4/6/18. A clinical and practical presentation of Celiac Disease. Objectives. History of Celiac disease. Lacey Yzeik, MS, RDN, LDN Clinical Dietitian
|
|
|
- Eugene Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A clinical and practical presentation of Celiac Disease Lacey Yzeik, MS, RDN, LDN Clinical Dietitian Objectives Define Celiac disease and the modern clinical practices (Type, pathophysiology, symptoms, screening, testing, diagnosis). Define Gluten and the Gluten Free Diet (sources, risks, products, lifestyle). Differentiate between gluten intolerance, gluten allergy and celiac disease. Relationship between celiac disease, Type 1 Diabetes and other autoimmune disorders. Discuss current research. History of Celiac disease First identified in 2 nd Century AD Aretaeus of Cappadocia, a Greek Physician, describes a malabsorptive diarrhea affecting children Referred to it as The Coeliac Affection AKA: Koiliakos (from the Greek word Koelia for abdomen) If the stomach be irretentive of the food and if it pass through undigested and crude and nothing ascends into the body, we call such person coeliacs Guandalini S. (2007). A Brief History of Celiac Disease. Impact: A Publication of the University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center. Volume 7 Issue 3. 1
2 History of Celiac disease Relationship of diet 19 th century Dr. Mathew Baillie published observations on a chronic diarrheal disorder of adults causing malnutrition and characterized by gas-distended abdomen Suggested advantage to living on rice 1888 Samuel Gee, leading pediatrician Documented improvement following the reduction/removal of certain foods from diet and the relapse after reintroduction Sidney Haas, an American pediatrician - Carbohydrates are the culprit in celiac disease and treats 10 children with a banana diet (eliminated bread, crackers, potatoes, all cereals) 1930 s William Dicke, a Dutch pediatrician - shows wheat and rye protein, not starch was the only culprit During WWII children with celiac disease improve when they lack access to wheat, further strengthening the relationship between wheat ingestion and celiac disease Guandalini S. (2007). A Brief History of Celiac Disease. Impact: A Publication of the University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center. Volume 7 Issue 3. History of Celiac disease 1950 s Margot Shiner, a pediatric gastroenterologist, develops biopsy technique to examine the small intestines to observe the pathologic changes in celiac disease 1964 The anti-gliadin antibody is discovered 1980 s Celiac disease associated with other autoimmune disease: Thyroid, diabetes, down s syndrome 1990 s The genetic markers HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 are identified and the antitransglutaminase antibodies are identified Guandalini S. (2007). A Brief History of Celiac Disease. Impact: A Publication of the University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center. Volume 7 Issue 3. Prevalence Estimated to affect 1 in 100 people worldwide 2.5 million Americans are undiagnosed Celiac Disease (2018, January) Retrieve from 2
3 Epidemiology Diagnosed vs. undiagnosed varies from country to country: One to two in Finland One to 10 in the US, Argentina and Germany Wide regional differences: Germany 0.3% compared to Finland 2.4% 1.5 to 2 times as high among women as men Affects all races and ethnic groups 0.2% in African Americans and 0.3% in Hispanics 1% in whites Affects all age groups 70% of new patients are diagnosed above the age of 20 years Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: What is Celiac disease (CD)? AKA: Celiac sprue, non-tropical sprue, gluten sensitive enteropathy Inappropriate T cell-mediated autoimmune response to the ingestion of gluten that affects the small intestine When T cells present the gluten peptide molecules, they produce cytokines that start the inflammatory and autoimmune reaction and stimulate plasma cells to produce antibodies to gliadin, transglutaminase and endomysium Characterized by a broad range of symptoms, a specific serum autoantibody response and variable damage to the small intestinal mucosa Simply: Ingestion of gluten damages the villi of the small intestines causing paralysis Nutrients cannot be absorbed properly leading to malnutrition Mahan K, Escott-Stump S. (2008). Krause s Food and Nutrition Therapy. St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier. Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: VISUAL DISPLAY OF CELIAC DAMAGE Figure 1: Celiac Disease. (Keough Institute, 2015) 3
4 Screening and Diagnosis Must be consuming gluten prior to testing Gluten Challenge (approximately 8 weeks) Screening tests: Widely used and most accurate: Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies (ttg-iga) Elevated levels Other tests included: IgA Endomysial Antibody (EMA) under 2 years old Total Serum IgA Deaminated gliadin peptide (DGP IgA and IgG) Genetic Testing Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Genetic Testing CD is highly genetic HLA DQ2 and DQ8 genes Carried by people with CD but also 25-30% of general population Not diagnostic, not indicative development of CD Increases risk of development: 3% with gene, 1% of general population First-degree family members with the same genotype as the family member with CD, have up to a 40% risk of developing CD. The overall risk of developing CD when the genotype is unknown is 7% to 20%. Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Who should be screened: 1. Patients with symptoms, signs or labs suggestive or malabsorption (chronic diarrhea with weight loss, steatorrhea, post prandial abdominal pain and bloating). 2. Patients with symptoms, signs or laboratory evidence for which CD is treatable cause. 3. Patients with first degree family member with confirmed diagnosis of CD who show signs or symptoms or are asymptomatic. 4. Patients who have elevated serum aminotransferase levels when no other etiology is found. 5. Patients with Type 1 Diabetes with digestive symptoms, signs or laboratory evidence suggestive of CD. Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5):
5 Diagnosis Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies (ttg-iga) Intestinal biopsy via Upper GI Confirms CD diagnosis An intestinal (duodenal) biopsy is considered the gold standard for diagnosis because it will tell you (1) if you have CD (2) if your symptoms improve on a gluten-free diet due to a placebo effect (you feel better because you think you should) (3) if you have a different gastrointestinal disorder or sensitivity which responds to change in your diet Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Intestinal Biopsy Characteristic histological findings in patients with CD: Increased density of intra-epithelial lymphocytes IELS (white blood cells found in the immune system) <25/100 epithelial cells is significant Crypt hyperplasia with a decreased villi/crypt ratio Blunted or atrophic villi shrinking or flattening due to gluten exposure Mononuclear cell infiltration in the lamina propria Epithelial changes, including structural abnormalities in epithelial cells May show scalloping and/or flattening of duodenal folds, fissuring over the folds, and a mosaic pattern of mucosa of folds A modified Marsh classification for villous abnormalities Use to assess the severity of villous atrophy Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Modified Marsh Classification of Gluten-induced smallintestinal damage Figure 2: Marsh Staging. (Celiac.org 2018) 5
6 Healthy vs Disease Endoscopy Normal Celiac Disease Figure 3: Endoscopic and biopsy findings in patients with and without celiac disease. (American Family Physicians. 2007) Algorithm for Diagnosing Celiac Disease Figure 4: Algorithm for Diagnosis Celiac Disease. (Bai J, Ciacci C, Corazza G, Fried M, Olano C. et al. 2016) Why is it difficult to diagnose? Wide spectrum of clinical characteristics, which can vary during a lifetime Symptoms may overlap with those of irritable bowel syndrome Patients may have mainly extra-intestinal manifestations, or even no symptoms There is a lack of awareness about CD among clinicians (and patients) There is a lack of diagnostic capabilities in some geographic areas Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367:
7 Types of Celiac Disease 1. Classical 2. Non-classical 3. Asymptomatic 4. Refractory Classical Celiac Disease Classic signs and symptoms of malabsorption Abdominal bloating and pain Chronic diarrhea Pale, foil smelling or fatty stool (steatorrhea) Weight loss Fatigue Irritability and behavioral issues Dental enamel defects of the permanent teeth Delayed growth and puberty (kids) Failure to thrive Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Non-Classical Celiac Disease Mild gastrointestinal symptoms without clear signs of malabsorption or seemingly unrelated symptoms Unexplained iron deficiency anemia Vitamin deficiency (B12 and folate) Fatigue Bone or joint pain Osteoporosis or osteopenia (bone loss) Depression or anxiety Peripheral neuropathy Seizures or migraines Missed menstrual period Infertility or recurrent miscarriages Canker sores inside the mouth Dermatitis herpetiformis (itchy skin rash) Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5):
8 Asymptomatic Celiac Disease Patients do not complain of any symptoms Still experience villous atrophy damage to their small intestine Tested due to high likelihood of CD: familial CD, autoimmune disease and associated conditions Positive results and better overall feeling/health after implementing gluten free diet Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Refractory Celiac Disease AKA: Refractory Sprue Definition: Persistent or recurrent symptoms of malabsorption and villous atrophy despite strict adherence to a gluten-free diet (GFD) for at least 6-12 months in the absence of other causes of non-responsive treated CD. Seen in adults (middle aged or elderly), never encountered in pediatric population Symptoms are severe and require additional therapeutic intervention besides GFD Classified as Type 1 or Type 2 Type 1: nutrition, adherence, pharmacologic Type 2: clinical response less certain and prognosis poor Rubio-Tapia A, Murray J. Classification and Management of Refractory Celiac Disease. Gut. 2010; 59: [PubMed: } Possible CD Symptoms Over 200 identified symptoms Abdominal bloating and pain Chronic diarrhea Vomiting Constipation Pale, foil smelling or fatty stool (steatorrhea) Weight loss Fatigue Irritability and behavioral issues Dental enamel defects of the permanent teeth Delayed growth and puberty Short stature Failure to thrive ADHD Unexplained iron deficiency anemia Fatigue Bone or joint pain Arthritis Osteoporosis or osteopenia (bone loss) Liver and biliary tract disorders (transaminitis, fatty liver, etc.) Depression or anxiety Peripheral neuropathy Seizures or migraines Missed menstrual period Infertility or recurrent miscarriages Canker sores inside the mouth **Digestive symptoms are more common in infants and children Dermatitis herpetiformis (itchy skin rash) 8
9 Autoimmune and other conditions associated with CD Autoimmune Thyroid Disease 26% Dermatitis Herpetiformis 25% Down s Syndrome 12% Liver disease 10% Peripheral neuropathy 10-12% Lymphocytic colitis 15-27% Type 1 Diabetes 6-10% Unexplained infertility 12% Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Celiac Disease and Type 1 Diabetes Link first established in the 1960 s Prevalence is about 6% in Type 1 Diabetes compared to 1% in general population Autoimmune mediated diseases with common susceptibility factors Genetics (HLA) Environmental Factors: introduction's of solids, breast-feeding, viral infections Gut microbiome More research is needed Recommendation: Type 1 Diabetes: get screened for CD CD: get screened for Type 1 Diabetes Crohn A, Sofia AM, Kupfer SS. Type 1 Diabetes and celiac disease: clinical overlap and new insights into disease pathogenesis. Current diabetes reports. 2014;14:517 Long term health effects of Undiagnosed or untreated CD Iron deficiency anemia Early onset osteoporosis or osteopenia Infertility and miscarriage Lactose intolerance Vitamin and mineral deficiencies Central and peripheral nervous system disorders Pancreatic insufficiency Intestinal lymphomas and other GI cancers (malignancies) Gall bladder malfunction Neurological manifestations including ataxia, epileptic seizures, dementia, migraine, neuropathy, myopathy, and multifocal leucoencephalopathy 9
10 Recommendations after diagnosis Follow-up with physician Monitor symptoms Laboratory test Full blood count, iron status, Vitamin B12, calcium, Vitamin D CD serology tests abnormal IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies indicate poor dietary adherence Duodenal biopsies controversial if labs are OK Healing takes anywhere between 6-24 months Every 2-3 years or if symptoms re-occur after strict adherence Counseling by a Registered Dietitian: Assessment of nutritional status and adherence to gluten-free diet Support groups (shown to aid in level of adherence) Psychological consult (if needed) Treatment There is only one: Lifelong adherence to a Gluten free diet (GFD) Implementation of Gluten free diet Removal of gluten will result in symptomatic, serologic, and histological remission in most Approx. 70% report improvement in symptoms within 2 weeks of starting the gluten free diet Growth and development in children return to normal with adherence to a gluten free diet. Strict adherence results in normalization of celiac disease-specific antibodies Villous changes can happen within months after starting gluten free diet. Complete resolution may take years and may not be achieved in some. 10
11 What is Gluten? Definition: rubbery protein mass that remains when wheat dough is washed to remove starch Storage protein of wheat, rye and barley Wheat peptides: gliadin and glutenin Rye peptides: secalinus Barley peptides: hordeins Used widely in food processing to give dough desired baking properties, add flavors and improve texture Limited nutritional value that can be replaced by other dietary proteins Wide range of gluten free substitutes are available Mahan K, Escott-Stump S. (2008). Krause s Food and Nutrition Therapy. St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier. Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): Gluten Containing Grains and their Derivatives Various forms of wheat and wheat derivatives such as : Rye Wheat, Wheat berries, Durum, Emmer, Semolina, Spelt, Farina, farro, graham, KAMUT Khorasan wheat, einkorn wheat Barley Triticale Malt Various forms: malted barley flour, malted milk or milkshakes, malt extract, malt syrup, malt flavoring, malt vinegar Brewer s Yeast Wheat starch can be processed to remove presence of gluten to below 20ppm to adhere to labeling law What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf Oats Oat protein has a different chemical structure Shown to be tolerated by most 70g (~2.5oz) per day for adults and 25g (0.88oz) per day for children If symptoms occur it is usually because: Intolerance to increase fiber, contamination with gluten, development of immune response to oat protein (like gluten) MUST be Gluten-free oats With Inclusion: Monitoring Anti-tTG antibody levels Biopsy 2-3 years Follow-up and monitoring by physician and dietitian What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf 11
12 Gluten Containing Foods Pastas, noodles Crackers, pancakes, waffle, breads, pastries, and baked goods Cereal and granola Corn flakes and rice cereals often contain Malt extract/flavoring Granola is often made with regular oats, not gluten free oats Breading and coating mixes Sauces, gravies and soups Anything made with traditional wheat flours Beer and malt beverages What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf Hidden Sources of Gluten Postage stamps/envelope glue Makeup Herbal or nutritional supplements Communion wafers Drugs and over the counter medications Vitamins and supplements Play-dough Ingredients of another name: Modified food starch, caramel color, dextrin, soy sauce, brewer s yeast, etc. Cross contamination toaster, eating out of the house, shared condiments, etc. What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf Gluten-Free Foods Fruit and vegetables Meat and poultry Fish and seafood Dairy Beans, legumes and nuts Grains/starch rice, corn, soy, potato, tapioca, quinoa, millet, sorghum, etc. May still contain gluten if processed, seasoned, boxed, canned, frozen, sauced, marinated, breaded, cooked in a shared facility, and so on. 12
13 Eating Gluten Free Read the ingredients label avoid all products with wheat, rye, barley, malt or triticale Wheat free doesn t mean gluten free Confirm the GF status with the product manufacturer or use an app (GF scanner) Look for the words or symbol: Gluten-Free Contains shared facility warning Educate yourself about cross-contamination Eating out of the house Toasters, cutting boards, flour sifters, shared containers, cooking surfaces, pizzerias, non-certified baked goods, fried foods (French fries and wings in the same fryer) Be cautious of hidden sources of gluten Find favorite products both GF specific and standard Pay attention to symptoms If not improving may need to re-evaluate and alter diet/habits Plan and pack food When it doubt, go without Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf Complications with Gluten-Free Diet Nutritional deficiencies: lack of fortified foods (bread, cereals) Iron, calcium, and folate Lack of fiber Time consuming (plan everything, pack food, etc.) Inconvenient Expensive Restrictive What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from Combined-Gluten-Free-Diet-and-Food-Label-Reading-Guide.pdf Gluten-Free Diet and T1D MAY improve glycemic control not always the case Untreated CD (intestinal damage) can increase risk of hypoglycemia due to malabsorption of sugars and nutrients Processed GF foods can be higher in sugar, lower fiber, higher fat Quick or delayed absorption leading to irregular or unexplained BG levels Crohn A, Sofia AM, Kupfer SS. Type 1 Diabetes and celiac disease: clinical overlap and new insights into disease pathogenesis. Current diabetes reports. 2014;14:517 13
14 Gluten Free Labeling Law enacted : August 5 th, 2013 Can only be labeled GF if a product has been processed to remove any gluten AND tests below 20ppm of gluten Under the Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004, if a food or an ingredient contains wheat or protein from wheat, the word wheat must be clearly stated on the food label If another term for wheat is used in an ingredient list, the word wheat must be included on the food label either in the ingredient list or in a separate Contains statement All packaged food products regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that are labeled on or after January 1, 2006, must be in compliance For foods regulated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (meat products, poultry products, egg products), only the common or usual name of ingredients is currently required Gluten-Free Food Labeling Final Rule. (2018, March). Retrieved from RegulatoryInformation/Allergens/ucm htm Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of (2018, March). Retrieved from GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryInformation/Allergens/ucm htm GLUTEN FREE PRODUCT SYMBOLS Figure 4: Gluten Free Product Symbols (Google Images, 2018) Gluten-Free Products Gluten properties are not present so they must be replaced. Highly processed: Usually higher fat Higher carbs and sugar, Low fiber Higher sodium Not fortified with vitamins and minerals Products are getting better 14
15 Gluten-free fads No real research to support except for celiac disease Common Fads: Weight loss Anti-inflammatory/joint health Aids in resolution of other disease symptoms (autism, MS) One bit of advice: Get tested while still eating gluten to first rule out CD, go to an allergist to see if you have an allergy, do an elimination diet Other Gluten Related disorders 1. Non-Celiac gluten sensitivity 2. Wheat allergy Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity AKA: Gluten Sensitivity, Gluten Intolerance, Non-Celiac Gluten Intolerance. Non-Celiac wheat sensitivity Some signs and symptoms of CD No atrophy or damage Negative for celiac disease Lack of tests and biomarkers Relies on patient description/reporting Improvement after removal of gluten per pt. reporting Questionable intolerance is it really gluten? Leanard M, Sapone A, Catassi C and Fasano, A. Celiac Disease and Nonceliac Gluten-sensitivity: A Review. JAMA. 2017:318(7): Fasano A. A clinical guide to Gluten-Related Disorders. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA
16 Wheat Allergy Defined as adverse Type-2 helper T cell-immunologic reaction to wheat proteins Presents soon after wheat ingestion Signs of anaphylaxis swelling or itching of mouth, throat or skin; nasal congestion; water eyes and difficulty breathing More common in children 2% and 9% in children 0.5% and 3% in adults Fasano A. A clinical guide to Gluten-Related Disorders. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA Differences among CD, Allergy, Sensitivity Figure 5: Fasano A, Catassi C (Celiac Disease 2012) Future Therapies Various companies looking at testing and treatment options Various options being tested Pre-Clinical, Phase I and Phase II studies Future Therapies for Celiac Disease. (2018, January) Retrieve from 16
17 In-Office Testing for CD in pediatric patients Study done in Spain using a Point-of-care test (POCT) 100 children 18 years of younger, all experiencing GI symptoms, none following gluten free diet 48 were diagnosed with CD prior to POCT POCT found to be 100% accurate in children under 10 POCT found to be about 90% accurate in children over 10 Accuracy of In-Office Testing For Celiac Disease in Pediatric Patients. (2018, February). Retrieved from blog/2018/02/accuracy-office-testing-celiac-disease-pediatric-patients/ New testing option Use of HLA-DQ-gluten tetrameter test 143 individuals with genotype HLA-DQ2 4 groups: confirmed CD following GF diet confirmed CD who were NOT following a GF diet CD ruled out but were following GF diet control group of 52 without CD and who were consuming gluten Able to predict presence of CD in 2/3 cases 100% accurate in predicting the ABSENCE of the disease Simply: quickly and easily eliminate possibility of CD for majority of patients, leaving only a small percentage to follow standard CD diagnosis path New Testing Option for Possible Celiac Disease Sufferers. (2018, February). Retrieved from new-testing-option-possible-celiac-disease-sufferers/ A few possible treatment options Immunogenx: IMGX003 A mixture of two gluten-specific enzymes that break down gluten proteins into small, harmless fragments. Administered as a supplement to a gluten-free diet for the potential treatment of celiac disease The only CD treatment that has been shown to lessen gluten-induced intestinal mucosal injury, as well as improve symptoms in clinical trials. Innovate Biopharmaceuticals: INN-202 (Larozetide Acetate) A tight junction regulator, which helps restore leaky or open junctions to a normal state (caused by ingestion of gluten in CD The reaction that causes intestinal villi damage Ingested prior to meal, Larazotide may help keep the tight junctions closed, thus reducing the intestinal-inflammatory process in response to gluten. Plus many more 17
18 Key Clinical Points Once considered a GI disorder mainly effecting children and Caucasians, CD is now known to affect different ages, races and ethnic groups and it may manifest without GI symptoms Measurements of the IgA-anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies is the preferred initial screening test for CD because of high sensitivity and specificity Diagnosis confirmed by upper endoscopy with duodenal biopsy May not be necessary in children with strong clinical and serological evidence Gluten causes celiac disease enteropathy, cornerstone treatment is a strict gluten free diet for life. Gluten sensitivity may occur in the absence of CD and a definitive diagnosis should be made before implementing lifelong gluten-free diet Several new testing and treatment options are being researched to improve treatment and the process of diagnosing and screening for CD. Helpful websites/resources Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Celiac Disease Nutrition Guide Websites: American Celiac Society Celiac Disease Foundation Celiac Sprue Association/USA Inc. Gluten Intolerance Group of North America Gluten-Free Apps Find me Gluten-Free Gluten-Free scanner References 1. Accuracy of In-Office Testing For Celiac Disease in Pediatric Patients. (2018, February). Retrieved from celiac.org/blog/2018/02/accuracy-office-testing-celiac-disease-pediatric-patients/ 2. Bai J, Ciacci C, Corazza G, Fried M, Olano C. et al. World Gastroenterology Organization Global Guidelines: Celiac Disease Coeliac Disease. (2018, March). (Image) Retrieved from 4. Celiac Disease. (2018, March) (image) Retrieved from 5. Celiac Disease? (2018, January) Retrieve from 6. Crohn A, Sofia AM, Kupfer SS. Type 1 Diabetes and celiac disease: clinical overlap and new insights into disease pathogenesis. Current diabetes reports. 2014;14: Fasano A. A clinical guide to Gluten-Related Disorders. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA Fasano A, Catassi C. Clinical Practice: Celiac Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;367: Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of (2018, March). Retrieved from ucm htm 10. Future Therapies for Celiac Disease. (2018, January) Retrieve from future-therapies-celiac-disease/ 18
19 References 11. Gluten Free Diet and Food Label Reading Guide. (2018, February). Retrieved from wp/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/combined-gluten-free-diet-and-food-label-reading-guide.pdf 12. Gluten-Free Food Labeling Final Rule. (2018, March). Retrieved from GuidanceRegulation/GuidanceDocumentsRegulatoryInformation/Allergens/ucm htm 13. Guandalini S. (2007). A Brief History of Celiac Disease. Impact: A Publication of the University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center. Volume 7 Issue Leanard M, Sapone A, Catassi C and Fasano, A. Celiac Disease and Nonceliac Gluten-sensitivity: A Review. JAMA. 2017:318(7): Mahan K, Escott-Stump S. (2008). Krause s Food and Nutrition Therapy. St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier. 16. New Testing Option for Possible Celiac Disease Sufferers. (2018, February). Retrieved from celiac.org/blog/2018/01/new-testing-option-possible-celiac-disease-sufferers/ 17. Rubio-Tapia A, Hill I, Kelly C, Calderwood A, Murray J. American College of Gastroenterology Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108(5): What is Gluten? (2018, March). Retrieved from 19
Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums
 Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums Alia Hasham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition What is the Preferred Initial Test
Primary Care Update January 26 & 27, 2017 Celiac Disease: Concepts & Conundrums Alia Hasham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition What is the Preferred Initial Test
November Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease. Inflammation in Celiac Disease
 November 2011 Gary Copland, MD Chair, Department of Pathology, Unity Hospital Laboratory Medical Director, AMC Crossroads Chaska and AMC Crossroads Dean Lakes Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease Celiac
November 2011 Gary Copland, MD Chair, Department of Pathology, Unity Hospital Laboratory Medical Director, AMC Crossroads Chaska and AMC Crossroads Dean Lakes Laboratory Testing for Celiac Disease Celiac
Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH
 Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH Case in point 42 year old woman with bloating, gas, intermittent diarrhea alternating with constipation, told she has IBS
Meredythe A. McNally, M.D. Gastroenterology Associates of Cleveland Beachwood, OH Case in point 42 year old woman with bloating, gas, intermittent diarrhea alternating with constipation, told she has IBS
Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth. Disclosures OBJECTIVES 18/09/2013. Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta. None Relevant
 Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta Disclosures None Relevant OBJECTIVES Understand the spectrum of gluten disorders Develop a diagnostic algorithm for gluten
Gluten Sensitivity Fact from Myth Justine Turner MD PhD University of Alberta Disclosures None Relevant OBJECTIVES Understand the spectrum of gluten disorders Develop a diagnostic algorithm for gluten
Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD. No financial disclosures
 Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD No financial disclosures Patient NP 21 year old male with chronic headaches for 6 years extensively evaluated and treated Acupuncturist suggests testing for celiac
Am I a Silly Yak? Laura Zakowski, MD No financial disclosures Patient NP 21 year old male with chronic headaches for 6 years extensively evaluated and treated Acupuncturist suggests testing for celiac
Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease
 Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Melissa R. Snyder, Ph.D. Co-Director, Antibody Immunology Laboratory Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic
Diagnostic Testing Algorithms for Celiac Disease HOT TOPIC / 2018 Presenter: Melissa R. Snyder, Ph.D. Co-Director, Antibody Immunology Laboratory Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic
Challenges in Celiac Disease. Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
 Challenges in Celiac Disease Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Disclosures None Overview Celiac disease Cases Celiac disease Inappropriate
Challenges in Celiac Disease Adam Stein, MD Director of Nutrition Support Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Disclosures None Overview Celiac disease Cases Celiac disease Inappropriate
What is celiac disease?
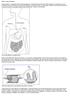 What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
CELIAC SPRUE. What Happens With Celiac Disease
 CELIAC SPRUE Celiac Disease (CD) is a lifelong, digestive disorder affecting children and adults. When people with CD eat foods that contain gluten, it creates an immune-mediated toxic reaction that causes
CELIAC SPRUE Celiac Disease (CD) is a lifelong, digestive disorder affecting children and adults. When people with CD eat foods that contain gluten, it creates an immune-mediated toxic reaction that causes
Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A
 Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A Akiko Natalie Tomonari MD akiko.tomonari@parkway.cn Gastroenterology Specialist ParkwayHealth Introduction (of myself) Born in Japan, Raised in Maryland, USA Graduated from
Gluten-Free China Gastro Q&A Akiko Natalie Tomonari MD akiko.tomonari@parkway.cn Gastroenterology Specialist ParkwayHealth Introduction (of myself) Born in Japan, Raised in Maryland, USA Graduated from
Spectrum of Gluten Disorders
 Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2018 Spectrum of Gluten Disorders Wheat allergy - prevalence 3-8 % (up to 3 years old) Non-celiac gluten
Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2018 Spectrum of Gluten Disorders Wheat allergy - prevalence 3-8 % (up to 3 years old) Non-celiac gluten
Diseases of the gastrointestinal system Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine
 Diseases of the gastrointestinal system 2018 Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine Small intestinal villi Small intestinal villi -Villi are tall, finger like mucosal projections, found
Diseases of the gastrointestinal system 2018 Dr H Awad Lecture 5: diseases of the small intestine Small intestinal villi Small intestinal villi -Villi are tall, finger like mucosal projections, found
Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key
 Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key Mary Twohig Chairperson Coeliac Society of Ireland What is Coeliac Disease? LIVING WITH COELIAC DISEASE Fact Not Fad Auto immune disease - the body
Living with Coeliac Disease Information & Support is key Mary Twohig Chairperson Coeliac Society of Ireland What is Coeliac Disease? LIVING WITH COELIAC DISEASE Fact Not Fad Auto immune disease - the body
Slides and Resources.
 Update on Celiac Disease Douglas L. Seidner, MD, AGAF, FACG Director, Center for Human Nutrition Vanderbilt University As revised/retold by Edward Saltzman, MD Tufts University None Disclosures This ppt
Update on Celiac Disease Douglas L. Seidner, MD, AGAF, FACG Director, Center for Human Nutrition Vanderbilt University As revised/retold by Edward Saltzman, MD Tufts University None Disclosures This ppt
Epidemiology. The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology:
 Epidemiology 1 1 Epidemiology The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology: A rare disorder typical of infancy Wide incidence fluctuates in space (1/400 Ireland to 1/10000 Denmark) and in time A disease of essentially
Epidemiology 1 1 Epidemiology The old Celiac Disease Epidemiology: A rare disorder typical of infancy Wide incidence fluctuates in space (1/400 Ireland to 1/10000 Denmark) and in time A disease of essentially
EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES. NGx-Gluten TM. Personalized Nutrition Report
 EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report Introduction Hello Caroline: Nutrigenomix is pleased to provide you with your NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report based on
EAT ACCORDING TO YOUR GENES NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report Introduction Hello Caroline: Nutrigenomix is pleased to provide you with your NGx-Gluten TM Personalized Nutrition Report based on
Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating
 Diagnosis 1 1 Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating Diagnosis of Celiac Disease mandates a strict gluten-free diet for life following the diet is not easy QOL implications Failure
Diagnosis 1 1 Diagnosis Diagnostic principles Confirm diagnosis before treating Diagnosis of Celiac Disease mandates a strict gluten-free diet for life following the diet is not easy QOL implications Failure
Celiac Disease. Definition & Facts. What is celiac disease? How common is celiac disease? Who is more likely to develop celiac disease?
 Celiac Disease Definition & Facts What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disorder that damages the small intestine. The disease is triggered by eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is
Celiac Disease Definition & Facts What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disorder that damages the small intestine. The disease is triggered by eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is
Celiac Disease 1/13/2016. Objectives. Question 1. Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD)
 Celiac Disease MONTE E. TROUTMAN, DO, FACOI JANUARY 6, 2016 Objectives Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD) Develop a knowledge of testing needed
Celiac Disease MONTE E. TROUTMAN, DO, FACOI JANUARY 6, 2016 Objectives Understand the plethora of conditions or symptoms that require testing for Celiac Disease (CD) Develop a knowledge of testing needed
Celiac Disease Ce. Celiac Disease. Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. baystatehealth.org/bch
 Celiac Disease Ce Celiac Disease Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition baystatehealth.org/bch Autoimmune Disease Inappropriate inflammation 1 1/21/15 Celiac Disease Classic
Celiac Disease Ce Celiac Disease Barry Z. Hirsch, M.D. Baystate Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition baystatehealth.org/bch Autoimmune Disease Inappropriate inflammation 1 1/21/15 Celiac Disease Classic
DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE. Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012
 DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012 OVERVIEW Definition Susceptibility The Changing Clinical Presentation Medical
DDW WRAP-UP 2012 CELIAC DISEASE Anju Sidhu MD University of Louisville Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 21, 2012 OVERVIEW Definition Susceptibility The Changing Clinical Presentation Medical
CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium
 CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium 5.1 Introduction Celiac disease is a chronic immune-mediated
CELIAC DISEASE - GENERAL AND LABORATORY ASPECTS Prof. Xavier Bossuyt, Ph.D. Laboratory Medicine, Immunology, University Hospital Leuven, Belgium 5.1 Introduction Celiac disease is a chronic immune-mediated
See Policy CPT CODE section below for any prior authorization requirements
 Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: LAB Policy No: 404 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 12/17; 12/18 1/1/19 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: All lines of business See Policy CPT CODE section below
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: LAB Policy No: 404 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 12/17; 12/18 1/1/19 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: All lines of business See Policy CPT CODE section below
Celiac Disease. Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. January 2015
 Celiac Disease Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition January 2015 Objectives Review the clinical presentation of celiac disease, including intestinal
Celiac Disease Sheryl Pfeil, MD The Ohio State University Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition January 2015 Objectives Review the clinical presentation of celiac disease, including intestinal
Celiac Disease. Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue
 Celiac Disease Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Celiac Disease Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Celiac Sprue Non-tropical Sprue Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Understanding Celiac Disease
 Understanding Celiac Disease Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State
Understanding Celiac Disease Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State
Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else
 Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else Ciarán P Kelly, MD Celiac Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Celiac Program Harvard Medical School Boston Gluten Free Diet (GFD) Very good but
Diet Isn t Working, We Need to Do Something Else Ciarán P Kelly, MD Celiac Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center & Celiac Program Harvard Medical School Boston Gluten Free Diet (GFD) Very good but
Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity?
 Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity? Mark T. DeMeo MD, FACG Rush University Med Center Case Study 35 y/o female Complains of diarrhea, bloating, arthralgias, and foggy mentation Cousin with celiac
Is It Celiac Disease or Gluten Sensitivity? Mark T. DeMeo MD, FACG Rush University Med Center Case Study 35 y/o female Complains of diarrhea, bloating, arthralgias, and foggy mentation Cousin with celiac
Disclosures GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 6/9/2015
 Disclosures CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 2015 Scientific Advisory Board: Alvine Pharmaceuticals, Alba Therapeutics, ImmunsanT Peter HR Green MD Columbia University New York, NY GLUTEN
Disclosures CELIAC DISEASE UPDATE OR GLUTEN RELATED DISORDERS 2015 Scientific Advisory Board: Alvine Pharmaceuticals, Alba Therapeutics, ImmunsanT Peter HR Green MD Columbia University New York, NY GLUTEN
Understanding Celiac Disease
 Understanding Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
Understanding Diagnostic Challenges Sheryl Pfeil, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
Coeliac disease catering gluten-free
 Coeliac disease catering gluten-free About Coeliac UK National Charity for people with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis Founded in 1968 and is the largest coeliac charity in the world Mission:
Coeliac disease catering gluten-free About Coeliac UK National Charity for people with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis Founded in 1968 and is the largest coeliac charity in the world Mission:
Celiac Disease. Etiology. Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles
 Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2017 Celiac Disease World s most common genetic food disorder Rising prevalence - over past 5 decades,
Food Intolerance:Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity-A Guide for Healthy Lifestyles Ellen Karlin 2017 Celiac Disease World s most common genetic food disorder Rising prevalence - over past 5 decades,
CELIAC DISEASE. Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD
 CELIAC DISEASE Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE? In short In this disease, exposure to gluten results in damge to the intestinal mucosa. Immune-mediated disorder Also known as
CELIAC DISEASE Molly Jennings Deb McCafferty MS, RD WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE? In short In this disease, exposure to gluten results in damge to the intestinal mucosa. Immune-mediated disorder Also known as
Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease
 Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease C. CUFFARI, MD, FRCPC, FACG, AGAF The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD. Main Points Celiac disease is not rare (1 in 100-300) It can present in many ways:
Presentation and Evaluation of Celiac Disease C. CUFFARI, MD, FRCPC, FACG, AGAF The Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD. Main Points Celiac disease is not rare (1 in 100-300) It can present in many ways:
Peter HR Green MD. Columbia University New York, NY
 CELIAC DISEASE, 2008 Peter HR Green MD Celiac Disease Center Columbia University New York, NY pg11@columbia.edu DIAGNOSIS OF CELIAC DISEASE Presence of consistent pathology and response to a gluten-free
CELIAC DISEASE, 2008 Peter HR Green MD Celiac Disease Center Columbia University New York, NY pg11@columbia.edu DIAGNOSIS OF CELIAC DISEASE Presence of consistent pathology and response to a gluten-free
Nicole Cerillo, RD Kogan Celiac Center
 Nicole Cerillo, RD Kogan Celiac Center The Kogan Celiac Center is designed to address the lifestyle changes associated with living well with celiac disease. Intended to be a complement to and an extension
Nicole Cerillo, RD Kogan Celiac Center The Kogan Celiac Center is designed to address the lifestyle changes associated with living well with celiac disease. Intended to be a complement to and an extension
BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE
 BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE Steffen Husby Hans Christian Andersen Children s Hospital Odense University Hospital DK-5000 Odense C, Denmark Agenda Background Algorithm Symptoms HLA Antibodies
BIOPSY AVOIDANCE IN CHILDREN: THE EVIDENCE Steffen Husby Hans Christian Andersen Children s Hospital Odense University Hospital DK-5000 Odense C, Denmark Agenda Background Algorithm Symptoms HLA Antibodies
Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity
 Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity Update: Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease A. Sapone, L.
Activation of Innate and not Adaptive Immune system in Gluten Sensitivity Update: Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease A. Sapone, L.
No relevant financial relationships to disclose
 CELIAC DISEASE Michael H. Piper, MD, FACP, FACG Gastroenterology Program Director Chief of Gastroenterology Providence-Providence Park Hospitals/St. John Macomb Hospital No relevant financial relationships
CELIAC DISEASE Michael H. Piper, MD, FACP, FACG Gastroenterology Program Director Chief of Gastroenterology Providence-Providence Park Hospitals/St. John Macomb Hospital No relevant financial relationships
Evidence Based Guideline
 Evidence Based Guideline Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: serologic_diagnosis_of_celiac_disease 4/2012 Description of Procedure
Evidence Based Guideline Serologic Diagnosis of Celiac Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: serologic_diagnosis_of_celiac_disease 4/2012 Description of Procedure
Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals
 Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals Jocelyn Silvester, MD PhD FRCPC April 27, 2017 Research grants Disclosures Canadian Institutes of Health Research
Follow-up Management of Patients with Celiac Disease: Resource for Health Professionals Jocelyn Silvester, MD PhD FRCPC April 27, 2017 Research grants Disclosures Canadian Institutes of Health Research
Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE
 Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE What is it? Auto-immune disorder affecting the small intestine. Triggered by gluten (protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats) Strong genetic link: 1 st
Coeliac Disease BE AWARE OF HOW YOU PREPARE What is it? Auto-immune disorder affecting the small intestine. Triggered by gluten (protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats) Strong genetic link: 1 st
Functional Medicine Is the application of alternative holistic measures to show people how to reverse thyroid conditions, endocrine issues, hormone
 Functional Medicine Is the application of alternative holistic measures to show people how to reverse thyroid conditions, endocrine issues, hormone issues, fibromyalgia, autoimmunity diseases and the like.
Functional Medicine Is the application of alternative holistic measures to show people how to reverse thyroid conditions, endocrine issues, hormone issues, fibromyalgia, autoimmunity diseases and the like.
Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease
 Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease Debby Kryszak 1, Henry McGill 2, Michelle Leland 2,, Alessio Fasano 1 1. Center for Celiac Research,
Baboons Affected by Hereditary Chronic Diarrhea as a Possible Non-Human Primate Model of Celiac Disease Debby Kryszak 1, Henry McGill 2, Michelle Leland 2,, Alessio Fasano 1 1. Center for Celiac Research,
Going Gluten Free: Off to a Fresh Start
 Going Gluten Free: www.neceliac.org Off to a Fresh Start The New England Celiac Organization does not endorse any of the products mentioned in this presentation March 5, 2015 Disclosures None Presentation
Going Gluten Free: www.neceliac.org Off to a Fresh Start The New England Celiac Organization does not endorse any of the products mentioned in this presentation March 5, 2015 Disclosures None Presentation
Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION
 Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION Food Intolerance & Expertise What is food intolerance? Common food intolerances Why are consumers claiming more food
Food Intolerance & Expertise SARAH KEOGH CONSULTANT DIETITIAN EATWELL FOOD & NUTRITION Food Intolerance & Expertise What is food intolerance? Common food intolerances Why are consumers claiming more food
What is celiac disease? How common is celiac disease? Who gets celiac disease?
 FAQ General What is celiac disease? How common is celiac disease? Who gets celiac disease? What are the symptoms of celiac disease? When does celiac disease usually develop? What is the difference between
FAQ General What is celiac disease? How common is celiac disease? Who gets celiac disease? What are the symptoms of celiac disease? When does celiac disease usually develop? What is the difference between
Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education
 Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education Objectives Following this program, participants will 1. List the clinical situations where celiac disease should be suspected 2. Distinguish between celiac
Alliance for Best Practice in Health Education Objectives Following this program, participants will 1. List the clinical situations where celiac disease should be suspected 2. Distinguish between celiac
What is celiac disease?
 Topic Page: Celiac Disease Summary Article: Celiac Disease from Health Reference Series: Gastrointestinal Diseases and Disorders Sourcebook Image from: Celiac disease When people with celiac disease...
Topic Page: Celiac Disease Summary Article: Celiac Disease from Health Reference Series: Gastrointestinal Diseases and Disorders Sourcebook Image from: Celiac disease When people with celiac disease...
Celiac Disease. Samuel Gee (1888) first described Celiac disease in On the Coeliac Affection Gluten sensitive entropathy Non-tropical sprue
 Celiac disease Mohammad Rostami Nejad, PhD Head of Celiac disease department Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Celiac Disease
Celiac disease Mohammad Rostami Nejad, PhD Head of Celiac disease department Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Celiac Disease
Gluten-Free Diet: General Information
 Gluten-Free Diet: General Information Gluten is a protein found in certain grains such as wheat, barley, and rye. Anyone with celiac disease must follow a gluten-free diet. Read the ingredient list on
Gluten-Free Diet: General Information Gluten is a protein found in certain grains such as wheat, barley, and rye. Anyone with celiac disease must follow a gluten-free diet. Read the ingredient list on
Understanding Food Intolerance and Food Allergy
 Understanding Food Intolerance and Food Allergy There are several different types of sensitivities or adverse reactions to foods. One type is known as a food intolerance ; an example is lactose intolerance.
Understanding Food Intolerance and Food Allergy There are several different types of sensitivities or adverse reactions to foods. One type is known as a food intolerance ; an example is lactose intolerance.
Larazotide Acetate. Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine
 Larazotide Acetate Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine Alternative/Integrative Approaches To The Gluten Free Diet
Larazotide Acetate Alessio Fasano, M.D. Mucosal Biology Research Center and Center for Celiac Research University of Maryland School of Medicine Alternative/Integrative Approaches To The Gluten Free Diet
Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum
 TEST NAME: Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity (Serum) Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum ANTIBODIES REFERENCE RESULT/UNIT INTERVAL NEG WEAK POS POSITIVE Tissue Transglutaminase (ttg) IgA 1420 U < 20.0 Tissue
TEST NAME: Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity (Serum) Celiac & Gluten Sensitivity; serum ANTIBODIES REFERENCE RESULT/UNIT INTERVAL NEG WEAK POS POSITIVE Tissue Transglutaminase (ttg) IgA 1420 U < 20.0 Tissue
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Clinical Utility of Serologic Testing for Celiac Disease in Ontario Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in April and October, 2010 December 2010 Background
OHTAC Recommendation Clinical Utility of Serologic Testing for Celiac Disease in Ontario Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in April and October, 2010 December 2010 Background
Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic
 How many celiac patients are affected? Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic 6.2% of all celiac patients have continuing diarrhea after 2 years on a gluten free diet 18% will develop constipation in this time
How many celiac patients are affected? Gluten Free and Still Symptomatic 6.2% of all celiac patients have continuing diarrhea after 2 years on a gluten free diet 18% will develop constipation in this time
Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE
 Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE Celiac disease definition, a hereditary digestive disorder involving intolerance to gluten, usually occurring in young children, characterized
Celiac Disease For Dummies By Sheila Crowe, Ian Blumer READ ONLINE Celiac disease definition, a hereditary digestive disorder involving intolerance to gluten, usually occurring in young children, characterized
Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital
 Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital Nothing to disclose Objectives Better understanding pathogenesis celiac disease Better understanding
Esperanza Garcia-Alvarez MD Medical Director Pediatric Celiac Center at Advocate Children s Hospital Nothing to disclose Objectives Better understanding pathogenesis celiac disease Better understanding
Sequoia Education Systems, Inc. 1
 Functional Medicine University s Functional Diagnostic Medicine Program Module 3 * FDMT 527C The Elimination Diet & The Modified Elimination Diet Wayne L. Sodano, D.C., D.A.B.C.I. & Ron Grisanti, D.C.,
Functional Medicine University s Functional Diagnostic Medicine Program Module 3 * FDMT 527C The Elimination Diet & The Modified Elimination Diet Wayne L. Sodano, D.C., D.A.B.C.I. & Ron Grisanti, D.C.,
GUIDANCE ON THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE
 GUIDANCE ON THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE These are the lactose intolerance guidelines and it is recommended that they are used in conjunction with the Cow s Milk Allergy guidance.
GUIDANCE ON THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE These are the lactose intolerance guidelines and it is recommended that they are used in conjunction with the Cow s Milk Allergy guidance.
'Every time I eat dairy foods I become ill, could I have a milk allergy.? '. Factors involved in the development of cow's milk allergy:
 'Every time I eat dairy foods I become ill, could I have a milk allergy.? '. Dairy allergy is relatively common in the community. The unpleasant symptoms some people experience after eating dairy foods
'Every time I eat dairy foods I become ill, could I have a milk allergy.? '. Dairy allergy is relatively common in the community. The unpleasant symptoms some people experience after eating dairy foods
Celiac Disease: An Overview and Personal
 Celiac Disease: An Overview and Personal Perspective By: Rie-ann Jansen BSN RN CGRN January 20, 2016 Celiac Disease an Overview and Personal Perspective OBJECTIVES: At the conclusion of this presentation,
Celiac Disease: An Overview and Personal Perspective By: Rie-ann Jansen BSN RN CGRN January 20, 2016 Celiac Disease an Overview and Personal Perspective OBJECTIVES: At the conclusion of this presentation,
Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition. Disclosures. Gluten Confusion 2/10/2014
 Disclosures Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition Author: South Beach Diet Gluten Solution Arthur Agatston Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Confusion What is gluten? What
Disclosures Gluten Sensitivity: Today s Most Under Recognized Medical Condition Author: South Beach Diet Gluten Solution Arthur Agatston Should you be Gluten Free? Gluten Confusion What is gluten? What
Gluten-Free Living: Helping People to Eat Safely, Healthfully and Happily
 Gluten-Free Living: Helping People to Eat Safely, Healthfully and Happily Rachel Begun, MS, RDN www.rachelbegun.com @RachelBegunRD What is Gluten? What is Gluten? Gluten is the collective term for a group
Gluten-Free Living: Helping People to Eat Safely, Healthfully and Happily Rachel Begun, MS, RDN www.rachelbegun.com @RachelBegunRD What is Gluten? What is Gluten? Gluten is the collective term for a group
A growing list of athletes claim that going gluten-free has enhanced their performance. What are the myths and truths of this trend?
 Grains of Truth A growing list of athletes claim that going gluten-free has enhanced their performance. What are the myths and truths of this trend? By Lisa Lutchka Lisa Lutchka, MS, RD, CSSD, CSCS, is
Grains of Truth A growing list of athletes claim that going gluten-free has enhanced their performance. What are the myths and truths of this trend? By Lisa Lutchka Lisa Lutchka, MS, RD, CSSD, CSCS, is
New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity
 New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Department of Medicine University of California, San Diego Page 1 1 low fat diet low carb diet gluten free diet low fat diet
New Insights on Gluten Sensitivity Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Department of Medicine University of California, San Diego Page 1 1 low fat diet low carb diet gluten free diet low fat diet
Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD.
 Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD..... Celiac Disease Autoimmune Diseases What are they? How do you get them? Why does it matter? Celiac Disease Autoimmune
Celiac Disease: The Quintessential Autoimmune Disease Ivor D. Hill, MB, ChB, MD..... Celiac Disease Autoimmune Diseases What are they? How do you get them? Why does it matter? Celiac Disease Autoimmune
The Gluten Syndrome. Why? Gluten Syndrome vs. Celiac Symptoms Testing Implementing Social Issues Caveats
 The Gluten Syndrome Why? Gluten Syndrome vs. Celiac Symptoms Testing Implementing Social Issues Caveats Why? What s wrong with today s wheat? Is it TODAY S Wheat??? Our grains have been x ray irradiated,
The Gluten Syndrome Why? Gluten Syndrome vs. Celiac Symptoms Testing Implementing Social Issues Caveats Why? What s wrong with today s wheat? Is it TODAY S Wheat??? Our grains have been x ray irradiated,
Seriously, CELIAC. talk.
 Seriously, Celiac Disease. talk. If you have celiac disease, your family members might have it too. Talk to them about your experience and how celiac disease runs in families. Tell them the facts. Urge
Seriously, Celiac Disease. talk. If you have celiac disease, your family members might have it too. Talk to them about your experience and how celiac disease runs in families. Tell them the facts. Urge
UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE
 UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE COELIAC DISEASE Coeliac Disease (CD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder generated by gluten intake in genetically susceptible individuals. When someone with coeliac disease
UNDERSTANDING COELIAC DISEASE COELIAC DISEASE Coeliac Disease (CD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder generated by gluten intake in genetically susceptible individuals. When someone with coeliac disease
DR.RAJIV SHARMA BOOK SERIES 2
 DR.RAJIV SHARMA BOOK SERIES 2 CELIAC DISEASE AND GLUTEN 1 DR.RAJIV SHARMA CELIAC DISEASE AND GLUTEN GLUTEN IS LIKE AIR. ITS EVERYWHERE. As long as you have a beating heart you cannot avoid Gluten. Gluten
DR.RAJIV SHARMA BOOK SERIES 2 CELIAC DISEASE AND GLUTEN 1 DR.RAJIV SHARMA CELIAC DISEASE AND GLUTEN GLUTEN IS LIKE AIR. ITS EVERYWHERE. As long as you have a beating heart you cannot avoid Gluten. Gluten
Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG
 1A: Upper Gut Celiac Disease: When to Look and How? Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, the successful learner should be able to: Identify the many groups of
1A: Upper Gut Celiac Disease: When to Look and How? Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FACG Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation, the successful learner should be able to: Identify the many groups of
5/27/2014 WEBINAR. Suggested CDR Learning Codes: 3000, 5000, 5110, 5220; Level 2
 WEBINAR Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research
WEBINAR Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research
Wheat, Gluten and Health. WheatFoods.org
 Wheat, Gluten and Health WheatFoods.org Wheat: The Latest Dietary Villain Close to 30% of US adults* are interested in cutting down or avoiding gluten in their diets. And, most are not doing so out of
Wheat, Gluten and Health WheatFoods.org Wheat: The Latest Dietary Villain Close to 30% of US adults* are interested in cutting down or avoiding gluten in their diets. And, most are not doing so out of
What is celiac disease?
 What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food. People who have celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten,
All about Gluten? Celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, wheat sensitivity, and other considerations
 College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences Dr. Raquel Garzon, RDN NMSU Cooperative Extension Services Nutrition and Wellness State Specialist All about Gluten? Celiac disease, gluten
College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences Dr. Raquel Garzon, RDN NMSU Cooperative Extension Services Nutrition and Wellness State Specialist All about Gluten? Celiac disease, gluten
Celiac disease Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Pseudomembranous colitis
 2017 / 2018 2nd semester/3rd practice Celiac disease Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Pseudomembranous colitis Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pathology CELIAC DISEASE = Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
2017 / 2018 2nd semester/3rd practice Celiac disease Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Pseudomembranous colitis Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pathology CELIAC DISEASE = Gluten-sensitive enteropathy
Celiac Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Celiac Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is celiac disease? Celiac disease
Celiac Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is celiac disease? Celiac disease
 Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic digestive disease in which individuals that consume the grain protein gluten experience damage (inflammation/irritation) to the lining of the small intestine (leading to
Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic digestive disease in which individuals that consume the grain protein gluten experience damage (inflammation/irritation) to the lining of the small intestine (leading to
 Created By: Nelson Narciso Keepwell@symaptico.ca National Product Education Consultant Body Plus Copyright Nelson Narciso 2009 What Is Celiac Disease Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic digestive disease
Created By: Nelson Narciso Keepwell@symaptico.ca National Product Education Consultant Body Plus Copyright Nelson Narciso 2009 What Is Celiac Disease Celiac disease (CD) is a chronic digestive disease
Food Allergies and Intolerances
 Food Allergies and Intolerances Training for foodservice staff D e v e l o p e d b y K a r l a W e s s l i n g K U M C D i e t e t i c I n t e r n M a y 2 0 1 3 Objectives Become familiar with food allergies
Food Allergies and Intolerances Training for foodservice staff D e v e l o p e d b y K a r l a W e s s l i n g K U M C D i e t e t i c I n t e r n M a y 2 0 1 3 Objectives Become familiar with food allergies
Immune mediated enteropathies. Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017
 Immune mediated enteropathies Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017 Definition/classification Systemic disease, mediated by antibodies, caracterised by histological changes of the small bowel Coeliac and noncoeliac
Immune mediated enteropathies Aurora Tatu Bern 26/07/2017 Definition/classification Systemic disease, mediated by antibodies, caracterised by histological changes of the small bowel Coeliac and noncoeliac
Gluten-Free Summer Meals
 Gluten-Free Summer Meals By Andrea Holwegner BSc, RD The May long weekend marks the beginning of summer and some of our favourite foods, like juicy barbecued burgers and picnics with fresh pasta salad
Gluten-Free Summer Meals By Andrea Holwegner BSc, RD The May long weekend marks the beginning of summer and some of our favourite foods, like juicy barbecued burgers and picnics with fresh pasta salad
2013 NASPGHAN FOUNDATION
 2 Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research Director,
2 Alessio Fasano, MD Visiting Professor of Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition MassGeneral Hospital for Children Director, Center for Celiac Research Director,
Coeliac disease. Do I have coeliac. disease? Diagnosis, monitoring & susceptibilty. Laboratory flowsheet included
 Laboratory flowsheet included I have coeliac disease. What monitoring tests should be performed? Do I have coeliac disease? Are either of our children susceptible to coeliac disease? Monitoring tests Diagnostic
Laboratory flowsheet included I have coeliac disease. What monitoring tests should be performed? Do I have coeliac disease? Are either of our children susceptible to coeliac disease? Monitoring tests Diagnostic
Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present
 Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present The Center for Celiac Research and Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland, U.S.A. 1 Celiac Disease Roadmap:
Celiac Disease: The Past and The Present The Center for Celiac Research and Mucosal Biology Research Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland, U.S.A. 1 Celiac Disease Roadmap:
Health Canada s Position on Gluten-Free Claims
 June 2012 Bureau of Chemical Safety, Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch 0 Table of Contents Background... 2 Regulatory Requirements for Gluten-Free Foods... 2 Recent advances in the knowledge
June 2012 Bureau of Chemical Safety, Food Directorate, Health Products and Food Branch 0 Table of Contents Background... 2 Regulatory Requirements for Gluten-Free Foods... 2 Recent advances in the knowledge
FOOD ALLERGY AND MEDICAL CONDITION ACTION PLAN
 CAMPUS DINING AT HOLY CROSS COLLEGE FOOD ALLERGY AND MEDICAL CONDITION ACTION PLAN Accommodating Individualized Dietary Requirements Including Food Allergies, Celiac Disease, Intolerances, Sensitivities,
CAMPUS DINING AT HOLY CROSS COLLEGE FOOD ALLERGY AND MEDICAL CONDITION ACTION PLAN Accommodating Individualized Dietary Requirements Including Food Allergies, Celiac Disease, Intolerances, Sensitivities,
Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients
 Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients Joe Murray The Mayo Clinic 1 DISCLOSURES Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Current Management of Celiac Disease and Identifying an Appropriate Patient Population(s) for Pharmacologic Therapies in Adult Patients Joe Murray The Mayo Clinic 1 DISCLOSURES Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Celiac Disease and the Gluten-Free Diet
 Celiac Disease and the Gluten-Free Diet Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder affecting 1 in every 133 not at risk Americans. The incidence is substantially higher in the at risk populations i. Celiac
Celiac Disease and the Gluten-Free Diet Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder affecting 1 in every 133 not at risk Americans. The incidence is substantially higher in the at risk populations i. Celiac
Celiac Disease Myths. Objectives. We Now Know. Classical Celiac Disease. A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease
 4:15 5:00pm Presenter Disclosure Information A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease SPEAKER Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS
4:15 5:00pm Presenter Disclosure Information A Clinical Update in Celiac Disease SPEAKER Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, MS
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older.
 Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD
 Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD Disclosures Dr. Anca Safta - none Angie Almond, M.Ed., RD, LDN invited attendee of The Gluten Free Summit sponsored by General Mills Wake Forest Baptist
Celiac Disease The Great Masquerader Anca M. Safta MD Disclosures Dr. Anca Safta - none Angie Almond, M.Ed., RD, LDN invited attendee of The Gluten Free Summit sponsored by General Mills Wake Forest Baptist
Understanding CELIAC DISEASE
 Understanding What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a bowel disorder caused by a reaction to ingested gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye and barley and contaminating all commercial-grade oats. If
Understanding What is celiac disease? Celiac disease is a bowel disorder caused by a reaction to ingested gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye and barley and contaminating all commercial-grade oats. If
What is coeliac disease?
 What is coeliac disease? How do you say coeliac? Seel ee ak. Coeliac disease means you can not eat food with gluten. Gluten is in wheat, rye, barley and oats. If you eat gluten, it will make you feel sick.
What is coeliac disease? How do you say coeliac? Seel ee ak. Coeliac disease means you can not eat food with gluten. Gluten is in wheat, rye, barley and oats. If you eat gluten, it will make you feel sick.
Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby!
 Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby! Celiac Disease (CD): How You ve Changed Increasing numbers of people have celiac disease Changing ways in which celiac disease presents A better understanding
Celiac Disease: You ve Come A Long Way Baby! Celiac Disease (CD): How You ve Changed Increasing numbers of people have celiac disease Changing ways in which celiac disease presents A better understanding
Celiac Disease. Detlef Schuppan HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL
 Celiac Disease Detlef Schuppan Falk Symposium in the Intestinal Tract: Pathogenesis and Treatment, Kiev,, Ukraine, May 15-16, 16, 2009 HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Celiac Disease Intolerance to gluten from wheat,
Celiac Disease Detlef Schuppan Falk Symposium in the Intestinal Tract: Pathogenesis and Treatment, Kiev,, Ukraine, May 15-16, 16, 2009 HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Celiac Disease Intolerance to gluten from wheat,
Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent. Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018
 Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018 Learning Objectives Identify risk factors for food allergies Identify clinical manifestations
Pediatric Food Allergies: Physician and Parent Robert Anderson MD Rachel Anderson Syracuse, NY March 3, 2018 Learning Objectives Identify risk factors for food allergies Identify clinical manifestations
Celiac Disease. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
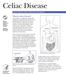 Celiac Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is celiac disease? Celiac disease
Celiac Disease National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is celiac disease? Celiac disease
ImuPro shows you the way to the right food for you. And your path for better health.
 Your personal ImuPro Screen + documents Sample ID: 33333 Dear, With this letter, you will receive the ImuPro result for your personal IgG food allergy test. This laboratory report contains your results
Your personal ImuPro Screen + documents Sample ID: 33333 Dear, With this letter, you will receive the ImuPro result for your personal IgG food allergy test. This laboratory report contains your results
