Commerce and Religion
|
|
|
- Britton Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 New England: Commerce and Religion TERMS & NAMES Backcountry subsistence farming triangular trade Navigation Acts smuggling MAIN IDEA Fishing and trade contributed to the growth and prosperity of the New England Colonies. WHY IT MATTERS NOW Coastal cities in New England continue to engage in trade. ONE AMERICAN S STORY Peleg Folger, a New England sailor, was only 18 years old when he began whaling. Folger kept a journal that describes what whaling was like in the 1750s. In one journal entry, Folger explained what happened after whales were sighted and small boats were launched to pursue them. A VOICE FROM THE PAST So we row d about a mile and a Half from the [ship], and then a whale come up under us, & [smashed in] our boat... and threw us every man overboard [except] one. And we all came up and Got Hold of the Boat & Held to her until the other boat (which was a mile and half off) came up and took us in, all Safe, and not one man Hurt, which was remarkable, the boat being threshed to pieces very much. Peleg Folger, quoted in The Sea-Hunters When Folger and his mates did manage to kill a whale, they cut a hole in its head. Then a man got in up to his armpits and Dipt out [barrels] of clear oil. When the ship returned to port, this oil was sold to colonists, who used it as fuel in their lamps. Many settlers in the New England Colonies Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, and Rhode Island turned to the Atlantic Ocean to make a living. The majority of New Englanders, however, were farmers. Whales hunted by New Englanders, such as Peleg Folger, might weigh as much as 50 tons and be over 60 feet in length. Distinct Colonial Regions Develop Between 1700 and 1750, the population of England s colonies in North America doubled and then doubled again. At the start of the century, the colonial population stood at about 257,000. By 1750, more than 1,170,000 settlers called the English colonies home. By the 1700s, the colonies formed three distinct regions: the New England Colonies, the Middle Colonies, and the Southern Colonies. Another area was the Backcountry. It ran along the Appalachian Mountains through the far western part of the other regions. The Colonies Develop 109
2 Skillbuilder Answers 1. Hudson River 2. ships, fish, and whales Several factors made each colonial region distinct. Some of the most important were each region s climate, resources, and people. 1. New England had long winters and rocky soil. English settlers made up the largest group in the region s population. 2. The Middle Colonies had shorter winters and fertile soil. The region attracted immigrants from all over Europe. 3. The Southern Colonies had a warm climate and good soil. There, some settlers used enslaved Africans to work their plantations. 4. The Backcountry s climate and resources varied, depending on the latitude. Many Scots-Irish immigrants settled there. During the colonial era, the majority of people made their living by farming. However, the type of agriculture they practiced depended on the climate and resources in the region where they settled. The Farms and Towns of New England Life in New England was not easy. The growing season was short, and the soil was rocky. Most farmers practiced subsistence farming. That is, they produced just enough food for themselves and sometimes a little extra to trade in town. Most New England farmers lived near a town. This was because colonial officials usually did not sell scattered plots of land to individual Vocabulary latitude: the distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees The New England Colonies, W 45 N 75 W St. Lawrence R. Claimed by N.Y. and N.H. 70 W MAINE (part of MASS.) Cattle Fish Shipbuilding Timber Whaling Connecticut R. Falmouth NEW HAMPSHIRE Portsmouth Miles 200 Kilometers Lake Ontario CONNECTICUT Hud son R. ATLANTIC Salem Boston OCEAN Plymouth Newport MASSACHUSETTS 40 N New Haven RHODE ISLAND GEOGRAPHY SKILLBUILDER Interpreting Maps 1. Location All of the New England Colonies are to the east of what major river? 2. Region What ocean-related products was colonial New England known for? This New England meetinghouse is located in Sturbridge Village, Massachusetts. 110
3 A. Recognizing Effects How did the way land was sold in New England affect the way people lived? A. Possible Response Because colonial officials sold large plots of land to groups, many New Englanders lived together in towns. Background In 1742, over 16,000 people lived in Boston. farmers. Instead, they sold larger plots of land to groups of people often to the congregation of a Puritan church. A congregation then settled the town and divided the land among the members of its church. This pattern of settlement led New England towns to develop in a unique way. Usually, a cluster of farmhouses surrounded a green a central square where a meetinghouse was located and where public activities took place. Because people lived together in small towns, shopkeepers had enough customers to make a living. Also, if the townspeople needed a blacksmith or a carpenter, they could pool their money and hire one. Harvesting the Sea New England s rocky soil made farming difficult. In contrast, the Atlantic Ocean offered many economic opportunities. In one story, a group of settlers was standing on a hill overlooking the Atlantic. One of them pointed out to sea and exclaimed, There is a great pasture where our children s grandchildren will go for bread! The settler s prediction came true. Not far off New England s coast were some of the world s best fishing grounds. The Atlantic was filled with mackerel, halibut, cod, and many other types of fish. New England s forests provided everything needed to harvest these great pastures of fish. The wood cut from iron-hard oak trees made excellent ship hulls. Hundred-foot-tall white pines were ideal for masts. Shipbuilders used about 2,500 trees to produce just one ship! New England s fish and timber were among its most valuable articles of trade. Coastal cities like Boston, Salem, New Haven, and Newport grew rich as a result of shipbuilding, fishing, and trade. Atlantic Trade New England settlers engaged in three types of trade. First was the trade with other colonies. Second was the direct exchange of goods with Europe. The third type was the triangular trade. Triangular trade was the name given to a trading route with three stops. For example, a ship might leave New England with a cargo of rum Triangular Trade, 1750 New England Sugar, molasses Rum, iron There were several different triangular trade routes. Almost all involved the trade of enslaved Africans. In this example, slaves were sold in the West Indies. On other routes, they were sold in America. West Indies Middle Passage: Slaves, gold AFRICA 111
4 BLACKBEARD THE PIRATE Of all the pirates who attacked colonial ships, Blackbeard (shown below) was the most famous. He was a fearsome man known to stick matches in his hair to light up his face during battle. Blackbeard s pirate career finally came to an end in 1718, when Virginia s governor sent an expedition against him. Nearly half the expedition s men died in the key battle. Blackbeard himself did not fall until he had suffered nearly 25 wounds. Before sailing back to port, sailors cut off his head and put it on the front of their ship. and iron. In Africa, the captain would trade his cargo for slaves. Slaves then endured the horrible Middle Passage to the West Indies, where they were exchanged for sugar and molasses. Traders then took the sugar and molasses back to New England. There, colonists used the molasses to make rum, and the pattern started over. New England won enormous profits from trade. England wanted to make sure that it received part of those profits. So the English government began to pass the Navigation Acts in The Navigation Acts had four major provisions designed to ensure that England made money from its colonies trade. 1. All shipping had to be done in English ships or ships made in the English colonies. 2. Products such as tobacco, wood, and sugar could be sold only to England or its colonies. 3. European imports to the colonies had to pass through English ports. 4. English officials were to tax any colonial goods not shipped to England. But even after the passage of the Navigation Acts, England had trouble controlling colonial shipping. Merchants ignored the acts whenever possible. Smuggling importing or exporting goods illegally was common. England also had great difficulty preventing pirates like the legendary Blackbeard from interfering with colonial shipping. African Americans in New England There were few slaves in New England. Slavery simply was not economical in this region of small farms. Also, because the growing season was short, there was little work for slaves during the long winter months. Farmers could not afford to feed and house slaves who were not working. Even so, some New Englanders in larger towns and cities did own slaves. They worked as house servants, cooks, gardeners, and stable-hands. In the 1700s, slave owners seldom had enough room to house more than one or two slaves. Instead, more and more slave owners hired out their slaves to work on the docks or in shops or warehouses. Slave owners sometimes allowed their slaves to keep a portion of their wages. Occasionally, some enslaved persons were able to save enough to buy their freedom. In fact, New Background See Olaudah Equiano s descriptions of the Middle Passage on page 78. B. Analyzing Causes Why were there relatively few enslaved workers in New England? B. Possible Response Because of the small size of farms and the short growing season, slavery was not economical. 112 CHAPTER 4
5 C. Making Inferences Why might an interest in material things compete with the Puritan religion? C. Possible Response Many religions, including Puritanism, teach that too much concern with material things is wrong. Section 1. Terms & Names Explain the significance of: Backcountry subsistence farming triangular trade Navigation Acts smuggling 1 England was home to more free blacks than any other region. A free black man might become a merchant, sailor, printer, carpenter, or landowner. Still, white colonists did not treat free blacks as equals. Changes in Puritan Society The early 1700s saw many changes in New England society. One of the most important was the gradual decline of the Puritan religion. There were a number of reasons for this decline. One reason was that the drive for economic success competed with Puritan ideas. Many colonists, especially those who lived along the coast, seemed to care as much about business and material things as they did about religion. One observer had this complaint. A VOICE FROM THE PAST [Boston] is so conveniently Situated for Trade and the Genius of the people are so inclined to merchandise, that they seek no other Education for their children than writing and Arithmetick. An observer in 1713, quoted in A History of American Life Another reason for the decline of the Puritan religion was the increasing competition from other religious groups. Baptists and Anglicans established churches in Massachusetts and Connecticut, where Puritans had once been the most powerful group. Political changes also weakened the Puritan community. In 1691, a new royal charter for Massachusetts guaranteed religious freedom for all Protestants, not just Puritans. The new charter also granted the vote based on property ownership instead of church membership. This change put an end to the Puritan churches ability to control elections. To the south of New England were the Middle Colonies, which developed in quite different ways as the next section shows. Assessment 2. Taking Notes Use a chart like the one shown to record how New Englanders prospered from the Atlantic Ocean. Economic Activity Benefits to Colonists How did some profit illegally from the ocean? 3. Main Ideas a. How did most people in New England earn a living? b. Why did England pass the Navigation Acts? c. What factors led to the decline of the Puritan religion in New England? [Boston] is so conveniently Situated for Trade. An observer in Critical Thinking Making Inferences What advantages might there be in living near other people in small towns, such as those in New England? THINK ABOUT the transportation options available to colonists why shopkeepers chose to open businesses in towns ACTIVITY OPTIONS ART TECHNOLOGY Read more about whaling. Make a mobile that shows different kinds of whales or plan a multimedia presentation on whaling today. The Colonies Develop 113
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter
 Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
Chapter 4-1 Notes. The Economy of the Colonies
 Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
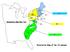 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
The 13 Colonies. Religious, Political and Economic Foundations
 The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
Wealth and resources. ! New beginning. ! Get out of debt. ! Escape political & religious persecution
 Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
New England Colonies Economy
 New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
MIDDLE COLONIES GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES. MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) IMPORTANT DEMOCRATIC PRINCIPALS ESTABLISHED HERE
 NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
13 Colonies New England Colonies
 13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
Early British Colonies
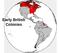 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies
 Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon Lord Baltimore
 Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
The Southern Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 4
 The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
John Smith The Starving Time
 The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
~VANIA ..- ~ ~ ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2. Land Use. Religion in the Middle Colonies, I 775
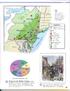 ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
Unit 8. The English Establish 13 Colonies
 Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
The Middle Colonies. If YOU were there. How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? SECTION. What You Will Learn
 The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary
 Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
Monday, September 11
 th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
The Thirteen Colonies
 The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies
 The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Necessary Components
 Mercantilism Introduction Dominated European thought promoted economic regulation by governments Increase power of state at the expense of other nations Favorable climate for the growth of capitalism Objectives
Mercantilism Introduction Dominated European thought promoted economic regulation by governments Increase power of state at the expense of other nations Favorable climate for the growth of capitalism Objectives
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism. Key Concept 2.2.I C&D
 Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
13 Colonies and Regions
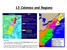 1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
U.S. History Project
 U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
Unit 4: Colonies. https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html. https://quizlet.com/class/ / Colonial America 1
 Unit 4: Colonies https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ Colonial America 1 Colonization of America As the European explorers claimed the vast lands of North
Unit 4: Colonies https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ Colonial America 1 Colonization of America As the European explorers claimed the vast lands of North
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d. Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary
 The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
Tea and Wars. Summary. Contents. Rob Waring. Level 3-8. Before Reading Think Ahead During Reading Comprehension... 5
 Level 3-8 Tea and Wars Rob Waring Summary This book is about wars that were caused by the import and export of tea by the British. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During Reading
Level 3-8 Tea and Wars Rob Waring Summary This book is about wars that were caused by the import and export of tea by the British. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During Reading
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date
 Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root ( )
 Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
English Establish 13 Colonies Unit 2 Answers Elosuk
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
Students will be assessed through answering of the questions that follow as well as with a reading quiz.
 Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
I want YOU to have a great summer and so does Uncle Sam:
 Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
The 13 English Colonies
 The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy g a t i o n A c t s The Colonies Raw Materials Manufactured Goods Every society has RESOURCES. NATURAL RESOURCES HUMAN RESOURCES CAPITAL RESOURCES which
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy g a t i o n A c t s The Colonies Raw Materials Manufactured Goods Every society has RESOURCES. NATURAL RESOURCES HUMAN RESOURCES CAPITAL RESOURCES which
JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT
 JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT 1. Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? for wealth and power 2. What did the English think they would find in America? silver and
JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT 1. Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? for wealth and power 2. What did the English think they would find in America? silver and
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
The Louisiana Purchase
 The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
Assessment: China Develops a New Economy
 Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Text 1: The Boston Tea Party. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 3: Taking Up Arms
 Text 1: The Boston Tea Party Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 3: Taking Up Arms OBJECTIVES Identify the point of the Tea Act of 1773 Discuss the reasons the colonists object to the Tea Act Explain
Text 1: The Boston Tea Party Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 3: Taking Up Arms OBJECTIVES Identify the point of the Tea Act of 1773 Discuss the reasons the colonists object to the Tea Act Explain
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES
 Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES Objectives: o We will examine the colonial economies of the various colonies by their geographic region. o We will examine the technology that the various colonists developed.
Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES Objectives: o We will examine the colonial economies of the various colonies by their geographic region. o We will examine the technology that the various colonists developed.
Topic of Discussion Colonial Economics
 I Introduction A. What does Economics mean and where did it come from? B. Economic issues have concerned human beings for millennia, ever since the early primitive hunters considered how to distribute
I Introduction A. What does Economics mean and where did it come from? B. Economic issues have concerned human beings for millennia, ever since the early primitive hunters considered how to distribute
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania
 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
Colonial Jeopardy. Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100. Puritans 200 Quakers 200 Native Americans 200
 Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages
 Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
Presenting... The 13 Colonies
 Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers
 A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution
 S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
Explorers.notebook. October 14, 2014
 Spices and silk The History!...Royalty and merchants of Europe desired silk and spices from Asia...Merchants sent out caravans(groups of traders) to buy desired products silk road. Nov 3 11:32 AM...Problem********two
Spices and silk The History!...Royalty and merchants of Europe desired silk and spices from Asia...Merchants sent out caravans(groups of traders) to buy desired products silk road. Nov 3 11:32 AM...Problem********two
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Factors Leading to The American Revolution. Part III
 Factors Leading to The American Revolution Part III BELLWORK How is the push and pull of the relationship between Parliament and the colonies establishing colonial independence rather that loyalty to England?
Factors Leading to The American Revolution Part III BELLWORK How is the push and pull of the relationship between Parliament and the colonies establishing colonial independence rather that loyalty to England?
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
