New Worlds: Americas & Oceania
|
|
|
- Clement Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Worlds: Americas & Oceania
2 Spanish mariners meet indigenous Tainos (Arawaks) Originally from Orinoco River valley in South America, settled in Caribbean in late centuries BCE through 900 CE Columbus uses Hispaniola (Haiti-Dominican Republic) as base for trading with Tainos Disappointed that Tainos had no spices, silks Recruit locals to mine gold instead Encomienda: Forced labor 2
3
4 The Colonial Encomienda System Peninsulares Creoles Mestizos Mulattos Native Indians Black Slaves
5 Tainos occasionally rebel, but outgunned by Spanish military technology Smallpox epidemics begin 1518 Spaniards launch raids to kidnap and replace workers, spread disease further Taino society disappears by middle of 16 th century Limited gold production causes new interest in exploiting Caribbean for sugarcane production Requires massive importation of slaves 5
6 Spanish conquerors (conquistadores) explore other territories Hernán Cortés and 450 men bring down Aztec empire in Mexico ( ) Smallpox destroys besieged Tenochtitlan Francisco Pizarro and 600 men bring down Inca empire in Peru ( ) Calls conference of warring Inca rulers, massacres them all 6
7
8 Conquests of Mexico, Peru not the result of imperial policy, but inspired greater efforts to expand Spanish empire Spanish administration based in New Spain (Mexico) and New Castile (Peru), extended to Florida and Buenos Aires Mexico city built atop Tenochtitlan, founded Lima in Peru Viceroys rule, but supervised by local courts called audiencias designed to prevent buildup of local power bases Considerable dispute with Spanish homeland 8
9 European Explorations
10 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas divides entire (non- Christian) world between Spain and Portugal Portugal claims Brazil Little interest at first, but increases as other imperial powers take notice Exploited for sugarcane production 10
11 The Treaty of Tordesillas, 1494 & The Pope s Line of Demarcation
12 Spanish towns, forts, missions on east coast of North America, some on west coast Dislodged in 17 th century by French, English, Dutch mariners Permanent colonies in North America France: Nova Scotia (1604), Quebec (1608) England: Jamestown (1607), Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630) Netherlands: New Amsterdam (1623) English take it in 1664, rename it New York 12
13 European Empires and colonies in the Americas about
14 Exceptionally difficult conditions Starvation rampant, cannibalism occasionally practiced French, English private merchants invest heavily in expansion of colonies Greater levels of self-government than Spanish and Portuguese colonies 14
15 North American peoples loosely organized, migratory Unlike Aztec, Inca empires European colonists stake out forested land, clear it for agriculture Increasing number of Europeans arrive seeking ample land: 150,000 from England in 17 th century 15
16
17 Colonists displace indigenous peoples, trespass on hunting grounds English settlers negotiate treaties, poorly understood by natives Military conflict frequent Natives also devastated by epidemic disease 17
18 Native European African
19 European, African migrants primarily men Relationships with native women formed Mestizo (mixed) societies formed People of Spanish and native parentage Descendants of Spaniards and African slaves ( mulattoes ) Descendants of African slaves and natives ( zambos ) Less pronounced in Peru 19
20 Race-based hierarchy Top: peninsulares, i.e. migrants from Iberian peninsula Criollos (creoles), i.e. children of migrants Mestizos, mulattoes, zambos, other combinations of parentage Bottom: slaves, conquered peoples 20
21 Higher ratio of French, English female migrants than in South America Higher social stigma attached to relationships with natives, African slaves Fur traders have relationships with North American native women Children: métis 21
22 Hunt for gold and silver Conquistadores loot Aztec, Inca treasures and melt them down for their value as raw precious metals Gold not extensive in Spanish holdings, but silver relatively plentiful Extensive employment of natives Incan mita system of conscripted labor Dangerous working conditions Eventually assimilate into Spanish culture 1/5 reserved for crown (quinta), hugely profitable 22
23 Major resource of income for Spanish crown Manila Galleons take it to the Pacific rim for trading Very popular with Chinese markets Also trade in the Atlantic basin 23
24 24
25 Large estates produce products of European origin Wheat, grapes, meat Encomienda system of utilizing native labor force Rampant abuses Gradually replaced by debt patronage Peasants repay loans with cheap labor 25
26 26
27 Rebellion 1680 Pueblo Revolt Led by Popè 12 year success 1780 Túpac Amaru rebellion 60,000 2 years, ends in failure Half-hearted work Retreat into mountains and forests Appeal to Spanish crown 1,200 page letter of Guaman Poma de Ayala, El Primer Nueva Corónica y Buen Gobierno (The First New Chronicle and Good Government) 27
28 Sugar mill: engenho, refers to complex of land, labor, etc. all related to production of sugar Sugarcane to molasses, or refined to sugar for export Low profit margins, most complex industry in Americas Unlike Spanish system of forced native labor, Portuguese rely on imported African slaves Natives continually evaded Portuguese forces Large-scale importing of slaves begins 1580s Working conditions poor: 5-10% die annually Approximately one human life per ton of sugar 28
29 Indigenous peoples trade pelts for wool blankets, iron pots, firearms, alcohol Beaver hunts cause frequent incursions into neighboring territories, conflicts European settler-cultivators also displacing natives from traditional lands Albeit initially dependent on native assistance, as European grains did not grow well in many areas 29
30 Products developed for European markets Tobacco - Jean Nicot Rice Indigo Cotton Increases demand for imported slave labor European indentured servants, 4-7 year terms Chronically unemployed, orphans, political prisoners and criminals 30
31 Pounds
32 African slaves in Virginia from 1610 Increasingly replace European indentured laborers, late 17 th -early 18 th centuries Less prominent in north due to weak nature of cashcrop industry Slave trading still important part of economy Also, products made through slave labor Rum, based on sugar from plantations 32
33 Franciscan, Dominican, Jesuit missionaries from 16 th century Taught Christian doctrine, literacy Often accumulated cultural knowledge to better communicate their message Bernardino de Sahagún Due to conquest and plague, many natives in Spanish America concluded that their gods had abandoned them, converted to Catholicism Yet often retained elements of pagan religion in Christian worship 33
34 34
35 Less effective than Spanish missions Spaniards ruled native populations more directly Migration patterns of North American natives made it more difficult to conduct Missions English colonists little interest in converting natives 35
36 Broadly similar experiences to American natives Portuguese mariners long in the region, but Dutch sailors make first recorded sighting of Australia in 1606 VOC surveys territory, conclude that it is of little value Limited contact with indigenous peoples Nomadic, fishing and foraging societies British Captain James Cook lands at Botany Bay, 1770 Convicts shipped to Australia, outnumber free settlers until
37 Manila Galleons interested in quick trade routes, little exploration of Pacific Islands of Guam and the Marianas significant, lay on trade routes 1670s-1680s took control of islands, smallpox destroys local population James Cook visits Hawai i in 1778 Good relationship with Hawaiians Sailors spread venereal disease Cook not welcomed in 1779, killed in dispute over petty thefts 37
Chapter 24. New Worlds: The Americas and Oceania
 Chapter 24 New Worlds: The Americas and Oceania 1 The Spanish Caribbean! Spanish mariners meet indigenous Tainos (Arawaks)! Originally from Orinoco River valley in South America, settled in Caribbean in
Chapter 24 New Worlds: The Americas and Oceania 1 The Spanish Caribbean! Spanish mariners meet indigenous Tainos (Arawaks)! Originally from Orinoco River valley in South America, settled in Caribbean in
Reminders: C TEST = WED 3/1 40 MC (10 from Unit 2) 1 SAQ. C 25 Q/V/A due TODAY! C 26 Q/V/A Due TH 3/2. Field Trip? C 23 matching?
 Reminders: C 23-25 TEST = WED 3/1 40 MC (10 from Unit 2) 1 SAQ C 25 Q/V/A due TODAY! C 26 Q/V/A Due TH 3/2 Field Trip? C 23 matching? What s happening in this painting? HAPP? C 24: New Worlds: The Americas
Reminders: C 23-25 TEST = WED 3/1 40 MC (10 from Unit 2) 1 SAQ C 25 Q/V/A due TODAY! C 26 Q/V/A Due TH 3/2 Field Trip? C 23 matching? What s happening in this painting? HAPP? C 24: New Worlds: The Americas
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Spain Builds an Empire
 Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Exploration & Colonization. Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School
 Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory
 Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration
 The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1
 Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
Bartholomeu Dias. Cape of Good Hope 1487
 Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe.
 I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Colonial Encounters. Europeans Colonize the Americas
 Colonial Encounters Europeans Colonize the Americas Learning Objectives 1. Summarize the characteristics of the colonies of New Spain, New France, New Netherland, and Virginia. 2. Compare and contrast
Colonial Encounters Europeans Colonize the Americas Learning Objectives 1. Summarize the characteristics of the colonies of New Spain, New France, New Netherland, and Virginia. 2. Compare and contrast
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Chapter 16: The First Global Age ( ) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in
 Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
Vocabulary. Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming notes. Jump to first page
 Vocabulary Conquistador Royal Fifth Francisco Pizarro Monopoly Hacienda Social class Treaty Hernan Cortes Debt peonage Mestizo Peninsular (Montezuma) Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming
Vocabulary Conquistador Royal Fifth Francisco Pizarro Monopoly Hacienda Social class Treaty Hernan Cortes Debt peonage Mestizo Peninsular (Montezuma) Red = in book Black = terms to be used in our upcoming
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations
 Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Conquest in the Americas. World History
 Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
Binder Page Name Period New Spain & New France
 Binder Page Name Period New Spain & New France Date When the explorers arrived in the New World, why did they think that they could take the land for their countries when the Native Americans were already
Binder Page Name Period New Spain & New France Date When the explorers arrived in the New World, why did they think that they could take the land for their countries when the Native Americans were already
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Mexican History and Systems of Empire
 Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Empires of the Early Modern Era. The Emergence of a New World Order
 Empires of the Early Modern Era The Emergence of a New World Order 1450-1750 Agenda Mongol Essay wrap-up Aztec vs Inca Essay? European Empires discussion Learning Targets Explain what s new about the empires
Empires of the Early Modern Era The Emergence of a New World Order 1450-1750 Agenda Mongol Essay wrap-up Aztec vs Inca Essay? European Empires discussion Learning Targets Explain what s new about the empires
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century. By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham
 Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST
 WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
Chapter 4-1 Notes. The Economy of the Colonies
 Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas. Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain
 Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain Conquistadors Bernal Díaz del Castillo was one of the many Spanish conquistadors or conquerors, who marched
Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain Conquistadors Bernal Díaz del Castillo was one of the many Spanish conquistadors or conquerors, who marched
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter One: The Meeting of Cultures
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America Before Columbus The Peoples of the Pre-contact Americas Migrations from Eurasia over Bering Strait The Clovis People Archaeologists and Population Diversity
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
Chapter 23. Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections
 Chapter 23 Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections 1 Portuguese Exploration Originally for fishing Land hunger Discovery of Azores, Madeiras Islands Acquisition of land to plant sugarcane 2 The
Chapter 23 Transoceanic Encounters and Global Connections 1 Portuguese Exploration Originally for fishing Land hunger Discovery of Azores, Madeiras Islands Acquisition of land to plant sugarcane 2 The
First Visitors From Europe
 THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
Columbus was thrilled. In a later letter, he wrote, I write this to tell you how in thirty-three
 Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Chapter 1-1 The New Global World,
 Chapter 1-1 The New Global World, 1450-1620 The Native American Experience The First Americans Migrants from Asia crossed Siberia (15,000-9000 years ago) Tuscarora (NC) Second migration by water (Navajos
Chapter 1-1 The New Global World, 1450-1620 The Native American Experience The First Americans Migrants from Asia crossed Siberia (15,000-9000 years ago) Tuscarora (NC) Second migration by water (Navajos
APWH chapter 18.notebook January 11, 2013
 Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Name: Date: Period: VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution. Filled In. Notes VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution 1
 Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Big Ideas: A tribe s culture and way of life was heavily influenced by the natural resources of the region they occupied.
 Converging Cultures Big Ideas: South and Central American natives had advanced and well established cultures. The native tribes of North America were numerous and diverse. A tribe s culture and way of
Converging Cultures Big Ideas: South and Central American natives had advanced and well established cultures. The native tribes of North America were numerous and diverse. A tribe s culture and way of
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL. AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS
 CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
CLAYTON HIGH SCHOOL AP U.S. History I SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS Mr. Ahern Summer 2017 On-line text https://tusd.haikulearning.com/dgoldenberg/apunitedstateshistory/cms_page/view/15905333 Welcome to AP
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Founding Economic Structure/Activities Trade Sources of Econ. Development Economic sources
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Founding Economic Structure/Activities Trade Sources of Econ. Development Economic sources
Section 3-1: The Conquistadores
 Name: Date: Chapter 3 Study Guide Section 3-1: The Conquistadores 1. Spanish mercenaries and soldiers who led military expeditions to the Americas were called conquistadores. 2. The Aztecs were a large
Name: Date: Chapter 3 Study Guide Section 3-1: The Conquistadores 1. Spanish mercenaries and soldiers who led military expeditions to the Americas were called conquistadores. 2. The Aztecs were a large
CIVILIZATIONS OF EARLY CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA
 CIVILIZATIONS OF EARLY CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA STANDARD 6-4.3: COMPARE THE CONTRIBUTIONS AND THE DECLINE OF THE MAYA, AZTEC, AND INCA CIVILIZATIONS IN CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA, INCLUDING THEIR FORMS
CIVILIZATIONS OF EARLY CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA STANDARD 6-4.3: COMPARE THE CONTRIBUTIONS AND THE DECLINE OF THE MAYA, AZTEC, AND INCA CIVILIZATIONS IN CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA, INCLUDING THEIR FORMS
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
December 11, Study Guide
 Epic Epic Epic Study Guide "Hands down, this is the best study guide I've ever seen," - Abraham Lincoln Bonjour! I wish I were alive today so that I myself might be able to complete this study guide. Au
Epic Epic Epic Study Guide "Hands down, this is the best study guide I've ever seen," - Abraham Lincoln Bonjour! I wish I were alive today so that I myself might be able to complete this study guide. Au
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2.
AP U.S. History 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2.
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s
 European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado 1 New World Beginnings, 33,000 B.C.-A.D. 1769 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
Global Empires of the 1500s
 Global Empires of the 1500s In World History, we will spend a lot of time talking about Europe. This is strange because in 1500s, Europe isn t the center of world. At all! They are not powerful! They are
Global Empires of the 1500s In World History, we will spend a lot of time talking about Europe. This is strange because in 1500s, Europe isn t the center of world. At all! They are not powerful! They are
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Europe- 2. How did the nobles in Europe gain their wealth?
 Name Period Video: America Before Columbus Date 1. What types of natural wealth were in the Americas before Europeans arrived? Europe- 2. How did the nobles in Europe gain their wealth? What problem has
Name Period Video: America Before Columbus Date 1. What types of natural wealth were in the Americas before Europeans arrived? Europe- 2. How did the nobles in Europe gain their wealth? What problem has
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
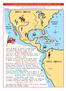 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
February 10, Study Guide
 Epic Epic Epic Study Guide "Hands down, this is the best study guide I've ever seen," - Abraham Lincoln Bonjour! I wish I were alive today so that I myself might be able to complete this study guide. Au
Epic Epic Epic Study Guide "Hands down, this is the best study guide I've ever seen," - Abraham Lincoln Bonjour! I wish I were alive today so that I myself might be able to complete this study guide. Au
Renaissance Economics. The Age of Discovery
 Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
The Arrival of the Spanish. Mexico 1519 Peru 1526
 The Arrival of the Spanish Mexico 1519 Peru 1526 The strangers bodies are completely covered, so that only their faces can be seen. Their skin is white, as if it were made of lime. They have yellow hair,
The Arrival of the Spanish Mexico 1519 Peru 1526 The strangers bodies are completely covered, so that only their faces can be seen. Their skin is white, as if it were made of lime. They have yellow hair,
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? Age of Exploration and Trade Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Before Contact with Europeans
 Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
Before Contact with Europeans Introduction Migration to the Americas Early migrations from northern Asia to Alaska occurred 35,000 to 15,000 years ago Some contact with Polynesians possible Geography Great
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Name Period Test Date September Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East Asia? (page 122)
 Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
