Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae
|
|
|
- Felix Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 eissn: X Taeckholmia 38 (2018): Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Azza A. F. Khafagi 1, Abbas A. El- Ghamery 1, Omran N. Ghaly 2 and Osama G. Ragab 1* 1 Botany and Microbiology Department, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt 2 The Herbarium, Ecology and Ranges Department, Desert Research Center, Matariya, Egypt *Corresponding author: osama_gamal84@azhar.edu.eg Abstract The fruit and seed morphology of 24 species, representing seven genera of Solanaceae were investigated by using a binocular stereomicroscope and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), to determine the significance of fruit and seed coat features as taxonomic characters. Morphological characters, including color, texture, shape, fruit type, hilum position, anticlinal shape and periclinal shape. There were three major patterns of seed ornamentation: irregular reticulate, regular reticulate and verrucate reticulate. The dendrogram showed that species could be grouped into two major clusters, the first cluster (I) contains 15 species and divided into two groups, while the second cluster (II) contains nine species that can be divided into two groups. The data proved useful in the construction of a dichotomous indented key to the studied species. Twenty characters were used to create systematic Key using DELTA key-generating programs. The results indicate that the morphological characteristics of fruits and seeds would be helpful for the identification of Solanaceae species. Key words: Morphology, Seed, Fruit, SEM, Solanaceae Introduction The Solanaceae is one of the most important and large families of flowering plants. The family is widely distributed in a diversity range of ecological habitats in both tropical and temperate regions. It consists of about 98 genera and 2700 species (Olmstead and Bohs 2007). In Egypt Solanaceae is a wellrepresented family, about wild species belonging to eight genera according to (Tãckholm 1974 and Boulos 2002; 2009). Moreover (Hepper 1998) reported that the family is represented by 25 genera and about 91 species including cultivated species. The first systematic classification of the Solanaceae was proposed by (Dunal 1852) and consisted of a division of the 61 genera known at the time, into two tribes and 11 subtribes, while (Wettstein 1895) divided the Solanaceae into two series A and B which comprise three and two tribes respectively. Recently, Hunziker (2001) classified the family into 6 subfamilies and about 21 tribes. Several workers (Dachyshyn 1965, Srivastava 1969, Nha & Danert 1973, Dave et al., 1980, Symon 1979 & 1984, Chiarini & Barboza 2007 and Zhigila et al., 2014) described the morphological characters of fruit in some species of Solanaceae. Seed micro and macromorphology have been shown to provide useful characters for taxonomic relationship of plant families (Esau 1953, Mohana 1974, Corner 1976, Barthlott 1981 & 1984 and Shetler 1986). Recent studies on Solanaceae have shown that seed morphology characters are of considerable systematic significance, both at the generic and specific levels. Several previous studies have examined seed morphology of various members of some species of Solanaceae using both light and scanning electron microscopy. (Bahadur & Farooqui 1986, Axelius 1992; Zhang & Wen 1996 Hoare & Knapp 1997; Carvalho et al., 1999, Zhang & Lu 1999; Kong et al., 2011; Ghimire et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2005, Kaya et al., 2016 and Ahmed & Fadl 2016). The aim of the present study is to describe the diagnostic characters of fruit and seed of the studied species as important tools in the delimitation of clade within Solanaceae. Materials and Methods The present study included 24 species of Solanaceae belonging to two subfamilies and five tribes according to the classification of Hunziker (2001). The study was based on fresh materials collected from different Received on 10/07/2018 and accepted on 28/08/2018
2 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae localities in Egypt in addition to Herbarium specimens, in few cases, kept in Cairo University Herbarium (CAI) and the Herbarium of the Desert Research Center (CAIH). Specimens of studied taxa were prepared and kept in the herbarium of Botany and Microbiology Department, Faculty of Science (Boys branch) Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. Data of the collected materials are shown in Table 1. (N.B. specimens of S. sinaicum collected from cultivated specimen grown in Agricultural Museum). The collected materials were identified by means of comparison with specimens kept in different Herbaria. In addition, keys of Tãckholm (1974) and Boulos (2002) were also used. Fruit and seed details were examined with the aid of binocular stereo microscope under incident light and photographs. Also for the study of seed using SEM, three seed were mounted on metal stubs, coated, golden, examined and photographed by JEOL Scanning electron microscope at the accelerating voltage of 18kv, at the Electron Microscope at The Regional Center for Mycology and Biotechnology, Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. All the examined species were used as operational taxonomic units (OUT's). The 20 character states which resulted from morphological data were analyzed by means of Hierarchical Cluster analysis used distance and similarity measure Bray-Curtis Sorensen. The relationships between the studied species of Solanaceae have been demonstrated as dendrograms (Fig. 1-A and 1-B) by using statistical programs PC-ORD (Software, version 5) and Primer (Software, version 6.0). A total of 20 comparative morphological characters for studied species were scored and coded for creating data matrix used for numerical analysis. The relationships between the studied species have been demonstrated as generating Key by using the statistical program DELTA software of programs (Dallwitz 2010). 124 Results and Discussion 1. Fruit morphology Fruit is very variable in shape, type, texture, color, size and dehiscence (Table 2 and Plate 1). The fruit color varied from black in L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii and S. nigrum var. nigrum, black-red in L. europaeum, yellow-orange in S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium, S. forsskaolii and S. incanum, orange in L. shawii, P. peruviana, S. sinaicum and S. villosum subsp. villosum, grey in P. ixocarpa, bright red in W. somnifera, yellowish green in P. angulata, orange red in W. obtusifolia to brown in the rest. The fruit types of the studied species ranged between capsule in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. muticus, H. pusillus, N. glauca and N. rustica and berry in all the rest of the studied taxa. Fruit dehiscence by valves in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, N. glauca and N. rustica, circumscissile in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. muticus and H. pusillus and indehiscence in the rest. The shape of fruit ranged between globose in most studied species, spheroidal in D. innoxia, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium, S. forsskaolii, S.incanum, S. nigrum var. nigrum, S. sinaicum and S. villosum subsp. villosum, ovoid in D. stramonium, N. glauca and N. rustica and oblong in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. muticus and H. pusillus. The length of the fruits ranged between; cm. in most studied species and cm. in S. incanum while cm in D. innoxia and D. stramonium. On the other hand, the width recorded cm. in D. innoxia, D. stramonium and S. incanum while cm. in the remainders. The fruit included in opened calyx in all studied species of Hyoscyamus and Nicotiana, it was included in closed calyx in studied species of Physalis and Withania and exposed in the rest of the studied taxa. The texture of the fruit ranged between spiny in D. innoxia and D. stramonium, Glabrescent in S. elaeagnifolium, tuberculate in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. muticus and H. pusillus and glabrous in the remainders.
3 Khafagi et al. Table 1: List of the collected species for the present study Species According to Hunziker, 2001 Subfamily Tribe Collection data 1- Datura innoxia Mill. 2- Datura stramonium L. 3- Hyoscyamus albus L. 4- Hyoscyamus boveanus (Dunal) Asch. & Schweinf. 5- Hyoscyamus desertorum (Asch. & Boiss.) Täckh. 6- Hyoscyamus muticus L. 7- Hyoscyamus pusillus L. 8- Lycium europaeum L. 9- Lycium schweinfurthii Dammer var. aschersonii (Dammer) Feinbrun 10- Lycium shawii Roem & Schult. 11- Physalis angulata L. 12- Physalis ixocarpa Brot. ex Hornem. 13- *Physalis peruviana L. 14- Solanum coagulans Forssk. 15- Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. 16- Solanum forsskaolii Dunal 17- Solanum incanum L. 18- Solanum nigrum L. var. nigrum 19- Solanum sinaicum Boiss. 20- Solanum villosum Mill. subsp. villosum 21- Withania obtusifolia Täckh. 22- Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal 23- Nicotiana glauca R.C. Graham 24- Nicotiana rustica L. *Cultivated species Solanoideae Cestroideae Datureae Hyoscyameae Lycieae Solaneae Nicotianeae Al-Azhar University Cairo, 5/11/2016; Osama Ragab (Al Azhar Univ.) Al-Azhar University Cairo, 23/5/2017 and Kafr El-Dwar, 29/6/2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Burg El Arab- El Hammam Coastal road, 15/5/2017; O.N. Ghaly, (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi El Messerdy, Saint Katherine, South Sinai, 2/5/2010; O.N. Ghaly, (CAIH) Wadi El-Arish, 14/9 /1965; L. Boulos, (CAI) Cairo-Alexandria road, 100km, 13/ 12/ 2016; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Shalateen-Abu Ramad road, 60 km, 7/4/2017; O.N. Ghaly (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Tiniya, Saint Katherine Protectorate, 20/4/2008; H. Shabana, (CAIH) Alexandria - Matruh Coastal road, 237 km, 12/3/2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Alkom Alakhdar island, El Brullus, 20/3/2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Hagul, 26/12/2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Pajour, Minufiyah, 7/11/2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Kafr El-Dwar, 27/10/2016; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Nasr City- Cairo, 14/3/2018; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Darweena, Gabel Elba, 1/4/ 2000; Iman Al- Gohary, (CAIH) Burg El Arab City, 15/5/2017; O.N. Ghaly, (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Maarafaii,Gebel Elba, 8/4/2017; O.N. Ghaly, (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Kanthesrob, Gebel Elba, 9/4/2017; O.N. Ghaly, (Al Azhar Univ.) Kafr El-Dwar, 27/10/2016; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Agriculture Museum Garden, Giza, 10/1/2018; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.), Minufiyah, 5/4/2017 and Burg El Arab City, 15/5/2017; Osama Ragab (Al Azhar Univ.) Wadi Akaw, Gebel Elba, 26/4/2013; O.N. Ghaly and M. Abutaha, (CAIH) Cairo University, 10/4/2017; Minufiyah, 4/2017 and Nasr City- Cairo, 3/4/2018; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.), Alexandria-Matrouh road, 237 km, 12/3/ 2017; Osama Ragab, (Al Azhar Univ.) Agriculture Museum Garden, 4/1988; S. Khalifa, (CAIH) 125
4 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Table 2: Morphological characters of fruit Species Character Fruit mean length/ cm Fruit mean width/ cm fruit color Fruit type Fruit dehiscence Fruit shape Fruit calyx Fruit texture Datura innoxia Datura stramonium Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus muticus Hyoscyamus pusillus Lycium europaeum Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii Lycium shawii Nicotiana glauca Nicotiana rustica Physalis angulata Physalis ixocarpa Physalis peruviana Solanum coagulans Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum forsskaolii Solanum incanum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum sinaicum Solanum villosum subsp. villosum Withania obtusifolia Withania somnifera Fruit color: 1= brown / 2= black / 3=black red/ 4=yellow-orange / 5=orange / 6=grey / 7=bright red / 8= yellowish green / 9=orange red Fruit type: 1= capsule /2= berry Fruit dehiscence: 1=valve /2=circumscissile /3=indehiscence Fruit shape: 1= spherical /2= ovoid /3=oblong /4=globose Fruit calyx: 1= exposed /2= included in opened calyx /3=included in closed calyx Fruit texture: 1= spiny /2= glabrous /3=glabrescent /4=tuberculate 126
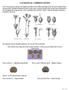
5 Khafagi et al Datura innoxia 5 Datura stramonium 6 Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus muticus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus pusillus Lycium europaeum Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii Lycium shawii Nicotiana glauca Nicotiana rustica Plate 1 (Figs. 1-12): Fruit morphology in studied species. 127
6 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Physalis angulata Physalis ixocarpa Physalis peruviana Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum forsskaolii Solanum coagulans Solanum sinaicum Solanum incanum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum villosum subsp. villosum Withania somnifera Withania obtusifolia Plate 1 (Figs ): Fruit morphology in studied species. 128
7 Khafagi et al. 2. Seed morphology The morphology of mature seed showed some variation in size, shape, color, texture, measurement, ornamentation and hilum position (Table 3 and plate 2 and 3). The number of seed / fruit is many, more than 8 seeds in most studied species but few (4-8 seeds) in L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii, L. shawii, S. coagulans and S. forsskaolii. Seed shape ranged between reniform in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, H. boveanus, L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii, L. shawii, S. forsskaolii and W. obtusifolia, oblong- obovate in N. glauca, broadly ovoid in H. desertorum, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium, S. incanum and S. sinaicum and obovoid in the remainders. Seed is flattened in D. innoxia, P. ixocarpa, P. peruviana, S. forsskaolii, S. sinaicum, S. villosum subsp. villosum and W. somnifera, slightly convex in H. albus, H. boveanus, L. shawii, P. angulata, S. elaeagnifolium, S. incanum, S. nigrum var. nigrum and W. obtusifolia and convex in the remainders. The color of seed: varied from light brown, black, brown, yellow to brown, yellow, yellowish brown and dark brown. The yellowish brown in most studied species, light brown in D. innoxia and W. obtusifolia, black in D. stramonium, brown in L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii, L. shawii and N. glauca, yellow to brown in S. incanum, yellow in P. angulata, P. ixocarpa, P. peruviana, S. sinaicum and W. somnifera and dark brown in N. rustica, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium and S. forsskaolii. Seed texture smooth in S. elaeagnifolium, rough in D. innoxia and D. stramonium, slightly tuberculate in P. angulata, Ph. ixocarpa, Ph. peruviana, S. coagulans, S. incanum, S. nigrum var. nigrum, S. sinaicum and S. villosum subsp. villosum, striate in N. glauca and tuberculate in the rest. The length of seeds ranged between; mm. in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. pusillus, N. glauca and N. rustica while it was 2.8 mm. in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium and S. forsskaolii and mm. in the remainders. The width of seed was less than 2 mm. in most studied species and 2 mm or more in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii, L. shawii, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium and S. forsskaolii. The hilum position: is usually terminal while it was subterminal in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium, S. sinaicum and W. obtusifolia and lateral in H. albus, H. desertorum, L. europaeum, N. glauca, N. rustica, P. angulata, P. ixocarpa and P. peruviana. Hilum shape inconspicuous in most studied species and conspicuous in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, H. desertorum, L. europaeum, L. shawii, N. glauca, N. rustica, P. angulata, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium and S. forsskaolii. Seeds were shiny in S. coagulans and S. elaeagnifolium and dull in the remainders. Seed ornamentation There were three major patterns of seed ornamentation: Irregular reticulate in most studied species (Plate 3); regular reticulate in S. forsskaolii (Plate 3; Fig. 18) and verrucate reticulate in D. innoxia and D. stramonium (Plate 3; Figs. 1-2) Anticlinal wall shape: was usually undulate, slightly undulate in D. stramonium, D. innoxia, H. muticus, L. shawii, S. elaeagnifolium, S. sinaicum and S. villosum subsp. villosum, slightly straight in L. europaeum and L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii and straight in S. forsskaolii. Anticlinal thickness: is thin in H. muticus, N. glauca, N. rustica, S. forsskaolii and W. obtusifolia, thick in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, S. coagulans, S. elaeagnifolium and S. villosum subsp. villosum and very thick in the rest. Anticlinal level: was raised in most of the studied species, slightly raised in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, H. desertorum, H. muticus, L. shawii, N. glauca, S. elaeagnifolium, S. incanum, S. nigrum var. nigrum, S. villosum subsp. villosum and W. obtusifolia and grooved in P. angulata, P. ixocarpa and P. peruviana. Periclinal wall: may be flat, slightly concave and concave. The slightly concave in D. 129
8 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae innoxia, S. elaeagnifolium and S. forsskaolii, concave in H. albus, H. boveanus, H. desertorum, H. muticus, L. shawii, S. incanum and W. obtusifolia and flat in the reminders. Also the cells are usually wide, narrow in D. innoxia, D. stramonium, H. pusillus, L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii, S. elaeagnifolium, S. incanum, S. nigrum var. nigrum, S. villosum subsp. villosum and W. somnifera and very wide in H. muticus, N. glauca and N. rustica. From the SEM data, it was noticed that the seed surface sculpture, aspects of the anticlinal and periclinal walls could serve as good diagnostic parameters at the generic and specific level in the studied Solanaceae. Table 3: Morphological characters of seed Character Species Number of seeds in fruit Seed shape Seed Seed color Seed texture Seed length (mm) Seed width (mm) Anticlinal Hilum position Hilum shape Seed shines Seed ornamentation Shape Thickness Datura innoxia Datura stramonium Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus muticus Hyoscyamus pusillus Lycium europaeum Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii Lycium shawii Nicotiana glauca Nicotiana rustica Physalis angulata Physalis ixocarpa Physalis peruviana Solanum coagulans Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum forsskaolii Solanum incanum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum sinaicum Solanum villosum subsp. villosum Withania obtusifolia Withania somnifera Number of seeds in fruit: 1= (4-8 seeds) few /2=many more than 8 seeds Seed shape: 1=reniform /2=obovoid /3=oblong obovate /4= broad ovate Seed: 1=flattened /2=slightly convex /3=convex Seed color: 1=light brown / 2= black /3=brown /4= yellow to brown /5=yellow /6=yellowish brown / 7= dark brown Seed texture: 1= smooth/2=rough/3=tuberculate /4= slightly tuberculate/5=striate Hilum position: 1= terminal /2=subterminal /3= lateral Hilum shape: 1=conspicuous /2=inconspicuous Seed shines: 1=shiny /2=dull Seed ornamentation: 1= regular reticulate / 2=irregular reticulate / 3=verrucate reticulate Anticlinal shape: 1=slightly undulate / 2= undulate / 3= slightly straight / 4=straight Anticlinal thickness: 1=thin / 2=thick/ 3= very thick Anticlinal level: 1= slightly raised /2= raised / 3= grooved Periclinal shape: 1=flat / 2=slightly concave / 3=concave Cells: 1=narrow / 2=wide / 3=very wide Level Periclina l shape Cells 130
9 Khafagi et al Datura innoxia Datura stramonium Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus muticus Hyoscyamus pusillus 11 Lycium europaeum Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii 12 Lycium shawii Nicotiana glauca Nicotiana rustica Plate 2 (Figs. 1-12): LM micrographs of the seed morphology in studied species. 131
10 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Physalis angulata 17 Physalis ixocarpa 18 Physalis peruviana Solanum coagulans Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum forsskaolii Solanum incanum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum sinaicum Solanum villosum Withania obtusifolia Withania somnifera subsp. villosum Plate 2 (Figs ): LM micrographs of the seed morphology in studied species. 132
11 Khafagi et al Datura innoxia Datura stramonium Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus muticus Hyoscyamus pusillus 11 Lycium europaeum Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii 12 Lycium shawii Nicotiana glauca Nicotiana rustica Plate 3 (Figs. 1-12): SEM micrographs of seed surface in studied species 133
12 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Physalis angulata Physalis ixocarpa Physalis peruviana Solanum coagulans Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum forsskaolii Solanum incanum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum sinaicum Solanum villosum subsp. villosum Withania obtusifolia Withania somnifera Plate 3 (Figs ): SEM micrographs of seed surface in studied species 134
13 Khafagi et al. 3. Numerical analysis: 3. A. Cluster analysis The 20 morphological characters of fruit and seed used in cluster analysis are included in data matrix occupy in operational taxonomic units OUT's to analyse the relationships between the 24 studied species by means of Hierarchical Cluster analysis using the PC- ORD software, version 5 and PRIMER software, version 6.0 analysis used similarity and distance measure Bray Curtis. In the dendrogram produced from using PC-ORD program used distance measure Bray Curtis (Fig. 1-A) showed that twenty four species were grouped into two major clusters. The first cluster (I) consisted of (15 species) and divided into two groups: group 1 consisted of eight species, and subdivided into two subgroups: subgroup a contains three species L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii and L. shawii. At the same time, the subgroup b consists of five species P. angulata, P. ixocarpa, P. peruviana, W. obtusifolia and W. somnifera. The group 2 which subdivided into two subgroups: subgroup 2a incorporated; S. coagulans, S. incanum, S. sinaicum, S. nigrum var. nigrum, S. villosum subsp. villosum and S. elaeagnifolium and the subgroup 2b consists of only one species S. forsskaolii. The second cluster (II) comprises the remainders (9 species) and divided into two groups: group 3 consisted of two species, D. innoxia and D. stramonium. The group 4 consisted of seven species and subdivided into two subgroups: subgroup 3a contains five species H. albus, H. desertorum, H. boveanus, H. pusillus and H. muticus and subgroup 3b comprises two species N. glauca and N. rustica. In the dendrogram produced from using PRIMER program used similarity measure Bray Curtis (Fig. 1-B) showed that twenty four species were grouped into two major clusters. The first cluster (I) consisted of two species D. innoxia and D. stramonium and the second cluster (II) comprises the rest. The results of cluster analysis using PCORD program Fig. 1-A agreed with that produced by PRIMER program Fig. 1-B. 3a 3b a b G1 G3 G4 II I 2a 2b G2 Fig. 1-A: Dendrogram showing the interrelationships between 24 species of Solanaceae based on fruit and seed characters by using PC-ORD Program. 135
14 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Group average Resemblance: S17 Bray Curtis similarity II I G1 G2 a b 2a 2b Physalis peruviana Physalis ixocarpa Physalis angulata Withania somnifera Withania obtusifolia Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii Lycium europaeum Lycium shawii Solanum sinaicum Solanum incanum Solanum villosum subsp. villosum Solanum nigrum var. nigrum Solanum elaeagnifolium Solanum coagulans Solanum forsskaolii Hyoscyamus boveanus Hyoscyamus albus Hyoscyamus desertorum Hyoscyamus pusillus Hyoscyamus muitcus Nicotiana rustica Nicotiana glauca Datura stramonium Datura innoxia Samples Similarity Fig. 1-B: Dendrogram showing the interrelationships between 24 species of Solanaceae based on fruit and seed characters by using PRIMER Program. 3. B. Computer generating Key: In the present study, 24 species were used as the Operational Taxonomic Units. A total of selected 20 attribute. These attribute representing the morphology aspects. The construction of the key was carried by using DELTA (Description Language for Taxonomy). Characters: 20 in data, 20 included, 15 in key. Items: 24 in data, 24 included, 24 in key. Characters included: 1 20 Character reliabilities: 1 20, 5 1. Fruit color brown..2 Fruit color black...6 Fruit color black red Lycium europaeum Fruit color yellow-orange.7 Fruit color orange.9 Fruit color grey.physalis ixocarpa Fruit color bright red Withania somnifera Fruit color yellowish green.. Physalis angulata Fruit color orange red.. Withania obtusifolia 2(1). Seed color light brown. Datura innoxia Seed colorblack.datura stramonium Seed color brown.. 3 Seed color yellowish brown.4 Seed color dark brown.. Nicotiana rustica 3(2). Fruit dehiscence valve; Fruit shape ovoid; Fruit texture glabrous; Seed shape oblong obovat Nicotiana glauca Fruit dehiscence circumscissile; Fruit shape oblong; Fruit Texture tuberculate; Seed shape obovoid. Hyoscyamus muticus 136
15 Khafagi et al. 4(2). Seed shape reniform. Hyoscyamus boveanus Seed shape obovoid..5 Seed shape broad ovate. Hyoscyamus desertorum 5(4). Hilum position terminal; Seed convex; Anticlinal thickness very thick; Periclinal shape flat...hyoscamus pusillus Hilum position lateral; Seed slightly convex; Anticlinal thickness thick; Periclinal shape concave Hyoscyamus albus 6(1). Seed color brown; Fruit shape globose; Number of seeds in fruit few; Seed shape reinform Lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii Seed color yellowish brown; Fruit shape spherical; Number of seeds in fruit many; Seed shape obovoid.solanum nigrum var. nigrum 7(1). Seed texture smooth; Anticlinal shape slightly undulate...solanum elaeagnifolium Seed texture tuberculate; Anticlinal shape straight...solanum forsskaolii Seed texture slightly tuberculate; Anticlinal shape undulate...8 8(7). Seed color yellow to brown; Hilum position terminal; Number of seeds in fruit many; Hilum inconspicuous... Solanum incanum Seed color dark brown; Hilum position subterminal; Number of seeds in fruit few; Hilum conspicuous.. Solanum coagulans 9(1). Seed color brown Lycium shawii Seed color yellow...10 Seed color yellowish brown.. Solanum villosum subsp. villosum 10(9). Hilum position subterminal; Fruit shape spherical; Fruit exposed; Seed shape broad ovate. Solanum sinaicum Hilum position lateral; Fruit shape globose; Fruit included in closed calyx; Seed shape obovoid... Physalis peruviana 3. C. Artificial Key to the studied species of family Solanaceae 1.a. Fruit capsule b. Fruit berry a. Fruit dehiscence by valves b. Fruit dehiscence by circumscissile a. Fruit exposed, Fruit texture spiny, Seed ornamentation verrucate reticulate b Fruit included in opened calyx, Fruit texture glabrous, Seed ornamentation. irregular reticulate 5 4.a. Fruit spheroidal, Seed light brown, flattened; periclinal wall slightly concave..... Datura innoxia 4.b. Fruit ovoid; seed black, convex; periclinal wall flat.. Datura stramonium 5.a. Seed oblong - obovoid, brown, striate; anticlinal wall slightly raised..nicotiana glauca 5.b. Seed obovoid, dark brown, tuberculate; anticlinal wall raised. Nicotiana rustica 6.a. Seed reniform Hyoscyamus boveanus 6.b. Seed broadly ovoid-obovate a. Seed ovoid Hyoscyamus desertorum 7.b. Seed obovate. 8 8.a. Seed brown; anticlinal wall slightly undulate hyoscyamus muticus 8.b. Seed yellowish brown; anticlinal shape undulate a. Hilum lateral; anticlinal wall thick; periclinal wall concave. Hyoscyamus albus 9.b. Hilum terminal; anticlinal wall very thick; periclinal wall flat.. Hyoscyamus pusillus 10.a. Fruit spheroid b. Fruit globose a. Seed ornamentation regulary reticulate.... Solanum forsskaolii 137
16 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae 11.b. Seed ornamentation irregularly reticulate a. Seed shiny b. Seed dull a. Number of seeds in fruit few; seed slightly tuberculate, convex; anticlinal wall undulate, raised; periclinal wall flat, cells wide. Solanum coagulans 13.b. Number of seeds in fruit many, seed smooth, slightly convex; anticlinal wall slightly undulate, slightly raised; periclinal wall concave, cells narrow..solanum elaeagnifolium 14.a. Seed slightly convex; anticlinal wall undulated b. Seed flattened; anticlinal shape slightly undulated a. Fruit yellow-orange, Seed broadly ovoid; periclinal wall concave...solanum incanum 15.b. Fruit black, seed obovoid, periclinal wall flat.. Solanum nigrum var. nigrum 16.a. Seed yellow; anticlinal wall raised; cells wide... Solanum sinaicum 16.b. Seed yellowish brown; anticlinal level slightly raised, cells narrow Solanum villosum subsp. villosum 17.a. Fruit exposed b. Fruit included in closed calyx a. Seed slightly convex, Anticlinal shape slightly undulate, Anticlinal level slightly raised, Periclinal shape concave, Cells wide... Lycium shawii 18.b. Seed convex, Anticlinal shape slightly straight, Anticlinal level raised, Periclinal shape flat, Cells narrow a. Fruit color black-red, Hilum position lateral..... Lycium europaeum 19.b. Fruit color black, Hilum position terminal...lycium schweinfurthii var. aschersonii 20.a. Hilum position terminal or sub terminal, Anticlinal level raised b. Hilum position lateral, Anticlinal level grooved a. Fruit orange red, Hilum sub terminal, Anticlinal slightly raised...withania obtusifolia 21.b. Fruit bright red, Hilum terminal, Anticlinal raised... Withania somnifera 22.a. Seed convex, Seed length < 2mm, Hilum conspicuous.... Physalis angulata 22.b. Seed flattened, Seed length >2mm, Hilum inconspicuous a. Fruit grey Physalis ixocarpa 23.b. Fruit orange.... Physalis peruviana The main results of the numerical analysis are: D. innoxia and D. stramonium to be separated from the rest of the genera as a distinct tribe Datureae. This result agrees and supports the view of Wettestein, (1895) and Hunziker (2001). N. glauca and N. rustica (Nicotianeae Cestroideae) are deeply immersed in group 4 together with Hyoscyamus species (Hyoscyameae Solanoideae). This result agrees and supports the view of Dunal classification, (1852). L. europaeum, L. schweinfurthii var. aschersonii and L. shawii (Lycieae) are deeply seated in group1 among an assortment of genera belonging to Solaneae this result agrees and support the view of Dunal, (l.c.). The variability in seed surface patterns is seemingly very useful in the recognition of all species studied. This agrees with the results reported by Kong et al., (2011). They showed that the finer details of the seed surface appear useful for delimitation at generic level and also species level among the species investigated of Solanaceae. In conclusion, it could be confirmed that valuable taxonomic evidence has been obtained from studying fruit and seed characteristics in some species of Solanaceae. Many of these characteristics are diagnostic at both the generic and specific levels. References Ahmed, S.M. and Fadl, M.A. (2016). Genetic relatedness among solanum L. species assayed by seed morphology and isozyme markers. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 48(5): Axelius, B. (1992). Testa patterns in some species of Physalis and some other genera in 138
17 Khafagi et al. the tribe Solaneae (Solanaceae). International Journal of Plant Sciences, 153: Bahadur, B. and Farooqui, S.M. (1986). Seed and seed coat characters in Australian Nicotiana, In W.G.: D Arcy, (ed.), Solanaceae Biology and Systematics. New York, Columbia University Press. pp.: Barthlott, W. (1981). Epidermal and seed surface characters of plants: systematic applicability and some evolutionary aspects. Nordic Journal of Botany, 1: Barthlott, W. (1984). Microstructural features of seed surface. In: V. H. Heywood and M. Moore (eds.), Current Concepts in Plant Taxonomy. Academic Press, London. pp.: Boulos, L. (2002). Flora of Egypt. Verbenaceae - Compositae. Al-Hadara Publishing, Cairo. Boulos, L. (2009). Flora of Egypt: Checklist. Revised annotated edition. Al -Hadara Publishing, Cairo, Egypt, 410 pages. Carvalho L. d`a.f.; Machado, R.D. and Bovini, M.G. (1999). Seed coat micromorphology of Brazilian species of Schwenckia, In: M.H. Nee, D.E. Symon, R.N. Lester and J.P. Jessop, (eds.), Solanaceae IV: Advances in Biology and Utilization. Kew, Royal Botanic, Gardens. pp Chiarini, F.E. and Barboza, G.E. (2007). Placentation patterns and seed number in fruits of South American Solanum subgen. Leptostemonum (Solanaceae) species. Darwiniana, 45(2): Corner, E.J.H. (1976). The Seeds of Dicotyledons. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge. Dachyshyn, O.T. (1965). The microscopic diagnosis of the fruit and seeds of Datura innoxia. Farmatsevtychnyĭ zhurnal, 20: Dallwitz, M.J. (2010). Overview of the DELTA system < overview. htm>. Dave, Y.S.; Patel, N.D. and Rao, K.S. (1980). Morpho- Histogenesis in the fruit sculpture of Datura innoxia. Phyton, 20: Dunal, M.F. (1852): Solanaceae. In A.P. De Candolle, Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis. Victoris Masson, Paris, 13(1): Esau, K. (1953). Anatomy of Seed Plants. John Wiley and Sons, New York. Ghimire, B.; Ghimire, B.K. and Heo, K. (2011). Seed characteristics of Withania somnifera (Solanaceae). Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy, 41(2): Hepper, F.N. (1998). Family 159: Solanaceae in M.N. El Hadidi (ed.) Flora of Egypt. Taeckholmia Additional Series, 6: Hoare, A.L. and Knapp, S. (1997). A phylogenetic conspectus of the tribe Hyoscyameae (Solanaceae). Bulletin of the Natural History Museum, London (Botany), 27: Hunziker, A.T. (2001). Genera Solanacearum: The Genera of Solanaceae Illustrated, Arranged According to a New System, Gantner, Ruggell, 500 pages. Kaya, A.; Satıl, F. and Aslan, M. (2016). Seed morphology of the genus Hyoscyamus L. In Turkey and its systematic significance. Acta Microscopica 25(2): Kong, M.J., Lee, J.S. and Hong, S.P. (2011). Comparative seed morphology of Solanaceae in Korea. Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy, 41(1): Mohana, R.P.R. (1974). Seed anatomy in some Hamamelidaceae and phytogeny. Phytomorphology, 24: Nha, N.T. and Danert, S. (1973). Über die fruchtentwicklung und über zentrische Leitbündel in der Gattung Datura (Solanaceae). Kulturpflanze, 21: Olmstead, R.G. and Bohs, L. (2007). A Summary of molecular systematic research in Solanaceae: Acta Horticulturae, 745: Shetler, S.J. (1986). Seed morphology in North American Campanulaceae. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 73: Srivastava, G. N. (1969). Fruit and seed morphology of some Datura species. Scientific Culture, 35: Symon, D.E. (1979). Fruit diversity and dispersal in Solanum in Australia. Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Garden, 1: Symon, D.E. (1984). A new form of Solanum fruit. Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Garden, 7(1): Tãckholm, V. (1974). Students' Flora of Egypt. 2 nd ed. Cairo University, Cairo. 139
18 Fruit and Seed Morphology of Some Species of Solanaceae Wettstein, R.V. (1895). Solanaceae. In Engler, A. and Prantl, K. (ed.), Die Natürlichen pflanzenfamilien, 4(36): Zhang, Z.Y. and Lu, A.M. (1999). A comparative study of Physalis, Capsicum and Tubocapsicum, three genera of Solanaceae. In: M.H. Nee, D.E. Symon and J. P. Jessop, (eds.), Solanaceae IV: Advances in Biology and Utilization. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp Zhang, Z.Y. and Wen, J. (1996). Charactersof leaf epidermis and seed coats in Physalis (Solanaceae) from China and its systematic significance. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 18: Zhang, Z.Y.; Yang, D.Z.; Lu, A.M. and Knapp, S. (2005). Seed morphology of the tribe Hyoscyameae (Solanaceae). Taxon, 54: Zhigila, D.A.; Abdul Rahaman, A.A.; Kolawole, O.S. and Oladele, F.A. (2014). Fruit morphology as taxonomic features in five varieties of Capsicum annuum L. Solanaceae. Journal of Botany, 2014:
Leaf Surface Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 151-156 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Leaf Surface Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan Mariam Al-Khatib and Dawud Al-Eisawi*
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 151-156 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Leaf Surface Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan Mariam Al-Khatib and Dawud Al-Eisawi*
Seed Morphology of Some Trigonella L. Species (Fabaceae) and its Taxonomic Significance
 Seed Morphology of Some Trigonella L. Species (Fabaceae) and its Taxonomic Significance Zaki Turki 1, Fathi El-Shayeb 2, Ann Abozeid 3 1, 2, 3 Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Menoufia University,
Seed Morphology of Some Trigonella L. Species (Fabaceae) and its Taxonomic Significance Zaki Turki 1, Fathi El-Shayeb 2, Ann Abozeid 3 1, 2, 3 Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Menoufia University,
THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-IV OXALIDACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(3): 1429-1433, 2010. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-IV OXALIDACEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER* Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan *Federal Urdu
Pak. J. Bot., 42(3): 1429-1433, 2010. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-IV OXALIDACEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER* Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan *Federal Urdu
CYPSELAR CHARACTERS OF SOME SPECIES OF THE TRIBE- SENECIONEAE (ASTERACEAE), ON THE BASIS OF MORPHOLOGICALL STUDY
 Research Article Bidyut Kumar Jana,, 2013; Volume 2(1): 261-266 ISSN: 2277-8713 CYPSELAR CHARACTERS OF SOME SPECIES OF THE TRIBE- SENECIONEAE (ASTERACEAE), ON THE BASIS OF MORPHOLOGICALL STUDY BIDYUT KUMAR
Research Article Bidyut Kumar Jana,, 2013; Volume 2(1): 261-266 ISSN: 2277-8713 CYPSELAR CHARACTERS OF SOME SPECIES OF THE TRIBE- SENECIONEAE (ASTERACEAE), ON THE BASIS OF MORPHOLOGICALL STUDY BIDYUT KUMAR
THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-I. AIZOACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 41(4): 1557-1564, 2009. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-I. AIZOACEAE DURDANA KANWAL, RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER * Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-72570, Pakistan * Federal
Pak. J. Bot., 41(4): 1557-1564, 2009. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-I. AIZOACEAE DURDANA KANWAL, RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER * Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-72570, Pakistan * Federal
CYPSELA MORPHOLOGY OF GNAPHALIUM L. AND ITS ALLIED GENERA (GNAPHALIEAE-ASTERACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 25-31, 2008. CYPSELA MORPHOLOGY OF GNAPHALIUM L. AND ITS ALLIED GENERA (GNAPHALIEAE-ASTERACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER * Department of Botany, University of Karachi,
Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 25-31, 2008. CYPSELA MORPHOLOGY OF GNAPHALIUM L. AND ITS ALLIED GENERA (GNAPHALIEAE-ASTERACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER * Department of Botany, University of Karachi,
Genetic Variation of Populations Scutellaria slametensis sp. nov. (Lamiaceae) on Mt. Slamet, Central Java, Indonesia
 Genetic Variation of Populations Scutellaria slametensis sp. nov. (Lamiaceae) on Mt. Slamet, Central Java, Indonesia Scutellaria sp. pop. Baturraden Scutellaria sp. pop. Kaligua Scutellaria sp. pop. Kaliwadas
Genetic Variation of Populations Scutellaria slametensis sp. nov. (Lamiaceae) on Mt. Slamet, Central Java, Indonesia Scutellaria sp. pop. Baturraden Scutellaria sp. pop. Kaligua Scutellaria sp. pop. Kaliwadas
UC BERKELEY McCOWN ARCHAEOBOTANY LABORATORY REPORT #84 Pachacamac Archaeological Capsicum seed analysis II
 UC BERKELEY McCOWN ARCHAEOBOTANY LABORATORY REPORT #84 Pachacamac Archaeological Capsicum seed analysis II Written for: Dr. Peter Eeckhout and Tatiana Stellian, Université Libre de Bruxelles Authors: Katherine
UC BERKELEY McCOWN ARCHAEOBOTANY LABORATORY REPORT #84 Pachacamac Archaeological Capsicum seed analysis II Written for: Dr. Peter Eeckhout and Tatiana Stellian, Université Libre de Bruxelles Authors: Katherine
Solanaceae. Physalis L. Withania Pauq. Lycium L.) (Solanaceae. Solanaceae (6) family Solanum 90)
 007 Solanaceae (Solanum L. (Solanaceae Physalis L. Withania Pauq. Lycium L.) (6) 9 (8) 90) (9) 90) (7) 000 000 000 (7 Solanaceae Nightshade Potato family family Solanum Solanum melongena L. tubersum L.
007 Solanaceae (Solanum L. (Solanaceae Physalis L. Withania Pauq. Lycium L.) (6) 9 (8) 90) (9) 90) (7) 000 000 000 (7 Solanaceae Nightshade Potato family family Solanum Solanum melongena L. tubersum L.
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION BY MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIORS AND PRODUCTIVITY ON DIFFERENT GENOTYPE OF CAPE GOOSEBERRY
 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION BY MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIORS AND PRODUCTIVITY ON DIFFERENT GENOTYPE OF CAPE GOOSEBERRY (Physalis peruviana L.) Nikolay Panayotov Agricultural University of Plovdiv, 12 Mendeleev Str.,
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION BY MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIORS AND PRODUCTIVITY ON DIFFERENT GENOTYPE OF CAPE GOOSEBERRY (Physalis peruviana L.) Nikolay Panayotov Agricultural University of Plovdiv, 12 Mendeleev Str.,
THE MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION WITHIN SEEDS OF PASSIFLORA SUBGENUS DECALOBA
 THE MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION WITHIN SEEDS OF PASSIFLORA SUBGENUS DECALOBA By Anthony Myers, Dr. Peter Jørgensen, and Dr. John MacDougal Institutions: Harris-Stowe State University (amyers480@hornets.hssu.edu);
THE MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL VARIATION WITHIN SEEDS OF PASSIFLORA SUBGENUS DECALOBA By Anthony Myers, Dr. Peter Jørgensen, and Dr. John MacDougal Institutions: Harris-Stowe State University (amyers480@hornets.hssu.edu);
STUDIES ON THE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS OF SOME SPECIES IN SOLANACEAE. Kanemasa TOKUNAGA
 STUDIES ON THE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS OF SOME SPECIES IN SOLANACEAE Kanemasa TOKUNAGA INTRODUCTION In Capsicum annuum, there are many garden varieties showing 12 chromosomes in haploid and 24 in diploid (Vilmorin
STUDIES ON THE CHROMOSOME NUMBERS OF SOME SPECIES IN SOLANACEAE Kanemasa TOKUNAGA INTRODUCTION In Capsicum annuum, there are many garden varieties showing 12 chromosomes in haploid and 24 in diploid (Vilmorin
Lam. Boraginaceae. Cordia sinensis
 LOCAL NAMES English (grey-leaved saucer berry,grey-leaved cordia); Somali (marer,mareer); Swahili (mnya mate,mkamasi) BOTANIC DESCRIPTION is a low leafy shrub or bush, multi-stemmed tree 3-12 m high and
LOCAL NAMES English (grey-leaved saucer berry,grey-leaved cordia); Somali (marer,mareer); Swahili (mnya mate,mkamasi) BOTANIC DESCRIPTION is a low leafy shrub or bush, multi-stemmed tree 3-12 m high and
Řepka R., Veselá P. & Mráček J. (2014): Are there hybrids between Carex flacca and C. tomentosa
 Řepka R., Veselá P. & Mráček J. (2014): Are there hybrids between Carex flacca and C. tomentosa in the Czech Republic and Slovakia? Preslia 86: 367 379. Electronic Appendix 1. Comparison of morphological
Řepka R., Veselá P. & Mráček J. (2014): Are there hybrids between Carex flacca and C. tomentosa in the Czech Republic and Slovakia? Preslia 86: 367 379. Electronic Appendix 1. Comparison of morphological
The host range of the eriophyid mite Aceria vitalbae, a biological control agent for Clematis vitalba.
 The host range of the eriophyid mite Aceria vitalbae, a biological control agent for Clematis vitalba. Host range tests were carried out in Serbia for Landcare Research by Dr Biljana Vidovic of the University
The host range of the eriophyid mite Aceria vitalbae, a biological control agent for Clematis vitalba. Host range tests were carried out in Serbia for Landcare Research by Dr Biljana Vidovic of the University
B. CYANOTIS Cyanotis fasciculata Plate 35 J L
 B. C A P S U L E A N D S E E D M O R P H O L O G I C A L D I V E R S I T Y I N C Y A N O T I S, M U R D A N N I A A N D R H O P A L E P H O R A Typically, loculicidal dehiscent capsule is one of the important
B. C A P S U L E A N D S E E D M O R P H O L O G I C A L D I V E R S I T Y I N C Y A N O T I S, M U R D A N N I A A N D R H O P A L E P H O R A Typically, loculicidal dehiscent capsule is one of the important
Classification Lab (Jelli bellicus) Lab; SB3 b,c
 Classification Lab (Jelli bellicus) Lab; SB3 b,c A branch of biology called taxonomy involves the identification, naming, and classification of species. Assigning scientific names to species is an important
Classification Lab (Jelli bellicus) Lab; SB3 b,c A branch of biology called taxonomy involves the identification, naming, and classification of species. Assigning scientific names to species is an important
Genetic Variability in Eggplant for Agro-Morphological Traits
 Science, Technology and Development 34 (1): 35-40, 2015 ISSN 0254-6418 / DOI: 10.3923/std.2015.35.40 2015 Pakistan Council for Science and Technology Genetic Variability in Eggplant for Agro-Morphological
Science, Technology and Development 34 (1): 35-40, 2015 ISSN 0254-6418 / DOI: 10.3923/std.2015.35.40 2015 Pakistan Council for Science and Technology Genetic Variability in Eggplant for Agro-Morphological
Part 1: Naming the cultivar
 IPC Logo REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of SALIX L. Nomenclature and Registration Addresses for correspondence: FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 2013 as the ICRA for the genus
IPC Logo REGISTRATION FORM FOR a CULTIVAR NAME of SALIX L. Nomenclature and Registration Addresses for correspondence: FAO - International Poplar Commission (appointed in 2013 as the ICRA for the genus
Morphological Characterization of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) Accessions
 I J T A Serials Publications Morphological Characterization of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) Accessions A. Aswini*, K. Lila Mathew**, T. Radha***, A.K. Babylatha****, P.S. Abida*****, S. Krishnan******
I J T A Serials Publications Morphological Characterization of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.) Accessions A. Aswini*, K. Lila Mathew**, T. Radha***, A.K. Babylatha****, P.S. Abida*****, S. Krishnan******
Museum Victoria CRC National Plant Biosecurity
 1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith 1896) Yabuuchi et al. 1996 race 2 (Bacteria: Proteobacteria: Burkholderiales: Burkholderiaceae) Common Name Moko disease of banana
1. PaDIL Species Factsheet Scientific Name: Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith 1896) Yabuuchi et al. 1996 race 2 (Bacteria: Proteobacteria: Burkholderiales: Burkholderiaceae) Common Name Moko disease of banana
Morphological Characteristics of Greek Saffron Stigmas from Kozani Region
 Morphological Characteristics of Greek Saffron Stigmas from Kozani Region Theodora Mitsopoulou and Maria Z. Tsimidou Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, School of Chemistry Laboratory of Food Science
Morphological Characteristics of Greek Saffron Stigmas from Kozani Region Theodora Mitsopoulou and Maria Z. Tsimidou Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, School of Chemistry Laboratory of Food Science
COCKLES & CAMPION STUDY
 COCKLES & CAMPION STUDY In the Caryophyllaceae family, seed shapes and surface textures differ depending on how the seed is dispersed from the parent plant. Methods of dispersal include by wind, water,
COCKLES & CAMPION STUDY In the Caryophyllaceae family, seed shapes and surface textures differ depending on how the seed is dispersed from the parent plant. Methods of dispersal include by wind, water,
PRUNUS AMERICANA (ROSACEAE) IN THE ARKANSAS FLORA
 Johnson, G.P. 2013. Prunus americana (Rosaceae) in the Arkansas flora. Phytoneuron 2013-33: 1 5. Published 20 May 2013. ISSN 2153 733X PRUNUS AMERICANA (ROSACEAE) IN THE ARKANSAS FLORA GEORGE P. JOHNSON
Johnson, G.P. 2013. Prunus americana (Rosaceae) in the Arkansas flora. Phytoneuron 2013-33: 1 5. Published 20 May 2013. ISSN 2153 733X PRUNUS AMERICANA (ROSACEAE) IN THE ARKANSAS FLORA GEORGE P. JOHNSON
Classification and Botanical Description of Imported Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus) in Nelson, New Zealand
 New Zealand Journal of Botany ISSN: 0028-825X (Print) 1175-8643 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnzb20 Classification and Botanical Description of Imported Varieties of Hops (Humulus
New Zealand Journal of Botany ISSN: 0028-825X (Print) 1175-8643 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tnzb20 Classification and Botanical Description of Imported Varieties of Hops (Humulus
CARTHAMUS TINCTORIUS L., THE QUALITY OF SAFFLOWER SEEDS CULTIVATED IN ALBANIA.
 CARTHAMUS TINCTORIUS L., THE QUALITY OF SAFFLOWER SEEDS CULTIVATED IN ALBANIA. Valdete VORPSI, Fatos HARIZAJ, Nikoll BARDHI, Vjollca VLADI, Erta DODONA Faculty of Agriculture and Environment, Agriculture
CARTHAMUS TINCTORIUS L., THE QUALITY OF SAFFLOWER SEEDS CULTIVATED IN ALBANIA. Valdete VORPSI, Fatos HARIZAJ, Nikoll BARDHI, Vjollca VLADI, Erta DODONA Faculty of Agriculture and Environment, Agriculture
Performance of lemon and guava as middle layer crops under coconut based multistoried Agroforestry system
 Performance of lemon and guava as middle layer crops under coconut based multistoried Agroforestry system 1 M A Jahir, 2 M A Rahim, 3 M S Bari, 4 S M Islam 1 Department of Horticulture, BAU, Mymensingh,
Performance of lemon and guava as middle layer crops under coconut based multistoried Agroforestry system 1 M A Jahir, 2 M A Rahim, 3 M S Bari, 4 S M Islam 1 Department of Horticulture, BAU, Mymensingh,
SEM (SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY) STUDIES ON SEEDS OF TWO SPECIES OF DIANTHUS (CARYOPHYLLACEAE) SUSHMA SHARMA
 J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468, e-issn: 2455-7218 Vol. 95 (3 & 4) 2016: 288-292 SEM (SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY) STUDIES ON SEEDS OF TWO SPECIES OF DIANTHUS (CARYOPHYLLACEAE) SUSHMA SHARMA Botany
J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468, e-issn: 2455-7218 Vol. 95 (3 & 4) 2016: 288-292 SEM (SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY) STUDIES ON SEEDS OF TWO SPECIES OF DIANTHUS (CARYOPHYLLACEAE) SUSHMA SHARMA Botany
THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-II GREWIOIDEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 41(6): 2647-2656, 2009. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-II GREWIOIDEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, RUBINA ABID AND M. QASIER* Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan *Fedral Urdu
Pak. J. Bot., 41(6): 2647-2656, 2009. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-II GREWIOIDEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, RUBINA ABID AND M. QASIER* Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan *Fedral Urdu
Carex kobomugi (Japanese sedge Asiatic sand sedge )
 1 of 6 9/24/2007 3:33 PM Home Early Detection IPANE Species Data & Maps Volunteers About the Project Related Information Catalog of Species Search Results :: Catalog of Species Search Carex kobomugi (Japanese
1 of 6 9/24/2007 3:33 PM Home Early Detection IPANE Species Data & Maps Volunteers About the Project Related Information Catalog of Species Search Results :: Catalog of Species Search Carex kobomugi (Japanese
TAXONOMIC SIGNIFICANCE OF ACHENE MORPHOLOGY IN THE GENUS CYPERUS L. (CYPERACEAE) IN GOA, INDIA
 TAXONOMIC SIGNIFICANCE OF ACHENE MORPHOLOGY IN THE GENUS CYPERUS L. (CYPERACEAE) IN GOA, INDIA *Ramchandra T. Patil 1 and V.P. Prasad 2 1 Department of Botany, Br. Balasaheb Khardekar College, Vengurla,
TAXONOMIC SIGNIFICANCE OF ACHENE MORPHOLOGY IN THE GENUS CYPERUS L. (CYPERACEAE) IN GOA, INDIA *Ramchandra T. Patil 1 and V.P. Prasad 2 1 Department of Botany, Br. Balasaheb Khardekar College, Vengurla,
Elemental Analysis of Yixing Tea Pots by Laser Excited Atomic. Fluorescence of Desorbed Plumes (PLEAF) Bruno Y. Cai * and N.H. Cheung Dec.
 Elemental Analysis of Yixing Tea Pots by Laser Excited Atomic Fluorescence of Desorbed Plumes (PLEAF) Bruno Y. Cai * and N.H. Cheung 2012 Dec. 31 Summary Two Yixing tea pot samples were analyzed by PLEAF.
Elemental Analysis of Yixing Tea Pots by Laser Excited Atomic Fluorescence of Desorbed Plumes (PLEAF) Bruno Y. Cai * and N.H. Cheung 2012 Dec. 31 Summary Two Yixing tea pot samples were analyzed by PLEAF.
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT APPLICATIONS ON FRUIT YIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF STRAWBERRIES CULTIVATED UNDER VAN ECOLOGICAL CONDITION ABSTRACT
 Gecer et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 23(5): 2013, Page: J. 1431-1435 Anim. Plant Sci. 23(5):2013 ISSN: 1018-7081 THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT APPLICATIONS ON FRUIT YIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF
Gecer et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 23(5): 2013, Page: J. 1431-1435 Anim. Plant Sci. 23(5):2013 ISSN: 1018-7081 THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT APPLICATIONS ON FRUIT YIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF
SEEDCOAT SEM STUDIES OF SELECTED TAXA OF THE TRIBE PHASEOLEAE (FABACEAE)
 Legume Res., 28 (4) : 235-243, 2005 SEEDCOAT SEM STUDIES OF SELECTED TAXA OF THE TRIBE PHASEOLEAE (FABACEAE) Baisakhi Bandyopadhyay, Subhas Chandra Santra and Mashahiro Kato [kparlment of Environmental
Legume Res., 28 (4) : 235-243, 2005 SEEDCOAT SEM STUDIES OF SELECTED TAXA OF THE TRIBE PHASEOLEAE (FABACEAE) Baisakhi Bandyopadhyay, Subhas Chandra Santra and Mashahiro Kato [kparlment of Environmental
A new species of Potentilla (Rosaceae): P. baekdusanensis M. Kim
 Korean J. Pl. Taxon. 48(1): 37 42 (2018) https://doi.org/10.11110/kjpt.2018.48.1.37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1225-8318 eissn 2466-1546 Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy A new species of Potentilla (Rosaceae):
Korean J. Pl. Taxon. 48(1): 37 42 (2018) https://doi.org/10.11110/kjpt.2018.48.1.37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1225-8318 eissn 2466-1546 Korean Journal of Plant Taxonomy A new species of Potentilla (Rosaceae):
THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-XVI. ACANTHACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 50(5): 1831-1841, 2018. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-XVI. ACANTHACEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, * RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan * Corresponding
Pak. J. Bot., 50(5): 1831-1841, 2018. THE SEED ATLAS OF PAKISTAN-XVI. ACANTHACEAE AFSHEEN ATHER, * RUBINA ABID AND M. QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan * Corresponding
Three new species of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) from Sumatra, Indonesia
 KEW BULLETIN VOL. 67: 731 Y 737 (2012) ISSN: 0075-5974 (print) ISSN: 1874-933X (electronic) Three new species of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) from Sumatra, Indonesia Nanda Utami 1 Summary. Three new species
KEW BULLETIN VOL. 67: 731 Y 737 (2012) ISSN: 0075-5974 (print) ISSN: 1874-933X (electronic) Three new species of Impatiens (Balsaminaceae) from Sumatra, Indonesia Nanda Utami 1 Summary. Three new species
Principal components analysis of morphological variation of the Ptelea trifoliata species complex
 Principal components analysis of morphological variation of the Ptelea trifoliata species complex Erin Skornia and Wendy Applequist, Ph.D. Missouri Botanical Garden What is Ptelea trifoliata? Family Rutaceae,
Principal components analysis of morphological variation of the Ptelea trifoliata species complex Erin Skornia and Wendy Applequist, Ph.D. Missouri Botanical Garden What is Ptelea trifoliata? Family Rutaceae,
THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT
 THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT Adrienne La Favre, Ph.D. Jeffrey La Favre, Ph.D. In this lesson we will begin to learn about the Solanaceae. We will spend most of our effort over the next year on the potato.
THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT Adrienne La Favre, Ph.D. Jeffrey La Favre, Ph.D. In this lesson we will begin to learn about the Solanaceae. We will spend most of our effort over the next year on the potato.
MORPHOLOGICAL DIVERSITY OF TEA GROWN IN LAM DONG PROVINCE (VIET NAM)
 MORPHOLOGICAL DIVERSITY OF TEA GROWN IN LAM DONG PROVINCE (VIET NAM) Thai Dan Vo, Heiko C. Becker Institute of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Germany Abstract Assessing
MORPHOLOGICAL DIVERSITY OF TEA GROWN IN LAM DONG PROVINCE (VIET NAM) Thai Dan Vo, Heiko C. Becker Institute of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Germany Abstract Assessing
(12) Plant Patent Application Publication
 (19) United States (12) Plant Patent Application Publication Pate US 201001.38965P1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0138965 P1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) BLUEBERRY VARIETY NAMED BLUE MOON (75) Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Plant Patent Application Publication Pate US 201001.38965P1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0138965 P1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 3, 2010 (54) BLUEBERRY VARIETY NAMED BLUE MOON (75) Inventor:
EVALUATION OF SOME VARIETIES AND SEEDLINGS OF DATE PALM GROWN AT BAHRIYA OASIS
 EVALUATION OF SOME VARIETIES AND SEEDLINGS OF DATE PALM GROWN AT BAHRIYA OASIS By AHMED MOHAMED ABD-ALLAH B.Sc. Agric. Sci. (Pomology. Dept.) Fac. Agric., Cairo Univ., Egypt, 2010 THESIS Submitted in Partial
EVALUATION OF SOME VARIETIES AND SEEDLINGS OF DATE PALM GROWN AT BAHRIYA OASIS By AHMED MOHAMED ABD-ALLAH B.Sc. Agric. Sci. (Pomology. Dept.) Fac. Agric., Cairo Univ., Egypt, 2010 THESIS Submitted in Partial
ANALYSIS OF CLIMATIC FACTORS IN CONNECTION WITH STRAWBERRY GENERATIVE BUD DEVELOPMENT
 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES (CROP SCIENCES, ANIMAL SCIENCES) ANALYSIS OF CLIMATIC FACTORS IN CONNECTION WITH STRAWBERRY GENERATIVE BUD DEVELOPMENT Ieva Kalniņa 1,, Sarmīte Strautiņa 1 Latvia University of Agriculture
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES (CROP SCIENCES, ANIMAL SCIENCES) ANALYSIS OF CLIMATIC FACTORS IN CONNECTION WITH STRAWBERRY GENERATIVE BUD DEVELOPMENT Ieva Kalniņa 1,, Sarmīte Strautiņa 1 Latvia University of Agriculture
New subspecies of Ardisia crenata (Primulaceae) from Thailand
 Taiwania 62(2): 116 120, 2017 DOI: 10.6165/tai.2017.62.116 New subspecies of Ardisia crenata (Primulaceae) from Thailand Wannachai CHATAN * and Wilawan PROMPROM Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Taiwania 62(2): 116 120, 2017 DOI: 10.6165/tai.2017.62.116 New subspecies of Ardisia crenata (Primulaceae) from Thailand Wannachai CHATAN * and Wilawan PROMPROM Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Identification and Classification of Pink Menoreh Durian (Durio Zibetinus Murr.) Based on Morphology and Molecular Markers
 RESEARCH Identification and Classification of Pink Durian (Durio Zibetinus Murr.) Based on Morphology and Molecular Markers Nandariyah a,b * adepartment of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, Sebelas Maret
RESEARCH Identification and Classification of Pink Durian (Durio Zibetinus Murr.) Based on Morphology and Molecular Markers Nandariyah a,b * adepartment of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, Sebelas Maret
A New Approach for Smoothing Soil Grain Size Curve Determined by Hydrometer
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 4, 1285-1291 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.49123 A New Approach for Smoothing Soil Grain
International Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 4, 1285-1291 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.49123 A New Approach for Smoothing Soil Grain
Plant Propagation Protocol for [Solanum americanum] ESRM 412 Native Plant Production. (Picture obtained from source 11) TAXONOMY
![Plant Propagation Protocol for [Solanum americanum] ESRM 412 Native Plant Production. (Picture obtained from source 11) TAXONOMY Plant Propagation Protocol for [Solanum americanum] ESRM 412 Native Plant Production. (Picture obtained from source 11) TAXONOMY](/thumbs/85/92763018.jpg) Plant Propagation Protocol for [Solanum americanum] ESRM 412 Native Plant Production (Picture obtained from source 11) Family Names Family Scientific Name: Family Common Name: Scientific Names Genus: Species:
Plant Propagation Protocol for [Solanum americanum] ESRM 412 Native Plant Production (Picture obtained from source 11) Family Names Family Scientific Name: Family Common Name: Scientific Names Genus: Species:
Reported of four new subspecies of Ziziphora clinopodioides (Lamiaceae) for the flora of Turkey
 Issues in Biological Sciences and Pharmaceutical Research Vol. 5(2),pp.5-11, February 2017 Available online at https://www.journalissues.org/ibspr/ https://doi.org/10.15739/ibspr.17.002 Copyright 2017
Issues in Biological Sciences and Pharmaceutical Research Vol. 5(2),pp.5-11, February 2017 Available online at https://www.journalissues.org/ibspr/ https://doi.org/10.15739/ibspr.17.002 Copyright 2017
SEM studies of Achenes in some taxa of Asteraceae
 Volume International II Number Journal 2 2011 for [23-28] Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume IV No. 2 2013 [87 97] Received: February 28, 2013 Accepted: June 27, 2013 Online: October
Volume International II Number Journal 2 2011 for [23-28] Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume IV No. 2 2013 [87 97] Received: February 28, 2013 Accepted: June 27, 2013 Online: October
PHENETIC STUDY OF SOME INDIAN SOLANACEAE BASED ON FOLIAR MICROMORPHOLOGY, PALYNOLOGY AND REPRODUCTIVE POTENTIALITY
 Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 2, 2017 pp. 1267-1273 ISSN 0972-5210 PHENETIC STUDY OF SOME INDIAN SOLANACEAE BASED ON FOLIAR MICROMORPHOLOGY, PALYNOLOGY AND REPRODUCTIVE POTENTIALITY Mridushree Basak, Aparna
Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 2, 2017 pp. 1267-1273 ISSN 0972-5210 PHENETIC STUDY OF SOME INDIAN SOLANACEAE BASED ON FOLIAR MICROMORPHOLOGY, PALYNOLOGY AND REPRODUCTIVE POTENTIALITY Mridushree Basak, Aparna
Exploring the horticultural potential of native Australian. flowering shrubs in the Solanum brownii group
 Exploring the horticultural potential of native Australian flowering shrubs in the Solanum brownii group Adam Marchant, Andrew Perkins, George Orel, Gillian Towler Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney Final report
Exploring the horticultural potential of native Australian flowering shrubs in the Solanum brownii group Adam Marchant, Andrew Perkins, George Orel, Gillian Towler Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney Final report
VARIABILITY OF SOME APRICOT VARIETIES AND HYBRIDS QUALITY TRAITS CREATED IN ROMANIA
 Scientific Papers, UASVM Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LIV, 2011, ISSN 1222-5339 VARIABILITY OF SOME APRICOT VARIETIES AND HYBRIDS QUALITY TRAITS CREATED IN ROMANIA VALERICA TUDOR, A. ASĂNICĂ University of
Scientific Papers, UASVM Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LIV, 2011, ISSN 1222-5339 VARIABILITY OF SOME APRICOT VARIETIES AND HYBRIDS QUALITY TRAITS CREATED IN ROMANIA VALERICA TUDOR, A. ASĂNICĂ University of
Flowering and Fruiting Morphology of Hardy Kiwifruit, Actinidia arguta
 Flowering and Fruiting Morphology of Hardy Kiwifruit, Actinidia arguta Chantalak Tiyayon and Bernadine Strik Department of Horticulture, Oregon State University 4017 ALS, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA Email:
Flowering and Fruiting Morphology of Hardy Kiwifruit, Actinidia arguta Chantalak Tiyayon and Bernadine Strik Department of Horticulture, Oregon State University 4017 ALS, Corvallis, OR 97331, USA Email:
sensory universe of men.
 - sense and as species of the genus Camellia to cultural, economic, ornamental or sociologic processes. Examples of these processes are the - - sensory universe of men. family, occupy a broad stripe around
- sense and as species of the genus Camellia to cultural, economic, ornamental or sociologic processes. Examples of these processes are the - - sensory universe of men. family, occupy a broad stripe around
EXPLORING FOR PERSEA IN LATIN AMERICA
 California Avocado Society 1978 Yearbook 62: 60-65 EXPLORING FOR PERSEA IN LATIN AMERICA Eugenio Schieber and G. A. Zentmyer Plant Pathologist, Antigua, Guatemala; and Professor, Department of Plant Pathology,
California Avocado Society 1978 Yearbook 62: 60-65 EXPLORING FOR PERSEA IN LATIN AMERICA Eugenio Schieber and G. A. Zentmyer Plant Pathologist, Antigua, Guatemala; and Professor, Department of Plant Pathology,
Sugar maple tree named Legacy
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent PP4,979 Wandell February 1, 1983 Sugar maple tree named Legacy Abstract This disclosure concerns a new and distinct variety of Acer saccharum (commonly known as sugar maple
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent PP4,979 Wandell February 1, 1983 Sugar maple tree named Legacy Abstract This disclosure concerns a new and distinct variety of Acer saccharum (commonly known as sugar maple
Corresponding author: Ornella K Sangma
 Occurrence of Gymnopetalum cochinchinense (Lour.) Kurz. (Apolka) in Garo Hills of Meghalaya, India Ornella K Sangma 1, Arindam Barman 2, Chinky M Marak 3 and Cheana S Sangma 4 1 PG Scholar, Department
Occurrence of Gymnopetalum cochinchinense (Lour.) Kurz. (Apolka) in Garo Hills of Meghalaya, India Ornella K Sangma 1, Arindam Barman 2, Chinky M Marak 3 and Cheana S Sangma 4 1 PG Scholar, Department
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9073589209* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2015 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9073589209* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2015 1 hour Candidates
Nectria flute canker
 Forest Pathology in New Zealand No. 23 (Second Edition 2009) Nectria flute canker M.A. Dick (Revised by A.J.M Hopkins and M.A. Dick) Causal organism Neonectria fuckeliana (C. Booth) Castlebury & Rossman
Forest Pathology in New Zealand No. 23 (Second Edition 2009) Nectria flute canker M.A. Dick (Revised by A.J.M Hopkins and M.A. Dick) Causal organism Neonectria fuckeliana (C. Booth) Castlebury & Rossman
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5342618795* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2017 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5342618795* BIOLOGY 0610/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2017 1 hour Candidates
Miscellany. Nine new yellow flowering Camellia (Theaceae) species from Viet Nam
 Miscellany 149 Nine new yellow flowering Camellia (Theaceae) species from Viet Nam George Orel & Anthony S. Curry Royal Botanic Gardens, Mrs Macquaries Road, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia e-mail george.orel@rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au
Miscellany 149 Nine new yellow flowering Camellia (Theaceae) species from Viet Nam George Orel & Anthony S. Curry Royal Botanic Gardens, Mrs Macquaries Road, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia e-mail george.orel@rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au
How to identify American chestnut trees. American Chestnut Tree. Identification Resources. For the Appalachian Trail Mega-Transect.
 American Chestnut Tree Identification Resources For the Appalachian Trail Mega-Transect Chestnut Project May 2008 How to identify American chestnut trees Excerpt from: Field Guide for locating, pollinating,
American Chestnut Tree Identification Resources For the Appalachian Trail Mega-Transect Chestnut Project May 2008 How to identify American chestnut trees Excerpt from: Field Guide for locating, pollinating,
STUDIES ON THE COMMON SMUT DISEASE OF CORN
 -68- Summary of STUDIES ON THE COMMON SMUT DISEASE OF CORN A Thesis Presented to the Graduate School, Faculty of Agriculture, Damanhour University In Partial Fullfilment of the Requirements For the Degree
-68- Summary of STUDIES ON THE COMMON SMUT DISEASE OF CORN A Thesis Presented to the Graduate School, Faculty of Agriculture, Damanhour University In Partial Fullfilment of the Requirements For the Degree
Solanum dulcamara (Bittersweet nightshade Climbing nightshade European bittersweet Woody nightshade Fellenwort )
 1 of 6 9/21/2007 2:15 PM Home Early Detection IPANE Species Data & Maps Volunteers About the Project Related Information Catalog of Species Search Results :: Catalog of Species Search Solanum dulcamara
1 of 6 9/21/2007 2:15 PM Home Early Detection IPANE Species Data & Maps Volunteers About the Project Related Information Catalog of Species Search Results :: Catalog of Species Search Solanum dulcamara
INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH DIRECTORATE OF RAPESEED-MUSTARD RESEARCH, BHARATPUR, INDIA
 INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH DIRECTORATE OF RAPESEED-MUSTARD RESEARCH, BHARATPUR, INDIA Pathogenic variability of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates on Brassica differentials Pankaj Sharma ICAR-Directorate
INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH DIRECTORATE OF RAPESEED-MUSTARD RESEARCH, BHARATPUR, INDIA Pathogenic variability of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates on Brassica differentials Pankaj Sharma ICAR-Directorate
NEW ΤΑΧΑ FOR THE FLORA OF TURKEY
 Doğa-Tr.J. of Botany 14(1990), 49-54 TÜBİTAK NEW ΤΑΧΑ FOR THE FLORA OF TURKEY Sadık ERİK Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Department of Biology, Bey tepe Campus, Ankara Turkey Received 10/1/1989
Doğa-Tr.J. of Botany 14(1990), 49-54 TÜBİTAK NEW ΤΑΧΑ FOR THE FLORA OF TURKEY Sadık ERİK Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Department of Biology, Bey tepe Campus, Ankara Turkey Received 10/1/1989
Microanalytical Quality of Ground and Unground Marjoram, Sage and Thyme, Ground Allspice, Black Pepper and Paprika
 Journal of Food Protection, Vol., No., Pages - (March ) Copyright International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Microanalytical Quality of and Marjoram, Sage and Thyme, Allspice,
Journal of Food Protection, Vol., No., Pages - (March ) Copyright International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Microanalytical Quality of and Marjoram, Sage and Thyme, Allspice,
Identification of haplotypes controlling seedless by genome resequencing of grape
 Identification of haplotypes controlling seedless by genome resequencing of grape Soon-Chun Jeong scjeong@kribb.re.kr Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology Why seedless grape research
Identification of haplotypes controlling seedless by genome resequencing of grape Soon-Chun Jeong scjeong@kribb.re.kr Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology Why seedless grape research
Plant Profiles: HORT 2242 Landscape Plants II
 Botanical Name: Pinus ponderosa Common Name: ponderosa pine, western yellow pine Family Name: Pinaceae pine family Plant Profiles: HORT 2242 Landscape Plants II General Description: As the botanical and
Botanical Name: Pinus ponderosa Common Name: ponderosa pine, western yellow pine Family Name: Pinaceae pine family Plant Profiles: HORT 2242 Landscape Plants II General Description: As the botanical and
Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata (Magnoliaceae), a new taxon from Yunnan, China
 Ann. Bot. Fennici 49: 417 421 ISSN 0003-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 30 November 2012 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2012 Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata (Magnoliaceae),
Ann. Bot. Fennici 49: 417 421 ISSN 0003-3847 (print) ISSN 1797-2442 (online) Helsinki 30 November 2012 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2012 Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata (Magnoliaceae),
SELECTION STUDIES ON FIG IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION OF TURKEY
 Pak. J. Boti., 37(3): 567-574, 2005. SELECTION STUDIES ON FIG IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION OF TURKEY A. AYTEKİN POLAT 1 AND MELİSA ÖZKAYA 2 1 Professor of Pomology and Corresponding Author; University of
Pak. J. Boti., 37(3): 567-574, 2005. SELECTION STUDIES ON FIG IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REGION OF TURKEY A. AYTEKİN POLAT 1 AND MELİSA ÖZKAYA 2 1 Professor of Pomology and Corresponding Author; University of
College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology
 College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology Academic year: 2014-2015 Subject: Plant taxonomy Class: Third Grade Lecturer:Dr.Hadeel R.,Dr.Rana A.,Dr.Aseel M.,Dr.Zena K. Lecture: 6 ***Fruits:
College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology Academic year: 2014-2015 Subject: Plant taxonomy Class: Third Grade Lecturer:Dr.Hadeel R.,Dr.Rana A.,Dr.Aseel M.,Dr.Zena K. Lecture: 6 ***Fruits:
Fig. 3: Leaves of Corchorus aestuans L.
 4.1 Corchorus aestuans L. Synonym : Corchorus acutangulus Lam. Tamil Name : Perumpinnakkukkirai, Punaku, Peratti, kattuttuti Fig. 3: Leaves of Corchorus aestuans L. 4.1.1. Taxonomy Kingdom Subkingdom Super
4.1 Corchorus aestuans L. Synonym : Corchorus acutangulus Lam. Tamil Name : Perumpinnakkukkirai, Punaku, Peratti, kattuttuti Fig. 3: Leaves of Corchorus aestuans L. 4.1.1. Taxonomy Kingdom Subkingdom Super
GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS
 GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS ALSTROEMERIACEAE By Mark T. Strong (16 Jun 2017) A family of 4 genera and about 200 species that occur in Mexico, Central America, West
GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS ALSTROEMERIACEAE By Mark T. Strong (16 Jun 2017) A family of 4 genera and about 200 species that occur in Mexico, Central America, West
Fagaceae - beech family! Quercus alba white oak
 Fagaceae - beech family! Quercus alba white oak Sight ID characteristics Vegetative Features: Leaf: simple, alternate, deciduous, 4-9" long, pinnately 7-9 lobed, alternate, deciduous. Twig: red-brown to
Fagaceae - beech family! Quercus alba white oak Sight ID characteristics Vegetative Features: Leaf: simple, alternate, deciduous, 4-9" long, pinnately 7-9 lobed, alternate, deciduous. Twig: red-brown to
VALIDATION OF A SCIENTIFIC NAME FOR THE TAHITIAN LIME
 Grayum, M.H., B.E. Hammel, and Q. Jiménez Madrigal. 2012. Validation of a scientific name for the Tahitian lime. Phytoneuron 2012-101: 1 5. Published 26 November 2012. ISSN 2153 733X VALIDATION OF A SCIENTIFIC
Grayum, M.H., B.E. Hammel, and Q. Jiménez Madrigal. 2012. Validation of a scientific name for the Tahitian lime. Phytoneuron 2012-101: 1 5. Published 26 November 2012. ISSN 2153 733X VALIDATION OF A SCIENTIFIC
A new petrified pentalocular capsular fruit from the deccan intertrappean beds of Mohgaonkalan, M.P., India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 483-487 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.057
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 483-487 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.057
Comparison of the OTAKE and SATAKE Rice Mills Performance on Milled Rice Quality
 Research article erd Comparison of the OTAKE and SATAKE Rice Mills Performance on Milled Rice Quality MENG BUN* Email: mengbun99@gmail.com DYNA THENG LYHOUR HIN VARY VUN SAVATH SENG Department of Agricultural
Research article erd Comparison of the OTAKE and SATAKE Rice Mills Performance on Milled Rice Quality MENG BUN* Email: mengbun99@gmail.com DYNA THENG LYHOUR HIN VARY VUN SAVATH SENG Department of Agricultural
OXYLOBUS SUBGLABER KING & H. ROB. (ASTERACEAE: EUPATORIEAE) - ACCEPTANCE OF ITS SPECIFIC STATUS
 Turner, B.L. 2011. Oxylobus subglaber King & H. Rob. (Asteraceae: Eupatorieae) acceptance of its specific status. Phytoneuron 2011-35: 1 5. OXYLOBUS SUBGLABER KING & H. ROB. (ASTERACEAE: EUPATORIEAE) -
Turner, B.L. 2011. Oxylobus subglaber King & H. Rob. (Asteraceae: Eupatorieae) acceptance of its specific status. Phytoneuron 2011-35: 1 5. OXYLOBUS SUBGLABER KING & H. ROB. (ASTERACEAE: EUPATORIEAE) -
DEVELOPMENT AND SENSORY EVALUATION OF READY-TO- COOK IDLI MIX FROM BROWNTOP MILLET (Panicum ramosa)
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 2, 2016, 816 821 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DEVELOPMENT AND SENSORY EVALUATION OF READY-TO- COOK IDLI MIX FROM BROWNTOP MILLET
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 2, 2016, 816 821 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DEVELOPMENT AND SENSORY EVALUATION OF READY-TO- COOK IDLI MIX FROM BROWNTOP MILLET
Plantaginaceae plantain family
 Plantaginaceae plantain family The three genera comprising this herbaceous family, are typified by having simple leaves, either basal or cauline, and oppositely arranged. Their veins are mostly parallel.
Plantaginaceae plantain family The three genera comprising this herbaceous family, are typified by having simple leaves, either basal or cauline, and oppositely arranged. Their veins are mostly parallel.
Brief information about the species status of Utricularia cornigera Studnička.
 Brief information about the species status of Utricularia cornigera Studnička. MILOSLAV STUDNIČKA Liberec Botanic Gardens, Purkyňova 630/1, CZ-460 01 Liberec, botangarden@volny.cz Abstract: The carnivorous
Brief information about the species status of Utricularia cornigera Studnička. MILOSLAV STUDNIČKA Liberec Botanic Gardens, Purkyňova 630/1, CZ-460 01 Liberec, botangarden@volny.cz Abstract: The carnivorous
Systematic CoLLections of the Agricultural ResearchService
 USDA ~ United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service Systematic CoLLections of the Agricultural ResearchService Miscellaneous Publication Number 1343 August 1998 '" PotatoHerbarium
USDA ~ United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service Systematic CoLLections of the Agricultural ResearchService Miscellaneous Publication Number 1343 August 1998 '" PotatoHerbarium
Evaluate Characteristics of new cherry tomato varieties of Mahasarakham University
 International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2018 Vol. 14(7):1583-1588 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN: 2630-0613 (Print) 2630-0192 (Online) Evaluate Characteristics of new cherry
International Journal of Agricultural Technology 2018 Vol. 14(7):1583-1588 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN: 2630-0613 (Print) 2630-0192 (Online) Evaluate Characteristics of new cherry
Stevia reinana (Asteraceae: Eupatorieae), a new species from near Yecora, Sonora, Mexico
 Phytologia (August 2013) 95(3) 233 Stevia reinana (Asteraceae: Eupatorieae), a new species from near Yecora, Sonora, Mexico Billie L. Turner Plant Resources Center, The University of Texas, Austin TX 78712,
Phytologia (August 2013) 95(3) 233 Stevia reinana (Asteraceae: Eupatorieae), a new species from near Yecora, Sonora, Mexico Billie L. Turner Plant Resources Center, The University of Texas, Austin TX 78712,
Lea Manor Farm, Aldford, Chester,
 Lea Manor Farm, Aldford, Chester, Cheshire Palaeoenvironmental Assessment Oxford Archaeology North October 2014 Nick Higham Issue No: 2014-10/1575 OAN Job No: L10794 NGR: SJ 435 579 Lea Manor Farm, Aldford,
Lea Manor Farm, Aldford, Chester, Cheshire Palaeoenvironmental Assessment Oxford Archaeology North October 2014 Nick Higham Issue No: 2014-10/1575 OAN Job No: L10794 NGR: SJ 435 579 Lea Manor Farm, Aldford,
2. Materials and methods. 1. Introduction. Abstract
 Standardizing Peanut Roasting Process Of Peanut Butter Production N. K. Dhamsaniya and N. C. Patel Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh, Gujarat, India Abstract The current practice of roasting peanut
Standardizing Peanut Roasting Process Of Peanut Butter Production N. K. Dhamsaniya and N. C. Patel Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh, Gujarat, India Abstract The current practice of roasting peanut
Introduction Methods
 Introduction The Allium paradoxum, common name few flowered leek, is a wild garlic distributed in woodland areas largely in the East of Britain (Preston et al., 2002). In 1823 the A. paradoxum was brought
Introduction The Allium paradoxum, common name few flowered leek, is a wild garlic distributed in woodland areas largely in the East of Britain (Preston et al., 2002). In 1823 the A. paradoxum was brought
Biological Molecules Question Paper 4
 Biological Molecules Question Paper 4 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Biological Molecules Sub-Topic Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 4 Time Allowed: 56 minutes
Biological Molecules Question Paper 4 Level IGCSE Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Biological Molecules Sub-Topic Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 4 Time Allowed: 56 minutes
My research in Ecoinformatics and Biodiversity and my experiences as a PhD student in Aarhus
 My research in Ecoinformatics and Biodiversity and my experiences as a PhD student in Aarhus Saowalak Bunma Ecoinformatics and Biodiversity, Aarhus University Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Henrik Balslev Co-supervisor:
My research in Ecoinformatics and Biodiversity and my experiences as a PhD student in Aarhus Saowalak Bunma Ecoinformatics and Biodiversity, Aarhus University Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Henrik Balslev Co-supervisor:
Development of Value Added Products From Home-Grown Lychee
 Development of Value Added Products From Home-Grown Lychee S. Ahammed 1, M. M. H. Talukdar 1, M. S. Kamal 2 1 Department of Food Engineering and Technology Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology
Development of Value Added Products From Home-Grown Lychee S. Ahammed 1, M. M. H. Talukdar 1, M. S. Kamal 2 1 Department of Food Engineering and Technology Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology
Supplemental Data. Jeong et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Suppmemental Figure 1. Alignment of amino acid sequences of Glycine max JAG1 and its homeolog JAG2, At-JAG and NUBBIN from Arabidopsis thaliana, LYRATE from Solanum lycopersicum, and Zm- JAG from Zea mays.
Suppmemental Figure 1. Alignment of amino acid sequences of Glycine max JAG1 and its homeolog JAG2, At-JAG and NUBBIN from Arabidopsis thaliana, LYRATE from Solanum lycopersicum, and Zm- JAG from Zea mays.
SOME HISTO-ANATOMICAL ASPECTS CONCERNING THE LEAF STRUCTURE OF BASELLA ALBA AND BASELLA RUBRA
 Buletinul Grădinii Botanice Iaşi Tomul 12, 2004 95 SOME HISTO-ANATOMICAL ASPECTS CONCERNING THE LEAF STRUCTURE OF BASELLA ALBA AND BASELLA RUBRA GABRIELA BUSUIOC, CAMELIA IFRIM Abstract: We analyze the
Buletinul Grădinii Botanice Iaşi Tomul 12, 2004 95 SOME HISTO-ANATOMICAL ASPECTS CONCERNING THE LEAF STRUCTURE OF BASELLA ALBA AND BASELLA RUBRA GABRIELA BUSUIOC, CAMELIA IFRIM Abstract: We analyze the
FLOWERING BEHAVIORS OF TAIWAN AVOCADO CULTIVARS
 Proceedings V World Avocado Congress (Actas V Congreso Mundial del Aguacate) 2003. pp. 243-249. FLOWERING BEHAVIORS OF TAIWAN AVOCADO CULTIVARS Iou-Zen Chen 1, Ming-Te Lu 1, Tru-Ming Jong 2 and Tsu-Liang
Proceedings V World Avocado Congress (Actas V Congreso Mundial del Aguacate) 2003. pp. 243-249. FLOWERING BEHAVIORS OF TAIWAN AVOCADO CULTIVARS Iou-Zen Chen 1, Ming-Te Lu 1, Tru-Ming Jong 2 and Tsu-Liang
DIVERSIFICATION OF SUNFLOWER GERMPLASM FOR DIFFERENT ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTICS
 Scientific Papers. Series A. Agronomy, Vol. LVIII, 15 ISSN 2285-5785; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5793; ISSN Online 2285-57; ISSN-L 2285-5785 DIVERSIFICATION OF SUNFLOWER GERMPLASM FOR DIFFERENT ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT
Scientific Papers. Series A. Agronomy, Vol. LVIII, 15 ISSN 2285-5785; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5793; ISSN Online 2285-57; ISSN-L 2285-5785 DIVERSIFICATION OF SUNFLOWER GERMPLASM FOR DIFFERENT ECONOMICALLY IMPORTANT
Heyne ex Roth Combretaceae. Terminalia alata. laurel, Indian laurel
 LOCAL NAMES Burmese (taukyan); English (laurel,indian laurel); Hindi (sadora,piasal,usan,amari,karimaridi); Lao (Sino-Tibetan) (suak 'mon,suak kieng,suak dam); Nepali (saj,asna); Thai (hok fa); Trade name
LOCAL NAMES Burmese (taukyan); English (laurel,indian laurel); Hindi (sadora,piasal,usan,amari,karimaridi); Lao (Sino-Tibetan) (suak 'mon,suak kieng,suak dam); Nepali (saj,asna); Thai (hok fa); Trade name
Cotoneaster dammeri Schneid. (Rosaceae): A New Record to the Flora of Taiwan
 Taiwania, 50(1): 57-61, 2005 Cotoneaster dammeri Schneid. (Rosaceae): A New Record to the Flora of Taiwan Fu-Yuan Lu (1), Kun-Cheng Chang (1,3), Kwo-Shang Lai (2) (Manuscript received 30 December, 2004;
Taiwania, 50(1): 57-61, 2005 Cotoneaster dammeri Schneid. (Rosaceae): A New Record to the Flora of Taiwan Fu-Yuan Lu (1), Kun-Cheng Chang (1,3), Kwo-Shang Lai (2) (Manuscript received 30 December, 2004;
WINE RECOGNITION ANALYSIS BY USING DATA MINING
 9 th International Research/Expert Conference Trends in the Development of Machinery and Associated Technology TMT 2005, Antalya, Turkey, 26-30 September, 2005 WINE RECOGNITION ANALYSIS BY USING DATA MINING
9 th International Research/Expert Conference Trends in the Development of Machinery and Associated Technology TMT 2005, Antalya, Turkey, 26-30 September, 2005 WINE RECOGNITION ANALYSIS BY USING DATA MINING
Research on the potential alcohol of some local varieties and biotypes of wine grapes in Arad County
 Volume 17(1), 56-61, 2013 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Research on the potential alcohol of some local and biotypes of wine grapes in Arad County Dobrei
Volume 17(1), 56-61, 2013 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Research on the potential alcohol of some local and biotypes of wine grapes in Arad County Dobrei
G. Domina, P. A. Schäfer & A. Danin. Typification and taxonomic status of Portulaca macrantha (Portulacaceae) Introduction
 G. Domina, P. A. Schäfer & A. Danin Typification and taxonomic status of Portulaca macrantha (Portulacaceae) Abstract Domina, G., Schäfer, P. A. & Danin, A.: Typification and taxonomic status of Portulaca
G. Domina, P. A. Schäfer & A. Danin Typification and taxonomic status of Portulaca macrantha (Portulacaceae) Abstract Domina, G., Schäfer, P. A. & Danin, A.: Typification and taxonomic status of Portulaca
