LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies?
|
|
|
- Samson Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
2 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
3 The Middle Colonies The Middle Colonies were also known as the Breadbasket Colonies. Their rich farm lands allowed significant amounts of food to be grown and raised. There was a longer growing season in these colonies compared to the New England colonies. This image is courtesy of pbworks.com.
4 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
5 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
6 Virginia (starting with Jamestown) was the first English colony in North America. Virginia was one of the southern colonies. This map of the Commonwealth of Virginia is courtesy of GreenwichMeanTime.com.
7 Massachusetts (starting with Plymouth) was the second English colony in North America. Massachusetts was one of the New England colonies. This image is courtesy msfrederick7th.wikispaces.com.
8 Eventually, 13 British colonies were located from New England to Florida. This map shows the Thirteen British colonies. Maine, shown in red, was not one of the 13 original colonies. Maine was part of the colony of Massachusetts. This image is courtesy of socialstudiesforkids.com.
9 The Middle Colonies were located between the northern colonies of New England and the Southern colonies. The Middle colonies included New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware. This image is courtesy of mce.k12tn.net.
10 The first Europeans to settle New York were the Dutch. Their colony was known as New Netherland. This is a1685 reprint of a 1650 map of New Netherland. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
11 In 1609 on a voyage for the Dutch government, Henry Hudson sailed up a beautiful, wide river, which is now named for him. Henry Hudson ascended the Hudson River in his ship the Half Moon. This image is David B. Scott s A School History of the United States, Harper & Brothers, 1883 and is courtesy of ushistoryimages.com.
12 Hudson was looking for a Northwest Passage-- a sea route to Asia. This map shows Henry Hudson s fourth attempt to find the Northwest Passage in This image is courtesy of ianchadwick.com.
13 However, the Hudson River was not a route that would lead him to the Northwest Passage. The Hudson River is a 315 mile long river that flows through eastern New York. This image is courtesy of freeextras.com.
14 On his fourth attempt to find the Northwest Passage, his men became discouraged and mutinied. Henry Hudson, his teenage son, John, and six crewmen who were either too sick to continue the journey, or who were loyal to Hudson were set adrift in a small boat. They were never heard from again. This painting is titled: Henry Hudson The Celebrated and Unfortunate Navigator, Abandoned by His Crew in Hudson s Bay the 11 th of June The painting is by Francis Davignon (1813- circa 1870) and is courtesy of the Mariners Museum.
15 But Hudson discovered two important bodies of water, both named after him: Hudson Bay This map shows significant bodies of water in North America, including Hudson Bay located in Canada. It is courtesy of graphicmaps.com.
16 and the Hudson River which is near the border of New York and New England. This image is a map of the Hudson River watershed and the Mohawk River. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
17 Although a small country, the Netherlands (Holland) had a large fleet of trading ships that sailed all over the world. This painting shows the Noord-Nieuwland in Table Bay, South Africa in This image is in the William Fehr Collection at the Castle of Good Hope in Cape Town, South Africa. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
18 In 1621 the Dutch West India Company set up a trading colony-- New Netherland-- in the area Hudson had explored. The Dutch West India Company was chartered by a group of Dutch merchants in It was modeled on the better-known Dutch East India Company. The charter gave the company a trade monopoly that included West Africa and the New World. The New World was an expansive term and meant virtually anywhere not covered by the Dutch East India Company s monopoly. New Amsterdam, for example, included not only present-day New York, but also Connecticut, New Jersey, and Delaware. The Dutch West India Company went bankrupt and folded in This image of the West India House in Amsterdam, Holland is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
19 The center of the new colony of New Netherland was New Amsterdam, located on the tip of Manhattan Island where the Hudson River enters New York Harbor. This image is titled New Amsterdam, recently called New York, and now retaken by the Netherlanders 24 Aug This image by the map maker Hugo Allard ( ) was created facing north circa It is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
20 Peter Minuit, the governor of the Dutch Colony paid the Native Americans $24 in beads, knives, and other trading goods in exchange for the island of Manhattan. This painting shows the event on May 24, 1626, when Dutch governor Peter Minuit purchased Manhattan Island for approximately $24. This image is courtesy of thereformedbroker.com.
21 Compared to the New England Colonies, New Netherland grew very slowly. This is a map of New Netherland and New England. It was created by Nicolaes Il Visscher ( ) circa This image is courtesy of the Library of Congress and Wikimedia Commons.
22 Some reasons that New Netherlands grew slowly was first, the Netherlands was a prosperous country, and many residents were not that anxious to leave. By the early 1600s, Amsterdam was the world's greatest trading center and an important center of manufacturing. The Dutch found ways to make profits from the almost constant wars of the 1600s. By 1650, the Dutch owned 50% of the merchant ships in Europe. This painting, The Dam Square in Amsterdam was created by Gerrit Adriaensz Berckheyde ( ) and is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
23 Second, the Dutch were tolerant of different religions. This painting is titled The Market Square at Haarlem with the St. Bavokerk Cathedral. This painting is by Gerrit Adriaensz Berckheyde ( ) and is courtesy of the University of North Carolina at Pembroke.
24 So many Dutch did not feel the need to leave their country and settle in North America. This image shows the fort at New Amsterdam on Manhattan Island. It was published in George Bancroft s History of the Colonization of the United States, New York: Julius Hart and Company, 1886.
25 The Dutch West India Company let it be known that it would welcome any Europeans to its colony, even those who fled New England. This image of New Amsterdam was published in George Bancroft s History of the Colonization of the United States, New York: Julius Hart and Company, 1886.
26 The company also gave huge tracts of Hudson riverfront land to anyone who would bring 50 new settlers to New Netherland. This image is titled New Amsterdam, the first Dutch settlement. This image was published in Alexander H. Stephens A Comprehensive and Popular History of the United States, Chattanooga: Hickman and Fowler, 1882.
27 New Sweden was located in what are now parts of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware. This is a postage stamp commemorating the founding of Wilmington, Delaware. It was created in 1938 by the United States Postal Service. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
28 The fur trade brought settlers to America from Sweden. They settled south of New Netherland and named their colony New Sweden. This is an engraving of fur trade in New Sweden in the early 1600s. Peter Lindestrom, was the artist. This image is from Geographia Americae with An Account of the Delaware Indians, Based on Surveys and Notes Made by Peter Lindestrom, published by The Swedish Colonial Society, 1925.
29 In 1638 the Swedes built Fort Christina in the Delaware River Valley at present-day Wilmington, Delaware. This image is a model of Fort Christina, located at the American Swedish Historical Museum in Philadelphia. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
30 The Dutch, however, saw New Sweden as a rival for trade. This map shows New Netherland in purple and its physical relationship to New Sweden which is shown in gray. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
31 New Netherland seized New Sweden and made it a part of its colony. This painting, titled The Landing of the Swedes, shows the first meeting between the Swedish settlers and Native Americans in The meeting took place along the Christina River in present-day Wilmington, Delaware. This painting by Stanley Massey Arthurs ( ) is courtesy of the University of Delaware.
32 The Swedish colonists who stayed on under Dutch rule brought the American colonies the important new skill of building log cabins. The typical log cabin was a small, one-room hut with one door and perhaps one or more small windows. The spaces between the logs were packed with mud to keep out the wind and cold. Because there were no nails the logs were fastened with notched ends, or with wooden pegs. The roof was made of overlapping rows of short boards. The floor was hard-packed clay. The window openings were covered with oiled paper to let in a little light. The room was heated by an open fireplace that also served as the cook stove. This image is courtesy of howstuffworks.com.
33 Back in England, the English were fighting among themselves in an event known as the English Civil War. This painting is titled Marston Moore. It was one of the battles of the English Civil War and took place in This painting was created by John Barker. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
34 In 1642 the Civil War began between King Charles I and the English Parliament, which was now dominated by the Puritans. This image, titled Battle of Naseby, is by an unknown artist. The victory of the Parliamentarian New Model Army, under Sir Thomas Fairfax and Oliver Cromwell, over the Royalist army, commanded by Prince Rupert, at the Battle of Naseby (June 14, 1645) marked the decisive turning point in the English Civil War. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
35 Parliament (Puritans) won, and King Charles I was beheaded. This is a painting of the execution of Charles I at the Palace of Whitehall on January 30, The inset pictures on the left show Charles as he appeared at his trial, and below, Charles walking to the scaffold. Those on the right show the moments immediately after the execution: the axe man holds up Charles's severed head while spectators hurry to dip their handkerchiefs in royal blood. This image is courtesy of the National Galleries of Scotland.
36 The Puritans ruled England for 11 years. This painting shows Puritan leader Oliver Cromwell dissolving the Long Parliament in The royalists took control of the government within two years of Cromwell s death. This painting was created by Andrew Gow in This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
37 The English tired of living under the strict rules of the Puritans, and the royalists returned to power under the popular King Charles II. This painting shows King Charles II of England in his coronation robes. This painting by John Michael Wright ( ) is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
38 The new king looked to expand his empire in North America. This is an image of the Duke of York s plan for New Amsterdam in This image is courtesy of the British Library.
39 Only New Netherland kept King Charles II from holding all of the Atlantic Coast from New England to Florida. This map shows English colonization during the early part of the 1600s in red, and the Dutch colonization during this time period in blue. Notice New Netherland was mostly located along the Hudson River and the western part of Long Island. This image is courtesy of the National Park Service.
40 The English king sent the English Navy under the command of his brother James, Duke of York, to seize the Dutch Colony. The King s brother did not personally go to America and to New Netherland. However, as Lord High Admiral he commanded the Royal Navy. His trusted subordinate, Richard Nicolls, commanded the English ships that arrived in New Amsterdam. James, the Duke of York, later became King James II of England and King James VI of Scotland. This image was painted in 1686 by Nicolas de Largilliere ( ). This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
41 One morning, the people of New Amsterdam were surprised to see English warships anchored in their harbor. New Netherlands Governor Peter Stuyvesant is standing with his wooden leg among residents of New Amsterdam in August, They are pleading with him not to open fire on the British warships waiting in the harbor to claim the territory for England. This image, The Fall of New Amsterdam, was created by Jean Leon Gerome Ferris ( ). This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
42 New Netherland surrendered to the English without a fight. This image shows Dutch soldiers, lead by Governor Peter Stuyvesant, leaving New Amsterdam after surrendering it to the English. There was not a castle like structure in New Amsterdam at this time. This image is courtesy of sonofthesouth.net.
43 New Amsterdam and New Netherland were renamed New York in honor of the king s brother, the Duke of York. This map of New York State is courtesy of geology.com.
44 New York became a proprietary colony, which was a colony awarded to one person or a group of people by the king. This image is titled The First Settlement of Albany. This image appeared in William Cullen Bryant s, and Sydney Howard Gay s A Popular History of the United States. New York: Charles Scribners' Sons, This image is courtesy of ushistoryimages.com.
45 However many English people did not want settle in New York because of the methods by which the proprietors controlled the government. Proprietors made money off the colonies by collecting yearly land fees from settlers who had purchased land within the colony. The Proprietors created their own courts and made their own laws. Proprietors could establish their own churches, town, and ports. English settlers complained about the mismanagement of the colony. This is an image of New Amsterdam from what is now New York Harbor. This image is from: Richard Markham, Richard. Colonial Days: Being Stories and Ballads for Young Patriots. New York: Dodd, Mead, & Company, 1881.
46 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
47 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
48 New Jersey is located south of New York and east of Pennsylvania. This image shows a county map of the State of New Jersey. This image is courtesy of geology.com.
49 The Duke of York gave some of his land, between the Hudson and Delaware Rivers, to two friends, Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret. The Delaware River separates New Jersey from Pennsylvania. The Hudson River separates the northeast section of New Jersey from New York. This image is courtesy of netstate.com.
50 At first there were two separate colonies known as East Jersey and West Jersey until 1702, when they became the royal colony of New Jersey. This map shows the boundary of East Jersey and West Jersey. This image is courtesy of westjerseyhistory.org.
51 Pennsylvania was one of the largest English colonies. This is a map of Pennsylvania and the northern colonies in the 1700s. This map is courtesy of mapsofpa.com.
52 Near New Jersey, William Penn founded a colony as home to his religious community, the Quakers. William Penn ( ) the English Quaker and colonialist, and founder of Pennsylvania, is standing on the left. He was in conference with colonists in This engraving is from Harper's Weekly in 1883.
53 Quakers opposed war and would not serve in the military. This image shows Quakers being led to execution in the Massachusetts Bay Colony in the 1600s. This image was first published in Benson J. Lossing s, Our Country. New York: Johnson and Bailey, 1895.
54 Because Quakers opposed war, they did not pay taxes. This image shows William Penn in prison at the age of 22. He had been arrested for attending Quaker meetings. This image was first published in D. H. Montgomery s The Beginner's American History. Boston: Ginn and Company, 1902.
55 The Quakers were the first religious group in the colonies to take a stand against slavery. In this scene from the anti-slavery novel Uncle Tom s Cabin, George and Eliza are at the home of some Quakers after they have escaped from the South. This image by Adolphe Jean-Baptiste Bayot ( ). This image is courtesy of Swarthmore College.
56 The Quakers believed that all people were equal, and that women could speak in church. This image depicts a woman speaking at a Quaker meeting in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in This image was produced by Hesse-Warburg, and is courtesy of the Library of Congress.
57 Penn named his colony Pennsylvania, which in Latin means Penn s Woods, to honor his father. Even today Pennsylvania is heavily wooded. Areas shown in green on this image are predominantly forests. Yellows and browns represent cultivated lands. Reds and purples are developed areas. This image is courtesy of the United States Geological Society.
58 To attract settlers, Penn distributed pamphlets that described the colony s beauty and richness. This image shows William Penn s 1681 pamphlet of Pennsylvania. This version was written in German. This image is courtesy of rootsweb.com.
59 Penn s plan of government was based on religious freedom and on popular support of the government. This image shows the first draft of William Penn s plan of government which he wrote in It is found in The Papers of William Penn, Volume Two ( ), published by the University of Pennsylvania in This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
60 One large group of settlers were German farmers fleeing religious wars in their part of Europe. This German barn with hex signs is on the Guy Hoffman Farm in Oley, Berks County, Pennsylvania. This image was taken in 1941 for the Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) and is courtesy of the Library of Congress.
61 They settled on the rich farmland along the Delaware and Susquehanna Rivers in tight-knit communities that kept alive their German customs. The Susquehanna River is 464 miles long. It flows through New York, Pennsylvania, and Maryland. This view was taken on May 31, 2009 from the Marie Antoinette Overlook along Route 6 in Asylum Township, Bradford County, Pennsylvania. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
62 These people became known as the Pennsylvania Dutch, from the word Deutsch, meaning German. This is a postcard showing the artistry of Johnny Ott, Hexologist at his Pennsylvania Dutch Folk Art Antique and Novelty Shop located between Allentown and Hamburg, Pennsylvania at Lenhartsville, Pennsylvania. This image was taken circa the 1950s-1970s and is courtesy of playle.com.
63 Delaware originally was a part of Pennsylvania. This map of Delaware is courtesy of greenwichmeantime.com.
64 One problem that landlocked Pennsylvania faced was the lack of seaports from which to ship its farm products. This image shows the port of Chester, Pennsylvania along the Delaware River. This image appeared in William Cullen Bryant s, and Sydney Howard Gay s A Popular History of the United States. New York: Charles Scribners' Sons, This image is courtesy of ushistoryimages.com.
65 William Penn received a grant from the Duke of York for three counties along the Delaware River that had once been part of New Sweden. This map shows Delaware and its three counties. This image is courtesy of datamil.udel.edu.
66 These three counties gave the colony access to the Atlantic Ocean and shipping to England. This image shows William Penn s arrival in America. This image is courtesy of the Hezekia Butterworth s (editor) Young Folks History of America. Boston: Estes and Lauriate, 1881.
67 The three counties later broke away to form the separate colony of Delaware. This image is titled Mill on the Brandywine, Delaware by John Rubens Smith ( ). This image was produced circa 1828 and is courtesy of the Library of Congress.
68 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
69 LEQ: What were the Middle Colonies? Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania The Middle colonies at first were smaller than the current Middle states. This map is courtesy of the trochwikispaces.com.
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies
 The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
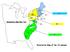 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
13 Colonies New England Colonies
 13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
Presenting... The 13 Colonies
 Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Early British Colonies
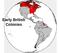 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root ( )
 Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Unit 8. The English Establish 13 Colonies
 Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date
 Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
The Middle Colonies. If YOU were there. How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? SECTION. What You Will Learn
 The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Thirteen Colonies
 The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Colonial Jeopardy. Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100. Puritans 200 Quakers 200 Native Americans 200
 Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
Wealth and resources. ! New beginning. ! Get out of debt. ! Escape political & religious persecution
 Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution
 S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages
 Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
The 13 Colonies. Religious, Political and Economic Foundations
 The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
Why did the European countries want to establish colonies in America?
 Why did the European countries want to establish colonies in America? 1. With the emergence of the new merchant class and cottage industry there was a need new sources of raw materials and markets for
Why did the European countries want to establish colonies in America? 1. With the emergence of the new merchant class and cottage industry there was a need new sources of raw materials and markets for
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies
 Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Two: Transplantations and Borderlands
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
The Southern Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 4
 The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon Lord Baltimore
 Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
~VANIA ..- ~ ~ ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2. Land Use. Religion in the Middle Colonies, I 775
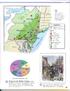 ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
U.S. History Project
 U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania
 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Roanoke 9/21/2017. The First English Colonies in North America. Roanoke & Jamestown. Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585
 The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
13 Colonies and Regions
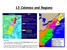 1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
The First English Settlements in America
 The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Names: Per. Frame: The Boston Tea Party
 Names: Per. Introduction Frame: The Boston Tea Party The Tea Tax A strange period of calm descended on Boston and the colonies after the Boston Massacre. Then the British made a huge mistake. The British
Names: Per. Introduction Frame: The Boston Tea Party The Tea Tax A strange period of calm descended on Boston and the colonies after the Boston Massacre. Then the British made a huge mistake. The British
John Smith The Starving Time
 The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
Binder Page Name Period. New Netherland: The Dutch in New York
 Binder Page Name Period New Netherland: The Dutch in New York Date The Dutch people are from the country known as the Netherlands (or sometimes as Holland). In the late 16th century, the Dutch economy
Binder Page Name Period New Netherland: The Dutch in New York Date The Dutch people are from the country known as the Netherlands (or sometimes as Holland). In the late 16th century, the Dutch economy
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
MIDDLE COLONIES GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES. MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) IMPORTANT DEMOCRATIC PRINCIPALS ESTABLISHED HERE
 NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
Colonial Encounters. Europeans Colonize the Americas
 Colonial Encounters Europeans Colonize the Americas Learning Objectives 1. Summarize the characteristics of the colonies of New Spain, New France, New Netherland, and Virginia. 2. Compare and contrast
Colonial Encounters Europeans Colonize the Americas Learning Objectives 1. Summarize the characteristics of the colonies of New Spain, New France, New Netherland, and Virginia. 2. Compare and contrast
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Causes of the American Revolution
 Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Freeze Frame: The Boston Tea Party
 Introduction Freeze Frame: The Boston Tea Party The Tea Tax A strange period of calm descended on Boston and the colonies after the Boston Massacre. Then the British made a huge mistake. The British wanted
Introduction Freeze Frame: The Boston Tea Party The Tea Tax A strange period of calm descended on Boston and the colonies after the Boston Massacre. Then the British made a huge mistake. The British wanted
Name: Date: Period: VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution. Filled In. Notes VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution 1
 Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
I want YOU to have a great summer and so does Uncle Sam:
 Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
April 28, 1788 Maryland Becomes a State
 April 28, 1788 Maryland Becomes a State Maryland is a state rich in history. It was first settled by Europeans in the 1600s. Maryland supported the American Revolution, even to the point of having a type
April 28, 1788 Maryland Becomes a State Maryland is a state rich in history. It was first settled by Europeans in the 1600s. Maryland supported the American Revolution, even to the point of having a type
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism. Key Concept 2.2.I C&D
 Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
Proclamation of 1763
 Proclamation of 1763 Sugar Act (1764) Angry crowd burning stamps used to indicate the paid sugar tax The Sugar Act, passed in 1764, was a tax passed specifically on molasses, the key ingredient in the
Proclamation of 1763 Sugar Act (1764) Angry crowd burning stamps used to indicate the paid sugar tax The Sugar Act, passed in 1764, was a tax passed specifically on molasses, the key ingredient in the
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary
 Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo
 Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
English Establish 13 Colonies Unit 2 Answers Elosuk
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
Acts What they did Writs of Assistance allowed customs (British) officers to search any location for smuggled goods (especially ships) Stamp Act
 Acts What they did Writs of Assistance allowed customs (British) officers to search any location for smuggled goods (especially ships) Stamp Act taxed all printed material; newspapers, pamphlets, playing
Acts What they did Writs of Assistance allowed customs (British) officers to search any location for smuggled goods (especially ships) Stamp Act taxed all printed material; newspapers, pamphlets, playing
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
WARM UP. 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday
 WARM UP 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday 2 Today you should do KEY EVENTS, TIME/DATE/ LOCATION, KEY EFFECTS (WHY) What are Push-Pull Factors? I. Push II.
WARM UP 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday 2 Today you should do KEY EVENTS, TIME/DATE/ LOCATION, KEY EFFECTS (WHY) What are Push-Pull Factors? I. Push II.
For Review Only. Contents. The World in the Year Columbus and His Big Plan The Big Voyage Land!... 12
 Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
The British in North America
 The British in North America hue you and your classmates are at the gym, the students in grade 7 come into your classroom. They sit at your desks and begin to use your school supplies. Soon, some grade
The British in North America hue you and your classmates are at the gym, the students in grade 7 come into your classroom. They sit at your desks and begin to use your school supplies. Soon, some grade
Exploration and Conquest of the New World
 Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Military Geography. MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York. Landforms and Elevations. Strategic Passages 10/28/2014.
 Military Geography MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Optional Exercise 6 (graded or extra credit) explores the interrelationship between the physical
Military Geography MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Optional Exercise 6 (graded or extra credit) explores the interrelationship between the physical
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
