Copyright JnF Specialties, LLC. All rights reserved worldwide.
|
|
|
- Judith Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING STANDARD REAGENTS, MISCELLANEOUS SOLUTIONS, AND INDICATORS (mo/yr) Revisions Rev: Letter E.O. Number - Description Date Used On Contract#: Your Company Name Prepared By: Your Dept: Your Dept: LABORATORY PROCEDURE Your Dept: Your Dept: Size: A CAGE: Form Rev: Orig 1 of 18 Your Logo
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose of Process Process Definition Equipment Materials Safety Requirements Technician Responsibilities Process Controls Procedures Preparing and standardizing 1N NaOH Preparing 1N NaOH from 2N NaOH liquid Preparing 1N NaOH from NaOH crystals Standardizing 1N NaOH using 1N HCl Standardizing 1N NaOH using Potassium Acid Phthalate Preparing 0.1N NaOH from 1N NaOH Preparing 0.1N NaOH from NaOH crystals Standardizing 0.1N NaOH using 0.1N HCl Standardizing 0.1N NaOH using Potassium Acid Phthalate Preparing and Standardizing 0.1N NaOH Preparing and Standardizing N NaOH Preparing 1N HCl and Standardizing 1N HCl with sodium carbonate Preparing and standardizing 0.1N HCl Preparing and standardizing 0.001N HCl Preparing and standardizing 0.05M EDTA Preparing and Standardizing 0.05M Magnesium Sulfate Preparing the Muspratt Reagent Preparing and standardizing 0.01M zinc sulfate Preparing 0.1M Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) Preparing decarbonated Type I water Preparing ph 1.68 buffer solution Preparing 6.86 buffer solution Preparing saturated KCl solution for production Preparing ph buffer solution Preparing 50% by weight sulfuric acid solution Preparing Nochromix Preparing 2Molar cadmium nitrate Preparing 3.5% Methocel Solution Preparing phenolphthalein indicator for process use Preparing phenolphthalein indicator for leak tests Preparing methyl orange indicator Preparing methyl red indicator Preparing methyl red indicator for production use Preparing methyl red-methylene blue indicator Preparing Eriochrome Black T indicator Preparing Standards for the AA spectrometer Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 2 of 18
3 1.0 Purpose of Process The purpose of this document is to describe the procedures to produce standard reagents, miscellaneous solutions and indicators. 2.0 Process Definition This document contains several procedures that describe how to produce each solution. 3.0 Equipment Various size beakers 3.11 Various size glass bottles 3.12 Various size glass pipets 3.13 Various size graduated cylinders 3.14 Various size nalgene bottles 3.15 Various size volumetric flasks 3.16 Weighing boats 4.0 Materials Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 3 of 18
4 Safety Requirements 5.1 Safety Equipment The technician performing the analysis must wear the appropriate gloves, lab coat and safety glasses. 5.2 Safety Procedures If any of the glassware breaks during the procedure, the technician should dispose of the remains in the receptacle in the lab specifically for broken glass. All of the gloves worn to perform the procedure should be disposed in the hazardous waste barrel in production. All electrical components should be examined to ensure that the components are in good working order to ensure that wires are not touching heat sources and to ensure that all electrical components are not located in or near water. If the technician has any trouble or questions, he/she should 6.0 Technician Responsibilities The technician should understand how to operate all measuring devices used in the procedure. The technician should have been trained to run titrations and to use the automatic titrators if necessary; specifically, the operator should The technician should understand the calculations and ask questions if the calculations seem unclear. The technician is responsible for Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 4 of 18
5 7.0 Process Controls The procedures must be performed according to the methods described herein. Any changes to the original document must be approved through the lab supervisor and sent through the signature process to maintain configuration control. All of the required data should be recorded. The lab supervisor should develop 8.0 Procedures 8.1 Preparing and standardizing NaOH solutions Preparing and standardizing 1N NaOH Preparing 1N NaOH from 2N NaOH liquid Measure of NaOH carbonate free liquid in a graduated cylinder and pour it into a flask Dilute the solution to volume with Type I water. Place stir bar in the solution and mix for at least 15 minutes on a magnetic stirrer Standardize the solution as described in Preparing 1N NaOH from NaOH crystals Weigh of low carbonate NaOH pellets in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with Type I water Fill half way with Type I water and mix until Then, dilute to volume with Type I water and add a stir bar. Stir on a magnetic stirrer for 30 minutes Standardize the solution as described in Standardizing 1N NaOH using 1N HCl Fill a buret with standardized 1N HCl Pipet of the prepared NaOH solution into Place a stir bar in the beaker Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution While stirring the beaker with a magnetic stirrer, titrate the prepared NaOH solution with the HCl to a color change. Note the amount of HCl used Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows Repeat steps to to titrate 2 additional samples Average the ml s from the 3 titrations to calculate an average normality. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 5 of 18
6 If it is not within of the intended normality, adjust it accordingly and titrate it again starting at step Pour the NaOH solution into Standardizing 1N NaOH using Potassium Acid Phthalate Fill a buret with prepared NaOH solution Dry of potassium acid phthalate at for 1-2 hours Cool it in a desiccator Tare a weigh boat and weigh out of primary standard potassium acid thalate Quantitatively transfer to beaker Add Type I water to beaker Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution Record initial volume of NaOH in buret Add a stir bar to beaker Gently stir solution and titrate with NaOH to a permanent color change Record volume of titrant used Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows Repeat steps to to titrate 2 additional samples Average the NaOH normality values from the 3 titrations If it is not within of the intended number, adjust it accordingly and titrate it again starting at step Preparing and Standardizing 0.1N NaOH Preparing 0.1N NaOH from 1N NaOH Measure of standardized NaOH in a graduated cylinder and pour it into a flask. Rinse the graduated cylinder into the flask with Type I water Dilute the solution to volume with Type I water. Place a stir bar in the flask and mix for at least 15 minutes on a magnetic stirrer Standardize the solution as described in Preparing 0.1N NaOH from NaOH crystals Weigh out of low carbonate NaOH pellets into weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask Rinse the weigh boat with Type I water. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 6 of 18
7 Fill half way with Type I water and mix until Dilute to volume with Type I water and add a stir bar. Stir on a magnetic stirrer for 30 minutes Standardize the solution as described in Standardizing 0.1N NaOH using 0.1N HCl Fill a buret with standardized 0.1N HCl Pipet of the prepared NaOH solution into beaker Place stir bar in the beaker Add 2 drops phenolphthalein indicator solution While stirring the beaker with a magnetic stirrer, titrate the prepared NaOH solution with the HCl solution to a color change. Note the amount of HCl titrant used Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows: Repeat steps to titrate 2 additional samples Average the ml s from the 3 titrations to calculate an average normality If it is not within of the intended number, adjust it accordingly and titrate it again starting at step Pour the NaOH solution into Standardizing 0.1N NaOH using Potassium Acid Phthalate Fill a buret with the prepared NaOH solution Dry of potassium acid phthalate at 100oC for 1-2 hours. Cool it in a desiccator Weigh of the dried potassium acid phthalate in a weigh boat. Note the weight to the nearest g Empty the weigh boat into beaker Rinse the weighing boat into the beaker with Type I water. Add Type I water to the beaker Place a stir bar in the beaker. Stir with a magnetic stirrer to dissolve the potassium acid phthalate. The beaker may have to be heated slightly to get the entire solid into solution Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution While continuing to stir the beaker, titrate the potassium acid phthalate solution with the prepared NaOH solution to a color change. Note the amount of NaOH titrant used Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows: Repeat steps to to titrate 2 additional samples. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 7 of 18
8 Average the NaOH normality values from the 3 titrations If it is not within of the intended number, adjust it accordingly and titrate it again starting at step Pour the NaOH solution into Preparing and Standardizing 0.1N NaOH Pipet of standardized NaOH into flask Dilute the flask to volume with Type I water. Stopper the flask and shake it to thoroughly mix the NaOH solution Fill buret with standardized 0.1N HCl Pipet of the prepared NaOH solution into beaker Place stir bar in the beaker Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the beaker While stirring the beaker with a magnetic stirrer, titrate the prepared NaOH solution with the HCl to a color change. Note the amount of HCl used Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows: Repeat steps to titrate two additional samples Average the ml s from the 3 titrations. Calculate the average normality If it is not within of the intended value, adjust it accordingly and titrate it again starting at step Pour the NaOH solution into Preparing and Standardizing N NaOH Pour of Type I water into flask. NOTE: 16ml is an approximation and it is not necessary to be completely accurate with the initial volume measurement Measure of 1N NaOH into a graduated cylinder and pour it into the volumetric Dilute the volumetric to volume with Type I water. Place a stir bar in the flask. Stopper the flask and stir it on a magnetic stirrer to thoroughly mix the NaOH solution Fill a buret with standardized 0.1N HCl Pipet of the prepared NaOH solution into beaker Place stir bar in the beaker Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution to the beaker While stirring the beaker with a magnetic stirrer, titrate the prepared NaOH solution with the HCl to a color change. Note the amount of titrant used. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 8 of 18
9 Calculate the normality of the NaOH solution as follows The normality of the NaOH solution should be If it is not N, add small amounts of or, mix thoroughly, and titrate the solution again as described in steps When the solution is N, repeat steps to titrate 2 additional samples. The average normality of the 3 titrations should be N Pour the NaOH solution into 8.2 Preparing and Standardizing HCl Solutions Preparing 1N HCl and Standardizing 1N HCl with sodium carbonate Dilute of hydrochloric acid to and mix thoroughly Weigh accurately sodium carbonate, Alkalimetric Standard that has previously been heated at for Dissolve the sodium carbonate in if Type I water Add 0.1ml of methyl red indicator solution Add a stir bar to the solution While stirring the solution, add the acid slowly from a buret until Heat the solution to boiling. Cool the solution to room temperature. Titrate again until Repeat this procedure until Repeat steps for two additional samples Calculate the normality of the HCl solution as follows Average the three samples' normalities. If the average is not within of the intended normality, adjust it accordingly and titrate again starting at step Preparing and standardizing 0.1N HCl Dilute of hydrochloric acid to and mix thoroughly Weigh accurately of sodium carbonate, Alkalimetric Standard that has previously been heated at for Dissolve the sodium carbonate in if Type I water Add l of methyl red indicator solution Add a stir bar to the solution While stirring the solution, add the acid slowly from a buret until Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 9 of 18
10 Heat the solution to boiling. Cool the solution to room temperature. Titrate again until Repeat this procedure until Repeat steps for two additional samples Calculate the normality of the HCl solution as follows Average the three samples' normalities. If the average is not within of the intended normality, adjust it accordingly and titrate again starting at step Preparing and standardizing 0.001N HCl Obtain of previously standardized 0.1N HCl Transfer to a flask Dilute the flask to volume with Type I water Obtain of the diluted solution Transfer to beaker Add 1 drop of phenolphthalein indicator to the solution Titrate with previously standardized 0.01N NaOH to a color change Calculate the normality with the following equation: 8.3 Preparing and Standardizing Miscellaneous Solutions Preparing and standardizing 0.05M EDTA Preparing EDTA Dry approximately of EDTA (disodium salt form) at for hour. Cool to room temperature in a desiccator for approximately 1 hour Weigh of the EDTA in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with Type I water Fill the flask to volume with Type I water Place a stir bar in the flask and stir with a magnetic stirrer until Standardize the EDTA mixture Standardizing the EDTA with Calcium carbonate Fill a buret with the prepared EDTA solution Weigh in a weigh boat. Note the weight to the nearest g Pour the calcium carbonate into beaker. Rinse the weigh boat into the beaker with Type I water. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 10 of 18
11 Swirl the beaker to form slurry Cover the beaker with a watch glass. Add 4-5 drops of concentrated HCl via a pipet inserted between the lip of the beaker and the edge of the watch glass Swirl the beaker to dissolve the calcium carbonate Rinse the sides of the beaker, the outer surface of the pipet, and the watch glass with Type I water. Dilute the beaker with Type I water to Place a stir bar in the beaker While stirring the solution with a magnetic stirrer, add of the EDTA being standardized from Add sodium hydroxide ( ) and of hydroxyl naphthol blue indicator Continue to titrate the solution with the EDTA until Calculate the molarity of the EDTA solution as follows Repeat steps to titrate 2 additional samples Average the ml s from the 3 titrations to calculate an average molarity If it is not within of the intended molarity, adjust it accordingly and titrate again starting at step Pour the mixture into Preparing and Standardizing 0.05M Magnesium Sulfate Weigh of MgSO 4 *7H 2 O in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask. Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with DI water Dilute the solution to volume with Type I water. Place a stir bar in the flask and stir with a magnetic stirrer until Fill burette with the prepared 0.05M MgSO 4 solution Pipet of standardized 0.05M EDTA solution into beaker Add of muspratt reagent to the beaker Add approximately of Eriochrome Black T indicator to the beaker While stirring the beaker with a magnetic stirrer, titrate it with the MgSO 4 solution (from ) until. Note the amount of titrant used Calculate the molarity of the MgSO 4 solution as follows Repeat steps for 2 additional samples Average the mls from the 3 titrations to calculate an average molarity If it is not within of the intended molarity, adjust it accordingly and titrate again starting at step Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 11 of 18
12 Pour the mixture into Preparing the Muspratt Reagent Weigh of NH 4 Cl in a weigh boat Empty the weighing boat into flask. Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with Type I water Add of Type I water to the flask. Shake the flask until Working under a laboratory hood measure in a graduated cylinder. Add this to the flask Shake the flask until Dilute the flask to volume with Type I water Pour the solution into Preparing and standardizing 0.01M zinc sulfate Weigh of ZnSO 4 (formula weight ) in a weigh boat Empty the ZnSO 4 into flask Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with Type I water Dilute the flask to volume with Type I water Place a stir bar in the flask. Stir the solution with a magnetic stirrer until Fill with the prepared ZnSO 4 solution Pipet into beaker Add of Muspratt reagent (buffer) to the beaker Add of Eriochrome Black T indicator to the beaker Add of the prepared ZnSO 4 solution (from step ) to the beaker Continue to titrate the beaker with the prepared ZnSO 4 solution until Calculate the molarity of the ZnSO 4 solution as follows Repeat steps to titrate 2 additional samples Average the ml s from the 3 titrations to calculate an average molarity If it is not within of the intended molarity, adjust it accordingly and titrate again starting at step Pour the solution into Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 12 of 18
13 8.3.5 Preparing 0.1M Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) Weigh of DMG in weigh boat Empty the DMG into flask Rinse the weigh boat into the flask with l of denatured ethyl alcohol Dilute the flask to volume with Type I water Place a stir bar in the flask. Stir with a magnetic stirrer to dissolve the DMG. It may be necessary to heat the flask slightly to get it all into solution Place a stopper in the flask. Label the flask with Preparing decarbonated Type I water Place of Type I water in beaker. Bubble nitrogen through the Type I water at SCFH for to remove the dissolved gasses from the Type I water. Cover the beaker As an alternative method for removing the dissolved gasses, Preparing ph 1.68 buffer solution Use SRM 189a Potassium Tetroxalate salt Measure of salt (un-dried) for each solution desired Record the temperature and resistivity of the Type I water Rinse a volumetric flask appropriate to the volume of solution desired with Type I water Pour the crystals into the volumetric flask and fill to the mark with Type I water. Add a clean stir bar and stir the solution until Use a new nalgene bottle or the bottle returned from production that previously contained the 1.68 buffer solution to contain the new solution. Rinse the bottle with a small amount of the new solution. Fill the bottle with the buffer and label appropriately. Solutions expire from preparation Record data in appropriate log book or log form Preparing 6.86 buffer solution Measure KCl Pour KCl into volumetric Rinse weigh boat with Type I water into the volumetric Dilute to volume with buffer Stir until Label appropriately Solution has shelf life. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 13 of 18
14 8.3.9 Preparing saturated KCl solution for production Determine the molarity of the solution that production needs. This molarity will=x in the following equation: Pour KCl into volumetric and dilute to volume with Type I water. Stir until Be patient...this will take time. The flask will be cold to the touch. This is normal Label appropriately Shelf life is Preparing ph buffer solution Pour of commercially prepared ph 10 buffer into a small beaker Place a stir bar in the beaker and stir with a magnetic stirrer Suspend a digital ph meter probe in the beaker While continuing to stir the beaker, add drops of until Place the buffer solution in a plastic bottle. Label the bottle with Preparing 50% by weight sulfuric acid solution Place a glass bottle with funnel on a scale. Tare the scale Add Type I water to fill the bottle approximately half full. Note the weight of the Type I water Slowly add the same weight of concentrated sulfuric acid to the bottle. Add the sulfuric acid very slowly as the solution will heat up After the sulfuric acid has been added, cap the bottle loosely. After the solution has cooled down, tighten the cap Label the bottle with Preparing Nochromix Pour one package of Nochromix crystals into Use safety coated glass bottles or heavy wall polyethylene containers only A half batch of Nochromix may be made Weigh a full package of Nochromix crystals Divide the weight by Add half the weight of a whole package to a half bottle of concentrated sulfuric acid. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 14 of 18
15 Save the rest of the crystals for future use Place cap loosely on bottle Let stand overnight. NOTE: Do not close or store the container tightly capped!! Label the bottle For best results, use When the cleaning solution is stale or discolored, it can be regenerated with Preparing 2Molar cadmium nitrate Clean a 5 gallon graduated pre-weighed bucket equipped with a spigot and lid Have production weight of cadmium nitrate into the bucket Get exact weight of cadmium nitrate and bucket Subtract bucket weight to get cadmium nitrate weight Divide cadmium nitrate weight by to get total volume Dilute with DI water to the volume obtained in Set up a mixer and let the solution mix for a minimum of 30 minutes. NOTE: The mixing should be done under a hood in the lab Dilute the solution according to the following: Set up the AA to analyze the solution Turn on the equipment to warm up for 10 minutes Set the slit width to for the cadmium program Set the wavelength to nm Use cadmium standards with the following concentrations: ppm ppm ppm Calculate the molarity of the solution using the following: If the solution is not with 2M ±, adjust it accordingly Pour the cadmium nitrate solution into Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 15 of 18
16 Preparing 3.5% Methocel Solution Check the conductivity of the laboratory DI water. Do not prepare the methocel solution unless the DI water conductivity is ohm-cm Measure of DI water into flask Use a hot plate to heat the water in the flask to Measure of DI water into another flask Place this flask in an ice water bath until Weigh out of type methocel into a weigh boat. NOTE: Methocel powder must always be kept in a tightly closed container. The container should have a green tag. If the powder does not have a green tag, do not use and notify QC Remove the flask from the hot plate and slowly add the methocel to the hot water, a little bit at a time. Agitate the solution while adding the methocel by rotating the flask. Agitate the solution until If a gel forms, stop adding the Methocel until Remove the other flask from the ice bath and slowly add the cold water to the hot solution, a little bit at a time. If a gel forms, stop adding the cold water until the gel dissolves After all the cold water has been added, the solution should Seal the Erlenmeyer flask tightly with a synthetic rubber stopper or a cork that has been covered with Label the flask with 8.4 Preparing indicator solutions Preparing phenolphthalein indicator for process use NOTE: Phenolphthalein can be prepared as either an aqueous or alcohol solution Aqueous solution: Dissolve of phenolphthalein disodium salt in Type I water in a volumetric. Dilute volumetric to volume with Type I water Alcohol solution: Dissolve of phenolphthalein disodium salt in of denatured ethyl alcohol in volumetric. Dilute volumetric to volume with Type I water The phenolphthalein solution should be within range. The titration end points are clear (8.2) to red-violet (9.8). Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 16 of 18
17 8.4.2 Preparing phenolphthalein indicator for leak tests Dissolve 1g phenolphthalein disodium salt in 100ml of 95% ethyl alcohol Dilute 1ml of the solute in 500ml of Type I water Adjust the ph of the solution to with potassium hydroxide, or sodium hydroxide If the ph drops below readjust it to with potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide Preparing methyl orange indicator Dissolve methyl orange powder in Type I water. Dilute to with Type I water Methyl orange should be in range. The titration end points are pink (3.1) to yellow (4.4) Preparing methyl red indicator Dissolve methyl red powder in Type I water. Dilute to with Type I water Methyl red indicator should be ph range. The titration end points are pink (4.2) to yellow (6.2) Preparing methyl red indicator for production use Dissolve 1g methyl red powder in Type I water Dilute to with Type I water, as production always uses Preparing methyl red-methylene blue indicator Weigh of methyl red indicator powder in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask Rinse the weigh boat with into the volumetric Dilute the flask to volume with Pour the solution into Weigh of the methylene blue indicator powder in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask Rinse the weigh boat with into the volumetric Dilute the flask to volume with 95% alcohol Pipette 50ml of the methylene blue into the plastic bottle and shake Preparing Eriochrome Black T indicator Weigh of Eriochrome Black T powder in a weigh boat Empty the weigh boat into flask. Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 17 of 18
18 Rinse the weigh boat into the volumetric flask with of Type I water Pipet l of buffer into the flask Dilute the flask to volume with Place a stir bar in the flask. Stir with a magnetic stirrer for 30 minutes Pour the solution into a plastic bottle. Label the bottle with Store the indicator in Discard the indicator after. 8.5 Preparing Standards for the AA spectrometer NOTE: This recipe is not used when analyzing the production solutions. The technician should only use this recipe for the environmental sample analysis Preparing stock standard mix Make a batch of fresh Nochromix. The glassware that is to be used should be as analytically clean as possible Clean a flask, a bottle, and the necessary number of thoroughly. The number of is dependent upon the number of elements that will be mixed Pipet of each element into flask: Add of concentrated nitric acid (trace metal grade) to the flask Dilute to volume with Type I water Shake the flask to Pour a small amount of the standard just made into the plastic bottle. Screw on the cap and shake the bottles Discard that small amount of solution Pour the remaining standard mix into Your Company Name REV CAGE DOC#: 18 of 18
Copyright JnF Specialties, LLC. All rights reserved worldwide.
 Laboratory Temperature Sensor Calibration (mo/yr) Revisions Rev: Letter E.O. Number - Description Date Used On Contract#: Your Company Name Prepared By: Originator: Your Dept: Your Dept: LABORATORY PROCEDURE
Laboratory Temperature Sensor Calibration (mo/yr) Revisions Rev: Letter E.O. Number - Description Date Used On Contract#: Your Company Name Prepared By: Originator: Your Dept: Your Dept: LABORATORY PROCEDURE
Chapter 14 Tex-619-J, Analysis of Water for Chloride and Sulfate Ions
 Chapter 14 Tex-619-J, Analysis of Water for Contents: Section 1 Overview... 14-2 Section 2 Apparatus... 14-3 Section 3 Reagents... 14-4 Section 4 Procedures... 14-5 Section 5 Calculations... 14-6 Section
Chapter 14 Tex-619-J, Analysis of Water for Contents: Section 1 Overview... 14-2 Section 2 Apparatus... 14-3 Section 3 Reagents... 14-4 Section 4 Procedures... 14-5 Section 5 Calculations... 14-6 Section
Royal Society of Chemistry Analytical Division East Anglia Region National Schools' Analyst Competition
 Royal Society of Chemistry Analytical Division East Anglia Region 2017 National Schools' Analyst Competition East Anglia Region Heat Thursday 20th April, 2017 School of Chemistry University of East Anglia
Royal Society of Chemistry Analytical Division East Anglia Region 2017 National Schools' Analyst Competition East Anglia Region Heat Thursday 20th April, 2017 School of Chemistry University of East Anglia
Introduction to the General Chemistry II Laboratory. Lab Apparatus and Glassware
 Introduction to the General Chemistry II Laboratory Lab Apparatus and Glassware Review the first of two photographs at the end of the Data Documentation section, near the beginning of your lab manual.
Introduction to the General Chemistry II Laboratory Lab Apparatus and Glassware Review the first of two photographs at the end of the Data Documentation section, near the beginning of your lab manual.
Gravimetric Analysis
 Experiment 1: Gravimetric Analysis with Calcium Chloride and Potassium Carbonate In this experiment, proper analytical experimental techniques will be utilized to perform a double displacement reaction.
Experiment 1: Gravimetric Analysis with Calcium Chloride and Potassium Carbonate In this experiment, proper analytical experimental techniques will be utilized to perform a double displacement reaction.
Making Hard Cider. A Guide for Small-Scale Producers. Lee Elliot Williams. Bellevue College. Technical Writing Certificate Program
 Making Hard Cider A Guide for Small-Scale Producers Lee Elliot Williams Bellevue College Technical Writing Certificate Program Winter 2018 Publishing Information This document was completed as a final
Making Hard Cider A Guide for Small-Scale Producers Lee Elliot Williams Bellevue College Technical Writing Certificate Program Winter 2018 Publishing Information This document was completed as a final
EXPERIMENT 6. Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Quinine Assay
 EXPERIMENT 6 Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Quinine Assay UNKNOWN Submit a clean, labeled 500-mL volumetric flask to the instructor so that your unknown quinine solution may be issued. Your name,
EXPERIMENT 6 Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Quinine Assay UNKNOWN Submit a clean, labeled 500-mL volumetric flask to the instructor so that your unknown quinine solution may be issued. Your name,
Gravimetric Analysis
 Gravimetric Analysis In this experiment you will determine the concentrations of two ions in an unknown solution. The ions are Cu 2+ and Pb 2+. You will also determine the percent copper in an unknown.
Gravimetric Analysis In this experiment you will determine the concentrations of two ions in an unknown solution. The ions are Cu 2+ and Pb 2+. You will also determine the percent copper in an unknown.
SYNTHESIS OF SALICYLIC ACID
 26 SYNTHESIS OF SALICYLIC ACID The purpose of this experiment is to synthesize salicylic acid, a white organic solid that was extracted from willow bark by Hippocrates in the fifth century BC. At that
26 SYNTHESIS OF SALICYLIC ACID The purpose of this experiment is to synthesize salicylic acid, a white organic solid that was extracted from willow bark by Hippocrates in the fifth century BC. At that
Student Handout Procedure
 Student Handout Procedure Lab period 1: Reaction: Measure 0.75 g of solid cinnamic acid and 25 ml of your unknown alcohol in a 100 ml round bottom flask. Add a stir bar and stir solution until it is completely
Student Handout Procedure Lab period 1: Reaction: Measure 0.75 g of solid cinnamic acid and 25 ml of your unknown alcohol in a 100 ml round bottom flask. Add a stir bar and stir solution until it is completely
LAB: One Tube Reaction Part 1
 AP Chemistry LAB: One Tube Reaction Part 1 Objective: To monitor and document the chemical changes occurring in a single test tube containing a predetermined mixture of chemicals. Materials: test tube,
AP Chemistry LAB: One Tube Reaction Part 1 Objective: To monitor and document the chemical changes occurring in a single test tube containing a predetermined mixture of chemicals. Materials: test tube,
Practical 1 - Determination of Quinine in Tonic Water
 Practical 1 - Determination of Quinine in Tonic Water Introduction Quinine has a fluorescence and a UV absorbance and so can be quantified using either of these. In the method described here the absorbances
Practical 1 - Determination of Quinine in Tonic Water Introduction Quinine has a fluorescence and a UV absorbance and so can be quantified using either of these. In the method described here the absorbances
IPPA SAG method revision 0,
 IPPA SAG method revision 0, 23.01.2017 This procedure is based on the method described by Cox and Higby, in Food Inds., 16, 441 (1944) and Joseph and Baier, Food Technol. 3, 18 (1949) and is a modification
IPPA SAG method revision 0, 23.01.2017 This procedure is based on the method described by Cox and Higby, in Food Inds., 16, 441 (1944) and Joseph and Baier, Food Technol. 3, 18 (1949) and is a modification
THE MAGIC OF CHEMISTRY SHOW
 THE MAGIC OF CHEMISTRY SHOW WARNING: These demonstrations are potentially dangerous and should be prepared and performed by someone with a sound training in chemistry. FLAG SPRAYING Chemicals & Apparatus:
THE MAGIC OF CHEMISTRY SHOW WARNING: These demonstrations are potentially dangerous and should be prepared and performed by someone with a sound training in chemistry. FLAG SPRAYING Chemicals & Apparatus:
Introduction to Measurement and Error Analysis: Measuring the Density of a Solution
 Introduction to Measurement and Error Analysis: Measuring the Density of a Solution Introduction: Most of us are familiar with the refreshing soft drink Coca-Cola, commonly known as Coke. The formula for
Introduction to Measurement and Error Analysis: Measuring the Density of a Solution Introduction: Most of us are familiar with the refreshing soft drink Coca-Cola, commonly known as Coke. The formula for
1. Blender: Osterizer, 10-speed, or equivalent. 2. Separatory Funnel: Kilborn or equivalent (see figure 1) 2. HCl Solution: HCl/water (7:93 by volume)
 EXTER.01-1 INFESTATION IN WHOLE CORN PRINCIPLE Whole corn is suspended in aqueous borax solution to float insects and insect fragments, which are collected on filter paper for microscopic identification
EXTER.01-1 INFESTATION IN WHOLE CORN PRINCIPLE Whole corn is suspended in aqueous borax solution to float insects and insect fragments, which are collected on filter paper for microscopic identification
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.6-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.6-2016 National food safety standard
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.6-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.6-2016 National food safety standard
COMPENDIUM OF INTERNATIONAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS - OIV Volatile acidity. Volatile Acidity
 Method OIV-MA-AS313-02 Type I method Volatile Acidity 1. Definition The volatile acidity is derived from the acids of the acetic series present in wine in the free state and combined as salts. 2. Principle
Method OIV-MA-AS313-02 Type I method Volatile Acidity 1. Definition The volatile acidity is derived from the acids of the acetic series present in wine in the free state and combined as salts. 2. Principle
WINEWORKS LABORATORY PRODUCTS & SERVICES
 WINEWORKS LABORATORY PRODUCTS & SERVICES February 2017 OUR SERVICES WineWorks contract laboratory provides services to wineries and breweries around New Zealand, offering a wide range of analytical and
WINEWORKS LABORATORY PRODUCTS & SERVICES February 2017 OUR SERVICES WineWorks contract laboratory provides services to wineries and breweries around New Zealand, offering a wide range of analytical and
HI-1017: Pharmacy Technician. Module 10 Pharmacy Equipment
 HI-1017: Pharmacy Technician Module 10 Pharmacy Equipment Slide 1 Main Objectives Types of Pharmacy Equipment Slide 2 Types of Pharmacy Equipment The Four Step Process Class a Prescription Balance Weighing
HI-1017: Pharmacy Technician Module 10 Pharmacy Equipment Slide 1 Main Objectives Types of Pharmacy Equipment Slide 2 Types of Pharmacy Equipment The Four Step Process Class a Prescription Balance Weighing
Separating the Components of a Mixture
 Separating the Components of a Mixture Introduction Many naturally occurring substances occur as mixtures rather than pure substances. There are two main types of mixtures, homogeneous and heterogeneous.
Separating the Components of a Mixture Introduction Many naturally occurring substances occur as mixtures rather than pure substances. There are two main types of mixtures, homogeneous and heterogeneous.
Ti-Pure TITANIUM DIOXIDE DETERMINATION OF UNBRUSHED 325 MESH GRIT, SLURRY METHOD: T
 Ti-Pure TITANIUM DIOXIDE DETERMINATION OF UNBRUSHED 325 MESH GRIT, SLURRY METHOD: T4400.300.01 DuPont Titanium Technologies Page 2 of 5 1. Principle A slurry sample of known percent solids is diluted with
Ti-Pure TITANIUM DIOXIDE DETERMINATION OF UNBRUSHED 325 MESH GRIT, SLURRY METHOD: T4400.300.01 DuPont Titanium Technologies Page 2 of 5 1. Principle A slurry sample of known percent solids is diluted with
15. Extraction: Isolation of Caffeine from Tea
 15. Extraction: Isolation of Caffeine from Tea In this experiment you will isolate a compound from a natural source using two extraction techniques. Such compounds are often referred to as natural products.
15. Extraction: Isolation of Caffeine from Tea In this experiment you will isolate a compound from a natural source using two extraction techniques. Such compounds are often referred to as natural products.
LABORATORY PRACTICES IN WINE ANALYSIS. Dpto. Nutrición y Bromatología II. Facultad de Farmacia. UCM
 LABORATORY PRACTICES IN WINE ANALYSIS Dpto. Nutrición y Bromatología II. Facultad de Farmacia. UCM ANALYTICAL DETERMINATIONS IN WINE ph TOTAL ACIDITY VOLATILE ACIDITY ALCOHOLIC STRENGTH SULPHUR DIOXIDE
LABORATORY PRACTICES IN WINE ANALYSIS Dpto. Nutrición y Bromatología II. Facultad de Farmacia. UCM ANALYTICAL DETERMINATIONS IN WINE ph TOTAL ACIDITY VOLATILE ACIDITY ALCOHOLIC STRENGTH SULPHUR DIOXIDE
Measuring Fluoride in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter
 Measuring Fluoride in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter Water and Lab Products, Thermo Fisher Scientific Technical Note 502 Key Words Thermo Scientific Orion
Measuring Fluoride in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter Water and Lab Products, Thermo Fisher Scientific Technical Note 502 Key Words Thermo Scientific Orion
Separating the Components of a Mixture
 Separating the Components of a Mixture Introduction Many naturally occurring substances occur as mixtures rather than pure substances. There are two main types of mixtures, homogeneous and heterogeneous.
Separating the Components of a Mixture Introduction Many naturally occurring substances occur as mixtures rather than pure substances. There are two main types of mixtures, homogeneous and heterogeneous.
Chestnut DNA extraction B3 Summer Science Camp 2014
 Experiment Type: Experiment Goals: Sample Label: Scientist Name: Date: General Idea: extract the nucleic acid from leaf tissue by grinding it in a reducing medium (the betamercaptoethanol, which smells
Experiment Type: Experiment Goals: Sample Label: Scientist Name: Date: General Idea: extract the nucleic acid from leaf tissue by grinding it in a reducing medium (the betamercaptoethanol, which smells
Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream
 Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream How do I make a stronger cup of coffee? How do I make ice cream? Prelab Spend 5 minutes doing the following
Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream How do I make a stronger cup of coffee? How do I make ice cream? Prelab Spend 5 minutes doing the following
2. Other constituents in the sample solution should not interfere with the precipitation of the component of interest.
 EXPERIMENT 15 Percentage Yield of Lead (II) Iodide in a Gravimetric Analysis INTRODUCTION In a gravimetric analysis, a substance is treated so that the component of interest is separated either in its
EXPERIMENT 15 Percentage Yield of Lead (II) Iodide in a Gravimetric Analysis INTRODUCTION In a gravimetric analysis, a substance is treated so that the component of interest is separated either in its
Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream
 Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream How do I make a stronger cup of coffee? How do I make ice cream? Prelab Spend 5 minutes doing the following
Lab 2. Drug Abuse. Solubility and Colligative Properties of Solutions: Coffee, Soda, and Ice Cream How do I make a stronger cup of coffee? How do I make ice cream? Prelab Spend 5 minutes doing the following
Prototocatechualdehyde methylenation. Photo-essay.
 Prototocatechualdehyde methylenation. Photo-essay. What follows is a slight variation of the commonly referenced catechol methylenation procedure, easily found copied and pasted all over the internet.
Prototocatechualdehyde methylenation. Photo-essay. What follows is a slight variation of the commonly referenced catechol methylenation procedure, easily found copied and pasted all over the internet.
ALWAYS WEAR LAB COAT. Fecal Float Protocol (To check for viable E.mac) (Do within 1 week of obtaining samples)
 ALWAYS WEAR LAB COAT Fecal Float Protocol (To check for viable E.mac) (Do within 1 week of obtaining samples) 1. Label each tube with the animals name 2. Obtain 2g feces- rule of thumb an amount approximately
ALWAYS WEAR LAB COAT Fecal Float Protocol (To check for viable E.mac) (Do within 1 week of obtaining samples) 1. Label each tube with the animals name 2. Obtain 2g feces- rule of thumb an amount approximately
CHEM Experiment 4 Introduction to Separation Techniques I. Objectives
 1 CHEM 0011 Experiment 4 Introduction to Separation Techniques I Objectives 1. To learn the gravity filtration technique 2. To learn the suction filtration technique 3. To learn about solvent extraction
1 CHEM 0011 Experiment 4 Introduction to Separation Techniques I Objectives 1. To learn the gravity filtration technique 2. To learn the suction filtration technique 3. To learn about solvent extraction
Introduction. Question. Hypothesis. Materials. Procedure
 Sujin Shin Orange Juice Lab Report Introduction Orange has lots of Vitamin C but when it is processed into commercial juice the amount of vitamin C decreases while sugar and other contents are added for
Sujin Shin Orange Juice Lab Report Introduction Orange has lots of Vitamin C but when it is processed into commercial juice the amount of vitamin C decreases while sugar and other contents are added for
EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR BUTYLTINS
 EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR BUTYLTINS Juan A. Ramirez, Donell S. Frank, Susanne J. McDonald, and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International/B&B Laboratories Inc. College Station, Texas 77845 ABSTRACT Determining
EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR BUTYLTINS Juan A. Ramirez, Donell S. Frank, Susanne J. McDonald, and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International/B&B Laboratories Inc. College Station, Texas 77845 ABSTRACT Determining
Lab 2: Phase transitions & ice cream
 Lab 2: Phase transitions & ice cream Lab sections on Tuesday Sept 18 Friday Sept 21 In this lab you will observe how changing two parameters, pressure and salt concentration, affects the two phase transitions
Lab 2: Phase transitions & ice cream Lab sections on Tuesday Sept 18 Friday Sept 21 In this lab you will observe how changing two parameters, pressure and salt concentration, affects the two phase transitions
EXTRACTION PROCEDURE
 SPE Application Note for Multiresidue Exraction and Clean Up from Fruit and Vegetables This note outlines solid phase extraction (SPE) methodology for the multiresidue extraction and clean up of fruits
SPE Application Note for Multiresidue Exraction and Clean Up from Fruit and Vegetables This note outlines solid phase extraction (SPE) methodology for the multiresidue extraction and clean up of fruits
Analytical Method for Coumaphos (Targeted to agricultural, animal and fishery products)
 Analytical Method for Coumaphos (Targeted to agricultural, animal and fishery products) The target compound to be determined is coumaphos. 1. Instruments Gas chromatograph-flame thermionic detector (GC-FTD)
Analytical Method for Coumaphos (Targeted to agricultural, animal and fishery products) The target compound to be determined is coumaphos. 1. Instruments Gas chromatograph-flame thermionic detector (GC-FTD)
Analysis of Beta-Carotene and Total Carotenoids from Pacific Sea Plasma (Spectrophotometric Method)
 Analysis of Beta-Carotene and Total Carotenoids from Pacific Sea Plasma (Spectrophotometric Method) Background: Spirulina has several carotenoids, the major components being β-carotene, zeaxanthin, echinenone,
Analysis of Beta-Carotene and Total Carotenoids from Pacific Sea Plasma (Spectrophotometric Method) Background: Spirulina has several carotenoids, the major components being β-carotene, zeaxanthin, echinenone,
PECTINASE Product Code: P129
 PECTINASE Product Code: P129 Enzyme for sample clarification prior to patulin analysis. For in vitro use only. P129/V1/02.06.16 www.r-biopharm.com Contents Page Test Principle... 3 Kit Components... 3
PECTINASE Product Code: P129 Enzyme for sample clarification prior to patulin analysis. For in vitro use only. P129/V1/02.06.16 www.r-biopharm.com Contents Page Test Principle... 3 Kit Components... 3
Lab 2-1: Measurement in Chemistry
 Name: Lab Partner s Name: Lab 2-1: Measurement in Chemistry Lab Station No. Introduction Most chemistry lab activities involve the use of various measuring instruments. The three variables you will measure
Name: Lab Partner s Name: Lab 2-1: Measurement in Chemistry Lab Station No. Introduction Most chemistry lab activities involve the use of various measuring instruments. The three variables you will measure
Experiment 3: Separation of a Mixture Pre-lab Exercise
 1 Experiment 3: Separation of a Mixture Pre-lab Exercise Name: The amounts of sand, salt, and benzoic acid that will dissolve in 100 g of water at different temperatures: Temperature 0 C 20 C 40 C 60 C
1 Experiment 3: Separation of a Mixture Pre-lab Exercise Name: The amounts of sand, salt, and benzoic acid that will dissolve in 100 g of water at different temperatures: Temperature 0 C 20 C 40 C 60 C
3230 Riverside Ave.Suite 140, Paso Robles, Ca Phone: (805) Fax: (805)
 The Vintner Vault Your Winery Supply Super Store 3230 Riverside Ave.Suite 140, Paso Robles, Ca. 93446 Phone: (805) 226-8100 Fax: (805) 226-8188 www.thevintnervault.com 2008 Wine Crush Laboratory, Price
The Vintner Vault Your Winery Supply Super Store 3230 Riverside Ave.Suite 140, Paso Robles, Ca. 93446 Phone: (805) 226-8100 Fax: (805) 226-8188 www.thevintnervault.com 2008 Wine Crush Laboratory, Price
HOW MUCH DYE IS IN DRINK?
 HOW MUCH DYE IS IN DRINK? Spectroscopic quantitative analysis Charles and Michael, they often go to restaurant to have a drink. Once, they had a sweet peppermint liqueur, which has a typical green color.
HOW MUCH DYE IS IN DRINK? Spectroscopic quantitative analysis Charles and Michael, they often go to restaurant to have a drink. Once, they had a sweet peppermint liqueur, which has a typical green color.
Bromine Containing Fumigants Determined as Total Inorganic Bromide
 Bromine Containing Fumigants Determined as Total Inorganic Bromide Introduction: Fumigants containing bromine, mainly methyl bromide, are used for soil disinfection as well as postharvest treatment of
Bromine Containing Fumigants Determined as Total Inorganic Bromide Introduction: Fumigants containing bromine, mainly methyl bromide, are used for soil disinfection as well as postharvest treatment of
Chemistry 212 MOLAR MASS OF A VOLATILE LIQUID USING THE IDEAL GAS LAW
 Chemistry 212 MOLAR MASS OF A VOLATILE LIQUID USING THE IDEAL GAS LAW To study the Ideal Gas Law. LEARNING OBJECTIVES To determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid. BACKGROUND The most common instrument
Chemistry 212 MOLAR MASS OF A VOLATILE LIQUID USING THE IDEAL GAS LAW To study the Ideal Gas Law. LEARNING OBJECTIVES To determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid. BACKGROUND The most common instrument
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Quartz dissolution in Hydrofluoric Acid
 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Quartz dissolution in Hydrofluoric Acid #1 General Process Description This SOP describes the initial Quartz-sample dissolution (digestion). The sample is dissolved
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Quartz dissolution in Hydrofluoric Acid #1 General Process Description This SOP describes the initial Quartz-sample dissolution (digestion). The sample is dissolved
3. Aspirin Analysis. Prelaboratory Assignment. 3.1 Introduction
 In this experiment, you will analyze the purity of your crude and recrystallized aspirin products using a method called thin layer chromatography (TLC). You will also determine the percent yield of your
In this experiment, you will analyze the purity of your crude and recrystallized aspirin products using a method called thin layer chromatography (TLC). You will also determine the percent yield of your
Title: Reagents Copy No: ## SOP No.: 3.13/3.1/S Effective Date: July 8, 2013 Location: ### Reagents
 QSM Approval: Reagents 1. Introduction Laboratory reagents are used in all procedural steps during the course of sample preparation. To ensure that reagents are of known quality and purity and free of
QSM Approval: Reagents 1. Introduction Laboratory reagents are used in all procedural steps during the course of sample preparation. To ensure that reagents are of known quality and purity and free of
I. INTRODUCTION I ITEMS:
 Experiment 4 Chem 110 Lab LABORATORY TECHNIQUES PURPOSE: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to develop safe laboratory skill and practice several laboratory techniques that will be used in many
Experiment 4 Chem 110 Lab LABORATORY TECHNIQUES PURPOSE: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to develop safe laboratory skill and practice several laboratory techniques that will be used in many
FED. TEST METHOD STD. 191A AND SHALL BE RETAINED UNTIL SUCH CHANGE NOTICE 3 TIME AS THE STANDARD IS REVISED. January 15, 1986
 CHANGE NOTICES ARE NOT CUMULATIVE AND SHALL BE RETAINED UNTIL SUCH CHANGE NOTICE 3 TIME AS THE STANDARD IS REVISED. January 15, 1986 FEDERAL TEST METHOD STANDARD TEXTILE TEST METHODS The following changes,
CHANGE NOTICES ARE NOT CUMULATIVE AND SHALL BE RETAINED UNTIL SUCH CHANGE NOTICE 3 TIME AS THE STANDARD IS REVISED. January 15, 1986 FEDERAL TEST METHOD STANDARD TEXTILE TEST METHODS The following changes,
Wine, Dry Red Recipe for 20 gallons, SteveG revised 2016-Sep-1
 Wine, Dry Red Recipe for 20 gallons, SteveG revised 2016-Sep-1 This recipe is for using 3 boxes of juice (called WineKit on Amazon.com). Each box of juice produce ~6+ gallons of wine. This recipe will
Wine, Dry Red Recipe for 20 gallons, SteveG revised 2016-Sep-1 This recipe is for using 3 boxes of juice (called WineKit on Amazon.com). Each box of juice produce ~6+ gallons of wine. This recipe will
In Vitro NER Assay. Auble Lab. Reagents:
 In Vitro NER Assay Reagents: Water YPD Yeast extraction Buffer (200 ml): 0.2 M Tris-acetate (ph 7.5) (40 ml), 0.39 M (NH 4 ) 2 S0 4 (78 ml), 10 mm MgSO 4 (2 ml), 20% Glycerol (40 ml), 1mM EDTA (ph8.0)
In Vitro NER Assay Reagents: Water YPD Yeast extraction Buffer (200 ml): 0.2 M Tris-acetate (ph 7.5) (40 ml), 0.39 M (NH 4 ) 2 S0 4 (78 ml), 10 mm MgSO 4 (2 ml), 20% Glycerol (40 ml), 1mM EDTA (ph8.0)
The grade 5 English science unit, Solutions, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This unit deals with how solids dissolve in liquids and what affects their dissolution. By studying the dissolution process and related factors, students develop an interest in and curiosity about solutions.
This unit deals with how solids dissolve in liquids and what affects their dissolution. By studying the dissolution process and related factors, students develop an interest in and curiosity about solutions.
General Supplies
 Compile your list and call us to place your order 505.883.0000 or email it to: yourfriends@victorshomebrew.com General Supplies Category Department Description Price General Additive Acid Blend 1lb 7.69
Compile your list and call us to place your order 505.883.0000 or email it to: yourfriends@victorshomebrew.com General Supplies Category Department Description Price General Additive Acid Blend 1lb 7.69
Experimental Procedure
 1 of 6 9/7/2018, 12:01 PM https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/foodsci_p013/cooking-food-science/chemistry-of-ice-cream-making (http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/foodsci_p013/cooking-food-science/chemistry-of-ice-cream-making)
1 of 6 9/7/2018, 12:01 PM https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/foodsci_p013/cooking-food-science/chemistry-of-ice-cream-making (http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/foodsci_p013/cooking-food-science/chemistry-of-ice-cream-making)
California State University Dominguez Hills Semester, 200X
 California State University Dominguez Hills Semester, 200X Chemistry 103L: Chemistry for the Citizens List of Experiments Orientation: Check-In and Safety Film Experiment #1: The Bunsen Burner Experiment
California State University Dominguez Hills Semester, 200X Chemistry 103L: Chemistry for the Citizens List of Experiments Orientation: Check-In and Safety Film Experiment #1: The Bunsen Burner Experiment
EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR AROMATIC AND CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS
 EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR AROMATIC AND CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS Juan. A. Ramirez, Bo Wang, Donell S. Frank, Thomas. J. McDonald, Rebecca Price, Susanne J. McDonald and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International./B&B
EXTRACTION OF SEDIMENTS FOR AROMATIC AND CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS Juan. A. Ramirez, Bo Wang, Donell S. Frank, Thomas. J. McDonald, Rebecca Price, Susanne J. McDonald and James M. Brooks TDI-Brooks International./B&B
Coffee-and-Cream Science Jim Nelson
 SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 5.11-1 Coffee-and-Cream Science Jim Nelson Topic Newton s law of cooling Time 1 hour! Safety Please click on the safety icon to view the safety precautions.
SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 5.11-1 Coffee-and-Cream Science Jim Nelson Topic Newton s law of cooling Time 1 hour! Safety Please click on the safety icon to view the safety precautions.
Setting up your fermentation
 Science in School Issue 24: Autumn 2012 1 Setting up your fermentation To carry out all the activities, each team of students will need about 200 ml of fermentation must, 200 ml of grape juice and about
Science in School Issue 24: Autumn 2012 1 Setting up your fermentation To carry out all the activities, each team of students will need about 200 ml of fermentation must, 200 ml of grape juice and about
The Separation of a Mixture into Pure Substances
 The Separation of a Mixture into Pure Substances The experiment is designed to familiarize you with some standard chemical techniques and to encourage careful work in separating and weighing chemicals.
The Separation of a Mixture into Pure Substances The experiment is designed to familiarize you with some standard chemical techniques and to encourage careful work in separating and weighing chemicals.
Acidity and Blending. The art of using Titratable Acidity as a tool for blending consistency
 Acidity and Blending The art of using Titratable Acidity as a tool for blending consistency An Acid is a Species having the tendency to lose a Proton. [H+] [H+] cation + [GLOB-] anion ph related benefits
Acidity and Blending The art of using Titratable Acidity as a tool for blending consistency An Acid is a Species having the tendency to lose a Proton. [H+] [H+] cation + [GLOB-] anion ph related benefits
C27 Chromatography. Collect: Column Mortar and pestle Dropper (229 mm) Capillary tube TLC plate Aluminum foil UV light
 C27 Chromatography (2017/04/24) Collect: Column Mortar and pestle Dropper (229 mm) Capillary tube TLC plate Aluminum foil UV light Prepare: Green leaves Beaker (30 100 ml) Erlenmeyer flask (50, 125 ml)
C27 Chromatography (2017/04/24) Collect: Column Mortar and pestle Dropper (229 mm) Capillary tube TLC plate Aluminum foil UV light Prepare: Green leaves Beaker (30 100 ml) Erlenmeyer flask (50, 125 ml)
1. What is made when a solute is dissolved in a solvent?
 A solution is made when a solute dissolves in a solvent. The solutions we will look at are those where a solid dissolves in a liquid. The solid is the solute and the liquid is the solvent. Solute + Solvent
A solution is made when a solute dissolves in a solvent. The solutions we will look at are those where a solid dissolves in a liquid. The solid is the solute and the liquid is the solvent. Solute + Solvent
E25 ISOLATION OF A BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUND The isolation of caffeine from tea leaves
 E25 ISLATI F A BILGICALLY ACTIVE CMPUD The isolation of caffeine from tea leaves ITRDUCTI The overwhelmin majority of bioloically active molecules are oranic compounds, e.. alcohol, salicylic acid and
E25 ISLATI F A BILGICALLY ACTIVE CMPUD The isolation of caffeine from tea leaves ITRDUCTI The overwhelmin majority of bioloically active molecules are oranic compounds, e.. alcohol, salicylic acid and
Smart Valve Cold Brew Coffee Maker { Instruction Manual
 Smart Valve Cold Brew Coffee Maker { Instruction Manual Table of Contents Important Safeguards... 2 Glass Decanter Safety Precautions... 3 Getting to Know Your Cold Brew Coffee Maker... 4 Easy-Grab Tab
Smart Valve Cold Brew Coffee Maker { Instruction Manual Table of Contents Important Safeguards... 2 Glass Decanter Safety Precautions... 3 Getting to Know Your Cold Brew Coffee Maker... 4 Easy-Grab Tab
EXPERIMENT NO. 3 HYDROMETER ANALYSIS ASTM D-422
 EXPERIMENT NO. 3 HYDROMETER ANALYSIS ASTM D-422 1. AIM To determine grain size distribution of soil, which contains appreciable quantity of soil passing ASTM 200 sieve ( 0.075 mm). 2. APPARATUS: Standard
EXPERIMENT NO. 3 HYDROMETER ANALYSIS ASTM D-422 1. AIM To determine grain size distribution of soil, which contains appreciable quantity of soil passing ASTM 200 sieve ( 0.075 mm). 2. APPARATUS: Standard
DNA extraction method as per QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Germany)
 APPENDIX 3 (MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES) 3.2.2a) DNA extraction method as per QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Germany) Two hundred microliters (200 µl) of the EDTA blood was added to 200 µl of Buffer AL and 20 µl
APPENDIX 3 (MOLECULAR TECHNIQUES) 3.2.2a) DNA extraction method as per QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Germany) Two hundred microliters (200 µl) of the EDTA blood was added to 200 µl of Buffer AL and 20 µl
5KEK1322 W A_v08.indd 1 5/13/16 2:25 PM
 5KEK1322 W10878653A_v08.indd 1 PARTS AND FEATURES PARTS AND ACCESSORIES Tea steeper lid (center section of lid with handle) Kettle lid (outer section) Stainless steel lime scale filter Removable stainless
5KEK1322 W10878653A_v08.indd 1 PARTS AND FEATURES PARTS AND ACCESSORIES Tea steeper lid (center section of lid with handle) Kettle lid (outer section) Stainless steel lime scale filter Removable stainless
The fermentation of glucose can be described by the following equation: C6H12O6 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 CO2 + energy glucose ethanol carbon dioxide.
 SUGAR FERMENTATION IN YEAST with LQ LAB 12 B From Biology with Vernier INTRODUCTION Westminster College Yeast are able to metabolize some foods, but not others. In order for an organism to make use of
SUGAR FERMENTATION IN YEAST with LQ LAB 12 B From Biology with Vernier INTRODUCTION Westminster College Yeast are able to metabolize some foods, but not others. In order for an organism to make use of
Respirometer Release: 2.1 [minor] Respirometer. A classic acid-base indicator can also be used as a simply made respirometer
![Respirometer Release: 2.1 [minor] Respirometer. A classic acid-base indicator can also be used as a simply made respirometer Respirometer Release: 2.1 [minor] Respirometer. A classic acid-base indicator can also be used as a simply made respirometer](/thumbs/90/101630946.jpg) Respirometer A classic acid-base indicator can also be used as a simply made respirometer Written By: Vishal Bhatt 2018 Page 1 of 13 INTRODUCTION Chemical reactions often create a change in colour. Here,
Respirometer A classic acid-base indicator can also be used as a simply made respirometer Written By: Vishal Bhatt 2018 Page 1 of 13 INTRODUCTION Chemical reactions often create a change in colour. Here,
FAT, TOTAL (Hydrolysis)
 FATTO.01-1 FAT, TOTAL (Hydrolysis) PRINCIPLE The major portions of the native fats in corn starch are bound in a manner as to render them unextractable by the usual methods of solvent extraction. When
FATTO.01-1 FAT, TOTAL (Hydrolysis) PRINCIPLE The major portions of the native fats in corn starch are bound in a manner as to render them unextractable by the usual methods of solvent extraction. When
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION The Growth of a Population of Yeast "The elephant is reckoned the slowest breeder of all known animals, and I have taken some pains to estimate its probable minimum rate of natural
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION The Growth of a Population of Yeast "The elephant is reckoned the slowest breeder of all known animals, and I have taken some pains to estimate its probable minimum rate of natural
PART I CENTRIFUGE EXTRACTION METHOD USING CHLORINATED SOLVENT
 Test Procedure for DETERMINING ASPHALT CONTENT OF BITUMINOUS MIXTURES BY TxDOT Designation: Tex-210-F Effective Dates: April 2008 October 2016. 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this test method to determine, by four cold
Test Procedure for DETERMINING ASPHALT CONTENT OF BITUMINOUS MIXTURES BY TxDOT Designation: Tex-210-F Effective Dates: April 2008 October 2016. 1. SCOPE 1.1 Use this test method to determine, by four cold
HI Formol Number Mini Titrator for Wine and Fruit Juice Analysis
 HI 84533 Formol Number Mini Titrator for Wine and Fruit Juice Analysis Piston Driven Pump with Dynamic Dosing The HI 84533 incorporates dynamic dosing to provide precison titrant delivery. Dynamic dosing
HI 84533 Formol Number Mini Titrator for Wine and Fruit Juice Analysis Piston Driven Pump with Dynamic Dosing The HI 84533 incorporates dynamic dosing to provide precison titrant delivery. Dynamic dosing
Pricelist "Beer" 2018 valid from
 2500 BREWERY-SACCHARIMETER 0-5%MA 27,20 2501 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 5-10%M 27,20 2502 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 10-15% 27,20 2503 BREWERY-SACCHARIMETER 15-20% 27,20 2504 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 20-25% 27,20 2510
2500 BREWERY-SACCHARIMETER 0-5%MA 27,20 2501 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 5-10%M 27,20 2502 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 10-15% 27,20 2503 BREWERY-SACCHARIMETER 15-20% 27,20 2504 BREWERY SACCHARIMETER 20-25% 27,20 2510
Experiment 2: ANALYSIS FOR PERCENT WATER IN POPCORN
 Experiment 2: ANALYSIS FOR PERCENT WATER IN POPCORN Purpose: The purpose is to determine and compare the mass percent of water and percent of duds in two brands of popcorn. Introduction: When popcorn kernels
Experiment 2: ANALYSIS FOR PERCENT WATER IN POPCORN Purpose: The purpose is to determine and compare the mass percent of water and percent of duds in two brands of popcorn. Introduction: When popcorn kernels
Investigating solutions
 Investigating solutions Part A: saturated solutions Sugar dissolved in water is an important component of soft drinks. You are going to investigate just how much sugar can be dissolved in water. sugar
Investigating solutions Part A: saturated solutions Sugar dissolved in water is an important component of soft drinks. You are going to investigate just how much sugar can be dissolved in water. sugar
Solubility Lab Packet
 Solubility Lab Packet **This packet was created using information gathered from the American Chemical Society s Investigation #4: Dissolving Solids, Liquids, and Gases (2007). It is intended to be used
Solubility Lab Packet **This packet was created using information gathered from the American Chemical Society s Investigation #4: Dissolving Solids, Liquids, and Gases (2007). It is intended to be used
Acidity and ph Analysis
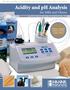 Broad supplier of analytical instruments for the dairy industry. Acidity and Analysis for Milk and Cheese HI 84429 Titratable Acids mini Titrator and Meter Perform a Complete Analysis with One Compact
Broad supplier of analytical instruments for the dairy industry. Acidity and Analysis for Milk and Cheese HI 84429 Titratable Acids mini Titrator and Meter Perform a Complete Analysis with One Compact
Determination of Alcohol Content of Wine by Distillation followed by Density Determination by Hydrometry
 Sirromet Wines Pty Ltd 850-938 Mount Cotton Rd Mount Cotton Queensland Australia 4165 www.sirromet.com Courtesy of Jessica Ferguson Assistant Winemaker & Chemist Downloaded from seniorchem.com/eei.html
Sirromet Wines Pty Ltd 850-938 Mount Cotton Rd Mount Cotton Queensland Australia 4165 www.sirromet.com Courtesy of Jessica Ferguson Assistant Winemaker & Chemist Downloaded from seniorchem.com/eei.html
Separations. Objective. Background. Date Lab Time Name
 Objective Separations Techniques of separating mixtures will be illustrated using chromatographic methods. The natural pigments found in spinach leaves, β-carotene and chlorophyll, will be separated using
Objective Separations Techniques of separating mixtures will be illustrated using chromatographic methods. The natural pigments found in spinach leaves, β-carotene and chlorophyll, will be separated using
Roast Beef Jan. 1, 2009
 Operation Procedures Manual Production Levels Roast Beef INT OPM 1434 Roast Beef Jan. 1, 2009 Prepare only enough product for the day s sales. Use WC-326-R Daily Prep Chart or the Manager-On-Duty should
Operation Procedures Manual Production Levels Roast Beef INT OPM 1434 Roast Beef Jan. 1, 2009 Prepare only enough product for the day s sales. Use WC-326-R Daily Prep Chart or the Manager-On-Duty should
Unit Test: Nature of Science
 Unit Test: Nature of Science Some questions (c) 2015 by TEKS Resource System. Some questions (c) 2015 by Region 10 Educational Service enter. Page 2 1 Students who participated in a frog dissection investigation
Unit Test: Nature of Science Some questions (c) 2015 by TEKS Resource System. Some questions (c) 2015 by Region 10 Educational Service enter. Page 2 1 Students who participated in a frog dissection investigation
Specific Heat of a Metal
 Specific Heat of a Metal Introduction: When we wish to determine the amount of heat gained or lost during a process, we use a calorimeter (literally, a calorie counter) in which a thermometer or temperature
Specific Heat of a Metal Introduction: When we wish to determine the amount of heat gained or lost during a process, we use a calorimeter (literally, a calorie counter) in which a thermometer or temperature
phd Pitcher UltraWater Owner s Manual Delicious Great Tasting Antioxidant Alkaline Energized
 Owner s Manual UltraWater phd Pitcher Delicious Great Tasting Antioxidant Alkaline Energized READ ME FIRST! 1. Be sure to flush your UltraWater filter before using the first time. (See Instructions for
Owner s Manual UltraWater phd Pitcher Delicious Great Tasting Antioxidant Alkaline Energized READ ME FIRST! 1. Be sure to flush your UltraWater filter before using the first time. (See Instructions for
Caffeine in Energy Drinks
 Page 1 of 7 (Too Much??) Learning Objectives: Caffeine in Energy Drinks Preparation of energy drink sample for testing Separation of caffeine from other components in energy drinks using HPLC (high performance
Page 1 of 7 (Too Much??) Learning Objectives: Caffeine in Energy Drinks Preparation of energy drink sample for testing Separation of caffeine from other components in energy drinks using HPLC (high performance
Maxiprep - Alkaline Lysis
 Maxiprep - Alkaline Lysis by A. Untergasser (contact address and download at www.untergasser.de/lab) Version: 1.0 - Print Version (.PDF) ATTENTION: This is a low priced protocol. Use it preferably! 1.
Maxiprep - Alkaline Lysis by A. Untergasser (contact address and download at www.untergasser.de/lab) Version: 1.0 - Print Version (.PDF) ATTENTION: This is a low priced protocol. Use it preferably! 1.
Measure the specific heat of lead. Identify an unknown metal from its specific heat (optional),
 Text reference: Sections 10.2, 10.3 On a sunny day, the water in a swimming pool may warm up a degree or two while the concrete around the pool may become too hot to walk on in your bare feet. This may
Text reference: Sections 10.2, 10.3 On a sunny day, the water in a swimming pool may warm up a degree or two while the concrete around the pool may become too hot to walk on in your bare feet. This may
Separation of a Mixture
 Separation of a Mixture The isolation of pure components of a mixture requires the separation of one component from another. Chemists have developed techniques for doing this. These methods take advantage
Separation of a Mixture The isolation of pure components of a mixture requires the separation of one component from another. Chemists have developed techniques for doing this. These methods take advantage
EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT
 EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT Inordertopromotepubliceducationandpublicsafety,equal justiceforal,abeterinformedcitizenry,theruleoflaw,world tradeandworldpeace,thislegaldocumentisherebymade availableonanoncommercialbasis,asitistherightofal
EDICT ± OF GOVERNMENT Inordertopromotepubliceducationandpublicsafety,equal justiceforal,abeterinformedcitizenry,theruleoflaw,world tradeandworldpeace,thislegaldocumentisherebymade availableonanoncommercialbasis,asitistherightofal
Introducing the Automated Fiber Analyzer
 Introducing the Automated Fiber Analyzer Performs Crude Fiber, ADF and NDF determinations Automatically adds required solutions and hot water rinses Batch Process up to 24 samples at one time Accurate
Introducing the Automated Fiber Analyzer Performs Crude Fiber, ADF and NDF determinations Automatically adds required solutions and hot water rinses Batch Process up to 24 samples at one time Accurate
In-Situ Hybridization with DIG-probes on paraffin sections
 Chuang Lab. Created on 2-26-01 by T Nay Kawcak. Updated: 3/5/01 In-Situ Hybridization with DIG-probes on paraffin sections A. Digoxigenin-labelled RNA probe: DdH 2 O 11.5 µl 10 Transcription Buffer 2.0
Chuang Lab. Created on 2-26-01 by T Nay Kawcak. Updated: 3/5/01 In-Situ Hybridization with DIG-probes on paraffin sections A. Digoxigenin-labelled RNA probe: DdH 2 O 11.5 µl 10 Transcription Buffer 2.0
COMBUSTIBLE DUST AWARENESS
 COMBUSTIBLE DUST AWARENESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject
COMBUSTIBLE DUST AWARENESS This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief description of the program and the subject
Paper Chromatography and Steam Distillation of Orange Oil EVERY STUDENT MUST BRING AN ORANGE TO LAB FOR THIS EXPERIMENT! Equipment
 Paper Chromatography and Steam Distillation of Orange Oil EVERY STUDENT MUST BRING AN ORANGE TO LAB FOR THIS EXPERIMENT! Equipment You will need a 600 ml beaker, a 50 ml graduated cylinder, 4 Expo Wet
Paper Chromatography and Steam Distillation of Orange Oil EVERY STUDENT MUST BRING AN ORANGE TO LAB FOR THIS EXPERIMENT! Equipment You will need a 600 ml beaker, a 50 ml graduated cylinder, 4 Expo Wet
Rapid Analysis of Soft Drinks Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System with the Waters Beverage Analysis Kit
 Rapid Analysis of Soft Drinks Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System with the Waters Beverage Analysis Kit Mark E. Benvenuti, Raymond Giska, and Jennifer A. Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA U.S.
Rapid Analysis of Soft Drinks Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System with the Waters Beverage Analysis Kit Mark E. Benvenuti, Raymond Giska, and Jennifer A. Burgess Waters Corporation, Milford, MA U.S.
INVITATION FOR QUOTATION. TEQIP-III/2018/mmug/Shopping/24
 INVITATION FOR QUOTATION TEQIP-III/2018/mmug/Shopping/24 04-July-2018 To, Sub: Invitation for Quotations for supply of Goods Dear Sir, 1. You are invited to submit your most competitive quotation for the
INVITATION FOR QUOTATION TEQIP-III/2018/mmug/Shopping/24 04-July-2018 To, Sub: Invitation for Quotations for supply of Goods Dear Sir, 1. You are invited to submit your most competitive quotation for the
Greenhouse Effect Investigating Global Warming
 Greenhouse Effect Investigating Global Warming OBJECTIVE Students will design three different environments, including a control group. They will identify which environment results in the greatest temperature
Greenhouse Effect Investigating Global Warming OBJECTIVE Students will design three different environments, including a control group. They will identify which environment results in the greatest temperature
Mathur Agar This medium is made up of the following reagents: dextrose, magnesium sulfate, potassium phosphate, neopeptone, yeast extract, and agar.
 Inoculum inoculation and media preparation of anthracnose, caused by Colletotrichum lindemuthuianum Halima E. Awale, Michigan State University, EL, MI 48824 Depending on the race of anthracnose you are
Inoculum inoculation and media preparation of anthracnose, caused by Colletotrichum lindemuthuianum Halima E. Awale, Michigan State University, EL, MI 48824 Depending on the race of anthracnose you are
ph and Color Change - Activity Sheet
 Name Date Period Page ph and Color Change - Activity Sheet Objective: 1. To be able to explain, on the molecular level, that is a measure of the in water and that adding an or a to water affects the concentration
Name Date Period Page ph and Color Change - Activity Sheet Objective: 1. To be able to explain, on the molecular level, that is a measure of the in water and that adding an or a to water affects the concentration
