Q.1) Define the following terms:-
|
|
|
- Madison Harris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q.1) Define the following terms:- 1) A la Catre :- In this style of menu each dish are priced separately. 2) Augratin :- A baked or grilled dish sprinkled with grated cheese or bread crums or both. 3) Baba :- Rich fermented sponge. It was popularized in Paris. Raisins are added to the recipe. 4) Bechamel:- It is one of the mother sauce created by Louis de Bechamel. 5) Bacon :- Boned pork usually the side or belly meat may be smoked or uncooked & cured with salt, sugar & spices. 6) Bain-Marie :- It is an equipment usually made of stainless steel with a small area to fill in water & to keep other containers on it so that the food could be kept warm. It is electrically operated. 7) Bouillon :- A clear soup stronger then broth but not as strong as consomme. Court bouillon is the cooking liquor for fish. 8) Bouquet garni: A bunch of herbs, usually bay leaves, thyme, marjoram and parsley tied together or enclosed in a muslin bag; if fresh bouquet garni is not available, use dried ones. This bunch is removed before serving a dish. 9) Brunoise: A garnish of diced vegetables; also any food cut or diced into small pieces. 10) Caviar: The prepared ripe eggs (ROE) of various species of sturgeon including beluga, osetra and sevruga. Colour ranges from black to white and from golden to orange brown. They are traditionally served in small dishes with a silver spoon accompanied by Melba toast, sour cream, lemon wedges 11) Croutons: small pieces of cubes of bread; fried or toasted. 12) Emulsion: An emulsion is formed from a mixture of two liquids that would normally repel each other (or are immiscible) but are kept together by a substance that is soluble in both. e.g., milk is an emulsion and it contains water and fat which are immiscible; but, both are kept together by the protein present in milk, since the protein can dissolve both in water and fat. 13) Fillet: A thin, tender boneless piece of meat or other foods; a boneless skinless side of a fish. Also spelled FILET. 14) Gluten: An elastic protein substance present in some cereal grains, chiefly wheat and corn. It stretches and absorbs water, giving support and lightness to dough. 15) Julienne: Foods cut into match stick size, thin strips. The term reportedly comes from a 17 th century chef named Julienne. 16) Knead: To manipulate or work dough by hand or machine, folding and pressing until air is incorporated and texture is smooth. 17) Roux: Equal quantity of Butter and refined flour heated and used as a thickener for gravies, sauces etc. It may be blond Roux or White Roux. 18) Biriyani: The most popular rice preparation which is steamed in dum style with the addition of spices and meat. They are slightly yellowish or light greenish in colour. 19) Do Pyazza: It means onions added twice (once ground and then fried) in to the meat curry. 20) Dum: A traditional, Mughalai way of cooking with slow steam to enhance all the goodness in cooking. E.g. : Biriyani and Dum alu. 21) Korma: Very rich thick red or, brown gravy out of Poppy seeds, coconut, spices, red chilly and cashew paste and curd. E.g.: chicken Korma, mutton korma. 22) Shammi Kebab: - Flattened lamb mince is added with ground spices, chopped coriander leaves and green chilies and then shallow fried. 23) Sheek Kebab: Minced lamb, herbs & spices with mashed potatoes are pressed in the skewer and roasted in a tandoor (Indian clay oven)
2 Q.2) write a note on Introduction to bakery & confectionery? A/s. Most of bakers products are made of the ingredients such as flour, sugar eggs, milk, stabilizers and leaveners. There are two departments in a bakery, namely the bake section & the pastry section. The Pastry Section Although pastry section is part of the kitchen and, under the supervision of the head chef or catering manager, it is considered to be a separate unit in a catering establishment. The main reasons for this are that specialist staff and equipment are required for it to work efficiently and to avoid contamination of sweet goods by the savory smells and flavors of the foods being prepared/stored in the kitchen and larder areas. The purpose of the pastry section is to prepare and serve all hot and cold sweet dishes, pastries, cakes, gateaux, petits fours, ice-cream dishes, confectionery and yeast goods. Often this includes breads and special customer requirements such as celebration cakes. The section has specialist facilities, equipment and staff, and will therefore liaise with the kitchen and larder sections on the production of savoury items; for example, pie coverings, vol-au-vents, sausage rolls, choux paste, cheese straws, fleurons, savoury flans and tartlets, pizzas and pastas. Pastes and other items will be supplied by the pastry section. In some cases they will be prepared and baked by them for completion and service in the main kitchen. Depending on the type of establishment, the section would provide food for lunch, dinner and supper menus, afternoon teas, buffets, banquets and possibly outdoor catering functions. If stewed fruits, croissants and brioche rolls are served at breakfast, these would also be prepared by the pastry section.
3 Q.3) What are the basic principles of bakery & also explain different measurement system used in Bakery? A/s Basic Principles: Most bakers products are made of the same few ingredients - flour, shortening agent, sugar, eggs, water or milk, and leavening agent. The accuracy is important in bakery, since slight variations in proportions or procedures can mean great differences in the final product. Formula: In case of cookery, the ratio of ingredients is called recipe. But here we call it a formula, since the proportion of mix has to be accurate. Measurement in the Metric system: There has always been confusion with the usage of measure; the U.S. System is not much in use in our Indian Bakeries and confectioneries. We use the metric system. In the metric system, there is one basic unit for each type of measurement. gram is the basic unit of weight litre is the basic unit of volume meter is the basic unit of length celsius is the basic unit of temperature. Metric Units Layman s conversion table:
4 1 ounce is approximately 30 ml decilitre is slightly less than 1 a cup centilitre is about 2 teaspoon tea spoon = 5 grams table spoon = 15 grams
5 Q.4) Write a note on various Baking process? A/s Baking process: The changes undergone by a dough or batter as it bakes are basically the same in all baked products, from bread to cookies. Following are the basic Baking process :-. Dough formation Wheat contains proteins called the glutenin and gliadin, which together form gluten, when wheat flour is moistened and mixed. Gluten also is a protein. When wheat flour is mixed with water and kneaded, it forms a sticky and elastic mass called the dough. Gluten is responsible for both the stickiness and the elasticity of the dough. At the time of grinding the grain into flour, gluten quality can be improved by the addition of small quantity of certain substances known as improvers. Gas Formation and leavening Leavening is the production or incorporation of gases into a baked product to increase volume and to produce shape and texture. These gases must be retained in the product until the structure is set. The gases primarily responsible for leavening baked goods are (i) carbon dioxide, which is released by the action of yeast, baking powder and baking soda, (ii) air, which is incorporated into dough and batters during mixing and (iii) steam or hot dry air, which is formed during baking. Acquiring the gases As the gases are formed, they expand and are trapped in a stretchable network formed by the proteins in the dough. The proteins are primarily gluten and, sometimes egg protein. Without gluten or egg protein, most of the gases would escape, and the product would be poorly leavened. Breads without enough gluten are heavy. Gelatinization The starches absorb moisture, expand, and become firmer. This contributes to structure. It begins to gelatinize (i.e., to form a soft some what elastic product like a fruit pulp) at about 65 0 C. Coagulation Like all proteins, gluten and egg proteins coagulate or solidify (i.e., the particles in the proteins gather together into a solid mass), when they reach high enough temperatures. This process gives most of the structure to baked goods. Coagulation begins at about 74 0 C. Correct baking temperature is very important. If it is too high, coagulation will start soon, even before the
6 expansion of gases has reached its peak. The resulting product will have poor volume or a split crust. If the temperature is too low, the proteins will not coagulate soon enough, and the product may collapse. Evaporation This takes place throughout the baking process. If a baked product of a specific weight is required, allowances must be made for moisture loss when scaling the dough. e.g., a loaf of 400 gram of baked bread shall need about 500 gram of dough. Shortening All fats are shortening agents. Films of fat get in between the layers of gluten in the flour and shorten or break the gluten thereby making the dough tender and flaky. On cooking, different shortening agents release trapped gases at different temperatures. The product when consumed melts in the mouth; e.g., biscuits. Proper shortening agent should be selected for each product. Browning A crust is formed as water evaporates from the surface and leaves it dry. Browning occurs when sugar caramelizes and, starch and sugar undergo certain chemical changes caused by heat. This contributes to flavour. Milk, sugar and egg increase browning. Staling Staling is the change in texture and aroma of baked goods due to a change of structure and a loss of moisture by the starch granules. Stale baked goods have lost their fresh baked aroma and are firmer, drier, and more crumbly than fresh products. Prevention of staling is major concern of the baker, because most baked goods loose quality rapidly. Staling begins almost as soon as the backed items are taken from the oven. There are apparently two factors for staling. The first is loss of moisture or drying. This is apparent, for example, when slices of fresh bread are left exposed to air. The bread becomes dry. The second factor is a chemical change in the starch structure. Bread should never be stored in a refrigerator; either it should be stored at room temperature for a short period or frozen for a long term storage.
7 Q.5) Name basic ingredients used in bakery? A/s The usual ingredients in Bakery are as follows: Wheat flour Starches Sugars Syrups Fats Shortenings Margarine Oil Lard Milk and cream Cheese Eggs Leavening Agents Nuts and fruits Chocolate and Cocoa Salt and spices
8 Q.6) Explain different types of Leavening Agent used in Bakery? A/s Yeast: Yeast is the leavening agent in breads, dinner rolls, Danish pastries, and similar products. Yeast causes fermentation of sugar into carbon dioxide gas and alcohol. This release of gas produces the leavening action in yeast products. The alcohol evaporates completely during and immediately after baking. Fermentable sugar in bread dough comes from two sources. It is added to the dough It is produced from flour by enzymes that breakdown the wheat starch into sugar. These enzymes are present in the flour and are added in the form of malt. Yeast is a microscopic plant that accomplishes this fermentation process by producing enzymes. Some of the enzymes change complex sugar (sucrose and maltose) into simple sugars (glucose and fructose). Others change the simple sugars into carbon dioxide gas and alcohol. Yeast is a living organism; it is sensitive to temperatures as shown below: At 1 0 C Yeast is inactive 15 0 C 20 0 C Yeast has slow action 20 0 C 32 0 C Best for growth of yeast 38 0 C Yeast reacts 60 0 C Yeast dies Yeast is available in two forms - compressed and active dry. Two chemicals used in bakery for releasing carbon dioxide. Baking Soda: Baking soda is the chemical, sodium bicarbonate. If moisture and an acid are present, baking soda releases carbon dioxide gas, which leavens the product. Heat is not necessary for the reaction.
9 Baking powder: Baking powders are mixtures of baking soda plus an acid to react with it. They also contain starch, which prevents lumping and brings the leavening power down to a standard level. The baking powder requires only moisture to be able to release gas. Like baking soda, baking powder can be used, only if the product is to be baked immediately after mixing.
10 Q.7) Describe the role of Fats & Oils in Bakery? A/s. Fats: There are many different varieties of fats available in the market. These fats have varying properties that make them suitable for different purposes. While selecting a fat for a specific use, a baker must consider the following properties; its melting point, it softness or hardness at different temperatures, its flavour and its ability to form emulsions. Earlier, under baking process, we mentioned regarding the ability of a fat to act as a shortening agent; films of fat get in between the layers of gluten in the flour and shorten or break the gluten thereby making the dough tender and flaky. We generally use the word shortening to mean any of a group of solid fats, usually white and tasteless, that have been especially formulated for baking. Shortenings may be made from vegetables oils (hydrogenated) and animal fats. There are two main types: Regular shortenings Emulsified shortenings Butter Any fresh butter consists of about 80% fat, 15% water and about 5% milk solids. Butter is available salted and unsalted. Unsalted butter is more perishable, it is hard when cold, very soft at room temperature and it melts easily. Butter is having high flavour when compared to the shortenings. Butter also has the melting qualities. Margarine: It is a butter substitute, cheaper than butter and less in cholesterol content. The flavour in margarine is less than that of Butter. It contains 80-85% fat, 10-15% moisture and 5% salt and milk solid. Usually this is made out of vegetable fat. Sometimes, animal fat is also used. Oil: It is liquid fat and used less for shortening. The main use of oil in the bakeshop is for greasing, deep frying, and as a wash for some kinds of Rolls. Lard: Lard is the rendered fat of pigs. Because of its plastic quality, it was once highly valued for making flaky pie crusts. Since the development of modern shortenings, however, it is not often used in the bakeshop.
11 Q.8) Write a note on milk & milk products? A/s Milk and Milk Products Milk and milk products are also highly utilized in bakery:- Types: Whole milk is fresh milk as it comes from the cow, with nothing removed and nothing added. Fresh whole milk is available in several forms. Pasteurized milk: Milk has been heated to kill bacteria at 72 o C for 15 seconds. Raw milk: Raw milk is that has not been pasteurized. It is not often used and, in fact, is generally not allowed to be sold. Homogenized milk: Homogenized milk is processed such that the cream does not separate out. This is done by forcing the milk through very tiny holes, which break up the fat into particles so small that they stay distributed in the milk. The above terms apply not only to the whole milk but also to skim and non - fat milk. Cream Various types of fresh cream, differing primarily in fat content, are available. Whipping Cream: Has fat content of 30-40%; within this category, you may find light whipping cream (30-35%) and heavy whipping cream (36-40%). Light Cream: It is also called table cream or coffee cream and contains 16 to 22% fat, usually about 18%. Half and Half: Has a fat content of 10-20%, too low for it to be called cream. You need to know about evaporated and condensed milk also.
12 Evaporated Milk: Milk, either whole or skim, is evaporated to remove about 60% of the water. It is then sterilized and canned. Evaporated milk has a somewhat cooked flavour. Condensed milk: Condensed milk is richer than evaporated milk, because more water has been removed. It can be sweetened or unsweetened. It is available canned and in bulk. Let us now study regarding fermented milk products. Fermentation means breakdown of an energy-rich compound like carbohydrate into simpler compounds using enzymes. Let us give two applications of fermentation in food preparation: (i) We shall study shortly how yogurt, a curd like food, is prepared from milk fermented by the action of bacteria, lactobacillus bacteria. (ii) Also, you will see the role of yeast, a living micro-organism as a leavening agent in breads based on its fermenting ability of sugars. Fermented Milk Products: Buttermilk: Buttermilk is fresh liquid milk, usually skim milk, which has been cultured or soured by bacteria. It is usually called cultured butter milk to distinguish it from the original buttermilk, which is the liquid left after butter making. Sour cream: Sour cream is cultured or fermented by adding lactic acid bacteria. This makes it thick and slightly tangy in flavour. It has about 18% fat. Yogurt: Yogurt is a curd like food and is prepared from milk fermented by the action of bacteria, lactobacillus bacteria. Various types of yogurts are prepared with varying amounts of fat, flavour and sweetness. Cheese Two types of cheese are used in the bakeshop, primarily in the production of cheese fillings and cheese cakes. Baker s cheese is a soft; un-aged cheese with a very low fat content. It is dry and pliable and can be kneaded somewhat like dough, generally available in packs. It can be frozen for longer time. Cream cheese is also soft cheese; un-aged, but has a high fat content, about 35%. It is mainly used in rich cheese cakes and in a few speciality products.
13 Q.9) Describe the role of sweeteners in bakery & confectionery? A/s Sugars Sugar occurs naturally in nearly all plant structures - fruits, leaves and stems; however sugar for general commercial use is obtained from two major sources, sugarcane and sugar beet. 60% of the world's supply of sugar is obtained from sugar cane and 40% from sugar beet. Cane contains approximately 18% sugar, while, beet contains approximately 15% sugar. Classification: Source - Beet and Cane Country - West Indies, Guyana, England, India. Catering uses - Specific types of sugar should be purchased for particular purposes. E.g.: Cube sugar would usually be purchased for table use to serve with tea and coffee; icing sugar would usually be purchased for dusting or royal icing. Chemical group Monosaccharide and Disaccharides Functions: To sweeten, cakes, pastries, sweet drinks etc. To act as preservative. To soften the gluten in flour and to make the baked product more tender to eat and lighter in texture. To colour the cooked product. e.g., the addition of sugar will assist bread and cakes having a good colour. Action of Heat on Sugar: 115ºc - Soft ball. Making of marzipan and fondant 121ºc - Hard ball. Making nougats, petit fours etc. 138ºc - Soft crack. Making Italian Meringue 143ºc - Pulled sugar. Making 01 baskets, ribbons, roses, bows, etc. 154ºc - Hard crack.
14 163 c - Caramel. Making for cream caramel. Sugars or sweetening agents have the following purposes in baking: To increase keeping qualities by retaining moisture. To give crust colour. To act as creaming agents with fats and as foaming agents. To tenderize and impart fineness of texture, partly by weakening the gluten structure. To make any dish sweeter and flavoured. Types of Sugars: Following are the variety of sugar used in bakery & confectionery:- Granulated Sugar: Very fine and ultra fine sugars are finer than regular granulated sugar. They are used for making cakes ad cookies, because they make a more uniform batter and can support higher quantities of fat. Sanding Sugar: These are coarser and are used for coating cookies, cakes, and other products. Coarse sugar, can be used in syrups, where its mixing properties are not a factor. Even a very coarse sugar will dissolve readily when boiled in water. Invert Sugar: When a sucrose solution is heated with an acid, cane sugar (sucrose) breaks down in to equal parts of two simple sugars, glucose and fructose. A mixture of glucose and fructose is called invert sugar. Invert sugar has two properties :- It holds moisture well and thereby helps to keep cakes fresh and moist. It resists crystallization Invert Sugar is produced commercially, and it is also present in honey.
15 Dehydrated Fondant: It is a soft creamy preparation of sugar, water, and glucose that is used as a basis for candies or icings. Recipe: Brown Sugar: Brown sugar is mostly sucrose (80-90%). It also contains varying amounts of caramel, molasses, and other impurities, which give flavour. Keep brown sugar in an air tight container to prevent it from drying out and hardening. Syrups: Few syrups used in bakery:- Molasses: It is concentrated sugar cane juice. It contains large amounts of sucrose and other sugars, including invert sugar. It also contains acids, moisture, and other constituents that give it its flavour and colour. Darker grades are stronger in flavour and contain less sugar than lighter grades. Molasses retains moisture in baked goods and therefore prolongs freshness. Malt Syrup: Malt is available in two forms. Dried malt extract is simply malt syrup that has been dried. It must be kept in an air tight container to keep it from absorbing moisture from the air. Malt flour is the dried, ground, malted (softened by steeping in water and allowed to germinate) barley that has not had the malt extracted from it. It is obviously a much less concentrated form of malt.
16 Q.10) What are the applications for enzymes in baking? A/s The Action of enzymes has been noted for as long as bread has been baked. The ancients attributed fermentation to a magical life force but today we understand it as a result of the way of enzymes change the make up of other ingredients. In breads it make the bread springy or some breads fresh for longer. They have application through out baking process, improving volume, texture & colour, making crumb soft & ensure the last long life of bread. Their unique modes of action not only reduce production cost & increase profit but also improve sustainability. Enzyme work same way as the catalyst. Enzyme has a structure which is called active site. Enzyme has optimum temperature at which they are most active. Below which there activity decrease and above also it donot work. In baking both yeast & sugar are used. Yeast cell contain enzymes that ferment sugar by an aerobic respiration producing Carbon dioxide which cause the dough to rise.
CAKES MAKING. Appearance: top crust slightly rounded pale golden brown.
 CAKES MAKING Cakes are excellent served with tea. They can also be served as a puddings / desserts. Cakes can contain fresh fruits, dried fruits and assorted nuts. Fancy cakes are made with glace icing,
CAKES MAKING Cakes are excellent served with tea. They can also be served as a puddings / desserts. Cakes can contain fresh fruits, dried fruits and assorted nuts. Fancy cakes are made with glace icing,
Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base
 CAKES Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base mixing methods. Understanding of recipe conversions
CAKES Perform various methods of scaling, baking and testing cakes. Understanding of the difference between Creaming, One Stage, 2 Stage, and Foam Base mixing methods. Understanding of recipe conversions
BINDING. Functional properties of food
 BINDING AERATION CARAMELISATION SHORTENING Functional properties of food COAGULATION HHYDROGENATION CRYSTALISATION DEXTRINISATION GELATINISATION FERMENTATION EMULSIFICATION To make successful products,
BINDING AERATION CARAMELISATION SHORTENING Functional properties of food COAGULATION HHYDROGENATION CRYSTALISATION DEXTRINISATION GELATINISATION FERMENTATION EMULSIFICATION To make successful products,
Functions of Raising Agents
 Objective Functions of Raising Agents To investigate how different types of raising agent (baking powder, baking soda, yeast) work. Principles Raising agents, also known as leavening agents, cause baked
Objective Functions of Raising Agents To investigate how different types of raising agent (baking powder, baking soda, yeast) work. Principles Raising agents, also known as leavening agents, cause baked
Foods 2: Unit Notebook. Page!1
 Page 1 Baking Basics: Ingredients Flour Flours- GLUTEN: All-Purpose-most common, moderate protein Whole-Wheat-makes products denser and heavier, mixed in = parts with AP Bread-high gluten, for making yeasty
Page 1 Baking Basics: Ingredients Flour Flours- GLUTEN: All-Purpose-most common, moderate protein Whole-Wheat-makes products denser and heavier, mixed in = parts with AP Bread-high gluten, for making yeasty
Milk and Dairy Food Lecture
 Milk and Dairy Food Lecture I. What is milk? A. 87% water B. 13% solids { fat and fat-soluble vitamins it contains and the solids not fat, include carbohydrates, protein, water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
Milk and Dairy Food Lecture I. What is milk? A. 87% water B. 13% solids { fat and fat-soluble vitamins it contains and the solids not fat, include carbohydrates, protein, water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
Coagulation of protein: fill in the missing words
 Activity: Coagulation of protein 4a 2.2.1 Proteins Coagulation of protein: fill in the missing words Denatured protein molecules are and take up more Chapter 4: Functional and chemical properties of food
Activity: Coagulation of protein 4a 2.2.1 Proteins Coagulation of protein: fill in the missing words Denatured protein molecules are and take up more Chapter 4: Functional and chemical properties of food
Dr.Nibras Nazar. Microbial Biomass Production: Bakers yeast
 Microbial biomass In a few instances the cells i.e. biomass of microbes, has industrial application as listed in Table 3. The prime example is the production of single cell proteins (SCP) which are in
Microbial biomass In a few instances the cells i.e. biomass of microbes, has industrial application as listed in Table 3. The prime example is the production of single cell proteins (SCP) which are in
Name: Date: Milk Products & Eggs Course 2060
 Name: Date: Milk Products & Eggs Course 2060 You must have credit for FOD 1010 Food Basics before starting this module. To receive credit for the course the following outcomes must be met: 1. Identify
Name: Date: Milk Products & Eggs Course 2060 You must have credit for FOD 1010 Food Basics before starting this module. To receive credit for the course the following outcomes must be met: 1. Identify
Factors affecting finished products
 Factors affecting finished products See separate word document on factors affecting finished product as shown on next slide Too little Less moist Product become stale quicker Less flavour and colour TOO
Factors affecting finished products See separate word document on factors affecting finished product as shown on next slide Too little Less moist Product become stale quicker Less flavour and colour TOO
A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION
 A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION Bake... To cook by dry heat in an oven, either covered or uncovered. Barbecue... To roast or cook slowly, basting with a highly
A. GENERAL INFORMATION No. 2 (1) DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN FOOD PREPARATION Bake... To cook by dry heat in an oven, either covered or uncovered. Barbecue... To roast or cook slowly, basting with a highly
HEALTH & FOOD TECHNOLOGY HIGHER FOOD PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT THE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES OF INGREDIENTS. Functional Properties of Ingredients
 HEALTH & FOOD TECHNOLOGY HIGHER FOOD PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT THE PROPERTIES OF INGREDIENTS ANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL HIGHER HEALTH & FOOD TECHNOLOGY Page 1 Page Aeration 3,4,5 Binding 3 Caramelisation 4 Coagulation
HEALTH & FOOD TECHNOLOGY HIGHER FOOD PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT THE PROPERTIES OF INGREDIENTS ANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL HIGHER HEALTH & FOOD TECHNOLOGY Page 1 Page Aeration 3,4,5 Binding 3 Caramelisation 4 Coagulation
Milk and Dairy Facts
 Milk and Dairy Facts What is milk? A. 87% water B. 13% solids {fat and fat-soluble vitamins it contains and the solids not fat, include carbohydrates, protein, water-soluble vitamins and minerals} Our
Milk and Dairy Facts What is milk? A. 87% water B. 13% solids {fat and fat-soluble vitamins it contains and the solids not fat, include carbohydrates, protein, water-soluble vitamins and minerals} Our
COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS
 Name: Due Date: COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics Description: Students further their skills in the handling of yeast dough through the preparation of a variety of yeast
Name: Due Date: COURSE FOD 3040: YEAST PRODUCTS Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics Description: Students further their skills in the handling of yeast dough through the preparation of a variety of yeast
Use a temperature probe, knife, skewer, finger or poke test, bite, visual colour check or sound to establish whether an ingredient or recipe is ready.
 SKILLS Weigh & measure Prepare ingredients & equipment Select and adjust cooking times Test for readiness Judge & modify sensory properties Accurate measurement of liquids & solids. Grease/oil, line, flour,
SKILLS Weigh & measure Prepare ingredients & equipment Select and adjust cooking times Test for readiness Judge & modify sensory properties Accurate measurement of liquids & solids. Grease/oil, line, flour,
Breads. Answer the following questions by using your Food for Today book. (Ch. 42 & 43)
 Breads Answer the following questions by using your Food for Today book. (Ch. 42 & 43) 1. What are the basic ingredients for baking? 2. The role of Gluten: Gluten develops when you mix with. It forms,
Breads Answer the following questions by using your Food for Today book. (Ch. 42 & 43) 1. What are the basic ingredients for baking? 2. The role of Gluten: Gluten develops when you mix with. It forms,
Yeast Breads. Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore!
 Yeast Breads Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore! Terminology Kneading: Process in which dough develops gluten to give the dough shape and structure. Gluten Protein that forms when flour and
Yeast Breads Terminology, Ingredients, & Procedures Galore! Terminology Kneading: Process in which dough develops gluten to give the dough shape and structure. Gluten Protein that forms when flour and
AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: shortening, sugar, eggs, water or milk, and leavenings you
 Basic Baking 5 Principles AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Explain the factors that control the development of gluten in baked products. 2. Explain the changes that take place in a
Basic Baking 5 Principles AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER, YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Explain the factors that control the development of gluten in baked products. 2. Explain the changes that take place in a
Nutrition 1 amino acids The chemical building blocks of proteins. 2 ascorbic acid Vitamin C 3 BMR Basal metabolism, or the rate of energy use by the
 C ULINARY ARTS Nutrition 1 amino acids The chemical building blocks of proteins. 2 ascorbic acid Vitamin C 3 BMR Basal metabolism, or the rate of energy use by the body for automatic processes. 4 calcium
C ULINARY ARTS Nutrition 1 amino acids The chemical building blocks of proteins. 2 ascorbic acid Vitamin C 3 BMR Basal metabolism, or the rate of energy use by the body for automatic processes. 4 calcium
The Story of Yeast. What Is Yeast?
 The Story of Yeast Yeast in History Man used yeast before he knew how to write. Hieroglyphics suggest that the ancient Egyptian civilizations were using living yeast and the process of fermentation to
The Story of Yeast Yeast in History Man used yeast before he knew how to write. Hieroglyphics suggest that the ancient Egyptian civilizations were using living yeast and the process of fermentation to
201-F & B Production & Bakery -I
 Jagannath Institute of Management Sciences Lajpat Nagar BBA.HMTCT-II-SEM 201-F & B Production & Bakery -I Unit-1 Culinary Terms Western Ala / al: In the style of A la carte: In the style of the menu (card),
Jagannath Institute of Management Sciences Lajpat Nagar BBA.HMTCT-II-SEM 201-F & B Production & Bakery -I Unit-1 Culinary Terms Western Ala / al: In the style of A la carte: In the style of the menu (card),
COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY
 Name: Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY Description: Students expand their knowledge and skills in the production of a variety of cake and pastry products. Outcomes:
Name: Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 2040: CAKE & PASTRY Description: Students expand their knowledge and skills in the production of a variety of cake and pastry products. Outcomes:
Table of Contents. Conversion Chart
 Breakfast: Breads: Bread Spreads: Salad Dressing and Dips: Salads: Muffins: Table of Contents Conversion Chart Raw Grain Muesli Granola Wheat Bread Nutty German Bread Dinner Rolls French Bread Raisin Bread
Breakfast: Breads: Bread Spreads: Salad Dressing and Dips: Salads: Muffins: Table of Contents Conversion Chart Raw Grain Muesli Granola Wheat Bread Nutty German Bread Dinner Rolls French Bread Raisin Bread
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL
 MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 3 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 FOOD PREPARTION This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. -- 2 -- SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 A 1.2 A 1.3 C
MARKING GUIDELINE NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 3 SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION 2010 FOOD PREPARTION This marking guideline consists of 8 pages. -- 2 -- SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 A 1.2 A 1.3 C
Identifying and Fixing Tortilla Problems. Steve Bright VP R&D, Quality Mesa Foods
 Identifying and Fixing Tortilla Problems Steve Bright VP R&D, Quality Mesa Foods Identifying Areas for Improvement No off flavor & aroma Microbial Stability Machinability 10 8 Pressability Stack height
Identifying and Fixing Tortilla Problems Steve Bright VP R&D, Quality Mesa Foods Identifying Areas for Improvement No off flavor & aroma Microbial Stability Machinability 10 8 Pressability Stack height
Bakeshop Formulas & Equipment
 Bakeshop Bakeshop Formulas & Equipment Formulas & Equipment Baking is an exact science that requires precise measuring and accuracy. Baking also requires the use of special baking equipment and small wares
Bakeshop Bakeshop Formulas & Equipment Formulas & Equipment Baking is an exact science that requires precise measuring and accuracy. Baking also requires the use of special baking equipment and small wares
Americans have enjoyed
 Cakes $1.50 Americans have enjoyed cakes for hundreds of years. Back in colonial days, the old recipes called for measurements like a lump of butter the size of a walnut or a dessert spoon full of sugar.
Cakes $1.50 Americans have enjoyed cakes for hundreds of years. Back in colonial days, the old recipes called for measurements like a lump of butter the size of a walnut or a dessert spoon full of sugar.
COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING
 Name: _Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING Description: Students learn about specialty cakes and pastry products by selecting and creating specialty cakes, pastries,
Name: _Due Date: Prerequisite: FOD1010: Food Basics COURSE FOD 3030: CREATIVE BAKING Description: Students learn about specialty cakes and pastry products by selecting and creating specialty cakes, pastries,
Bread Troubleshooting Guide
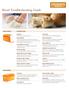 Holes in Bread weakens the dough and undermixing Dough forms a crust, trapping gas. Adjust proofer to proper humidity. Moulder Rollers in Poor Condition Trapped gas in dough causes holes. Check and repair
Holes in Bread weakens the dough and undermixing Dough forms a crust, trapping gas. Adjust proofer to proper humidity. Moulder Rollers in Poor Condition Trapped gas in dough causes holes. Check and repair
Honey. Bake It Up. Delicious home-baked treats sweetened with honey
 Honey. Bake It Up. Delicious home-baked treats sweetened with honey Home Baked and Better Who doesn t love the smell of bread baking in the oven? Or the rich fresh taste of home-baked cookies or scones?
Honey. Bake It Up. Delicious home-baked treats sweetened with honey Home Baked and Better Who doesn t love the smell of bread baking in the oven? Or the rich fresh taste of home-baked cookies or scones?
CHAPTER GELATIN. In this chapter you will learn to
 CHAPTER GELATIN In this chapter you will learn to Demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of gelatin: Types of gelatin available How to use gelatin Factors to ensure a successful product 1. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER GELATIN In this chapter you will learn to Demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of gelatin: Types of gelatin available How to use gelatin Factors to ensure a successful product 1. INTRODUCTION
FOOD SCIENCE GLUTEN FORMATION
 FOOD SCIENCE GLUTEN FORMATION 1. INTRODUCTION: It s not surprising that people have a difficult time understanding gluten, because it doesn t exist in nature. Gluten is a water-insoluble protein that is
FOOD SCIENCE GLUTEN FORMATION 1. INTRODUCTION: It s not surprising that people have a difficult time understanding gluten, because it doesn t exist in nature. Gluten is a water-insoluble protein that is
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FLOUR TORTILLAS
 Barcelona 2017 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FLOUR TORTILLAS By Steve Bright Tortilla Quality Evaluations Troubleshooting Tortillas Sticking Edges Shapes Staling Rollability / Foldability Mouthfeel Sticking Package
Barcelona 2017 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FLOUR TORTILLAS By Steve Bright Tortilla Quality Evaluations Troubleshooting Tortillas Sticking Edges Shapes Staling Rollability / Foldability Mouthfeel Sticking Package
Fruit Torte, page 972.
 Chapter 32 OD SERVICE INDUSTRY SANITATION AND SAFETY TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FOOD SCI CE MENUS RECIPES COST MANAGEMENT NUTRITION MISE EN PLACE STOCKS AND SAUCES SOUPS UNDER ANDING MEATS
Chapter 32 OD SERVICE INDUSTRY SANITATION AND SAFETY TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FOOD SCI CE MENUS RECIPES COST MANAGEMENT NUTRITION MISE EN PLACE STOCKS AND SAUCES SOUPS UNDER ANDING MEATS
Factors Affecting the Rising of Bread Dough - Ingredients
 Factors Affecting the Rising of Bread Dough - Ingredients Objective To study the effects of adding certain ingredients on the rising of bread dough. Principles* Yeast is a single-cell microbe that has
Factors Affecting the Rising of Bread Dough - Ingredients Objective To study the effects of adding certain ingredients on the rising of bread dough. Principles* Yeast is a single-cell microbe that has
Making flour mixtures
 Making flour mixtures Topics Flour and flour mixture Methods of raising flour mixture Mechanical air Physical steam Chemical carbon dioxide Functions of different ingredients Flour and flour mixture Flour
Making flour mixtures Topics Flour and flour mixture Methods of raising flour mixture Mechanical air Physical steam Chemical carbon dioxide Functions of different ingredients Flour and flour mixture Flour
Bread. Guided Inquiry Activity #27
 Bread Model 1: Wheat flour is ~70-80% starch and 7-15% protein. Surprisingly, it is that relatively small percentage of protein that makes it possible for wheat flour to turn into bread. Differences in
Bread Model 1: Wheat flour is ~70-80% starch and 7-15% protein. Surprisingly, it is that relatively small percentage of protein that makes it possible for wheat flour to turn into bread. Differences in
1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts
 Yeast Bread 1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts 2. What are the main ingredients in yeast bread and their functions. a. flour main ingredient, structure b.
Yeast Bread 1. What are the three categories of yeast breads? a. Rolls b. Loafs c. Doughnuts 2. What are the main ingredients in yeast bread and their functions. a. flour main ingredient, structure b.
Anaerobic Cell Respiration by Yeast
 25 Marks (I) Anaerobic Cell Respiration by Yeast BACKGROUND: Yeast are tiny single-celled (unicellular) fungi. The organisms in the Kingdom Fungi are not capable of making their own food. Fungi, like any
25 Marks (I) Anaerobic Cell Respiration by Yeast BACKGROUND: Yeast are tiny single-celled (unicellular) fungi. The organisms in the Kingdom Fungi are not capable of making their own food. Fungi, like any
Make Biscuits By Hand
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Biscuits By Hand Description In this activity, students will make and bake a batch of scones from scratch. The students will be able to identify the different stages of
Youth Explore Trades Skills Make Biscuits By Hand Description In this activity, students will make and bake a batch of scones from scratch. The students will be able to identify the different stages of
Los Angeles Mission College Culinary Fundamentals I 101 Fall-14 Mid-Term Exam
 1. Which of the following is not connective tissue? a. elastin b. collagen c. silverskin d. subcutaneous fat 2. What should you consider when purchasing meats? a. menu needs b. storage facilities c. staff
1. Which of the following is not connective tissue? a. elastin b. collagen c. silverskin d. subcutaneous fat 2. What should you consider when purchasing meats? a. menu needs b. storage facilities c. staff
Consumer and Family Sciences
 Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-145-W Substitutions and s in Food Ingredients Original author: Jean Howe, Extension Specialist, Foods and Nutrition*
Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-145-W Substitutions and s in Food Ingredients Original author: Jean Howe, Extension Specialist, Foods and Nutrition*
Ingredient Substitutions
 Page 1 of 13 Ingredient Substitutions HE-198, (Reviewed and Reprinted) July 1999 Julie Garden-Robinson, Food and Nutrition Specialist Have you ever been all set to prepare a food and suddenly discovered
Page 1 of 13 Ingredient Substitutions HE-198, (Reviewed and Reprinted) July 1999 Julie Garden-Robinson, Food and Nutrition Specialist Have you ever been all set to prepare a food and suddenly discovered
Module 2: Role of ingredients in baked products manufacture- i) wheat flour, flour improvers and water.
 Paper No. 09 Paper Title: Bakery and Confectionery Products Module 2: Role of ingredients in baked products manufacture- i) wheat flour, flour improvers and water. The different baking ingredients can
Paper No. 09 Paper Title: Bakery and Confectionery Products Module 2: Role of ingredients in baked products manufacture- i) wheat flour, flour improvers and water. The different baking ingredients can
Common Substitutions page 1
 page 1 Allspice, 1 teaspoon ground Apple juice Arrowroot starch, 1 teaspoon Baking mix, 1 cup Baking powder, Beer, 1 cup Brandy, 1 / 4 cup Bread crumbs, 1 cup Broth (beef or chicken) Brown sugar, 1 cup
page 1 Allspice, 1 teaspoon ground Apple juice Arrowroot starch, 1 teaspoon Baking mix, 1 cup Baking powder, Beer, 1 cup Brandy, 1 / 4 cup Bread crumbs, 1 cup Broth (beef or chicken) Brown sugar, 1 cup
100% WHOLE WHEAT BREAD MARY S WHOLE WHEAT BREAD
 8 to 8 ½ cups whole wheat flour 2 pkgs. yeast (4 ½ tsp.) 2 ½ tsp. salt 1 ½ cups water 1 ½ cups milk ¼ cup honey ¼ cup vegetable oil 100% WHOLE WHEAT BREAD In a large bowl combine 3 ½ cups flour, yeast,
8 to 8 ½ cups whole wheat flour 2 pkgs. yeast (4 ½ tsp.) 2 ½ tsp. salt 1 ½ cups water 1 ½ cups milk ¼ cup honey ¼ cup vegetable oil 100% WHOLE WHEAT BREAD In a large bowl combine 3 ½ cups flour, yeast,
contents 165 Custards and Puddings 8 Introduction 193 Frozen Desserts 35 Yeast Breads 215 Pastries 67 Quick Breads 239 Chocolates and Confections
 contents 8 Introduction 10 ABOUT BAKING 12 INGREDIENTS AND THEIR ROLES 21 TYPES OF EQUIPMENT 29 SAFETY 29 MIXING METHODS 35 Yeast Breads 38 TECHNIQUES 44 RECIPES 67 Quick Breads 69 TECHNIQUES 72 RECIPES
contents 8 Introduction 10 ABOUT BAKING 12 INGREDIENTS AND THEIR ROLES 21 TYPES OF EQUIPMENT 29 SAFETY 29 MIXING METHODS 35 Yeast Breads 38 TECHNIQUES 44 RECIPES 67 Quick Breads 69 TECHNIQUES 72 RECIPES
Technology of Baking
 Technology of Baking Assoc. Prof. Marie Hrušková, PhD Assoc. Prof. Marie Hrušková, PhD 30.9.2010 VŠCHT TechPek Příhoda-engl 1 Technology of Baking Flour main raw material for cereal food For yeast leavened
Technology of Baking Assoc. Prof. Marie Hrušková, PhD Assoc. Prof. Marie Hrušková, PhD 30.9.2010 VŠCHT TechPek Příhoda-engl 1 Technology of Baking Flour main raw material for cereal food For yeast leavened
Common Ingredient Substitutions. 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon, 1/4 teaspoon ginger, and 1/4 teaspoon cloves 1 tablespoon flour, OR 1 teaspoon cornstarch
 Common Ingredient Substitutions Out of baking powder? Make your own with our substitutions guide. Ingredient Amount Substitution Allspice Arrowroot starch 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon, 1/4 teaspoon ginger, and
Common Ingredient Substitutions Out of baking powder? Make your own with our substitutions guide. Ingredient Amount Substitution Allspice Arrowroot starch 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon, 1/4 teaspoon ginger, and
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT. Test Code: 4110 Version: 01
 JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT Test Code: 4110 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
JOB READY ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT RETAIL COMMERCIAL BAKING - PILOT Test Code: 4110 Version: 01 Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety and Sanitation Identify causes and prevention
QWIK-FLO SUGARS.
 www.asr-group.com 1 INTRODUCING QWIK-FLO Produced by our unique co-crystallisation process, Qwik-Flo Sugars are ASR Group s answer to many problems faced by food manufacturers. Providing solutions for
www.asr-group.com 1 INTRODUCING QWIK-FLO Produced by our unique co-crystallisation process, Qwik-Flo Sugars are ASR Group s answer to many problems faced by food manufacturers. Providing solutions for
Minestrone Soup. Method: Recipe: 1. In a large saucepan heat the oil and saute the onion, carrot, celery until they begin to colour.
 Minestrone Soup ½ can chopped tomatoes ½ onion ½ carrot ½ stick of celery ½ potato 25g French beans 250 ml stock Salt & pepper 1T pasta 1. In a large saucepan heat the oil and saute the onion, carrot,
Minestrone Soup ½ can chopped tomatoes ½ onion ½ carrot ½ stick of celery ½ potato 25g French beans 250 ml stock Salt & pepper 1T pasta 1. In a large saucepan heat the oil and saute the onion, carrot,
1. Milk that has been heat treated to kill disease-causing organisms is called a. certified. b. homogenized. c. pasteurized. d. fortified.
 Sample Test Questions Chapter 25: Dairy and Beverages Multiple Choice 1. Milk that has been heat treated to kill disease-causing organisms is called a. certified. b. homogenized. c. pasteurized. d. fortified.
Sample Test Questions Chapter 25: Dairy and Beverages Multiple Choice 1. Milk that has been heat treated to kill disease-causing organisms is called a. certified. b. homogenized. c. pasteurized. d. fortified.
McDonald s Australia McCafe Allergen - Ingredients - Nutrition Information
 McDonald s Australia McCafe Allergen - Ingredients - Nutrition Information Information correct as at August 2017. At McDonald's we believe in the nutritional principals of balance, variety and moderation
McDonald s Australia McCafe Allergen - Ingredients - Nutrition Information Information correct as at August 2017. At McDonald's we believe in the nutritional principals of balance, variety and moderation
Sticking and mold control. TIA Tech 2017 Los Angeles, California Steve Bright
 Sticking and mold control TIA Tech 2017 Los Angeles, California Steve Bright Sticking Package Sticking Defined: Two or more tortillas that will not separate from each other without tearing or ripping after
Sticking and mold control TIA Tech 2017 Los Angeles, California Steve Bright Sticking Package Sticking Defined: Two or more tortillas that will not separate from each other without tearing or ripping after
Objective 5: Review the nutrients found in breads and incorporate guidelines from MyPlate.
 Objective 1: Identify and prepare yeast breads. a. Lean Dough, Enriched Dough b. Mixing Methods: Straight dough, Modified straight-dough, Sponge method Objective 2: Identify and discuss the different types
Objective 1: Identify and prepare yeast breads. a. Lean Dough, Enriched Dough b. Mixing Methods: Straight dough, Modified straight-dough, Sponge method Objective 2: Identify and discuss the different types
From Field to Table Cookbook
 From Field to Table Cookbook A special thank you to all our wonderful volunteers who knead, mix and fill the Museum with tantalizing smells of freshly baked breads. Reynolds-Alberta Museum celebrating
From Field to Table Cookbook A special thank you to all our wonderful volunteers who knead, mix and fill the Museum with tantalizing smells of freshly baked breads. Reynolds-Alberta Museum celebrating
Barry s Forgotten Recipes: Bread, Biscuit, Fritter, Muffin and Roll Recipes
 Barry s Forgotten Recipes: Bread, Biscuit, Fritter, Muffin and Roll Recipes Bread, Biscuit, Fritter, Muffin and Roll Recipes Recipe Sampling: 6 Barry s Forgotten Recipes INTRODUCTION Rediscover the smells
Barry s Forgotten Recipes: Bread, Biscuit, Fritter, Muffin and Roll Recipes Bread, Biscuit, Fritter, Muffin and Roll Recipes Recipe Sampling: 6 Barry s Forgotten Recipes INTRODUCTION Rediscover the smells
Okara can be dried by spreading fresh okara onto flat surfaces, and then drying in 120 C (250 F) oven, stirring every minutes or so until dry.
 1 The Basics About Okara Okara is the solid by-product from processing soybeans into soymilk. It resembles a pale damp corn meal. How damp depends on the degree of pressure used when pressing the liquid
1 The Basics About Okara Okara is the solid by-product from processing soybeans into soymilk. It resembles a pale damp corn meal. How damp depends on the degree of pressure used when pressing the liquid
RECIPES PLAIN RICE STEWED TOMATOES
 RECIPES PLAIN RICE Put rice into one of the pot and add the usual amount of water (double) this is usually one part rice to 2 parts of water, but adjust if you prefer your drier or wetter. STEWED TOMATOES
RECIPES PLAIN RICE Put rice into one of the pot and add the usual amount of water (double) this is usually one part rice to 2 parts of water, but adjust if you prefer your drier or wetter. STEWED TOMATOES
Make & Taste DAIRY. Lesson Activity. Butter (Grades 3-5) LESSON OVERVIEW: LESSON OBJECTIVES: LESSON MATERIALS NEEDED: ACADEMIC INTEGRATION
 Lesson Activity LESSON OVERVIEW: During this lesson, students will be introduced to both the history and science behind the process of turning heavy whipping cream (which comes from milk) into butter.
Lesson Activity LESSON OVERVIEW: During this lesson, students will be introduced to both the history and science behind the process of turning heavy whipping cream (which comes from milk) into butter.
Food Science and Technology Notes Extension Division Deportment of Food Science and Technology Virginia Polytechnic Institute Blacksburg, Virginia
 Food Science and Technology Notes Extension Division Deportment of Food Science and Technology Virginia Polytechnic Institute Blacksburg, Virginia RECIPES FOR ICE CREAM NFST-546-3 Unless otherwise specified,
Food Science and Technology Notes Extension Division Deportment of Food Science and Technology Virginia Polytechnic Institute Blacksburg, Virginia RECIPES FOR ICE CREAM NFST-546-3 Unless otherwise specified,
Morning Moo s Milk Alternatative
 Morning Moo s Milk Alternatative Regular Low Fat Milk Alternative Reconstituted, Morning Moo s Low Fat Milk Alternative performs like non-fat powdered milk with the real taste of milk. Morning Moo s is
Morning Moo s Milk Alternatative Regular Low Fat Milk Alternative Reconstituted, Morning Moo s Low Fat Milk Alternative performs like non-fat powdered milk with the real taste of milk. Morning Moo s is
Apple Brie Omelet. 2 eggs 2 tsp cream (or milk) salt & pepper, to taste 2 tbs brie cheese, diced
 Breakfast Apple Brie Omelet 1/2 apple, peeled, cored and thinly sliced 2 1/2 tbs butter, divided 2 eggs 2 tsp cream (or milk) salt & pepper, to taste 2 tbs brie cheese, diced Melt 1 tablespoon butter in
Breakfast Apple Brie Omelet 1/2 apple, peeled, cored and thinly sliced 2 1/2 tbs butter, divided 2 eggs 2 tsp cream (or milk) salt & pepper, to taste 2 tbs brie cheese, diced Melt 1 tablespoon butter in
COOKING WITH ENTERGY. Breads
 COOKING WITH ENTERGY Breads COOKING WITH ENTERGY BREADS BREAD BASICS TO FREEZE BREADS: Breads freeze better baked. Bakery bread should be over-wrapped. Thaw in about 1 hour at room temperature - leave
COOKING WITH ENTERGY Breads COOKING WITH ENTERGY BREADS BREAD BASICS TO FREEZE BREADS: Breads freeze better baked. Bakery bread should be over-wrapped. Thaw in about 1 hour at room temperature - leave
"UNLEAVENED"RECIPES" Unleavened Cinnamon-Pecan Crisps
 Unleavened Cinnamon-Pecan Crisps 1 cup sugar 1/2 cup butter, slightly melted 1 large egg, separated 1 cup all-purpose flour 2 teaspoons ground cinnamon 1/2 cup finely chopped pecans Cream sugar and butter.
Unleavened Cinnamon-Pecan Crisps 1 cup sugar 1/2 cup butter, slightly melted 1 large egg, separated 1 cup all-purpose flour 2 teaspoons ground cinnamon 1/2 cup finely chopped pecans Cream sugar and butter.
GUIDELINES - BAKING QUICK BREAD
 GUIDELINES - BAKING QUICK BREAD These are fruit and nut breads chemically leavened and baked in deep loaf pans. BEST RESULTS FOR FINISHED PRODUCT Time to Judge: when the product is completely cooled. Outside
GUIDELINES - BAKING QUICK BREAD These are fruit and nut breads chemically leavened and baked in deep loaf pans. BEST RESULTS FOR FINISHED PRODUCT Time to Judge: when the product is completely cooled. Outside
Ingredients Volume Ounces Decimal Grams
 helpful cooking weights and measures Flours... Unbleached AP Flour 1 cup 4 ¼ 4.25 120 Bread Flour 1 cup 4 ¼ 4.25 120 Durum Flour 1 cup 4 3/8 4.375 124 First Clear Flour 1 cup 3 ¾ 3.75 105 Italian-Style
helpful cooking weights and measures Flours... Unbleached AP Flour 1 cup 4 ¼ 4.25 120 Bread Flour 1 cup 4 ¼ 4.25 120 Durum Flour 1 cup 4 3/8 4.375 124 First Clear Flour 1 cup 3 ¾ 3.75 105 Italian-Style
Advanced Candymaking. County 4-H Project
 Advanced Candymaking County 4-H Project Advanced 4-H Candymaking Project Prerequisites Equipment 1. Minimum Age High School or above Candymaking is an old art which is based upon the scientific principles
Advanced Candymaking County 4-H Project Advanced 4-H Candymaking Project Prerequisites Equipment 1. Minimum Age High School or above Candymaking is an old art which is based upon the scientific principles
Correct Flour Is Magical!
 Eating it, is pleasurable. Making it, is Doable! Correct Flour Is Magical! ALL A PIZZA-LOVER NEEDS TO KNOW Free Guide 1 INDEX THE CHARACTERISTICS/PARAMETERS TO LOOK FOR... 3 1. TYPE OF FLOUR (OR ASH CONTENT)...
Eating it, is pleasurable. Making it, is Doable! Correct Flour Is Magical! ALL A PIZZA-LOVER NEEDS TO KNOW Free Guide 1 INDEX THE CHARACTERISTICS/PARAMETERS TO LOOK FOR... 3 1. TYPE OF FLOUR (OR ASH CONTENT)...
Breads GINGERBREAD. Recipe from Linda Bernheim used for AAUW Supper Club Scottish Dinner, October 1977.
 Breads GINGERBREAD... 1 IRISH SODA 'COT BREAD... 2 BEER BREAD... 2 CHRISTMAS BREAD... 2 BAKED DONUTS... 3 WHEATGERM ZUCCHINI BREAD... 4 ORANGE-BANANA NUT BREAD... 5 HOT CROSS BUNS... 5 7or 9 GRAIN BREAD...
Breads GINGERBREAD... 1 IRISH SODA 'COT BREAD... 2 BEER BREAD... 2 CHRISTMAS BREAD... 2 BAKED DONUTS... 3 WHEATGERM ZUCCHINI BREAD... 4 ORANGE-BANANA NUT BREAD... 5 HOT CROSS BUNS... 5 7or 9 GRAIN BREAD...
Boston University Presents. Iraq. With Nawal Nasrallah
 Boston University Presents Iraq With Nawal Nasrallah March 2004 Menu 1. Basic flat bread with 2 variations (bread with cheese and herbs, and bread with meat mixture). 2. Black-eyed peas salad. 3. Hummus
Boston University Presents Iraq With Nawal Nasrallah March 2004 Menu 1. Basic flat bread with 2 variations (bread with cheese and herbs, and bread with meat mixture). 2. Black-eyed peas salad. 3. Hummus
Yeast Breads are Easy to Make
 Yeast Breads are Easy to Make Item Type text; Book Authors Gibbs, June C. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 16/08/2018 11:12:03 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/312209
Yeast Breads are Easy to Make Item Type text; Book Authors Gibbs, June C. Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 16/08/2018 11:12:03 Link to Item http://hdl.handle.net/10150/312209
IMMACULATE CONCEPTION HIGH SCHOOL HOME ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT SYLLABUSES
 IMMACULATE CONCEPTION HIGH SCHOOL HOME ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT SYLLABUSES MISSION STATEMENT We, the members of the Home Economics Department at the Immaculate Conception High School, inspired by the teachings
IMMACULATE CONCEPTION HIGH SCHOOL HOME ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT SYLLABUSES MISSION STATEMENT We, the members of the Home Economics Department at the Immaculate Conception High School, inspired by the teachings
TO BAKING WITH PZ-44 & REDDI-SPONGE
 AGROPUR INGREDIENTS ingredients@agropur.c om WWW.AGROPURINGREDIENTS.COM THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO BAKING WITH PZ-44 & REDDI-SPONGE FOR MORE INFORMATION Please call us at 1-800-359-2345 if you have questions
AGROPUR INGREDIENTS ingredients@agropur.c om WWW.AGROPURINGREDIENTS.COM THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO BAKING WITH PZ-44 & REDDI-SPONGE FOR MORE INFORMATION Please call us at 1-800-359-2345 if you have questions
Why are grains an important part of healthful eating?
 Grains Why are grains an important part of healthful eating? They are an excellent sources of complex carbohydrates and fiber Combined with animal protein or legumes they provide highquality protein They
Grains Why are grains an important part of healthful eating? They are an excellent sources of complex carbohydrates and fiber Combined with animal protein or legumes they provide highquality protein They
Cake Troubleshooting Guide
 Coarse, Open Grain Oven Temperature Too Low Use correct temperature: 370 F-380 F (187 C-193 C). Mix less in first stage. Batter Temperature Too High Use ingredients at correct temperature: 68 F-72 F (20
Coarse, Open Grain Oven Temperature Too Low Use correct temperature: 370 F-380 F (187 C-193 C). Mix less in first stage. Batter Temperature Too High Use ingredients at correct temperature: 68 F-72 F (20
Section 3 Dough Management
 Section 3 Dough Management Dough is the foundation of our pizza. Dough is the least expensive part of the pizza. Never use dough that is not perfect. If the dough is not perfect, throw it out. Without
Section 3 Dough Management Dough is the foundation of our pizza. Dough is the least expensive part of the pizza. Never use dough that is not perfect. If the dough is not perfect, throw it out. Without
Life Skills: Cooking Name
 Life Skills: Cooking Name Keep this form in the student portfolio for each child. It may take a few years before every item is checked. Define: Develop safe, sanitary, and practical skills for basic food
Life Skills: Cooking Name Keep this form in the student portfolio for each child. It may take a few years before every item is checked. Define: Develop safe, sanitary, and practical skills for basic food
INVERTS AND TREACLE SYRUPS.
 www.asr-group.com 1 INTRODUCING CANE SUGAR INVERTS With their unique characteristics, Invert Sugars and Syrups, made from natural cane sugars, benefit many aspects of food production by naturally improving
www.asr-group.com 1 INTRODUCING CANE SUGAR INVERTS With their unique characteristics, Invert Sugars and Syrups, made from natural cane sugars, benefit many aspects of food production by naturally improving
Oregon Agricultural College
 College Bulletin No. 83. Extension Series 3. No. 2 Issued Monthly Entered as second-class matter November 27. 1909, at the postoffice at Corvallis, Oregon, under Act of July 16, 1894 Oregon Agricultural
College Bulletin No. 83. Extension Series 3. No. 2 Issued Monthly Entered as second-class matter November 27. 1909, at the postoffice at Corvallis, Oregon, under Act of July 16, 1894 Oregon Agricultural
Breads. Biscuits. Muffins
 Breads Bagels Banana Chocolate Chip Bread Braided Lemon Bread Cheesy Beer Bread Cinnamon Rolls Cinnamon Swirl Bread Corn Bread Focaccia Bread Honey of an Oat Bread Lemon Loaf Soft Giant Pretzels Steakhouse
Breads Bagels Banana Chocolate Chip Bread Braided Lemon Bread Cheesy Beer Bread Cinnamon Rolls Cinnamon Swirl Bread Corn Bread Focaccia Bread Honey of an Oat Bread Lemon Loaf Soft Giant Pretzels Steakhouse
CONCENTRATED MILK. Dairy Processing Technology 2012/2013
 CONCENTRATED MILK Dairy Processing Technology 2012/2013 Introduction Concentrated milks are liquid milk preserves with a considerably reduced water content. Water removal is done by evaporation. Two type
CONCENTRATED MILK Dairy Processing Technology 2012/2013 Introduction Concentrated milks are liquid milk preserves with a considerably reduced water content. Water removal is done by evaporation. Two type
BULGUR. versatility plus for... hifeakfast. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 BULGUR versatility plus for... hifeakfast \ lunches S A Pacific Northwest, Cooperative Extension Publication PNW Bulletin 58 Reprinted October 1964 li BULGUR RECIPES \ /O Wheat treat cereal 4 Western nugget
BULGUR versatility plus for... hifeakfast \ lunches S A Pacific Northwest, Cooperative Extension Publication PNW Bulletin 58 Reprinted October 1964 li BULGUR RECIPES \ /O Wheat treat cereal 4 Western nugget
Perform various methods of scaling, cooking, baking and testing custards. Understanding of the difference ratio of creme brulee.
 CUSTARDS Perform various methods of scaling, cooking, baking and testing custards. Understanding of the difference ratio of creme brulee. Understanding of recipe conversions and order of operations. Demonstrate
CUSTARDS Perform various methods of scaling, cooking, baking and testing custards. Understanding of the difference ratio of creme brulee. Understanding of recipe conversions and order of operations. Demonstrate
Fall for Honey. Presented by:
 Fall for Honey Presented by: Kimberly Concra, LDN Cape Cod Cooperative Extension Nutrition Education & Food Safety Program 508-375-6690 www.capecodextension.org H O N E Y Honey contains carbs, proteins,
Fall for Honey Presented by: Kimberly Concra, LDN Cape Cod Cooperative Extension Nutrition Education & Food Safety Program 508-375-6690 www.capecodextension.org H O N E Y Honey contains carbs, proteins,
Cookies. After reading this chapter, you should be able to
 34 Cookies The word cookie means small cake, and that s exactly what a cookie is. In fact, some cookies are made from cake batter. Some products, such as certain kinds of brownies, are difficult to classify
34 Cookies The word cookie means small cake, and that s exactly what a cookie is. In fact, some cookies are made from cake batter. Some products, such as certain kinds of brownies, are difficult to classify
EDIBLE PRODUCTS Annexure-I of SRO. 800 (I)/98 dated LIST OF EDIBLE PRODUCTS DESCRIPTION
 EDIBLE PRODUCTS Annexure-I of SRO. 800 (I)/98 dated 06.07.1998 LIST OF EDIBLE PRODUCTS S. NO: H. S. NO: DESCRIPTION 1. 03.03 Fish, frozen excluding fish fillets and other fish meat of heading No. 03.04.
EDIBLE PRODUCTS Annexure-I of SRO. 800 (I)/98 dated 06.07.1998 LIST OF EDIBLE PRODUCTS S. NO: H. S. NO: DESCRIPTION 1. 03.03 Fish, frozen excluding fish fillets and other fish meat of heading No. 03.04.
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMBER 2009 FOOD PREPARATION
 MRKING GUIELINE NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMER 2009 These marking guidelines consist of 9 pages including cover page. (MRKING GUIELINE) - 2 - NC1090(E)(N3)V SECTION QUESTION 1 1.1 1.2
MRKING GUIELINE NTIONL CERTIFICTE (VOCTIONL) NQF LEVEL 3 NOVEMER 2009 These marking guidelines consist of 9 pages including cover page. (MRKING GUIELINE) - 2 - NC1090(E)(N3)V SECTION QUESTION 1 1.1 1.2
RECETTES DE PETIT-DÉJEUNER FACILES (EASY BREAKFAST RECIPES)
 RECETTES DE PETIT-DÉJEUNER FACILES (EASY BREAKFAST RECIPES) Muffins 1 ¾ cups all-purpose flour ⅓ cup sugar 2 teaspoons baking powder ¼ teaspoon salt 1egg, beaten ¾ cup milk ¼ cup cooking oil 1. Preheat
RECETTES DE PETIT-DÉJEUNER FACILES (EASY BREAKFAST RECIPES) Muffins 1 ¾ cups all-purpose flour ⅓ cup sugar 2 teaspoons baking powder ¼ teaspoon salt 1egg, beaten ¾ cup milk ¼ cup cooking oil 1. Preheat
Bacon-Jalapeno Rangoon s with Sweet and Sour Sauce Sweet and Sour Sauce
 Bacon-Jalapeno Rangoon s with Sweet and Sour Sauce 3¼ LBS Cream Cheese- Room Temperature 6½ LBS Bacon, Medium Dice or Crumble 39 Each Jalapenos, Seeded & Small Diced 39 Each Scallions, Sliced Thin 1 ½
Bacon-Jalapeno Rangoon s with Sweet and Sour Sauce 3¼ LBS Cream Cheese- Room Temperature 6½ LBS Bacon, Medium Dice or Crumble 39 Each Jalapenos, Seeded & Small Diced 39 Each Scallions, Sliced Thin 1 ½
Cookie Basics. General Preparation Guidelines
 Cookie Basics General Preparation Guidelines. About 5 minutes before baking your first batch, preheat your oven to the temperature in the recipe. If using a convection oven, reduce the baking temperature
Cookie Basics General Preparation Guidelines. About 5 minutes before baking your first batch, preheat your oven to the temperature in the recipe. If using a convection oven, reduce the baking temperature
Mushroom cigars with coffee aioli
 Mushroom cigars with coffee aioli Makes 25 Pair with espresso coffee 50g butter 1/2 onion, finely chopped 1 garlic clove, crushed 15g fresh thyme leaves, chopped 250g field mushrooms, finely chopped in
Mushroom cigars with coffee aioli Makes 25 Pair with espresso coffee 50g butter 1/2 onion, finely chopped 1 garlic clove, crushed 15g fresh thyme leaves, chopped 250g field mushrooms, finely chopped in
Knowledge booklet- Chicken products
 YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
Breakfast. Lunch. Dinner. Blueberry Coffee Cake. Tuna Salad Wraps Simple Fruit Salad
 Breakfast Lunch Dinner Blueberry Coffee Cake Tuna Salad Wraps Simple Fruit Salad Soup: South-of-the-Border Soup Entrée: Basic Chicken Burritos Side Dishes: Spanish Rice Black Beans and Rice Dessert: Chocolate
Breakfast Lunch Dinner Blueberry Coffee Cake Tuna Salad Wraps Simple Fruit Salad Soup: South-of-the-Border Soup Entrée: Basic Chicken Burritos Side Dishes: Spanish Rice Black Beans and Rice Dessert: Chocolate
89 Sugar and starch production
 The German Patent Classification, Class 89 Page 1 89 Sugar and starch production 89a Washing, conveying and storage devices for beets and potatoes Comminution of sugar beets and sugar cane; treatment of
The German Patent Classification, Class 89 Page 1 89 Sugar and starch production 89a Washing, conveying and storage devices for beets and potatoes Comminution of sugar beets and sugar cane; treatment of
Healthy Christmas Holiday Recipe Book
 Healthy Christmas Holiday Recipe Book Christmas Breakfast Mini Mushroom and Sausage Quiches 8 ounces turkey breakfast sausage, removed from casing and crumbled into small pieces 1 teaspoon extra- virgin
Healthy Christmas Holiday Recipe Book Christmas Breakfast Mini Mushroom and Sausage Quiches 8 ounces turkey breakfast sausage, removed from casing and crumbled into small pieces 1 teaspoon extra- virgin
Cooking. with Apples. Sweet and Savoury Recipes for Fall
 Cooking with Apples Sweet and Savoury Recipes for Fall Table of Contents Apple Gingerbread...1 Apple Spice Muffin Cake...2 Apple Cake with Molasses Cider Glaze...3 Whole Wheat Applesauce Cake...4 Apple
Cooking with Apples Sweet and Savoury Recipes for Fall Table of Contents Apple Gingerbread...1 Apple Spice Muffin Cake...2 Apple Cake with Molasses Cider Glaze...3 Whole Wheat Applesauce Cake...4 Apple
Real Food Weekly July 28, 2012
 Shopping List Flavor Baby! July 28, 2012 Real Food Weekly July 28, 2012 Flavor Baby! Don t be afraid of the title of this week. We are just adding a little bit of extra and unique flavor to our meals by
Shopping List Flavor Baby! July 28, 2012 Real Food Weekly July 28, 2012 Flavor Baby! Don t be afraid of the title of this week. We are just adding a little bit of extra and unique flavor to our meals by
CONFECTIONERY. Bakers' Confectionery
 CONFECTIONERY Confectionery also called sweets or candy is sweet food product. Confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categories, Bakers' Confections and Sugar Confections. Confections
CONFECTIONERY Confectionery also called sweets or candy is sweet food product. Confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categories, Bakers' Confections and Sugar Confections. Confections
