Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Celiac Disease
|
|
|
- Ronald Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Celiac Disease By Comitato Scientifico Nazionale
2 published in the Official Gazette of 7 February 2008 Comitato Scientifico Nazionale (CSN-AIC): Antonio Calabrò, Carlo Catassi, Italo De Vitis, Paolo Lionetti, Stefano Martelossi,Antonio Picarelli, Riccardo Troncone, Umberto Volta 2008 edition Edited by Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genoa tel fax Translated by: Debra Levine Graphic Project and Layout: Nova Era Conegliano TV Printed by: Grafiche Scarpis - San Vendemiano Tv No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the express authorization of the AIC
3 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Celiac Disease by Comitato Scientifico Nazionale AIC
4 Permanent Conference of the Government, Regions and Autonomous Provinces of 20 December 2007 Agreement, pursuant to article 4 of legislative decree n. 281 of 28 August 1997, between thegovernment, Regions and Autonomous Provinces on the Classification Document for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Celiac Disease and Associated Pathologies. Published in the Official Gazette of 7 February 2008, n. 32, S.O. (1) Of 20 December Agreement, pursuant to article 4 of legislative decree n. 281 of 28 August 1997, between the government, the regions and the autonomous provinces on the Classification Document for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Celiac Disease and (2) Associated Pathologies. (1) Published in the Official Gazette of 7 February 2008, n. 32, S.O. (2) Issued by the Permanent Conference for relations between the government, regions and autonomous provinces of Trento and Bolzano. The Permanent Conference for relations between the government, the regions and the autonomous provinces of Trento and Bolzano In today's session of 20 December 2007; Considering articles 2, paragraph 1, letter b) and 4 of legislative decree n. 281 of 28 August 1997, which give this Conference the authority to promote and sanction agreements between the government and the regions and the autonomous provinces, in carrying out the principle of fair competition, in order to coordinate the exercise of the respective competences and carry out activities of common interest; Considering law n. 123 of 4 July 2005, Regulations for the protection of subjects suffering from Celiac Disease and in particular art. 3, paragraph 1, letters b) and c) in which it is prescribed that the regions and the autonomous provinces of Trento and Bolzano show the local health authorities the operative interventions for preventing complications and monitoring the pathologies associated with Celiac Disease, as well as for defining the diagnostic and follow-up tests for subjects affected by Celiac Disease; 4 Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
5 Considering the note of 20 December 2006 with which the Ministry of Health submitted the proposal of a classification document for the diagnosis and monitoring of Celiac Disease and associated pathologies; Whereas technical meetings to examine the proposal were held on 29 January 2007 and 9 July 2007; Considering the note dated 21 November 2007 with which the Ministry of Health sent the final version of the proposed agreement to discuss, enclosure sub A, an integral part of the present agreement; Considering the letter dated 23 November 2007, with which the Ministry of the Economy and Finance expressed its approval of the above-mentioned final version; Whereas with the note dated 27 November 2007, the Tuscany region, the interregional health coordinator, expressed a favourable technical opinion; Having acquired in the course of the present session the approval of the government, the regions and the autonomous provinces; Sanctions the agreement Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 5
6 Text of the resolution Between the Government, the regions and the autonomous provinces of Trento and Bolzano in the terms reported below: 1. The Classification Document for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Celiac Disease and Associated Pathologies is approved in accordance with the terms in enclosure sub A, referred to in the premise, an integral part of the present document. 2. The implementation of the present agreement must not entail new or greater expenses for the public finance. The administrations concerned shall take steps to implement the provisions within the limits of the human, financial and instrumental resources available at the time of the current legislation. Enclosure A CLASSIFICATION DOCUMENT FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND MONITORING OF CELIAC DISEASE AND COMPLICATIONS PREMISE 1) INTRODUCTION 2) CLINICAL PICTURES AND DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH CELIAC DISEASE 3) DIAGNOSTIC PROTOCOL AND LABORATORY TESTS OF CELIAC DISEASE 4) MONITORING OF CELIAC DISEASE 5) COMPLICATIONS OF CELIAC DISEASE 6) BIBLIOGRAPHY PREMISE In reference to what is provided for by article 3, paragraphs b) and e) of law n. 123 of 4 July 2005, the Celiac Disease Work Group", on 3 March 2006, adopted the present document bearing the classification specified in the title. The document in question was subjected to a written procedure of acceptance by the Scientific Council on Food Safety and was approved on 24 April Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
7 1. Introduction Celiac Disease (CD) is an immune-mediated enteropathy that develops in genetically predisposed subjects following the ingestion of gluten, the alcohol-soluble protein component present in certain cereals like wheat, rye, and barley. Genetic predisposition consists in the condition of homozygosis and/or heterozygosis for the alleles DQ2/DQ8 of the major histocompatibility complex of class II (HLA). The disease manifests itself with very different and polymorphic clinical pictures. The classic form usually begins in the first 6-24 months, shortly after the introduction of gluten during weaning, and presents gastrointestinal symptoms such as chronic diarrhoea, vomiting, globose abdomen, meteorism, lack of appetite. These are accompanied by laboratory results and symptoms that are the consequence of malabsorption such as anaemia, alterations of coagulation, oedema, vitamin and mineral deficiencies. This form is becoming rare by now, but there has been an increasing incidence in the late-onset type characterised by atypical gastrointestinal symptoms and by extra-gastrointestinal manifestations, isolated or associated with each other. Moreover, the development of serological tests that can identify the presence of specific antibodies for CD (antiendomysium antibodies and anti-transglutaminase antibodies) has made it possible to define the silent form of the disease (presence of pathognomonic intestinal lesions in the absence of signs and symptoms) and the potential form (positive serology without intestinal lesions). In recent years, greater knowledge and awareness of the disease by health workers and the availability of serological tests to identify subjects at risk to send for endoscopic exams has made it possible to identify celiac subjects who would have remained undiagnosed otherwise. Currently it is estimated that one individual out of every 100/150 is affected by Celiac Disease, for a prevalence of 0.6-1% in the general population. Only some of these patients are aware of the disease however. In fact, in Italy there are just over 70,000 known celiac individuals, against a real number calculated to be around 500,000. Therefore, for every celiac individual that is diagnosed, roughly 7 go undiagnosed and/or are misdiagnosed. The only therapy available now for subjects affected by CD is the complete and permanent exclusion of gluten-containing foods from the diet. This therapy not only enables the rapid disappearance of the symptoms and diseases associated with CD (clinical recovery usually occurs about 1-2 months from the time that gluten is excluded), but prevents the development of the neoplastic and autoimmune complications that continued and prolonged exposure to gluten provokes in celiac subjects. Considering the diligence that the gluten-free diet requires, its costs for the National Health Service (due to the elevated number of patients and the costs of gluten-free products, a part of which are covered by the National Health Service) and its importance Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 7
8 not only in the short term, but above all in the prevention of complications in the long term, the diagnosis of Celiac Disease must be early and accurate. In recent years, there has been considerable scientific evidence regarding the eziopathogenesis and immunological alterations of CD, based on which new tests have been introduced to identify subjects at risk of Celiac Disease. The greater availability of clinical tests has led to wide variability in the diagnostic process, which, together with the clinical variability of CD and the invasiveness of the gastroduodenoscopy with biopsy, often makes the diagnosis difficult and late, if not altogether wrong. For these reasons, it is necessary to define a classification document for the diagnosis and monitoring of the subjects affected. The present document has the aim of harmonizing the diagnostic path of CD, increasing its sensitivity and specificity, allowing the diagnosis of cases that still escape medical attention, introducing the use of more effective serological and instrumental examinations in clinical practice and preventing the complications that celiac subjects are at greater risk of developing. 2. Clinical Pictures and Diseases Associated with Celiac Disease! In the classic form, with early onset (first 6-24 months of life), the disease generally presents itself shortly after weaning with chronic diarrhoea, vomiting, globose abdomen, lack of appetite, arrested growth or weight loss, and irritability.! Currently Celiac Disease tends to manifest itself ever more frequently in the late-onset form, with intestinal disturbances that are both typical and atypical (such as recurrent abdominal pain, constipation, meteorism) and especially with extra-intestinal manifestations (Tab. 1) Table 1. Extra-intestinal manifestations Herpetiform dermatitis Anaemia Low stature Delayed puberty Infertility and recurrent miscarriages Alopecia areata Aphthous stomatitis Dental enamel hypoplasia Hypertransaminasemia of unknown cause Neurological disturbances: drug-resistant epilepsy, ataxia, polyneuropathy Osteoporosis Dilative myocardiopathy Arthritis 8 Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
9 ! There also exist:! Silent forms: typical gluten enteropathy occasionally found in genetically predisposed, asymptomatic individuals with positive serology, often among those who undergo screening because they are members of at risk groups;! Potential forms: positive serology, normal mucosal architecture.! If Celiac Disease is not adequately treated, it predisposes the celiac individual to a series of complications such as osteoporosis and tumours, in particular non-hodgkin's lymphoma of the intestine. There are also various diseases associated with Celiac Disease (Tab. 2). Table 2. Associated diseases Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus Hashimoto's Thyroiditis Sjogren's Syndrome Down's Syndrome Turner Syndrome IgA deficiency Multiple sclerosis Primitive biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis! Finally, there is strong evidence that parents and siblings of celiac individuals have an increased risk of developing the disease, with a prevalence that ranges from 6-12%. * "Celiac disease" Work Group: S. Auricchio, A.Calabrò, E. Cardi, A.M.Castellazzi, M. De Vincenzi, P.Fagioli, G.B. Gasbarrini, L.Guidarelli, S.Moretti, M.P. Patrizi, N. Pogna, A.Pucci, F. Romano, V. Silano 3. Diagnostic protocol and laboratory tests of Celiac Disease From the perspective of public health, it is essential to establish guidelines that permit having simple protocols, based on essential tests, that are applicable throughout the national territory and that can identify the greatest number of celiac subjects possible and ensure that they are monitored (Tab.3). Table 3. Criteria of the Diagnostic Protocol for Celiac Disease Simple (few essential tests) Applicable in all the Centres in the national territory Able to identify the greatest number of celiac individuals (reducing the number of missed diagnoses) and to avoid false diagnoses (still very high) It is possible to identify three different diagnostic paths depending on whether one is up against a strong clinical suspicion of Celiac Disease, patients with a low probability of Celiac Disease, and parents and siblings of celiac individuals (Tab. 4). Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 9
10 Table 4. Diagnostic Protocol High clinical suspicion of Celiac Disease Moderate-low probability of Celiac Disease First-degree relatives of celiac individuals, including brothers and sisters The tests to use for the diagnosis of Celiac Disease are antibody markers and intestinal biopsy (Tab. 5). Table 5 First level tests Antibodies *(1) A. Human anti-ttg type IgA (IgG in presence of IgA deficiency) Duodenal Biopsy The Marsh classification, as modified by Oberhuber, to be set in the clinical, antibody and genetic context * EMA as a corroborating test to be performed in Centres of reference in doubtful cases * The search for AGA of IgA class should be confined to children under two years of age (1) The services to the search for anti-transglutaminase antibodies (IgG, IgA) and the search for anti-endomysium antibodies are not currently included in the list of ambulatory specialist services supplied by the National Health Service pursuant to the Ministerial Decree of 22 July 1996 (currently being updated) The Marsh classification, as modified by Oberhuber, is universally accepted and utilized to interpret histological alterations in the small intestine (Tab. 6). Table 6. Histological Classification of Intestinal Lesions in Celiac Disease Increasing IEL (greater than 40*/100 ec) *(according to new criteria, (type 1) greater than 25/100 ec) Crypt hyperplasia (type 2) Slight villous atrophy (type 3a) Partial villous atrophy (type 3b) Subtotal villous atrophy (type 3c) IEL: intraepithelial lymphocytes; ec: epithelial cells The Marsh classification, as modified by Oberhuber, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999 The HLA is a second level test able to assess compatibility with the diagnosis of Celiac Disease in those cases that are doubtful (Tab. 7). Table 7 II level tests: HLA (after non-diagnostic antibodies and/or biopsy) Test performed to exclude Celiac Disease Negative DQ2/DQ8: very low probability of Celiac Disease Positive DQ2 or DQ8: predisposition for the disease (e.g. in parents and siblings of celiac subjects) 10 Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
11 The detailed analysis of the various paths of the diagnostic protocol is illustrated in Figures 1, 2 and 3. Fig.1 Subjects with a high risk of Celiac Disease (forms of manifest malabsorption with weight loss, asthenia and diarrhoea) Celiac disease highly suspected Duodenal biopsy +serum IgA + anti ttg* IgG anti ttg (if IgA deficient) IgA anti ttg (if IgA are normal) Positive serology + normal biopsy HLA DQ2 DQ8 determination Positive serology + positive biopsy CELIAC DISEASE Negative serology + positive biopsy Exclusion of other causes of flat mucosa If positive, monitor anti-ttg and repeat multiple endoscopic biopsies or GFD trial to verify clinical antibody response If negative, anti ttg false positive^ HLA DQ2 DQ8 determination If positive, CELIAC DISEASE, to be confirmed by GFD and challenge (histology type 1-2 monitor and repeat multiple endoscopic biopsies) If negative, low probability of Celiac Disease^ and further investigation for other causes of mucosal damage *In subjects under 2 years of age test for AGA as well as anti-ttg ^ rare cases of DQ2-DQ8 negative Celiac Disease Particularly discordant cases as regards histology and serology to be sent to Centres of high specialisation Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 11
12 Fig.2 Subjects with a low or medium risk of Celiac Disease: with one or few symptoms Cases with one or few symptoms Serum IgA+anti ttg* IgG anti ttg (if IgA deficient) Negative serology Diagnosis of Celiac Disease excluded Positive histology (type 3a - 3c) IgA anti ttg (If IgA are normal) Positive serology Duodenal biopsy Negative histology or type 1-2 Fig.3 - First degree relatives, including siblings CELIAC DISEASE HLA DQ2 DQ8 determination If positive, monitor anti ttg and repeat multiple endoscopic biopsies If negative, false positive anti ttg^ *If under 2 years old, test for AGA as well as for anti ttg ^rare cases of Celiac Disease are not positive for DQ2, DQ8 Particularly discordant cases as regards histology and serology to be sent to Centres of high specialisation IgG anti ttg (if IgA deficient) First degree relatives, including siblings Serum IgA + anti ttg* IgA anti ttg (if IgA are normal) Negative serology HLA DQ2 DQ8 determination Positive serology Duodenal biopsy If positive, predisposition to Celiac Disease. Monitor with anti ttg If negative diagnosis of Celiac Disease is excluded Positive histology (type 3a-3c) CELIAC DISEASE If positive or normal histology, monitor. If positive and type1-2, evaluate case by case Negative histology or type 1-2 HLA DQ2 DQ8 determination If negative, anti ttg false positive^, check anti ttg *If under 2 years old, test for AGA as well as for anti ttg ^rare cases of Celiac Disease are not positive for DQ2, DQ8 Particularly discordant cases as regards histology and serology to be sent to Centres of high specialisation 12 Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
13 4. Monitoring of Celiac Disease The principal aims of monitoring are summarized in Table 8: Table 8. Indications for monitoring Verification of compliance with the diet Development of associated autoimmune pathology despite the gluten-free diet (e.g. autoimmune thyroiditis) Metabolic alterations (dyslipidemia, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) Possible development of neoplastic (lymphoma) and other complications (refractory Celiac Disease, ulcerative jejunum ileitis, collagenous sprue), particularly in cases diagnosed in an advanced age The recommended examinations for all celiac subjects are summarized in Table 9: Table 9. Monitoring of Celiac Disease in all cases It is suggested to have a first follow-up examination 6 months from diagnosis and then yearly by means of: Medical exam with dietary interview at a specialized centre blood absorption tests ferritin, blood count Immunological and autoimmune markers ttga IgA (of the IgG class if IgA deficit) TSH, anti-tpo, anti-thyroglobulin antibodies Motivation: assessment of the absorbing function of the intestine, of compliance with the gluten-free diet and the development of autoimmune thyroiditis The exams to perform in selected cases are summarized in Table 10: Table 10. Monitoring of Celiac Disease in selected cases Blood tests useful in selected cases: metabolic tests: cholesterol, HDL, triglycerides, glycaemia, transaminases immunological tests: organ and non-organ specific autoantibodies Motivation: assessment of the metabolic state (in relation to the possible weight gain favoured by resumed absorption and the gluten-free diet, which is high in lipids) and the possible development of autoimmune disorders (the longer the celiac subject follows an unrestricted diet, the greater the autoimmune disorders) One of the most important examinations involved in the follow-up of Celiac Disease is bone densitometry, which should always be carried out at the moment of diagnosis to document the presence of osteopenia or osteoporosis (table 1), and which has to be repeated every 18 months if it is pathological. The problem is known to be more important in adults, even though cases of osteopenia and osteoporosis have also been reported in children, in whom in general the gluten-free diet leads to significant Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 13
14 improvements within the first year of exclusion of gluten from the diet. 5. Complications of Celiac Disease Moving on to consider the complications of Celiac Disease, it has been widely documented how Celiac Disease, especially if diagnosed late (unfortunately still a frequent occurrence) and not followed by a rigorously gluten-free diet, can induce significantly higher mortality than what is found in the general population. Some of the most dangerous complications of Celiac Disease, fortunately very rare, include hyposplenism, "sprue or refractory Celiac Disease", collagen colitis, ulcerative jejunum-ileitis, non-hodgkin lymphoma and other neoplasms (especially those involving the small intestine and oesophagus). These complications are always suspected in any patient who complains about an unjustified persistence or reappearance of diarrhoea, abdominal pains, weight loss, fever, intense asthenia and sensation of serious malaise despite following a rigorously glutenfree diet. The possible onset of these complications should be considered especially in cases in which the diagnosis of Celiac Disease was made at an advanced age and/or in which the gluten-free diet was not followed painstakingly. The diagnosis and treatment of the complications often require specialist skills different from those that are purely gastroenterological (e.g., the contribution of a haematologist is often crucial). Even though the dangerous complications of Celiac Disease can reduce the celiac patient's hopes and quality of life, often dramatically so, it must be specified that in the overwhelming majority of cases early diagnosis and a strict diet can significantly reduce their incidence. 14 Associazione Italiana Celiachia Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso tel fax segreteria@celiachia.it
15 6. Bibliography 1. Oberhuber G, Granditsch G, Vogelsang H. The histopathology of Celiac Disease: time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol : National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement on Celiac Disease, June 28-30, Gastroenterology. 2005;128:Sl Chand N, Mihas AA. Celiac Disease: current concepts in diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40: Cataldo F, Marino V, Ventura A, Bottaro G, Corazza GR. Prevalence and clinical features of selective immunoglobulin A deficiency in Celiac disease: an Italian multicentre study. Italian Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology (SIGEP) and "Club del Tenue" Working Groups on Celiac Disease. Gut. 1998; 42: Collin P, Maki M, Keyrilainen 0, Hallstrom 0, Reunala T, Pasternack A.Selective IgA deficiency and Celiac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992; 27: Cataldo F, Marino V, Bottaro G, Greco P, Ventura A. Celiac Disease and selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. J Pediatr. 1997;131: Hill PG, CD Millan SA Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies and their role in thè investigation of Celiac disease Ann Clin Biochem 2006; 43: Burgin-Wolff A, Dahlbom I, Hadziselimovic F, Petersson CJ. Antibodies against human tissue transglutaminase and endomysium in diagnosing and monitoring Celiac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37: Tesei N, Sugai E, Vazquez H, Smecuol E, Niveloni S, Mazure R, Moreno ML, Gomez JC, Maurino E, Bai JC. Antibodies to human recombinant tissue transglutaminase may detect Celiac disease patients undiagnosed by endomysial antibodies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17: Hill PG, Forsyth JM, Semeraro D, Holmes GK. IgA antibodies to human tissue transglutaminase: audit of routine practice confirms high diagnostic accuracy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2004;39: Karell K, Louka AS, Moodie SJ, Ascher H, Clot F, Greco L, Ciclitira PJ, Sollid LM, Partanen J; European Genetics Cluster on Celiac Disease. HLA types in Celiac Disease patients not carrying the DQA1*O5-DQB1*O2 (DQ2) heterodimer: results from the European Genetics Cluster on Celiac Disease.Hum Immunol Apr;64(4): Louka AS, Moodie SJ, Karell K, Bolognesi E, Ascher H, Greco L, Momigliano-Richiardi P, Partanen J, Ciclitira PJ, Sollid LM; European Genetics Cluster on Celiac Disease A collaborative European search for non-dqal*05-dqbl*02 Celiac Disease loci on HLA- DR3 haplotypes: analysis of transmission from homozygous parents. Hum Immunol Mar;64 (3): Associazione Italiana Celiachia tel fax Genova, Via Caffaro, 68 A rosso segreteria@celiachia.it 15
16 Genova - Via Caffaro 68 A rosso Tel Fax segreteria@celiachia.it
November Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease. Inflammation in Celiac Disease
 November 2011 Gary Copland, MD Chair, Department of Pathology, Unity Hospital Laboratory Medical Director, AMC Crossroads Chaska and AMC Crossroads Dean Lakes Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease Celiac
November 2011 Gary Copland, MD Chair, Department of Pathology, Unity Hospital Laboratory Medical Director, AMC Crossroads Chaska and AMC Crossroads Dean Lakes Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease Celiac
Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums
 Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums Alia Hasham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition What is the Preferred Initial Test
Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums Alia Hasham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition What is the Preferred Initial Test
Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating
 Diagnosis 1 1 Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating Diagnosis of Celiac Disease mandates a strict gluten-free diet for life following the diet is not easy QOL implications Failure
Diagnosis 1 1 Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating Diagnosis of Celiac Disease mandates a strict gluten-free diet for life following the diet is not easy QOL implications Failure
Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease
 Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Melissa R. Snyder, Ph.D. Co-Director, Antibody Immunology Laboratory Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic
Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Melissa R. Snyder, Ph.D. Co-Director, Antibody Immunology Laboratory Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic
Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth. Disclosures OBJECTIVES 18/09/2013. Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta. None Relevant
 Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta Disclosures None Relevant OBJECTIVES Understand the spectrum of gluten disorders Develop a diagnostic algorithm for gluten
Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta Disclosures None Relevant OBJECTIVES Understand the spectrum of gluten disorders Develop a diagnostic algorithm for gluten
Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH
 Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH Case in point 42 year old woman with bloating, gas, intermittent diarrhea alternating with constipation, told she has IBS
Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH Case in point 42 year old woman with bloating, gas, intermittent diarrhea alternating with constipation, told she has IBS
Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A
 Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A Akiko Natalie Tomonari MD akiko.tomonari@parkway.cn Gastroenterology Specialist ParkwayHealth Introduction (of myself) Born in Japan, Raised in Maryland, USA Graduated from
Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A Akiko Natalie Tomonari MD akiko.tomonari@parkway.cn Gastroenterology Specialist ParkwayHealth Introduction (of myself) Born in Japan, Raised in Maryland, USA Graduated from
Diseases of the gastrointestinal system Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine
 Diseases of the gastrointestinal system 2018 Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine Small intestinal villi Small intestinal villi -Villi are tall, finger like mucosal projections, found
Diseases of the gastrointestinal system 2018 Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine Small intestinal villi Small intestinal villi -Villi are tall, finger like mucosal projections, found
Epidemiology. The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology:
 Epidemiology 1 1 Epidemiology The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology: A rare disorder typical of infancy Wide incidence fluctuates in space (1/400 Ireland to 1/10000 Denmark) and in time A disease of essentially
Epidemiology 1 1 Epidemiology The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology: A rare disorder typical of infancy Wide incidence fluctuates in space (1/400 Ireland to 1/10000 Denmark) and in time A disease of essentially
Celiac Disease. Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. January 2015
 Celiac Disease Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition January 2015 Objectives Review the clinical presentation of celiac disease, including intestinal
Celiac Disease Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition January 2015 Objectives Review the clinical presentation of celiac disease, including intestinal
CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium
 CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium 5.1 Introduction Celiac disease is a chronic immune-mediated
CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium 5.1 Introduction Celiac disease is a chronic immune-mediated
Celiac Disease 1/13/2016. Objectives. Question 1. Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD)
 Celiac Disease MONTE E. TROUTMAN, DO, FACOI JANUARY 6, 2016 Objectives Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD) Develop a knowledge of testing needed
Celiac Disease MONTE E. TROUTMAN, DO, FACOI JANUARY 6, 2016 Objectives Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD) Develop a knowledge of testing needed
See Policy CPT CODE section below for any prior authorization requirements
 Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: LAB Policy No: 404 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 12/17; 12/18 1/1/19 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: All lines of business See Policy CPT CODE section below
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: LAB Policy No: 404 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 12/17; 12/18 1/1/19 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: All lines of business See Policy CPT CODE section below
Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity?
 Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity? Mark T. DeMeo MD, FACG Rush University Med Center Case Study 35 y/o female Complains of diarrhea, bloating, arthralgias, and foggy mentation Cousin with celiac
Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity? Mark T. DeMeo MD, FACG Rush University Med Center Case Study 35 y/o female Complains of diarrhea, bloating, arthralgias, and foggy mentation Cousin with celiac
Challenges in Celiac Disease. Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
 Challenges in Celiac Disease Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Disclosures None Overview Celiac disease Cases Celiac disease Inappropriate
Challenges in Celiac Disease Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Disclosures None Overview Celiac disease Cases Celiac disease Inappropriate
Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD. No financial disclosures
 Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD No financial disclosures Patient NP 21 year old male with chronic headaches for 6 years extensively evaluated and treated Acupuncturist suggests testing for celiac
Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD No financial disclosures Patient NP 21 year old male with chronic headaches for 6 years extensively evaluated and treated Acupuncturist suggests testing for celiac
Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease
 Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease C. CUFFARI, MD, FRCPC, FACG, AGAF The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD. Main Points Celiac disease is not rare (1 in 100-300) It can present in many ways:
Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease C. CUFFARI, MD, FRCPC, FACG, AGAF The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD. Main Points Celiac disease is not rare (1 in 100-300) It can present in many ways:
BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE
 BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE Steffen Husby Hans Christian Andersen Children s Hospital Odense University Hospital DK-5000 Odense C, Denmark Agenda Background Algorithm Symptoms HLA Antibodies
BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE Steffen Husby Hans Christian Andersen Children s Hospital Odense University Hospital DK-5000 Odense C, Denmark Agenda Background Algorithm Symptoms HLA Antibodies
New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity
 New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Department of Medicine University of California, San Diego Page 1 1 low fat diet low carb diet gluten free diet low fat diet
New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Department of Medicine University of California, San Diego Page 1 1 low fat diet low carb diet gluten free diet low fat diet
Evidence Based Guideline
 Evidence Based Guideline Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: serologic_diagnosis_of_celiac_disease 4/2012 Description of Procedure
Evidence Based Guideline Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: serologic_diagnosis_of_celiac_disease 4/2012 Description of Procedure
Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease
 Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease Debby Kryszak 1, Henry McGill 2, Michelle Leland 2,, Alessio Fasano 1 1. Center for Celiac Research,
Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease Debby Kryszak 1, Henry McGill 2, Michelle Leland 2,, Alessio Fasano 1 1. Center for Celiac Research,
Peter HR Green MD. Columbia University New York, NY
 CELIAC DISEASE, 2008 Peter HR Green MD Celiac Disease Center Columbia University New York, NY pg11@columbia.edu DIAGNOSIS OF CELIAC DISEASE Presence of consistent pathology and response to a gluten-free
CELIAC DISEASE, 2008 Peter HR Green MD Celiac Disease Center Columbia University New York, NY pg11@columbia.edu DIAGNOSIS OF CELIAC DISEASE Presence of consistent pathology and response to a gluten-free
Name of Policy: Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Testing for Celiac Disease
 Name of Policy: Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Testing for Celiac Disease Policy #: 545 Latest Review Date: June 2015 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits
Name of Policy: Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Testing for Celiac Disease Policy #: 545 Latest Review Date: June 2015 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits
CELIAC SPRUE. What Happens With Celiac Disease
 CELIAC SPRUE Celiac Disease (CD) is a lifelong, digestive disorder affecting children and adults. When people with CD eat foods that contain gluten, it creates an immune-mediated toxic reaction that causes
CELIAC SPRUE Celiac Disease (CD) is a lifelong, digestive disorder affecting children and adults. When people with CD eat foods that contain gluten, it creates an immune-mediated toxic reaction that causes
Celiac Disease. Samuel Gee (1888) first described Celiac disease in On the Coeliac Affection Gluten sensitive entropathy Non-tropical sprue
 Celiac disease Mohammad Rostami Nejad, PhD Head of Celiac disease department Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Celiac Disease
Celiac disease Mohammad Rostami Nejad, PhD Head of Celiac disease department Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Celiac Disease
Disclosures GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 6/9/2015
 Disclosures CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 2015 Scientific Advisory Board: Alvine Pharmaceuticals, Alba Therapeutics, ImmunsanT Peter HR Green MD Columbia University New York, NY GLUTEN
Disclosures CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 2015 Scientific Advisory Board: Alvine Pharmaceuticals, Alba Therapeutics, ImmunsanT Peter HR Green MD Columbia University New York, NY GLUTEN
Clinical updates on diagnosing glutensensitive enteropathy
 Editorial Acta Medica Academica 2011;40(2):105-109 DOI 10.5644/ama2006-124.13 Clinical updates on diagnosing glutensensitive enteropathy Faruk Hadziselimovic 1, 2, Annemarie Bürgin-Wolff 1 1 Institute
Editorial Acta Medica Academica 2011;40(2):105-109 DOI 10.5644/ama2006-124.13 Clinical updates on diagnosing glutensensitive enteropathy Faruk Hadziselimovic 1, 2, Annemarie Bürgin-Wolff 1 1 Institute
Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital
 Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital Nothing to disclose Objectives Better understanding pathogenesis celiac disease Better understanding
Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital Nothing to disclose Objectives Better understanding pathogenesis celiac disease Better understanding
Celiac Disease. Detlef Schuppan HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL
 Celiac Disease Detlef Schuppan Falk Symposium in the Intestinal Tract: Pathogenesis and Treatment, Kiev,, Ukraine, May 15-16, 16, 2009 HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Celiac Disease Intolerance to gluten from wheat,
Celiac Disease Detlef Schuppan Falk Symposium in the Intestinal Tract: Pathogenesis and Treatment, Kiev,, Ukraine, May 15-16, 16, 2009 HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Celiac Disease Intolerance to gluten from wheat,
Understanding Celiac Disease
 Understanding Celiac Disease Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State
Understanding Celiac Disease Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State
Understanding Celiac Disease
 Understanding Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
Understanding Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
No relevant financial relationships to disclose
 CELIAC DISEASE Michael H. Piper, MD, FACP, FACG Gastroenterology Program Director Chief of Gastroenterology Providence-Providence Park Hospitals/St. John Macomb Hospital No relevant financial relationships
CELIAC DISEASE Michael H. Piper, MD, FACP, FACG Gastroenterology Program Director Chief of Gastroenterology Providence-Providence Park Hospitals/St. John Macomb Hospital No relevant financial relationships
Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG
 1A: Upper Gut Celiac Disease: When to Look and How? Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, the successful learner should be able to: Identify the many groups of
1A: Upper Gut Celiac Disease: When to Look and How? Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, the successful learner should be able to: Identify the many groups of
CELIAC DISEASE. Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD
 CELIAC DISEASE Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE? In short In this disease, exposure to gluten results in damge to the intestinal mucosa. Immune-mediated disorder Also known as
CELIAC DISEASE Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE? In short In this disease, exposure to gluten results in damge to the intestinal mucosa. Immune-mediated disorder Also known as
Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals
 Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals Jocelyn Silvester, MD PhD FRCPC April 27, 2017 Research grants Disclosures Canadian Institutes of Health Research
Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals Jocelyn Silvester, MD PhD FRCPC April 27, 2017 Research grants Disclosures Canadian Institutes of Health Research
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Clinical Utility of Serologic Testing for Celiac Disease in Ontario Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in April and October, 2010 December 2010 Background
OHTAC Recommendation Clinical Utility of Serologic Testing for Celiac Disease in Ontario Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in April and October, 2010 December 2010 Background
Coeliac disease. Do I have coeliac. disease? Diagnosis, monitoring & susceptibilty. Laboratory flowsheet included
 Laboratory flowsheet included I have coeliac disease. What monitoring tests should be performed? Do I have coeliac disease? Are either of our children susceptible to coeliac disease? Monitoring tests Diagnostic
Laboratory flowsheet included I have coeliac disease. What monitoring tests should be performed? Do I have coeliac disease? Are either of our children susceptible to coeliac disease? Monitoring tests Diagnostic
What is celiac disease?
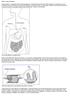 What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education
 Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education Objectives Following this program, participants will 1. List the clinical situations where celiac disease should be suspected 2. Distinguish between celiac
Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education Objectives Following this program, participants will 1. List the clinical situations where celiac disease should be suspected 2. Distinguish between celiac
Celiac Disease. Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue
 Celiac Disease Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Celiac Disease Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE. Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012
 DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012 OVERVIEW Definition Susceptibility The Changing Clinical Presentation Medical
DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012 OVERVIEW Definition Susceptibility The Changing Clinical Presentation Medical
Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key
 Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key Mary Twohig Chairperson Coeliac Society of Ireland What is Coeliac Disease? LIVING WITH COELIAC DISEASE Fact Not Fad Auto immune disease - the body
Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key Mary Twohig Chairperson Coeliac Society of Ireland What is Coeliac Disease? LIVING WITH COELIAC DISEASE Fact Not Fad Auto immune disease - the body
CONTEMPORARY CONCEPT ON BASIC APSECTS OF GLUTEN-SENSITIVE ENTEROPATHY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 VIII, 2014, 1 33. 1,. 2,. - 1,. 1. 3 1,., 2,., 3, CONTEMPORARY CONCEPT ON BASIC APSECTS OF GLUTEN-SENSITIVE ENTEROPATHY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Ts. Velikova 1, Z. Spassova 2,. Ivanova-Todorova 1, D. Kyurkchiev
VIII, 2014, 1 33. 1,. 2,. - 1,. 1. 3 1,., 2,., 3, CONTEMPORARY CONCEPT ON BASIC APSECTS OF GLUTEN-SENSITIVE ENTEROPATHY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Ts. Velikova 1, Z. Spassova 2,. Ivanova-Todorova 1, D. Kyurkchiev
Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present
 Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present The Center for Celiac Research and Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland, U.S.A. 1 Celiac Disease Roadmap:
Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present The Center for Celiac Research and Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland, U.S.A. 1 Celiac Disease Roadmap:
Celiac Disease Ce. Celiac Disease. Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. baystatehealth.org/bch
 Celiac Disease Ce Celiac Disease Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition baystatehealth.org/bch Autoimmune Disease Inappropriate inflammation 1 1/21/15 Celiac Disease Classic
Celiac Disease Ce Celiac Disease Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition baystatehealth.org/bch Autoimmune Disease Inappropriate inflammation 1 1/21/15 Celiac Disease Classic
Slides and Resources.
 Update on Celiac Disease Douglas L. Seidner, MD, AGAF, FACG Director, Center for Human Nutrition Vanderbilt University As revised/retold by Edward Saltzman, MD Tufts University None Disclosures This ppt
Update on Celiac Disease Douglas L. Seidner, MD, AGAF, FACG Director, Center for Human Nutrition Vanderbilt University As revised/retold by Edward Saltzman, MD Tufts University None Disclosures This ppt
Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity
 Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity Update: Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease A. Sapone, L.
Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity Update: Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease A. Sapone, L.
Coeliac disease catering gluten-free
 Coeliac disease catering gluten-free About Coeliac UK National Charity for people with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis Founded in 1968 and is the largest coeliac charity in the world Mission:
Coeliac disease catering gluten-free About Coeliac UK National Charity for people with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis Founded in 1968 and is the largest coeliac charity in the world Mission:
Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum
 TEST NAME: Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity (Serum) Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum ANTIBODIES REFERENCE RESULT/UNIT INTERVAL NEG WEAK POS POSITIVE Tissue Transglutaminase (ttg) IgA 1420 U < 20.0 Tissue
TEST NAME: Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity (Serum) Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum ANTIBODIES REFERENCE RESULT/UNIT INTERVAL NEG WEAK POS POSITIVE Tissue Transglutaminase (ttg) IgA 1420 U < 20.0 Tissue
Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD.
 Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD..... Celiac Disease Autoimmune Diseases What are they? How do you get them? Why does it matter? Celiac Disease Autoimmune
Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD..... Celiac Disease Autoimmune Diseases What are they? How do you get them? Why does it matter? Celiac Disease Autoimmune
Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else
 Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else Ciarán P Kelly, MD Celiac Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Celiac Program Harvard Medical School Boston Gluten Free Diet (GFD) Very good but
Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else Ciarán P Kelly, MD Celiac Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Celiac Program Harvard Medical School Boston Gluten Free Diet (GFD) Very good but
Health Canada s Position on Gluten-Free Claims
 June 2012 Bureau of Chemical Safety, Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch 0 Table of Contents Background... 2 Regulatory Requirements for Gluten-Free Foods... 2 Recent advances in the knowledge
June 2012 Bureau of Chemical Safety, Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch 0 Table of Contents Background... 2 Regulatory Requirements for Gluten-Free Foods... 2 Recent advances in the knowledge
Why Can t I Eat Bread?
 Why Can t I Eat Bread? Dealing With Celiac Disease In this article: By Flavio Habal, MD, PhD, FRCP 1. What is the investigation? 3. What is the treatment? 4. How do I followup? Case Study A 31-year-old
Why Can t I Eat Bread? Dealing With Celiac Disease In this article: By Flavio Habal, MD, PhD, FRCP 1. What is the investigation? 3. What is the treatment? 4. How do I followup? Case Study A 31-year-old
Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE
 Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE What is it? Auto-immune disorder affecting the small intestine. Triggered by gluten (protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats) Strong genetic link: 1 st
Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE What is it? Auto-immune disorder affecting the small intestine. Triggered by gluten (protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats) Strong genetic link: 1 st
DEAMIDATED GLIADIN PEPTIDES IN COELIAC DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS
 DEAMIDATED GLIADIN PEPTIDES IN COELIAC DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS Z. Vanickova 1, P. Kocna 1, K. Topinkova 1, M. Dvorak 2 1 Institute of Clinical Biochemistry & Laboratory Diagnostics; 2 4th Medical Department,
DEAMIDATED GLIADIN PEPTIDES IN COELIAC DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS Z. Vanickova 1, P. Kocna 1, K. Topinkova 1, M. Dvorak 2 1 Institute of Clinical Biochemistry & Laboratory Diagnostics; 2 4th Medical Department,
Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD
 Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD Disclosures Dr. Anca Safta - none Angie Almond, M.Ed., RD, LDN invited attendee of The Gluten Free Summit sponsored by General Mills Wake Forest Baptist
Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD Disclosures Dr. Anca Safta - none Angie Almond, M.Ed., RD, LDN invited attendee of The Gluten Free Summit sponsored by General Mills Wake Forest Baptist
The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing.
 Bio-Rad Laboratories BIOPLEX 2200 SYSTEM BioPlex 2200 Celiac IgA and IgG Kits The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing. The
Bio-Rad Laboratories BIOPLEX 2200 SYSTEM BioPlex 2200 Celiac IgA and IgG Kits The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing. The
Celiac Disease Myths. Objectives. We Now Know. Classical Celiac Disease. A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease
 4:15 5:00pm Presenter Disclosure Information A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease SPEAKER Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS
4:15 5:00pm Presenter Disclosure Information A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease SPEAKER Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS
2013 NASPGHAN FOUNDATION
 2 Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research Director,
2 Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research Director,
CELIAC DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS
 CELIAC DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS FOR PHYSICIANS OF GENERAL MEDICINE AND PRIMARY CARE PAEDIATRICIANS Quickly identify the symptoms of celiac disease. Guide patients towards correct diagnosis. Manage
CELIAC DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS FOR PHYSICIANS OF GENERAL MEDICINE AND PRIMARY CARE PAEDIATRICIANS Quickly identify the symptoms of celiac disease. Guide patients towards correct diagnosis. Manage
ImuPro shows you the way to the right food for you. And your path for better health.
 Your personal ImuPro Screen + documents Sample ID: 33333 Dear, With this letter, you will receive the ImuPro result for your personal IgG food allergy test. This laboratory report contains your results
Your personal ImuPro Screen + documents Sample ID: 33333 Dear, With this letter, you will receive the ImuPro result for your personal IgG food allergy test. This laboratory report contains your results
Celiac Disease. Educational Gaps. Objectives. Tracy R. Ediger, MD, PhD,* Ivor D. Hill, MB, CHB, MD
 Celiac Disease Tracy R. Ediger, MD, PhD,* Ivor D. Hill, MB, CHB, MD *Department of Clinical Pediatrics, The Ohio State University College of Medicine, and Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and
Celiac Disease Tracy R. Ediger, MD, PhD,* Ivor D. Hill, MB, CHB, MD *Department of Clinical Pediatrics, The Ohio State University College of Medicine, and Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and
The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing.
 Bio-Rad Laboratories bioplex 2200 SYSTEM BioPlex 2200 Celiac IgA and IgG Kits * The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing.
Bio-Rad Laboratories bioplex 2200 SYSTEM BioPlex 2200 Celiac IgA and IgG Kits * The first and only fully-automated, random access, multiplex solution for Celiac IgA and Celiac IgG autoantibody testing.
Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent. Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018
 Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018 Learning Objectives Identify risk factors for food allergies Identify clinical manifestations
Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018 Learning Objectives Identify risk factors for food allergies Identify clinical manifestations
Celiac disease is a unique disorder that is both a food
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2006;131:1981 2002 American Gastroenterological Association () Institute Technical Review on the Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease This technical review addresses the state of
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2006;131:1981 2002 American Gastroenterological Association () Institute Technical Review on the Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease This technical review addresses the state of
Update on Celiac Disease: New Standards and New Tests
 IMPROVING PATIENT CARE THROUGH ESOTERIC LABORATORY TESTING JUNE 2008 Update on Celiac Disease: New Standards and New Tests The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has reported that as many as 1% (3,000,000)
IMPROVING PATIENT CARE THROUGH ESOTERIC LABORATORY TESTING JUNE 2008 Update on Celiac Disease: New Standards and New Tests The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has reported that as many as 1% (3,000,000)
Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE
 Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE Celiac disease definition, a hereditary digestive disorder involving intolerance to gluten, usually occurring in young children, characterized
Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE Celiac disease definition, a hereditary digestive disorder involving intolerance to gluten, usually occurring in young children, characterized
Spectrum of Gluten Disorders
 Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2018 Spectrum of Gluten Disorders Wheat allergy - prevalence 3-8 % (up to 3 years old) Non-celiac gluten
Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2018 Spectrum of Gluten Disorders Wheat allergy - prevalence 3-8 % (up to 3 years old) Non-celiac gluten
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Blood TTG and Small Intestine Biopsy in Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Anil Batta Professor,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Blood TTG and Small Intestine Biopsy in Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Anil Batta Professor,
UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE
 UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE COELIAC DISEASE Coeliac Disease (CD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder generated by gluten intake in genetically susceptible individuals. When someone with coeliac disease
UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE COELIAC DISEASE Coeliac Disease (CD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder generated by gluten intake in genetically susceptible individuals. When someone with coeliac disease
Celiac Disease. Definition & Facts. What is celiac disease? How common is celiac disease? Who is more likely to develop celiac disease?
 Celiac Disease Definition & Facts What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disorder that damages the small intestine. The disease is triggered by eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is
Celiac Disease Definition & Facts What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disorder that damages the small intestine. The disease is triggered by eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is
Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic
 How many celiac patients are affected? Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic 6.2% of all celiac patients have continuing diarrhea after 2 years on a gluten free diet 18% will develop constipation in this time
How many celiac patients are affected? Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic 6.2% of all celiac patients have continuing diarrhea after 2 years on a gluten free diet 18% will develop constipation in this time
Celiac Disease and Immunoglobulin A Deficiency: How Effective Are the Serological Methods of Diagnosis?
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 1295 1300 Vol. 9, No. 6 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1295 1300.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 1295 1300 Vol. 9, No. 6 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1295 1300.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby!
 Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby! Celiac Disease (CD): How You ve Changed Increasing numbers of people have celiac disease Changing ways in which celiac disease presents A better understanding
Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby! Celiac Disease (CD): How You ve Changed Increasing numbers of people have celiac disease Changing ways in which celiac disease presents A better understanding
Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
 Evidence Synthesis Number 144 Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality U.S. Department of Health
Evidence Synthesis Number 144 Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality U.S. Department of Health
Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION
 Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION Food Intolerance & Expertise What is food intolerance? Common food intolerances Why are consumers claiming more food
Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION Food Intolerance & Expertise What is food intolerance? Common food intolerances Why are consumers claiming more food
Celiac disease (CD) is a gluten-sensitive enteropathy with. Comparative Usefulness of Deamidated Gliadin Antibodies in the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:426 432 Comparative Usefulness of Deamidated Gliadin Antibodies in the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease SHADI RASHTAK,* MICHAEL W. ETTORE, HENRY A. HOMBURGER,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:426 432 Comparative Usefulness of Deamidated Gliadin Antibodies in the Diagnosis of Celiac Disease SHADI RASHTAK,* MICHAEL W. ETTORE, HENRY A. HOMBURGER,
5/27/2014 WEBINAR. Suggested CDR Learning Codes: 3000, 5000, 5110, 5220; Level 2
 WEBINAR Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research
WEBINAR Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research
Celiac Disease and Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity. John R Cangemi, MD Mayo Clinic Florida
 Celiac Disease and Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity John R Cangemi, MD Mayo Clinic Florida DISCLOSURE Commercial Interest None Off Label Usage None Learning Objectives Review the clinical presentation of
Celiac Disease and Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity John R Cangemi, MD Mayo Clinic Florida DISCLOSURE Commercial Interest None Off Label Usage None Learning Objectives Review the clinical presentation of
EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES. NGx-Gluten TM. Personalized Nutrition Report
 EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report Introduction Hello Caroline: Nutrigenomix is pleased to provide you with your NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report based on
EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report Introduction Hello Caroline: Nutrigenomix is pleased to provide you with your NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report based on
Fedima Position Paper on Labelling of Allergens
 Fedima Position Paper on Labelling of Allergens Adopted on 5 March 2018 Introduction EU Regulation 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers (FIC) 1 replaced Directive 2001/13/EC. Article
Fedima Position Paper on Labelling of Allergens Adopted on 5 March 2018 Introduction EU Regulation 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers (FIC) 1 replaced Directive 2001/13/EC. Article
Licensing and gluten free markets in Estonia and other Nordic-Baltic countries. Katre Trofimov 2017
 Licensing and gluten free markets in Estonia and other Nordic-Baltic countries Katre Trofimov 2017 Who need gluten free food? Gluten-related disorders Coeliac disease blood markers + biopsy Dermatitis
Licensing and gluten free markets in Estonia and other Nordic-Baltic countries Katre Trofimov 2017 Who need gluten free food? Gluten-related disorders Coeliac disease blood markers + biopsy Dermatitis
L y mp h o c y t i c D i s o r d e r s of t h e. What does too many mean? Unifying theory 2/24/2011
 L y mp h o c y t i c D i s o r d e r s of t h e G a s t Robert r o M. i Genta n t e s t i Caris n alife l Sciences, T rirving, a ctexas t Dallas VAMC UT Southwestern Dallas, Texas Esophagus Stomach Small
L y mp h o c y t i c D i s o r d e r s of t h e G a s t Robert r o M. i Genta n t e s t i Caris n alife l Sciences, T rirving, a ctexas t Dallas VAMC UT Southwestern Dallas, Texas Esophagus Stomach Small
Diagnostic value of duodenal antitissue transglutaminase antibodies in gluten-sensitive enteropathy
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Diagnostic value of duodenal antitissue transglutaminase antibodies in gluten-sensitive enteropathy R. SANTAOLALLA*, F. FERNÁNDEZ-BAÑARES*, R. RODRÍGUEZ, M.ALSINAà,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Diagnostic value of duodenal antitissue transglutaminase antibodies in gluten-sensitive enteropathy R. SANTAOLALLA*, F. FERNÁNDEZ-BAÑARES*, R. RODRÍGUEZ, M.ALSINAà,
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.21 Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 2.04.21 Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
Larazotide Acetate. Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine
 Larazotide Acetate Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine Alternative/Integrative Approaches To The Gluten Free Diet
Larazotide Acetate Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine Alternative/Integrative Approaches To The Gluten Free Diet
Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition. Disclosures. Gluten Confusion 2/10/2014
 Disclosures Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition Author: South Beach Diet Gluten Solution Arthur Agatston Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Confusion What is gluten? What
Disclosures Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition Author: South Beach Diet Gluten Solution Arthur Agatston Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Confusion What is gluten? What
Immune mediated enteropathies. Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017
 Immune mediated enteropathies Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017 Definition/classification Systemic disease, mediated by antibodies, caracterised by histological changes of the small bowel Coeliac and noncoeliac
Immune mediated enteropathies Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017 Definition/classification Systemic disease, mediated by antibodies, caracterised by histological changes of the small bowel Coeliac and noncoeliac
The Clinical Response to Gluten Challenge: A Review of the Literature
 Nutrients 2013, 5, 4614-4641; doi:.3390/nu5114614 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients The Clinical Response to Gluten Challenge: A Review of the Literature Maaike
Nutrients 2013, 5, 4614-4641; doi:.3390/nu5114614 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients The Clinical Response to Gluten Challenge: A Review of the Literature Maaike
Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
 Evidence Synthesis Number 144 Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality U.S. Department of Health
Evidence Synthesis Number 144 Screening for Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality U.S. Department of Health
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Prospective study of the role of duodenal bulb biopsies in the diagnosis of celiac disease Susana Gonzalez, MD, Anupama Gupta, MD, Jianfeng Cheng, MD, Christina Tennyson,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Prospective study of the role of duodenal bulb biopsies in the diagnosis of celiac disease Susana Gonzalez, MD, Anupama Gupta, MD, Jianfeng Cheng, MD, Christina Tennyson,
Gliadin antibody detection in gluten
 The Ulster Medical Journal, Volume 55, No. 2, pp. 160-164, October 1986. Gliadin antibody detection in gluten enteropathy R G P Watson, S A McMillan, Clare Dolan, Cliona O'Farrelly, R J G Cuthbert, Margaret
The Ulster Medical Journal, Volume 55, No. 2, pp. 160-164, October 1986. Gliadin antibody detection in gluten enteropathy R G P Watson, S A McMillan, Clare Dolan, Cliona O'Farrelly, R J G Cuthbert, Margaret
Anti-Transglutaminase Antibody Assay of the Culture Medium of Intestinal Biopsy Specimens Can Improve the Accuracy of Celiac Disease Diagnosis
 Clinical Chemistry 52:6 1175 1180 (2006) Clinical Immunology Anti-Transglutaminase Antibody Assay of the Culture Medium of Intestinal Biopsy Specimens Can Improve the Accuracy of Celiac Disease Diagnosis
Clinical Chemistry 52:6 1175 1180 (2006) Clinical Immunology Anti-Transglutaminase Antibody Assay of the Culture Medium of Intestinal Biopsy Specimens Can Improve the Accuracy of Celiac Disease Diagnosis
Celiac Disease. Etiology. Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles
 Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2017 Celiac Disease World s most common genetic food disorder Rising prevalence - over past 5 decades,
Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2017 Celiac Disease World s most common genetic food disorder Rising prevalence - over past 5 decades,
Celiac Disease: The Future. Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine
 Celiac Disease: The Future Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Normal small bowel Celiac disease Gluten Gluten-free diet Treatment Only treatment
Celiac Disease: The Future Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Normal small bowel Celiac disease Gluten Gluten-free diet Treatment Only treatment
Gluten sensitivity in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental myth or clinical truth?
 Gluten sensitivity in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental myth or clinical truth? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Vol 1173, Issue 1, page 44, Issue published online 3 Sep 2009. Dana Ben-Ami Shor,
Gluten sensitivity in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental myth or clinical truth? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, Vol 1173, Issue 1, page 44, Issue published online 3 Sep 2009. Dana Ben-Ami Shor,
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES. Proposal for a COUNCIL REGULATION
 EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 19.10.1999 COM(1999) 489 final 99/0206 (ACC) Proposal for a COUNCIL REGULATION on the conclusion of Agreements in the form of Exchanges of Letters amending
EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 19.10.1999 COM(1999) 489 final 99/0206 (ACC) Proposal for a COUNCIL REGULATION on the conclusion of Agreements in the form of Exchanges of Letters amending
Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients
 Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients Joe Murray The Mayo Clinic 1 DISCLOSURES Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients Joe Murray The Mayo Clinic 1 DISCLOSURES Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
A young woman with fatigue
 IM BOARD REVIEW CME CREDIT KATHRYN A. TENG, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic JAMES K. STOLLER, MD, EDITOR A SELF-TEST ON A CLINICAL CASE A young woman with fatigue A 22-YEAR-OLD
IM BOARD REVIEW CME CREDIT KATHRYN A. TENG, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic JAMES K. STOLLER, MD, EDITOR A SELF-TEST ON A CLINICAL CASE A young woman with fatigue A 22-YEAR-OLD
Allergy Awareness and Management Policy
 Allergy Awareness and Management Policy Overview This policy is concerned with a whole school approach to the health care management of those members of our school community suffering from specific allergies.
Allergy Awareness and Management Policy Overview This policy is concerned with a whole school approach to the health care management of those members of our school community suffering from specific allergies.
