SOCIAL SCIENCES 2º ESO UNIT 8: THE AGE OF EXPLORATION
|
|
|
- Constance Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOCIAL SCIENCES 2º ESO UNIT 8: THE AGE OF EXPLORATION THE KNOWN WORLD IN THE FIFTEENTH CENTURY In the Middle Ages European trade with the East (silk, spices and other luxury goods) was done along the famous Silk Road from Constantinople overland through Asia this was the route taken by Marco Polo in the 13th century. However, in 1459 the Turks conquered Constantinople and the traditional trade routes were cut. The mid to late 15th century in Europe introduced a great age of travel and exchange, called the Age of Exploration and Discovery. In the two centuries that followed, European merchants and explorers travelled the world in search of goods and lands. Also, the wish to spread Christianity to newly-discovered territories should not be underestimated. The Portuguese and the Spanish were the earliest adventurers, soon followed by the British, French and Dutch; they wanted to acquire new lands and riches in their quest to become the supreme European power. It was a time of global expansion. The interest in travelling beyond their own territory came from a change in thinking by Europeans. They began looking beyond their familiar lands and thought about the benefits of new commerce and territorial expansion. New ideas and philosophies were circulating in Europe and a curiosity for new knowledge and new experience along with the promise of enormous riches persuaded monarchs of Europe, like Ferdinand and Isabella of Spain, to finance exploration. Famous European explorers that contributed to the changing world map included Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, Vasco da Gama, Sir Francis Drake, Sir Walter Raleigh, Hernando Cortes, John Cabot and Samuel de Champlain, among others. 1
2 The Portuguese were the first to send explorers to the East in search of spices and goods unavailable in Europe and as a result of this effort became a great sea-faring empire based on trade. Bartholomeu Dias and Vasco da Gama were the first Portuguese explorers to round Africa s Cape of Good Hope in voyages that returned to Portugal loaded with foreign goods. Vasco da Gama, c , Portuguese navigator, the first European to journey by sea to India. His historic voyage ( ) was made at the order of King Manuel I. With four ships, he rounded the Cape of Good Hope, passed the easternmost point reached by Bartholomeu Dias in 1488, continued up the east coast of Africa to Malindi, and sailed across the Indian Ocean to Calicut. This voyage opened up a way for Europe to reach the wealth of the Indies, and out of it grew the Portuguese Empire. Immediately Portugal gained great riches from the spice trade. Gama dictated the instructions for Cabral's voyage ( ) to India, and in 1502 he himself led a fleet of 20 ships on his second India voyage. With this force he attempted to establish Portuguese power in Indian waters and tried to secure the submission of a number of chiefs on the African coast. He was harsh in his methods and was not as good an administrator as many of the Portuguese captains who later went to the East. In 1524 he was sent back to India as viceroy, but he died soon after his arrival. Gama's voyage is the subject of Camoens's epic poem The Lusiads. FIND OUT: 1. Write a short biography of Prince Henry the Navigator. The following website may help: 2. What is a caravel? Find out basic information about the caravel and its importance in this age of exploration What is an astrolabe? 4. What is a compass? A CARAVEL 2
3 The Spanish also began explorations in their search for new lands that gave them a different form of wealth through the discovery and mining of gold and silver. The Spanish also were looking for routes to the East but discovered, instead, the lands of the New World. Christopher Columbus was commissioned by the Spanish monarchs, Isabella I and Ferdinand V, to sail East to India via a Western route. He discovered for the Europeans many of the Caribbean islands and on one of his last voyages touched Panama. Later Spanish explorers such as Vasco Nunez de Balboa, Ferdinand Magellan, Hernando de Soto, Juan Ponce de Leon and Francisco Pizarro would expand upon his initial explorations and eventually open the lands of North and South America to Spanish colonization. FIND OUT ABOUT CHRISTOPHER COLUMBUS AND DO THE QUIZ ON THIS BBC WEBSITE: Posthumous portrait of Christopher Columbus The French, the British and the Dutch entered the race of discovery soon afterwards and began an era of expansion and conquest, as well as commerce, unseen in the West since the fall of the Roman Empire. English exploration began with the explorers John and Sebastian Cabot, financed by Henry VII, and they discovered the islands of Labrador and Newfoundland in Following these discoveries and during the age of Queen Elizabeth I, explorers such as Sir Walter Raleigh, Sir Francis Drake, and Sir John Hawkins, among others, embarked on their voyages of discovery. They were referred to as pirates and privateers by their enemies. French explorers also made their contribution to the Age of Discovery, including Jacques Cartier, Jacques Marquette and Samuel de Champlain. The age of exploration and discovery transformed the continental powers of Europe into world powers. With the exploration of these newly discovered lands, the European powers accumulated wealth, economic influence and global aspirations through the subjugation of the native people and the exploitation of the natural resources of their colonial territories. Source: blog.aurorahistoryboutique.com/tag/vasco-nunez-de-balboa/ 3
4 Explorers Timeline EXPLORERS TIMELINE 1265: Marco Polo begins his exploration of China and Asia 1432: Early Portuguese navigators discovered the Azores 1456: The Cape Verde islands are explored by Portuguese 1470: The Portuguese begin 15 years of African exploration 1488: Bartholomeu Dias of Portugal first European to sail from the Iberian Peninsula to the south of Africa. 1492: The Discovery of America by Christopher Columbus 1496: First European settlement in the "New World" established at Hispaniola by Columbus 1497: John Cabot and his son Sebastian were the first Europeans to discover Canada, landing on the coast of Newfoundland 1498: Vasco da Gama sails around the Cape of Good Hope and reaches India 1500: Vicente Pinzon and Juan Dias de Solis discovered Brazil before Cabral 1500: Cabral credited with discovering Brazil Explorers Timeline : Amerigo Vespucci explores the coast of South America 1510: Portuguese ships conquer Goa in India which begins the era of Portuguese dominance in southern Asia 1513: Vasco Nunez de Balboa explores the Pacific coast of Panama and discovers Pacific Ocean 1513: Juan Ponce de Leon discovers Florida 1518: Juan de Grijalava discovers Mexico 1519: Ferdinand Magellan is the first to go around the world 1519: Hernando Cortez kidnaps Aztec Emperor Montezuma and loots the Aztec gold 1524: Giovanni Verrazano, an Italian explorer employed by France, sails along the coast of North America and discovers New York Bay 1524: Hernando Cortes conquers the Honduras 1528: Alvar Cabeza de Vaca explores Texas, Arizona and New Mexico 1530: The Portuguese begin their colonization of Brazil 1531: Francisco Pizarro conquers Peru 1532: Francisco Pizarro invades and loots the Incan Empire 1536: Pedro de Mendoza explores Paraguay 1540: Discovery of the Grand Canyon by Garcia Lopez de Cardenas Explorers Timeline : Portuguese establish port of Macau on Chinese coast 1562: John Hawkins sails to Africa - profits from the slave trade 1564: Spain begins conquest of the Philippines 1572: Spain establishes Manila 1576:The Englishman Sir Martin Frobisher begins three attempts to find the Northwest Passage and gold sailing to Baffin Bay and into the Hudson Strait 1577: Sir Francis Drake circumnavigates the world - December to September : Sir Walter Raleigh establishes the Roanoke colony 1593: Sir Richard Hawkins travels to the South Pacific 1595: Sir Walter Raleigh seeks golden city of El Dorado in South America 4
5 WEBSITES: Very good thinkquest on Great Explorers: Short video clip about the Age of Discovery: Age of Exploration The Mariners Museum: READING SIR FRANCIS DRAKE (see the website of the National Maritime Museum) Sir Francis Drake ( ) Francis Drake was an experienced and daring seafarer. Among many adventures, the famous voyage, his successful circumnavigation of the world between 1577 and 1580 ensured that he would be one of the best remembered figures of Tudor England. In his own lifetime, he was thought of with mixed feelings, both at home and abroad. Some English people regarded him as a hero, but he was distrusted by others, who saw him as having risen above his station. Although he was feared and hated by the Spanish, he was also regarded by some with secret admiration. What was England like at the time of Drake? Miniature of Drake, age 42 by Nicholas Hilliard in 1581 already doing. For most of Drake s life, Queen Elizabeth I ruled the country. It was a time when England was growing in population, power and wealth, and was also becoming more outward looking. New markets and colonies were needed, so that English produce, especially wool, could be traded. England was also keen to gain from the huge profits to be made from the New World of the Americas and from the Eastern spice trade, as Spain and Portugal were It was a time when religion was extremely important to people, especially the question of whether England was to be a Protestant or a Catholic country. Arguments about religion and trade meant that England was at war with Spain for much of Drake s life. Where was Francis Drake born? Francis Drake was born in Tavistock, Devon, sometime between 1541 and What sort of family did he come from? A very ordinary family, certainly not rich or powerful. His family was a devoutly religious one. When Francis was still a small boy, the Catholic Queen Mary came to the throne, and there were religious disturbances in Devon. The family left, and moved to Chatham in Kent where for a time they lived on an old, laid-up ship. Drake s father became a Protestant preacher. These early experiences had a profound effect on the young Francis. The Protestant religion was to be one of the most important things to him throughout his life. On his voyage around the world he led religious services on board ship twice a day. When did Drake first go to sea? He first started going to sea while living in Chatham, at the age of 12 or 13. He was an apprentice on a small trading ship which was left to him when the master died. After selling this ship, he returned to Devon and sailed with his relative John Hawkins. Together, Hawkins and Drake made the first English slaving voyages, bringing African slaves to work in the New World. 5
6 Did Francis Drake marry? Yes. He married twice. When he was 25 he married Mary Newman, who died in He married again in His second wife, Elizabeth Sydenham, came from a much more influential family. He did not have children with either of his wives. What was Drake looking for on his voyages? Spanish ships, sailing back from their new conquests in South America were extremely attractive, as they were laden with silver. Drake attacked such ships, and if he was successful in capturing them, took their treasure for himself and for his queen. He also raided Spanish and Portuguese ports in the 'New World' and the Atlantic. On Drake's voyage to Panama in , he was helped by cimarrones. The cimarrones were former slaves, who had escaped to live in the forest and mountains as outlaws. Many were prepared to help the English as they blamed the Spanish for their position. One cimarrone in particular, named Diego, became especially close to Drake, accompanying him to England and later around the world. How long did it take Drake to sail around the world? The circumnavigation took three years, from 1577 to Originally, the voyage was probably planned as a raid on Spanish ships and ports. Five ships, manned by 164 seamen, left Plymouth, with Drake himself sailing in the Pelican. Almost all the crew thought they were heading for the Mediterranean. After reaching America, Drake was worried that his ships might get separated from each other, so he gave orders for two of them to be destroyed. Then the Marigold was lost, with all her crew and the Elizabeth turned back and sailed home. By October 1578, as the company started up the western coast of South America, there were just 58 left, all on the Pelican. Drake renamed his ship the Golden Hind. What did Drake find out on his voyage around the world? A merchant ship, c.1580 Drake's voyage helped to give a more accurate picture of the true geography of the world. During the course of the voyage, Drake discovered that Tierra del Fuego, the land seen to the south of the Magellan Strait, was not part of a southern continent as had been believed previously, but an archipelago, or group of islands. Francis Fletcher, the chaplain on Drake's ship described it like this: In passing along we plainly discovered that same Terra Australis to be no continent, but broken islands and large passages amongst them... This meant that if the American continent was not connected to a southern continent, the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans met at Cape Horn. It should be possible to sail ships around the bottom of South America, south of Tierra. This was the Cape Horn route, eventually discovered in As Drake sailed further up the coast, he plundered Spanish ports in Chile and Peru and captured treasure ships. His biggest prize was the Cacafuego. Drake sailed further north along the coast of the Americas than any other European until then. On the way he landed in what is now California, naming it Nova Albion (New England) and claiming it for his queen. He then continued across the Pacific to the East Indies, or Spice Islands. Six tons of cloves were loaded onto the ship. Later, half had to be tossed into the sea in order to free the ship from a reef. His route through the East Indies lay along the uncharted southern coast of Java. Here Drake discovered that Java was an island, not connected to a southern continent as the Dutch believed. Drake returned from his voyage around the world with the little Golden Hind packed full of spices from the Indies, and plundered Spanish silver and treasure. The good health of the surviving members of his crew was a remarkable achievement in itself. This was in marked contrast to the dreadful condition of those who had accompanied Magellan on the first circumnavigation of the world 50 years earlier. How was Drake helped by others? During the Tudor period, it was important that each explorer built on the experience of those who had gone before. Portugal and Spain had been involved in ocean exploration long before England. Francis Drake obviously recognised this, as he made use of this previous knowledge and expertise by seizing the Portuguese pilot Nuna da Silva to guide him on his passage to Brazil and the east coast of America. In the Pacific, he seized the charts of two Spanish pilots bound for the Philippines. He already had a chart of the world made in Portugal, and three books on navigation. 6
7 How did the Queen treat Drake when he returned after his three-year voyage? Queen Elizabeth dined on board the Golden Hind at Deptford, on the River Thames. Afterwards, she knighted him so that for the rest of his life he was known as Sir Francis Drake. The king of Spain was insulted by the Queen's reward to Drake. His voyage may have been triumphant to the English, but to the Spanish it was highly destructive. Was the circumnavigation the end of Sir Francis Drake's career at sea? No. Drake was involved in several other battles with the Spanish. In 1585 he and more than 1000 men attacked Santiago in the Cape Verde islands. As no treasure was found, he ordered the town to be burnt down. In 1586 he captured Santo Domingo in Hispaniola (Santo Domingo is now the capital of the Dominican Republic). One of his most famous attacks was on Cadiz and Corunna in This incident is sometimes known as the 'singeing of the King of Spain's beard.' In a daring raid, between 20 and 30 ships were sunk or captured. Perhaps of even more importance though, was the destruction of supplies intended for King Philip's planned Spanish Armada. The attack delayed the Armada and the Spanish were short of some important supplies for their fleet. They were also forced to use unseasoned wood for barrels, as Drake had destroyed the seasoned wood. Later on this resulted in the rotting of many of their precious stocks of food for the Armada crews. What was Drake's role in the battles against the Spanish Armada? Sir Francis Drake was very active in the Armada battles of One of the most famous incidents involving Drake was when the Spanish flagship, the Rosario, collided with another ship. It lost its mast and became separated from the rest of the Spanish fleet. Drake captured it, even though he had been given the job of tracking the Armada with his stern lantern alight to guide all the other English ships following him. The prize of the Rosario must have been too difficult to resist. The ship was taken without a single shot being fired, still with the royal money chest on board. How did Sir Francis Drake die? He died at sea on his final voyage, off the coast of Panama, in Nombre de Dios Bay. He had been suffering from dysentery for several days and in January 1596 he finally died. His body was placed inside a lead casket and he was then slipped overboard. Two other ships, his most recent prizes, were sunk near his body. He was about 54 years old. Why is he still remembered today? His circumnavigation led to an increased knowledge of the geography of the world, particularly to a more accurate understanding of the 'southern continent'. As a navigator his skills put him in the same rank as Columbus. His claim of California, or Nova Albion, for England led directly to later plans to send people to live in colonies in America. Sir Francis Drake Questions 1. What was his famous voyage? 2. Which English monarch reigned for most of his life? 3. What was his religion? 4. What was his first trade? 5. Which country s ships did he attack? Why? 6. How long did it take him to sail round the world? 7. What geographical fact did he discover? 8. Which two Spanish ports did he attack? 9. In which famous sea battle did he participate in 1588? 10. How did he die? 7
8 ACTIVITIES THE AGE OF EXPLORATION EUROPEAN NATIONS P. S. E. H.. F.. V.de G. C C. Sir F..D. Voyage: Voyage: Voyage: REASONS 1. In Territorial expansion 3. Commerce (e.g. ) 4. Spreading Christianity 5. Spirit of adventure 6. New technology TECHNOLOGY Type of ship:.. 8
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Bartholomeu Dias. Cape of Good Hope 1487
 Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration
 The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Exploration & Colonization. Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School
 Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
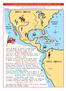 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY ( )
 THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1
 Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
For Review Only. Contents. The World in the Year Columbus and His Big Plan The Big Voyage Land!... 12
 Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
The Age of Exploration ( )
 The Age of Exploration (1450-1700) "Long live the high and mighty sovereigns of Castile! Thus in their names do I take possession of these seas and regions; and if any other prince, whether Christian or
The Age of Exploration (1450-1700) "Long live the high and mighty sovereigns of Castile! Thus in their names do I take possession of these seas and regions; and if any other prince, whether Christian or
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
Quiz Show. Chapter 2 European Explorers
 Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Why the New World. Crusades $ Spices Silks Marco Polo s Book Columbus Woops New World
 Why the New World Crusades $ Spices Silks Marco Polo s Book Columbus Woops New World Early America (discovery) Credited with the discovery of the New World in 1492. Looking for a new way to get to the
Why the New World Crusades $ Spices Silks Marco Polo s Book Columbus Woops New World Early America (discovery) Credited with the discovery of the New World in 1492. Looking for a new way to get to the
Exploration and Conquest of the New World
 Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Wrote book on his explorations that generated excitement in others to develop trade with China and India 1st European who traveled the length of Asia
 AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
Chapter Two. When Worlds Collide
 Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Spain Builds an Empire
 Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe.
 I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
Age of Discovery. SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
 Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA
 SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
First Visitors From Europe
 THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
The World of the 1400s. What Was Going On?
 The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
CAUSES OF EXPLORATION. READING and ASSIGNMENT. Read the excerpt below. Use the reading to complete the section of the graphic organizer.
 Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Exploration and Settlement Unit 2
 Exploration and Settlement Unit 2 Big Idea Cooperation (act of working together) and Conflict (disagreement or fight) Cultural differences and competition for land led to conflicts among different groups
Exploration and Settlement Unit 2 Big Idea Cooperation (act of working together) and Conflict (disagreement or fight) Cultural differences and competition for land led to conflicts among different groups
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
Renaissance Economics. The Age of Discovery
 Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Age of Exploration. Use the text to answer each question below.
 Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
The First English Settlements in America
 The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
New Ideas, New Nations
 New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
European Explorers. Student- Something to write with Colored Pencils Textbook Procedures. Day 1
 European Explorers USI. 4a- The student will demonstrate knowledge of European exploration in North America and West Africa by describing the motivations, obstacles, and accomplishments of the Spanish,
European Explorers USI. 4a- The student will demonstrate knowledge of European exploration in North America and West Africa by describing the motivations, obstacles, and accomplishments of the Spanish,
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration. Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture
 Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Reference: Vasco da Gama. Vasco da Gama
 Reference: http://www.ducksters.com/biography/explorers/vasco_da_gama.php Biography >> Explorers for Kids Vasco da Gama Vasco da Gama Occupation: Explorer Born: 1460 in Sines, Portugal Died: December 23,
Reference: http://www.ducksters.com/biography/explorers/vasco_da_gama.php Biography >> Explorers for Kids Vasco da Gama Vasco da Gama Occupation: Explorer Born: 1460 in Sines, Portugal Died: December 23,
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Additional Explorations:
 In The Beginning: Prince Henry The Navigator set up a school to teach geography, science and math so that Portugal could train sailors to find a water route to Asia. In 1486 Bartolomeu Dias became the
In The Beginning: Prince Henry The Navigator set up a school to teach geography, science and math so that Portugal could train sailors to find a water route to Asia. In 1486 Bartolomeu Dias became the
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL. AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS
 CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
Age of Discovery The New World. The New World II. Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Cantino World Map, 1502
 Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Age of Discovery 1450-1550 Cantino World Map, 1502 Allegorical engraving showing Vespucci "disembarking in the New World." The background shows the often-illustrated cannibal
Age of Discovery (Ren-Ref) Age of Discovery 1450-1550 Cantino World Map, 1502 Allegorical engraving showing Vespucci "disembarking in the New World." The background shows the often-illustrated cannibal
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
The Golden Age of Francis Drake and Piracy: The Conflict and the Compromise of the Anglo-Spanish War
 The Golden Age of Francis Drake and Piracy: The Conflict and the Compromise of the Anglo-Spanish War Luke Christopher Gotwald Senior Division Historical Paper Paper Length: 1065 Words The Golden Age of
The Golden Age of Francis Drake and Piracy: The Conflict and the Compromise of the Anglo-Spanish War Luke Christopher Gotwald Senior Division Historical Paper Paper Length: 1065 Words The Golden Age of
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s
 European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Name Period Test Date September Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East Asia? (page 122)
 Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations
 Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter One: The Meeting of Cultures
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02)
 American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
Spanish Conquistadors
 Exploration In 1492 Spain had just won a 700 year war with the Moors. Because they had the largest navy in the world, they were considered the most powerful nation. They were so powerful there was a saying
Exploration In 1492 Spain had just won a 700 year war with the Moors. Because they had the largest navy in the world, they were considered the most powerful nation. They were so powerful there was a saying
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? Age of Exploration and Trade Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST
 WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
Columbus was thrilled. In a later letter, he wrote, I write this to tell you how in thirty-three
 Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
ISN 4. #2. List reasons why people migrate.
 ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
Student s Name: Subject: Social Studies
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl
 Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
