : A d v a n c e d B a k i n g a n d P a s t r i e s ( 1 2 D ) 4 0 S / 4 0 E / 4
8 9 9 8 A d v a n c e d B a k i n g a n d P a s t r i e s ( 1 2 D ) 40S/40E/40M A Baking and Pastry Arts Course 8 9 9 8 : A d v a n c e d B a k i n g a n d P a s t r i e s ( 1 2 D ) 4 0 S / 4 0 E / 4
Preparation, cooking and finishing of hot sauces
 Preparation, cooking and finishing of hot sauces UV31172 F/600/1811 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality
Preparation, cooking and finishing of hot sauces UV31172 F/600/1811 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality
Overview of Assessment Tools PRACTICAL ASSESSMENT - PROFESSIONAL COOK 1. Candidate s Name:
 PRACTICAL ASSESSMENT - PROFESSIONAL COOK 1 Candidate s Name: Location: Date: Included in this package: Information about the practical assessment s to prepare your menu Instructions: Read all of the information
PRACTICAL ASSESSMENT - PROFESSIONAL COOK 1 Candidate s Name: Location: Date: Included in this package: Information about the practical assessment s to prepare your menu Instructions: Read all of the information
Principles of Producing Basic Pasta Dishes
 Unit 64: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Producing Basic Pasta Dishes F/502/8285 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 5 Unit aim This unit aims to provide learners with knowledge
Unit 64: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Producing Basic Pasta Dishes F/502/8285 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 5 Unit aim This unit aims to provide learners with knowledge
Overview. PPL2PC23 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, cook and finish basic bread and dough products
 Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic bread and dough products, for example: enriched dough products e.g. Chelsea buns, doughnuts bread, bread rolls naan breads pitta breads
Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic bread and dough products, for example: enriched dough products e.g. Chelsea buns, doughnuts bread, bread rolls naan breads pitta breads
UNIT TITLE: PREPARE AND PRESENT GATEAUX, TORTEN AND CAKES NOMINAL HOURS: 60
 UNIT TITLE: PREPARE AND PRESENT GATEAUX, TORTEN AND CAKES NOMINAL HOURS: 60 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HPA.CL4.07 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks, chefs and patissiers
UNIT TITLE: PREPARE AND PRESENT GATEAUX, TORTEN AND CAKES NOMINAL HOURS: 60 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HPA.CL4.07 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks, chefs and patissiers
Chef de Partie Apprenticeship Standard
 Chef de Partie Apprenticeship Standard NCFE Level 3 Certificate In Hospitality and Catering Principles (Professional Cookery) (601/7915/6) NCFE Level 3 NVQ Diploma in Professional Cookery (601/8005/5)
Chef de Partie Apprenticeship Standard NCFE Level 3 Certificate In Hospitality and Catering Principles (Professional Cookery) (601/7915/6) NCFE Level 3 NVQ Diploma in Professional Cookery (601/8005/5)
Principles of producing flour, dough and tray baked products
 Principles of producing flour, dough and tray baked products UV21103 H/502/8330 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary
Principles of producing flour, dough and tray baked products UV21103 H/502/8330 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary
FDFRBPY2B Produce yeast-raised products Version 1. Learner Resource SAMPLE
 FDFRBPY2B Produce yeast-raised products Version 1 Learner Resource FDFRBPY2B Produce yeast-raised products, V 1 i Acknowledgments TAFE NSW - Community Services, Health, Tourism and Recreation Curriculum
FDFRBPY2B Produce yeast-raised products Version 1 Learner Resource FDFRBPY2B Produce yeast-raised products, V 1 i Acknowledgments TAFE NSW - Community Services, Health, Tourism and Recreation Curriculum
Prepare, cook and finish complex bread and dough
 CU1034 Prepare, Cook and Finish Complex Bread and Dough Products Unit summary This unit is about preparing, cooking and finishing complex bread and dough. The unit covers a range of preparation and cooking
CU1034 Prepare, Cook and Finish Complex Bread and Dough Products Unit summary This unit is about preparing, cooking and finishing complex bread and dough. The unit covers a range of preparation and cooking
UHC64M Desserts. Overview. Learning outcomes. Unit reference number: A/615/0895 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30
 UHC64M Desserts Unit reference number: A/615/0895 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learner s knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing
UHC64M Desserts Unit reference number: A/615/0895 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learner s knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing
COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING
 Name: _Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING Description: Students learn about specialty cakes and pastry products by selecting and creating specialty cakes, pastries,
Name: _Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING Description: Students learn about specialty cakes and pastry products by selecting and creating specialty cakes, pastries,
Unit Summary. Achievement of this Unit will provide you with opportunities to develop the following SQA Core Skills:
 Unit Summary This Unit is about oven baking a range of dough based bakery products in a non automated bakery production environment. Dough products typically include bread and roll doughs, plain and fruited
Unit Summary This Unit is about oven baking a range of dough based bakery products in a non automated bakery production environment. Dough products typically include bread and roll doughs, plain and fruited
1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts
 Yeast Bread 1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts 2. What are the main ingredients in yeast bread and their functions. a. flour main ingredient, structure b.
Yeast Bread 1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts 2. What are the main ingredients in yeast bread and their functions. a. flour main ingredient, structure b.
Principles of preparing, cooking and finishing basic pastry products
 Principles of preparing, cooking and finishing basic pastry products UV21144 R/502/8310 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary
Principles of preparing, cooking and finishing basic pastry products UV21144 R/502/8310 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary
Bread Troubleshooting Guide
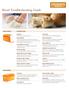 Holes in Bread weakens the dough and undermixing Dough forms a crust, trapping gas. Adjust proofer to proper humidity. Moulder Rollers in Poor Condition Trapped gas in dough causes holes. Check and repair
Holes in Bread weakens the dough and undermixing Dough forms a crust, trapping gas. Adjust proofer to proper humidity. Moulder Rollers in Poor Condition Trapped gas in dough causes holes. Check and repair
Overview. PPL3PC16 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, cook and finish complex cakes, sponges, biscuits and scones
 Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing complex cakes, sponges, biscuits, for example: Genoese/light fatless joconde sponge biscuits savarin sablé biscuits tuille biscuits fresh
Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing complex cakes, sponges, biscuits, for example: Genoese/light fatless joconde sponge biscuits savarin sablé biscuits tuille biscuits fresh
UNIT TITLE: PREPARE HOT, COLD AND FROZEN DESSERT NOMINAL HOURS: 55
 UNIT TITLE: PREPARE HOT, COLD AND FROZEN DESSERT NOMINAL HOURS: 55 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HCC.CL2.14 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks, chefs and patissiers to prepare,
UNIT TITLE: PREPARE HOT, COLD AND FROZEN DESSERT NOMINAL HOURS: 55 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HCC.CL2.14 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks, chefs and patissiers to prepare,
Section 3 Dough Management
 Section 3 Dough Management Dough is the foundation of our pizza. Dough is the least expensive part of the pizza. Never use dough that is not perfect. If the dough is not perfect, throw it out. Without
Section 3 Dough Management Dough is the foundation of our pizza. Dough is the least expensive part of the pizza. Never use dough that is not perfect. If the dough is not perfect, throw it out. Without
UHC76M Hot drinks and Barista
 UHC76M Hot drinks and Barista Unit reference number: J/615/0916 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 50 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop the learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills
UHC76M Hot drinks and Barista Unit reference number: J/615/0916 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 50 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop the learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills
Entry Level Assessment Blueprint Retail Commercial Baking
 Entry Level Assessment Blueprint Retail Commercial Baking Test Code: 4010 / Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
Entry Level Assessment Blueprint Retail Commercial Baking Test Code: 4010 / Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work
 Number of weeks 22 Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) 1 lesson a fortnight. This scheme of work has been developed to enable pupils to learn where food comes
Number of weeks 22 Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) 1 lesson a fortnight. This scheme of work has been developed to enable pupils to learn where food comes
Principles of Preparing, Cooking and Finishing Basic Pastry Products
 Unit 51: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Preparing, Cooking and Finishing Basic Pastry Products R/502/8310 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 9 Unit aim This unit aims to provide
Unit 51: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Preparing, Cooking and Finishing Basic Pastry Products R/502/8310 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 9 Unit aim This unit aims to provide
Overview. PPL2PC25 - SQA Unit Code HK8Y 04. Prepare, cook and finish basic cakes, sponges, biscuits and
 Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic cakes, sponges and, for example: victoria sponge fruit fruit cake shortbread The standard covers a range of types of preparation methods
Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic cakes, sponges and, for example: victoria sponge fruit fruit cake shortbread The standard covers a range of types of preparation methods
Unit title: Fermented Patisserie Products (SCQF level 7)
 Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: DL3F 34 Superclass: NE Publication date: August 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
Higher National Unit specification General information Unit code: DL3F 34 Superclass: NE Publication date: August 2015 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Unit purpose This Unit is designed
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT. Test Code: 4110 Version: 01
 JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT Test Code: 4110 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT Test Code: 4110 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
Certificate III in Hospitality. Patisserie THH31602
 Certificate III in Hospitality Aim Develop the skills and knowledge required by patissiers in hospitality establishments to prepare and produce a variety of high-quality deserts and bakery products. Prerequisites
Certificate III in Hospitality Aim Develop the skills and knowledge required by patissiers in hospitality establishments to prepare and produce a variety of high-quality deserts and bakery products. Prerequisites
PERFORMANCE CRITERIA To be competent you must achieve the following:
 U10001: Unit Descriptor: This unit describes the competence required to effectively prepare and bake food The unit describes the essential abilities of: Effectively maintaining safety and hygiene requirements
U10001: Unit Descriptor: This unit describes the competence required to effectively prepare and bake food The unit describes the essential abilities of: Effectively maintaining safety and hygiene requirements
Achievement of this Unit will provide you with opportunities to develop the following SQA Core Skills:
 Unit Summary This Unit is about preparing for mixing and mixing a range of fermented and non fermented dough in a non automated bakery production environment. Fermented dough typically include bread and
Unit Summary This Unit is about preparing for mixing and mixing a range of fermented and non fermented dough in a non automated bakery production environment. Fermented dough typically include bread and
UV21137 Prepare and cook fruit and vegetables
 Prepare and cook fruit and vegetables The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing and cooking fruit and vegetables to produce dishes at a professional
Prepare and cook fruit and vegetables The aim of this unit is to develop your knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing and cooking fruit and vegetables to produce dishes at a professional
Principles of preparing and cooking meat and poultry
 Principles of preparing and cooking meat and poultry UV11054 K/502/8264 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy,
Principles of preparing and cooking meat and poultry UV11054 K/502/8264 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy,
Cocktail service UV21493 F/504/4583 VRQ. Learner name: Learner number:
 Cocktail service F/504/4583 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport and Active
Cocktail service F/504/4583 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport and Active
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL
 MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 3 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 FOOD PREPARTION This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. -- 2 -- SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 A 1.2 A 1.3 C
MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 3 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 FOOD PREPARTION This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. -- 2 -- SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 A 1.2 A 1.3 C
Functions of Raising Agents
 Objective Functions of Raising Agents To investigate how different types of raising agent (baking powder, baking soda, yeast) work. Principles Raising agents, also known as leavening agents, cause baked
Objective Functions of Raising Agents To investigate how different types of raising agent (baking powder, baking soda, yeast) work. Principles Raising agents, also known as leavening agents, cause baked
NZQA registered unit standard version 1 Page 1 of 5
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of science and technology for the production of pastry products using manual methods Level 4 Credits 14 Purpose This unit standard is for people working or intending
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of science and technology for the production of pastry products using manual methods Level 4 Credits 14 Purpose This unit standard is for people working or intending
UHC62M Vegetables and vegetable dishes
 UHC62M Vegetables and vegetable dishes Unit reference number: K/615/0892 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical
UHC62M Vegetables and vegetable dishes Unit reference number: K/615/0892 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 30 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical
Principles of producing basic vegetable dishes
 Principles of producing basic vegetable dishes UV21100 H/502/8294 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality
Principles of producing basic vegetable dishes UV21100 H/502/8294 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality
UV21131 Principles of providing a buffet and carvery service
 UV21131 Principles of providing a buffet and carvery service The aim of this unit is to prepare you for service on a buffet or carvery. You will learn how to prepare the buffet or carvery in a safe and
UV21131 Principles of providing a buffet and carvery service The aim of this unit is to prepare you for service on a buffet or carvery. You will learn how to prepare the buffet or carvery in a safe and
Principles of Providing a Counter and Takeaway Service
 Unit 73: Unit code: QCF Level 1: Principles of Providing a Counter and Takeaway Service T/502/8297 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 1 Guided learning hours: 6 Unit aim The aim of this unit is to enable learners
Unit 73: Unit code: QCF Level 1: Principles of Providing a Counter and Takeaway Service T/502/8297 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 1 Guided learning hours: 6 Unit aim The aim of this unit is to enable learners
Make Holiday or Themed Cookies
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Holiday or Themed Cookies Description In this activity, students will prepare, make, and bake a sugar cookie recipe. They will finish the cookies by decorating them with
Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Holiday or Themed Cookies Description In this activity, students will prepare, make, and bake a sugar cookie recipe. They will finish the cookies by decorating them with
Yeast Breads are Easy to Make
 Yeast Breads are Easy to Make Item Type text; Book Authors Gibbs, June C. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 16/08/2018 11:12:03 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/312209
Yeast Breads are Easy to Make Item Type text; Book Authors Gibbs, June C. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 16/08/2018 11:12:03 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/312209
BINDING. Functional properties of food
 BINDING AERATION CARAMELISATION SHORTENING Functional properties of food COAGULATION HHYDROGENATION CRYSTALISATION DEXTRINISATION GELATINISATION FERMENTATION EMULSIFICATION To make successful products,
BINDING AERATION CARAMELISATION SHORTENING Functional properties of food COAGULATION HHYDROGENATION CRYSTALISATION DEXTRINISATION GELATINISATION FERMENTATION EMULSIFICATION To make successful products,
Q u i c k B r e a d s, C o o k i e s, D o u g h n u t s, a n d P i e s ( 1 1 A )
 8 3 3 8 Q u i c k B r e a d s, C o o k i e s, D o u g h n u t s, a n d P i e s ( 1 1 A ) 30S/30E/30M A Baking and Pastry Arts Course 8 3 3 8 : Q u i c k B r e a d s, C o o k i e s, D o u g h n u t s,
8 3 3 8 Q u i c k B r e a d s, C o o k i e s, D o u g h n u t s, a n d P i e s ( 1 1 A ) 30S/30E/30M A Baking and Pastry Arts Course 8 3 3 8 : Q u i c k B r e a d s, C o o k i e s, D o u g h n u t s,
UNIT TITLE: MANAGE AND OPERATE A COFFEE SHOP NOMINAL HOURS: 85
 UNIT TITLE: MANAGE AND OPERATE A COFFEE SHOP NOMINAL HOURS: 85 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HPA.CL4.01 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required in the planning, operating and managing of
UNIT TITLE: MANAGE AND OPERATE A COFFEE SHOP NOMINAL HOURS: 85 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HPA.CL4.01 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required in the planning, operating and managing of
Whole Wheat Sourdough Bread With Linseed
 Whole Wheat Sourdough Bread With Linseed The bread recipe described here owes much to two books: Peter Reinhard's Crust and Crumb and The Bread Builders by Daniel Wing and Alan Scott. I learned all my
Whole Wheat Sourdough Bread With Linseed The bread recipe described here owes much to two books: Peter Reinhard's Crust and Crumb and The Bread Builders by Daniel Wing and Alan Scott. I learned all my
Prepare and serve wines
 Prepare and serve wines K/601/4939 Learner name: Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport and
Prepare and serve wines K/601/4939 Learner name: Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport and
Overview. PPL2PC16 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, cook and finish basic hot sauces
 Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic hot sauces, for example: thickened gravy (jus lié) roast gravy (jus rôti) curry gravy white sauce (béchamel) brown sauce (demi glace)
Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic hot sauces, for example: thickened gravy (jus lié) roast gravy (jus rôti) curry gravy white sauce (béchamel) brown sauce (demi glace)
Overview. PPL2PC18 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, cook and finish basic rice dishes
 Overview This standard is about cooking and finishing basic rice dishes, for example: egg fried rice risotto pilaff/pilau kedgeree stir fry dolmades rice pudding sushi The standard covers several types
Overview This standard is about cooking and finishing basic rice dishes, for example: egg fried rice risotto pilaff/pilau kedgeree stir fry dolmades rice pudding sushi The standard covers several types
COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY
 Name: Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY Description: Students expand their knowledge and skills in the production of a variety of cake and pastry products. Outcomes:
Name: Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY Description: Students expand their knowledge and skills in the production of a variety of cake and pastry products. Outcomes:
Overview. PPL3PC19 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, process and finish marzipan, pastillage and sugar products
 Overview This standard is about preparing, processing and finishing marzipan, pastillage and sugar, for example: cake decoration wedding cakes nougatine / croquante sugar based Italian meringue fudge The
Overview This standard is about preparing, processing and finishing marzipan, pastillage and sugar, for example: cake decoration wedding cakes nougatine / croquante sugar based Italian meringue fudge The
Qualification Specification Highfield Level 2 Award in Food Allergen Awareness and Control in Catering (RQF)
 Qualification Specification Highfield Level 2 Award in Food Allergen Awareness and Control in Catering (RQF) Qualification Number: 603/1396/1 Version 1.1 May 2017 Copyright 2017. HABC Ltd. All rights reserved
Qualification Specification Highfield Level 2 Award in Food Allergen Awareness and Control in Catering (RQF) Qualification Number: 603/1396/1 Version 1.1 May 2017 Copyright 2017. HABC Ltd. All rights reserved
1. Copyright 2010 MobileHomeGourmet.com, all rights reserved.
 WHITE BREAD Makes 2 loaves By Dennis W. Viau; adapted from other recipes I think a lot of cooks shy away from making bread because they can t participate in the entire process. When you make a stir-fry
WHITE BREAD Makes 2 loaves By Dennis W. Viau; adapted from other recipes I think a lot of cooks shy away from making bread because they can t participate in the entire process. When you make a stir-fry
Make Biscuits By Hand
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Biscuits By Hand Description In this activity, students will make and bake a batch of scones from scratch. The students will be able to identify the different stages of
Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Biscuits By Hand Description In this activity, students will make and bake a batch of scones from scratch. The students will be able to identify the different stages of
A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION
 A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION Bake... To cook by dry heat in an oven, either covered or uncovered. Barbecue... To roast or cook slowly, basting with a highly
A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION Bake... To cook by dry heat in an oven, either covered or uncovered. Barbecue... To roast or cook slowly, basting with a highly
UNIT TITLE: PLAN, PREPARE AND DISPLAY A BUFFET SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 45
 UNIT TITLE: PLAN, PREPARE AND DISPLAY A BUFFET SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 45 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HCC.CL2.07 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks and chefs to plan, prepare,
UNIT TITLE: PLAN, PREPARE AND DISPLAY A BUFFET SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 45 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HCC.CL2.07 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required by cooks and chefs to plan, prepare,
Activity plan and risk assessment. Breadmaking
 Activity plan and risk assessment Breadmaking Session length: 165 minutes (2h45) Instructor/participants ratio: 1 /12 (note: two groups should never be put together) Session aim: To introduce children
Activity plan and risk assessment Breadmaking Session length: 165 minutes (2h45) Instructor/participants ratio: 1 /12 (note: two groups should never be put together) Session aim: To introduce children
The best baba is the one my colleagues from Napoli and Salerno make
 LEONARDO DI CARLO LEONARDO DI CARLO HAS ALWAYS HAD PASTRY INSIDE HIS MIND, AND SINCE A FEW MONTHS AGO ALSO IN A MONUMENTAL BOOK TITLED TRADIZIONE IN EVOLUZIONE. ARTE E SCIENCIA IN PASTICCERIA, PUBLISHED
LEONARDO DI CARLO LEONARDO DI CARLO HAS ALWAYS HAD PASTRY INSIDE HIS MIND, AND SINCE A FEW MONTHS AGO ALSO IN A MONUMENTAL BOOK TITLED TRADIZIONE IN EVOLUZIONE. ARTE E SCIENCIA IN PASTICCERIA, PUBLISHED
Cake Decorating NYS (NY only)
 Cake Decorating NYS (NY only) PURPOSE To evaluate each contestant s preparation for employment and to recognize outstanding students for excellence and professionalism in the advanced art of Cake Decorating,
Cake Decorating NYS (NY only) PURPOSE To evaluate each contestant s preparation for employment and to recognize outstanding students for excellence and professionalism in the advanced art of Cake Decorating,
Use a temperature probe, knife, skewer, finger or poke test, bite, visual colour check or sound to establish whether an ingredient or recipe is ready.
 SKILLS Weigh & measure Prepare ingredients & equipment Select and adjust cooking times Test for readiness Judge & modify sensory properties Accurate measurement of liquids & solids. Grease/oil, line, flour,
SKILLS Weigh & measure Prepare ingredients & equipment Select and adjust cooking times Test for readiness Judge & modify sensory properties Accurate measurement of liquids & solids. Grease/oil, line, flour,
Crackers, biscuits and cookies processing and factors that affect quality parameters and consumer s acceptability
 Grain Processing Technologies Class 6 September 12 th, 2017 Crackers, biscuits and cookies processing and factors that affect quality parameters and consumer s acceptability Dr. Shanise Lisie Mello El
Grain Processing Technologies Class 6 September 12 th, 2017 Crackers, biscuits and cookies processing and factors that affect quality parameters and consumer s acceptability Dr. Shanise Lisie Mello El
Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base
 CAKES Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base mixing methods. Understanding of recipe conversions
CAKES Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base mixing methods. Understanding of recipe conversions
Senior Chef Production Cooking Apprenticeship Standard
 Senior Chef Production Cooking Apprenticeship Standard NCFE Level 3 Certificate In Hospitality and Catering Principles (Professional Cookery) (601/7915/6) NCFE Level 3 NVQ Diploma in Professional Cookery
Senior Chef Production Cooking Apprenticeship Standard NCFE Level 3 Certificate In Hospitality and Catering Principles (Professional Cookery) (601/7915/6) NCFE Level 3 NVQ Diploma in Professional Cookery
Unit of competency Content Activity. Element 1: Organise coffee workstation n/a n/a. Element 2: Select and grind coffee beans n/a n/a
 SITHFAB005 Formative mapping Formative mapping SITHFAB005 Prepare and serve espresso coffee Unit of competency Content Activity Element 1: Organise coffee workstation n/a n/a 1.1 Complete mise en place
SITHFAB005 Formative mapping Formative mapping SITHFAB005 Prepare and serve espresso coffee Unit of competency Content Activity Element 1: Organise coffee workstation n/a n/a 1.1 Complete mise en place
Practice of Chinese Food II Hotel Restaurant and Culinary Science
 Practice of Chinese Food II Hotel Restaurant and Culinary Science Available Period for Learning Subject Unit Assessment Approved by the Ministry of Education: 2009.03.01~2017.02.28 Occupational Competency
Practice of Chinese Food II Hotel Restaurant and Culinary Science Available Period for Learning Subject Unit Assessment Approved by the Ministry of Education: 2009.03.01~2017.02.28 Occupational Competency
LEVEL 3 CERTIFICATE IN GENERAL PATISSERIE AND CONFECTIONERY ASSESSMENT GUIDANCE
 LEVEL 3 CERTIFICATE IN GENERAL PATISSERIE AND CONFECTIONERY ASSESSMENT GUIDANCE Issue 2 C3300-03 December 2011 Level 3 Certificate in General Patisserie and Confectionery Rules of Combination: Learners
LEVEL 3 CERTIFICATE IN GENERAL PATISSERIE AND CONFECTIONERY ASSESSMENT GUIDANCE Issue 2 C3300-03 December 2011 Level 3 Certificate in General Patisserie and Confectionery Rules of Combination: Learners
FOOD SAFETY HACCP CHARTS
 FOOD SAFETY HACCP CHARTS Latest Revision July 2016 Reviewer: H&S Mgr. Next Revision July 2017 Compliance Food Hygiene (England & Wales) Regulations 2006 Associated Policies Contents All H&S Policies 1.
FOOD SAFETY HACCP CHARTS Latest Revision July 2016 Reviewer: H&S Mgr. Next Revision July 2017 Compliance Food Hygiene (England & Wales) Regulations 2006 Associated Policies Contents All H&S Policies 1.
CREATIVE CAKE. Creative Cake, (Individual Event), recognizes a student s ability to create an artistically decorated cake.
 Creative Cake, (Individual Event), recognizes a student s ability to create an artistically decorated cake. EVENT CATEGORY Occupational Senior COMPETITION TOPIC sponge cold foaming method minimum 10 and
Creative Cake, (Individual Event), recognizes a student s ability to create an artistically decorated cake. EVENT CATEGORY Occupational Senior COMPETITION TOPIC sponge cold foaming method minimum 10 and
Make and Bake a Hand Stretched Neapolitan Pizza
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Make and Bake a Hand Stretched Neapolitan Pizza Description In this activity, students will make and bake Neapolitan-style pizza from scratch. The students will identify the
Youth Explore Trades Skills Make and Bake a Hand Stretched Neapolitan Pizza Description In this activity, students will make and bake Neapolitan-style pizza from scratch. The students will identify the
Principles of Preparing and Clearing Areas for Table Service
 Unit 36: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Preparing and Clearing Areas for Table Service R/502/8260 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 15 Unit aim The aim of this unit is to enable
Unit 36: Unit code: QCF Level 2: Principles of Preparing and Clearing Areas for Table Service R/502/8260 BTEC Specialist Credit value: 2 Guided learning hours: 15 Unit aim The aim of this unit is to enable
Knowledge booklet- Chicken products
 YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
UHC73M Drinks service
 UHC73M Drinks service Unit reference number: K/615/0911 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 50 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing
UHC73M Drinks service Unit reference number: K/615/0911 Level: 2 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 50 Overview The aim of this unit is to develop learners knowledge, understanding and practical skills in preparing
Contemporary World Food. Eleri Llwyd Jones
 Eleri Llwyd Jones 1 Contemporary world dishes; meaning dishes made from fresh regional ingredients, combining different cooking styles from around the world. Styles of food include: European, Mediterranean,
Eleri Llwyd Jones 1 Contemporary world dishes; meaning dishes made from fresh regional ingredients, combining different cooking styles from around the world. Styles of food include: European, Mediterranean,
UNIT TITLE: PROVIDE GUERIDON SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 25
 UNIT TITLE: PROVIDE GUERIDON SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 25 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HBS.CL5.11 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required to promote, prepare for and provide gueridon service
UNIT TITLE: PROVIDE GUERIDON SERVICE NOMINAL HOURS: 25 UNIT NUMBER: D1.HBS.CL5.11 UNIT DESCRIPTOR: This unit deals with skills and knowledge required to promote, prepare for and provide gueridon service
Overview. PPL2PC19 - SQA Unit Code HK Prepare, cook and finish basic pasta dishes
 Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic pasta dishes, for example: lasagne (alforno, open) macaroni cheese cannelloni spaghetti bolognaise ravioli The standard covers a range
Overview This standard is about preparing, cooking and finishing basic pasta dishes, for example: lasagne (alforno, open) macaroni cheese cannelloni spaghetti bolognaise ravioli The standard covers a range
Foods 2: Unit Notebook. Page!1
 Page 1 Baking Basics: Ingredients Flour Flours- GLUTEN: All-Purpose-most common, moderate protein Whole-Wheat-makes products denser and heavier, mixed in = parts with AP Bread-high gluten, for making yeasty
Page 1 Baking Basics: Ingredients Flour Flours- GLUTEN: All-Purpose-most common, moderate protein Whole-Wheat-makes products denser and heavier, mixed in = parts with AP Bread-high gluten, for making yeasty
Prepare and serve wines. unit 614
 unit 614 Prepare and serve wines There s a lot more to serving wine than simply taking the cork out of the bottle and filling up the glass. This unit will help guide you through what you need to know and
unit 614 Prepare and serve wines There s a lot more to serving wine than simply taking the cork out of the bottle and filling up the glass. This unit will help guide you through what you need to know and
Overview. PPL2PC29 - SQA Unit Code HK8T 04. Prepare, cook and finish dim sum
 Overview This standard is about preparing from raw ingredients, cooking and finishing the most common dim sum dishes. The standard looks at various preparation methods and then how to cook and finish dim
Overview This standard is about preparing from raw ingredients, cooking and finishing the most common dim sum dishes. The standard looks at various preparation methods and then how to cook and finish dim
Unit 292 Practice food safety methods in a hospitality establishment or demonstrated equivalent knowledge and skills.
 Unit ID: 533 Domain COMMERCIAL COOKERY AND CATERING Title: Apply advanced food preparation techniques to cook specialised meat, poultry and game dishes Level: 4 Credits: 8 Purpose This unit standard specifies
Unit ID: 533 Domain COMMERCIAL COOKERY AND CATERING Title: Apply advanced food preparation techniques to cook specialised meat, poultry and game dishes Level: 4 Credits: 8 Purpose This unit standard specifies
Gosford Hill School Year 7 Recipe Booklet September
 Gosford Hill School Year 7 Recipe Booklet September 2016-2017 Name:. Special Dietary Needs Every year the number of students and their family members with special dietary needs increases. Whether this
Gosford Hill School Year 7 Recipe Booklet September 2016-2017 Name:. Special Dietary Needs Every year the number of students and their family members with special dietary needs increases. Whether this
An Investigation into the relative gluten content of wheat flours
 An Investigation into the relative gluten content of wheat flours By Abbey.Kumar Student Number: 170312 Mrs Hendriks Background Research Earlier this year, my younger cousin was diagnosed with coeliac
An Investigation into the relative gluten content of wheat flours By Abbey.Kumar Student Number: 170312 Mrs Hendriks Background Research Earlier this year, my younger cousin was diagnosed with coeliac
MasterChef Plus Recipes. Dual Fuel 30", 36 and 48" Range Induction 30 Range
 MasterChef Plus Recipes Dual Fuel 30", 36 and 48" Range Induction 30 Range MasterChef Plus Programs Featured Recipes: 15 automatic bread programs can be found in the Gourmet Center of the MasterChef Plus
MasterChef Plus Recipes Dual Fuel 30", 36 and 48" Range Induction 30 Range MasterChef Plus Programs Featured Recipes: 15 automatic bread programs can be found in the Gourmet Center of the MasterChef Plus
CAKES MAKING. Appearance: top crust slightly rounded pale golden brown.
 CAKES MAKING Cakes are excellent served with tea. They can also be served as a puddings / desserts. Cakes can contain fresh fruits, dried fruits and assorted nuts. Fancy cakes are made with glace icing,
CAKES MAKING Cakes are excellent served with tea. They can also be served as a puddings / desserts. Cakes can contain fresh fruits, dried fruits and assorted nuts. Fancy cakes are made with glace icing,
Decorate with Basic Garnishes
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Description In this activity, students will identify, make, and select a variety of basic garnishes for decorating baked goods. This includes the writing of a basic greeting
Youth Explore Trades Skills Description In this activity, students will identify, make, and select a variety of basic garnishes for decorating baked goods. This includes the writing of a basic greeting
Yeast Bread (No Eggs Required)
 Yeast Bread (No Eggs Required) Most bread recipes require both yeast and eggs. Yeast causes the bread to rise and become light. Eggs add protein, color, and bulk to the bread. Under hardship conditions
Yeast Bread (No Eggs Required) Most bread recipes require both yeast and eggs. Yeast causes the bread to rise and become light. Eggs add protein, color, and bulk to the bread. Under hardship conditions
