World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
|
|
|
- Francis Montgomery
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
2 During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading routes connected the continents of Europe, Africa, and Asia.
3 Major trade patterns of the Eastern Hemisphere from 1000 to 1500 A.D. (see map): The Silk Roads crossed Asia and reached all the way to the Mediterranean basin. They connected China, India, and the Eastern Mediterranean.
4 Maritime routes across the Indian Ocean connected Asia to Africa.
5 Trans-Saharan routes across North Africa connected the Niger River valley to the Mediterranean basin.
6 Northern European links with the Black Sea allowed Europe to connect with markets in Asia. The Black Sea region was a crossroads between Europe and Asia.
7 Western European sea and river trade created connections between European cities.
8 South China Sea and the lands of Southeast Asia were connected by maritime routes.
9 Where were the major trade routes in the Eastern Hemisphere from 1000 to 1500 A.D. (C.E.)?
10 Regional trade networks and long-distance trade routes in the Eastern Hemisphere aided the diffusion and exchange of technology and culture between Europe, Africa, and Asia.
11 Goods: Gold from West Africa
12 Spices from lands around the Indian Ocean
13 Textiles from India, China, the Middle East, and later Europe
14 Porcelain from China and Persia
15 Amber, from the Baltic region, was used to make jewelry and other ornaments.
16 Technology: Paper, from China, diffused through the Muslim world to Byzantium and Western Europe.
17 Waterwheels and windmills from the Middle East became important labor saving technologies as they diffused into Europe. Wind and water power could be used to grind grain into flower.
18 Navigation technology like the compass from China, and the lateen sail from the Indian Ocean region would make long distance sea travel possible.
19 Ideas: Spread of religions across the hemisphere Buddhism from China to Korea and Japan Hinduism and Buddhism from India to Southeast Asia Islam into West Africa, Central and Southeast Asia
20 Printing and paper money from China
21 How did trade facilitate the diffusion of goods and ideas among different cultures?
22 African Civilizations Geography African civilizations developed in Sub- Saharan west and east Africa. Sub-Saharan Africa refers to parts of the African continent south of the Sahara Desert.
23 African geography includes a broad range of environments that can make life there difficult.
24 Most of the African coastline is narrow and has few harbors. It is difficult to travel to the interior of the continent by boat.
25 Deserts: Sahara (north) Kalahari (south)
26 Dense rain forests make agriculture and development difficult.
27 Savannas (grassy plains) cover 40% of the continent.
28 Mediterranean climates are found on the northern coast and southern tip on Africa.
29 African Civilization Trade brought important economic, cultural, and religious influences to African civilizations from other parts of the Eastern Hemisphere.
30 States and empires flourished in Africa during the medieval period, including Ghana, Mali, and Songhai in west Africa, Axum in east Africa, and Zimbabwe in southern Africa.
31 East African Kingdom of Axum Geography Axum was located on the upper Nile River near the Ethiopian Highlands of East Africa.
32 The kingdom of Axum was made up of many people groups, and they conquered their Nubian neighbors who also lived on the upper Nile.
33 Access to the Red Sea and the Nile, gave connected Axum to trade from across the Eastern Hemisphere. Merchants of Axum traded with Egypt, Arabia, Persia, India and the Roman Empire.
34 Religion Christianity also diffused into Axum when king Ezana became a Christian and made it the official religion.
35 The establishment of Christianity was the longest lasting achievement of Axum. Today, Ethiopia is home to millions of Christians.
36 West African Kingdoms Geography Ghana, Mali, and Songhai empires were on the Niger River, south of the Sahara Desert.
37 Trans-Saharan Trade The gold salt trade was the most important on the Trans-Saharan trade routes across North Africa.
38 Gold was mined in the forest region around the Niger River and was traded for salt from the Sahara Desert.
39 Religious Influences The native African religion of Animism was practiced early in West African history. Animism is a diverse religion that honors spirits believed to be present in animals, plants, and other natural objects.
40 Islam diffused to West Africa along the Trans Saharan gold salt trade routes. Islam spread through trade, rather than conquest, through Sub- Saharan Africa. Many people who converted to Islam blended their new faith with Animistic practices. Mansa Musa is an example of a prosperous Islamic king of Mali.
41 Trading Cities The cities of Timbuktu and Gao grew along the Niger River of West Africa to facilitate Trans Saharan trade. Timbuktu and Gao were centers of trade and Islamic learning. Timbuktu attracted Muslim doctors, judges, religious leaders, and scholars to its mosques and universities.
42 East African Coast and Southern Trading Centers By 1100, port cities on the east coast of Africa were growing in population and wealth. Muslim and African culture blended in these cosmopolitan trade centers.
43 Raw materials from Africa included: ivory gold leopard skins
44 Products sold in Africa: porcelain bowls (China) jewels (India) cotton cloth (India)
45 Great Zimbabwe Gold and ivory that enriched the coastal cities came from the interior of Southern Africa. The Shona people of southeastern Africa established the city of Great Zimbabwe on an important trade route.
46 Geography of Zimbabwe Zimbabwe was located on a fertile, well watered plateau. The region was between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers.
47 Trade Empire Between 1200 and 1400, the city of Great Zimbabwe was the capital of an empire built on the gold trade. Leaders of Zimbabwe taxed the traders who traveled the region.
48 The city of Great Zimbabwe was the economic, political and religious center of its empire. The walled city covered many acres. The population was more than 10,000.
49 By 1450, Great Zimbabwe was abandoned. Possibly because resources in the area had been exhausted.
50 What were the characteristics of civilizations in sub-saharan Africa during the medieval period?
51 Geography Japanese Civilization Japan is made up of a 4,000 island archipelago located off the coast of China and Korea. An archipelago is a large group or chain of islands.
52 The Japanese archipelago consist of four main islands. Honshu Hokkaido Kyushu Shikoku
53 The Japanese islands have steep volcanic mountains. Only 12% of the land is suitable for farming.
54 Japan s geographic location has shaped the development of its culture. The islands of Japan lie 120 miles from Korea and 500 miles from China.
55 The Sea of Japan or East Sea separates Japan and the Asian mainland. Japan is close enough to China to be influenced by their culture, but far enough away to be safe from invasion.
56 How has Japan s geography influenced its development?
57 Japanese Religion Shinto is an early Japanese religion. Shinto means way of the gods. Shinto is an ethnic religion unique to Japan. Shinto emphasizes the importance of natural features, forces of nature, and ancestors.
58 In Shinto religion, the Japanese emperor and his family were considered direct descendants of the gods. Emperor worship led to a deep loyalty to the state and a belief in Japanese supremacy. (The land was sacred too.)
59 Chinese Cultural Influence on Japan Buddhism Diffuses into Japan Korean travelers first brought Chinese ideas and customs to Japan. In the mid-700s Buddhism was officially accepted in Japan.
60 The teachings of Buddhism were compatible with ancient Shinto practices. Buddhism coexisted with Shinto in Japan and Shinto gods were even worshiped in Buddhist temples. Buddhism helped to shape Japanese aesthetics, politics, literature, philosophy and medicine.
61 Why were Shinto and Buddhism important to the development of Japanese culture?
62 Architecture Chinese architecture has had a major influence on the structures of Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.
63 Written Language The Japanese adopted the Chinese system of writing. Over time, Japanese, and Korea have modified the Chinese characters.
64 How did Chinese culture influence Japan?
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD.
 SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Packet 7. Movement of People and Goods
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
Review Questions 1. How did the Bantu migrations affect existing cultures?
 Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
African History. Return
 Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
AFRICA. Human Geography
 AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia
![[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia](/thumbs/89/98244476.jpg) [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
[ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia [ 1.2 ] Early Europe, Africa, and Asia Learning Objectives Describe how Europe changed in the Middle Ages, including through technological innovations. Describe patterns
Chapter Summary. Section 2: Kingdoms of West Africa. Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa
 Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: Early Civilizations of Africa Geography affected migration, cultural development, and trade during the time of early civilizations in Africa. The civilization
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Journal Journal A. Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire?
 Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
Note Taking Study Guide EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA
 SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
African Kingdoms and Salt
 African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
Journal What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa
 Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai
 Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai.SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. 1. Describe the development and decline of the Sudanic kingdoms (Ghana, Mali,
Sudanic Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, Songhai.SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. 1. Describe the development and decline of the Sudanic kingdoms (Ghana, Mali,
Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions
 Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Sea Road: Indian Ocean. By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton
 Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief.
 GHANA Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief. By the 700s, Ghana was a kingdom, and its rulers were growing
GHANA Many trade routes crossed the savanna through the region farmed by the Soninke people. The Soninke called their leader Ghana, or war chief. By the 700s, Ghana was a kingdom, and its rulers were growing
Where is our stuff made?
 Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
such as Great Zimbabwe, to get these items. The merchant would then wait for the next monsoon season to bring them back to Asia.
 These notes go over the geography of Africa and the development of some early civilizations in Africa. You may need to research some of this information on the internet. After you have read these notes,
These notes go over the geography of Africa and the development of some early civilizations in Africa. You may need to research some of this information on the internet. After you have read these notes,
The Qin and Han Dynasties
 The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700
 African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700 Setting the Stage Africa spreads across the equator. It includes a broad range of Earth s environments-from coastal plains to mountains. Some parts of Africa suffer
African Civilizations 1500 BC-AD 700 Setting the Stage Africa spreads across the equator. It includes a broad range of Earth s environments-from coastal plains to mountains. Some parts of Africa suffer
9/21/14. Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda. Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram. Take notes on Songhai
 Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
Bellringer T1D6. How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed?
 Bellringer T1D6 How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed? U.S. History Ch. 2.1 A Changing World Main Questions: How new tech made longer sea voyages possible. How great civilizations
Bellringer T1D6 How has the world changed in the last 200 years? What has changed? U.S. History Ch. 2.1 A Changing World Main Questions: How new tech made longer sea voyages possible. How great civilizations
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
The Earliest Americans. Chapter 1 Section 1
 The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES
 WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES DATE: AIM: Students will be able to compare and contrast the three major trading empires in Ancient West Africa. DO NOW: A Voice from the Past Pliny, a scholar and naturalist,
WEST AFRICAN TRADING EMPIRES DATE: AIM: Students will be able to compare and contrast the three major trading empires in Ancient West Africa. DO NOW: A Voice from the Past Pliny, a scholar and naturalist,
Indian Ocean. Routes from India to the Arabian Peninsula and Africa
 Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
Major Trades Routes Six Major Routes on or crossing three continents. Africa Asia Europe Trade routes connected most major civilizations. Major Trades Routes All of these routes would connect with others
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
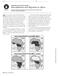 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE)
 AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World History
 AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1
 Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Post Classical Civs. F Block - Humanities
 Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes
 Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
Page 1 Chapter 1: Beginnings in Africa Notes Section 1: Human Origins and early Civilizations Human history began in Africa o appeared in East Africa about 3 million years ago Early hominids learned to
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes
 Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
Chapter 12: Establishing World Trade Routes Early long distance trade was limited to luxury items silk, gold, spices--that combined high value with low bulk Before 1500, most trade was local and focused
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
8 HOW DID THE WORLD ZONES CONNECT?
 8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
PACKET D. Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade. 9 Topic Workshop #26. Module
 PACKET D Module 9 Topic Workshop #26 Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade PERIOD 3 KEY CONCEPT 3.1 Expansion and Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks KEY CONCEPT 3.1 A deepening
PACKET D Module 9 Topic Workshop #26 Technology & Commercial Practices Intensify Trade PERIOD 3 KEY CONCEPT 3.1 Expansion and Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks KEY CONCEPT 3.1 A deepening
Contents. List of Acknowledgements. Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3
 Contents List List of Acknowledgements Preface xii xv xxii xxiv Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3 Chapter 1 prehistory of Africa 9 Human evolution 9 Homo sapiens, the
Contents List List of Acknowledgements Preface xii xv xxii xxiv Introduction 1 Historiography 1 Geography, climate and Vegetation 3 Chapter 1 prehistory of Africa 9 Human evolution 9 Homo sapiens, the
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
West Africa. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg
 West Africa https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg Geography Africa is located in the middle of the globe and is the second largest of the seven continents.
West Africa https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/mansa_musa.jpg/240px-mansa_musa.jpg Geography Africa is located in the middle of the globe and is the second largest of the seven continents.
New Ideas, New Nations
 New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries
 Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries Grade Level: Grades 6-12 National World History Standards: Era Four: Standard 5A The student understands state-building in...
Unit Two: Early African Kingdoms and Arabic Trade Routes, 7-16 th centuries Grade Level: Grades 6-12 National World History Standards: Era Four: Standard 5A The student understands state-building in...
In addition to salt list two other products a North African trader might bring to trade in West Africa.
 List three things that show the power of the ruler. In addition to salt list two other products a might bring to trade in West Africa. List five products the people of the southern forest areas brought
List three things that show the power of the ruler. In addition to salt list two other products a might bring to trade in West Africa. List five products the people of the southern forest areas brought
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013
 History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE. AP World History Notes Time Period:
 CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
List of Illustrations
 List of Maps p. xii List of Illustrations p. xv Acknowledgements p. xxii Preface p. xxiv Introduction p. 1 Historiography p. 1 Geography, climate and vegetation p. 3 Early prehistory of Africa p. 9 Human
List of Maps p. xii List of Illustrations p. xv Acknowledgements p. xxii Preface p. xxiv Introduction p. 1 Historiography p. 1 Geography, climate and vegetation p. 3 Early prehistory of Africa p. 9 Human
Medieval Adventures. Travel Brochure. 9/27/2017 Medieval Africa Time Travel Guide - Diego Soto - Google Docs
 Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
The World of the 1400s. What Was Going On?
 The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
Who Where the Mongols?
 11/5/14 The Yuan and Ming Dynasties The Chinese were ruled by foreigners during the Yuan dynasty, but they threw off Mongol rule and prospered during the Ming dynasty. Who Where the Mongols? The Mongols
11/5/14 The Yuan and Ming Dynasties The Chinese were ruled by foreigners during the Yuan dynasty, but they threw off Mongol rule and prospered during the Ming dynasty. Who Where the Mongols? The Mongols
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Tuesday, February 7, 17 THE SILK ROAD
 THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River)
 Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Student s Name: Subject: Social Studies
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
Holt African American History Chapter 1
 Beginnings in Africa Section 1 Human Origins and Early Civilizations Section 2 Great Empires of West Africa Section 3 Kingdoms of East and South Africa Section 1: Human Origins and Early Civilizations
Beginnings in Africa Section 1 Human Origins and Early Civilizations Section 2 Great Empires of West Africa Section 3 Kingdoms of East and South Africa Section 1: Human Origins and Early Civilizations
China and Mongols: Significant Changes
 China and Mongols: Significant Changes Lesson 3, Unit 9 Objectives & Key Terms Describe China s accomplishments under the Tang and Song dynasties Illustrate the changes that occurred after the Mongol invasion
China and Mongols: Significant Changes Lesson 3, Unit 9 Objectives & Key Terms Describe China s accomplishments under the Tang and Song dynasties Illustrate the changes that occurred after the Mongol invasion
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Early and. Medieval African Kingdoms. Timeline Cards
 Early and Medieval African Kingdoms Timeline Cards ISBN: 978-1-68380-138-2 Subject Matter Expert David Owusu-Ansah, PhD, Department of History, James Madison University Illustration and Photo Credits Title
Early and Medieval African Kingdoms Timeline Cards ISBN: 978-1-68380-138-2 Subject Matter Expert David Owusu-Ansah, PhD, Department of History, James Madison University Illustration and Photo Credits Title
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Tang and Song Dynasty. By Ms. Escalante
 Tang and Song Dynasty By Ms. Escalante 1. What do you think this poem is about? Poetry Warm-up: The Tang rulers developed an imperial state. This is related to an empire. The Tang used ideas from the Sui
Tang and Song Dynasty By Ms. Escalante 1. What do you think this poem is about? Poetry Warm-up: The Tang rulers developed an imperial state. This is related to an empire. The Tang used ideas from the Sui
Unit 9- Medieval Europe. Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review. Name:
 1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia
 1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
CHINESE EMPIRE. AP World History Notes Chapter 4
 CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties
 Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
 Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Standard Objective: To learn that China increased contact with the outside world, but eventually withdrew to isolationism.
 Standard 7.3.4: Standard 7.3.4 Objective: To learn that China increased contact with the outside world, but eventually withdrew to isolationism. The Mongol Empire Who were the Mongols? Nomadic peoples
Standard 7.3.4: Standard 7.3.4 Objective: To learn that China increased contact with the outside world, but eventually withdrew to isolationism. The Mongol Empire Who were the Mongols? Nomadic peoples
World History 3219 January 2017
 World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Trade Creates Links. 430 Unit 3
 Trade Creates Links A trade network exists when a group of people or countries buys from or sells to each other on a regular basis. Historically, trade networks arose as merchants traded local products
Trade Creates Links A trade network exists when a group of people or countries buys from or sells to each other on a regular basis. Historically, trade networks arose as merchants traded local products
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods. Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick
 Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia
 1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
1 I. Silk Roads: Exchange across Eurasia A. The Growth of the Silk Roads 1. Inner and Outer Eurasia: The Eurasia land mass, home to the majority of the world s population and many of its most economically
The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America.
 The Earliest Americans The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America. Main Ideas Climate changes allowed Paleo-Indians to begin the first migration to the Americas.
The Earliest Americans The Big Idea Native American societies developed across Mesoamerica and South America. Main Ideas Climate changes allowed Paleo-Indians to begin the first migration to the Americas.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
ISN 4. #2. List reasons why people migrate.
 ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Unit #2- Classical Period. Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 BCE to c. 600 CE
 Unit #2- Classical Period Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 BCE to c. 600 CE Period #2: 600 BCE to 600 CE Large empires appear in Eurasia & Americas These empires would grow in
Unit #2- Classical Period Organization and Reorganization of Human Societies c. 600 BCE to c. 600 CE Period #2: 600 BCE to 600 CE Large empires appear in Eurasia & Americas These empires would grow in
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The Qin and Han Dynasties For use with pages
 Name Date Class READING ESSENTIALS AND STUDY GUIDE 7-3 The Qin and Han Dynasties For use with pages 240 248 Key Terms acupuncture: sticking thin needles into specific points on a patient s body to relieve
Name Date Class READING ESSENTIALS AND STUDY GUIDE 7-3 The Qin and Han Dynasties For use with pages 240 248 Key Terms acupuncture: sticking thin needles into specific points on a patient s body to relieve
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere
 Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
