California Standards. English-Language Arts Writing 7.2.1b Develop complex major and minor characters and a definite setting.
|
|
|
- Berenice Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 California Standards History-Social Science 7.4 Students analyze the geographic, political, economic, religious, and social structures of the sub-saharan civilizations of Ghana and Mali in Medieval Africa. English-Language Arts Writing 7.2.1b Develop complex major and minor characters and a definite setting. Reading Describe and connect essential ideas, arguments, and perspectives of text using knowledge of text structure, organization, and purpose. Writing a Journal Entry Many people feel that recording their lives in journals helps them to understand their own experiences. Writing a journal entry from someone else's point of view can help you to understand what that person's life is like. In this chapter, you will read about the land and people of early West Africa. Then you will imagine a character and write a journal entry from his or her point of view. CHAPTER EVENTS WORLD c BC EVENTS Egyptians begin to write using hieroglyphics.
4 c. 500 BC The Nok culture begins using iron and makes clay sculptures. Camels are first used in North Africa, making Saharan trade easier. c. 480 BC Greece defeats Persia in the Persian Wars. 44BC Julius Caesar is assassinated in Rome. Trade routes link the Roman Empire and Mediterranean with East Asip. EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES
5 Focus on Themes In this chapter, you will read about West Africa-its physical geography and early cultures. You will see West Africa is a land of many resources and varied features. One feature, the Niger River, has been particularly important in the region's history, providing water, food, and transportation for people. In addition, salt and iron deposits can be found in the region. Such resources were the basis for a technology that allowed people to create strong tools and weapons. Organization of Facts and lnformatio.n Focus on Reading How are books organized in the library? How are the groceries organized in the store? Clear organization helps us find the product we need, and it also helps us find facts and information. Additional reading support can be found in the Understanding Structural Patterns Writers use structural patterns to organize information in sentences or paragraphs. What's a structural pattern? It's simply a way of organizing information. Learning to recognize those patterns will make it easier for you to read and understand social studies texts. Pattern Cause-effect shows how one thing leads to another Patterns of Organization Clue Words I as a result, because, therefore, this led to Chronological Order I after, before, first, shows the sequence of then, not long after, events or actions. finally listing presents information in categories such as size, location or importance. also, most important, for example, in fact Graphic Organizer Category Fact Fact Fact To use text structure to improve your understanding, follow these steps: 1. Look for the main idea of the passage you are reading. 2. Then look for clues that signal a specific pattern. 3. Look for other important ideas and think about how the ideas connect. Is there any obvious pattern? 4. Use a graphic organizer to map the relationships among the facts and details. 110 CHAPTERs
6 You Try It! The following passages are from the chapter you are about to read. As you read each set of sentences, ask yourself what structural pattern the writer used to organize the information. Recognizing Structural Patterns A. "Living in present day Nigeria, the Nok made iron farm tools. One iron tool, the hoe, allowed farmers to clear the land more quickly and easily than they could do with earlier tools. As a result, they could grow more food." (p. 118)' B. "Thousands of years ago, West Africa had a damp climate. About 5,000 years ago the climate changed, though, and the area became drier. As more land became desert, people had to leave areas where they could no longer survive. People who had once lived freely began to live closer together. Over time they settled in villages." (p. 116) ChapterS Section 1 rifts (p. 112) sub-saharan Africa (p. 112) Sahel {p. 114) savannah (p. 114) rain forests (p. 114) Section 2 extended family (p. 116) animism (p. 117) Academic Vocabulary Success in school is related to knowing academic vocabularythe words that are frequently used in school assignments and discussions. In this chapter, you will learn the following academic words: impact (p. 114) traditional (p. 117) C. "Four different regions make up the area surrounding the Niger River... The northern band across West Africa is the southern part of _the Sahara... The next band is the semiarid Sahel (sah-hel), a strip of land that divides the desert from wetter areas.... Farther south is a band of savannah or open grassland... The fourth band gets heavy rain." (p. 114) After you read the passages, answer the questions below: 1. What structural pattern did the writer use to organize the information in passage A? How can you tell? 2. What structural pattern did the writer use to organize the information in passage B? How can you tell? 3. What structural pattern did the writer use to organize the information in passage C? How can you tell? As you read Chapter 5, think about the organization of the ideas. Look for signal words and ask yourself why the author has arranged the text in the way he or she did. I Y WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES 1.11
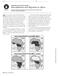
7 Main Ideas 1. The landforms, water, climate, and plant life affected history in West Africa. 2. West Africa's resources included farmland, gold, and salt. -, The Big Idea West Africa has varied environments and valuable resources. KeyTems rifts, p. 112 sub-saharan Africa, p. 112 Sahel, p. 114 savannah, p. 114 rain forests, p. 114 em Study the Niger River and the relationship of vegetation zones of forest, savannah, and desert to trade in gold, salt, food, and slaves; and the growth of the Ghana and Mali empires. If YOU were there... You live in a village near a great bend of the Niger River in Africa in about AD 800. The river is full of life-birds, f1sh, and croco-. diles. You use its water to grow crops and raise cattle. Tradtrs use the river to bring wood, gold, and other products from the forests..y is this a good place to live? BUILDING BACKGROUND The continent of Africa is so large that it includes many varied kinds of terrain, from barren deserts to thick rain forests. Each region has a different climate and provides different resources for the people who live there. In each area different cultures and ways of life developed. Landforms, Water, Climate, and Plant Life Africa is a big place. In fact, it is the second-largest continent on earth. Only Asia is bigger. This vast land is shaped roughly like a soup bowl. Forming the bowl's northwestern rim are the Atlas Mountains. The Drakensberg range forms the southeastern edge. In eastern Africa mountains extend alongside great rifts. These rifts are long, deep valleys formed by the movement of the earth's crust. From all these mountains the land dips into plateaus and wide, low plains. The plains of sub-saharan Africa, or Africa south of the Sahara, are crossed by mighty rivers. Among the main rivers are the Congo, the Zambezi, and the Niger. Along the Niger River in West Africa great civilizations arose. The role this river played in the development of civilizations is one example of the way the physical geography of West Africa affected history there. West Africa's Great River Look closely at the map on the next page and find the Niger River. As a source of water, food, and transportation, the river allowed many people to live in the area. 112 CHAPTER 5
8 largest desert, the Sahara, dominates North Africa. The world's longest river, the Nile, flows northward to the Mediterranean Sea. 4 C) e> ATLANTIC OCEAN N 10os w ~ * E I \!;~:>.,~,.,';!.. r...,_.. --rj.y s Eastern Africa's plateaus and valleys are covered with grasslands and scattered trees. 13,120 6,560 1, (Sea level) 0 Below - sea level ELEVATION Feet _ Meters 4,000 2, (Sea level) Below sea level Miles 700 Kilometers INDIAN OCEAN ~------r i ~~------
9 Natural Environments D Mediterranean Rain forest 0 Savannah 0 Semiarid Desert 1,000 2,000 Miles 0 1,000 2,000 Kilometers Location What type of environment is located just south ofthe Sahara? Human activities like logging and farming are rapidly destroying Africa's rain forest. ACADEMIC VOCABULARY impact effect, result Along the Niger's middle section is a low-lying area of lakes and marshes. This watery region is called the inland delta. Though it looks much like the area where a river flows into the sea, it is hundreds of miles from the coast. Many animals and birds find food and shelter in the area. Among them are crocodiles, geese, and hippopotamus. Fish are also plentiful. West Africa's Climates and Plants Four different regions make up the area surrounding the Niger River. These regions, which run from east to west, are like broad bands or stripes across West Africa. The entire area is warm, but rainfall varies from north to south. The amount of rainfall each region gets has an impact on what vegetation, or plant life, exists there. Desert lbe huge Sahara covers most of North Africa. Here, a traveler aosses a giant sea of sand. The northern band across West Africa is the southern part of the Sahara. This huge expanse of sand and gravel is the world's largest desert. Temperatures can climb above 120 F. Rain is very rare. The next band is the semiarid Sahel (sah-hel), a strip of land that divides the desert from wetter areas. Although the Sahel is fairly dry, it has enough vegetation to support hardy grazing animals. Farther south is a band of savannah, or open grassland with scattered trees. Tall grasses and shrubs also grow there, and grazing animals are common. The fourth band gets heavy rain. Near the equator are rain forests, or moist, [ densely wooded areas. They contain many different plants and animals. I READING (HECK Summarizing What are West Africa's four climate and vegetation regions? West Africa's Resources West Africa's land is one of the region's resources. With its many climates, the land could produce many different crops. Among the traditional West African crops are dates raised in desert oases and kola,. ~ 1./ (' :1.14 CHAPTER 5
10 t f) Savannah Much of Africa is covered by grasslands called savannah. Scattered across the savannah are clumps of trees like these acacia trees. C) Rain Forest lbick rain forests like this one are found in central and western Africa. lbe rain forests' tall trees provide homes for many different animals. nuts, used for medicines, from the forests' trees. Along the Niger, farmers could use the water to grow many food crops. Other resources were minerals. People who live mainly on plant foods, like many early Africans, must add salt to their diets. The Sahara was a source of this precious mineral. When ancient lakes there dried up, they left salt behind. Workers mined the salt by digging deep into the earth. Gold was another mineral resource of West Africa. Although gold is soft and therefore useless for tools or weapons, it makes beautiful jewelry and coins. Gold came from the southern forests. Miners kept the exact locations of the gold mines a secret. To this day, no one knows exactly where the mines were located, but gold became a valuable trade good. Reviewing Ideas. Terms. and People 1. a. Define What is a savannah? b. Contrast How might living in the Sahel be different from living in a rain forest? c. Evaluate In which African climate region would you most like to live? Why? 2. a. Identify What were two of early West Africa's important mineral resources? b. Explain How were these resources related to West Africa's physical geography? c. Elaborate Why do you think miners kept the location of the gold mines a secret? Critical Thinking 3. Summarizing Create a chart like the one below. Use it to describe the characteristics of West Africa's four climate regions. Climate region Characteristics READING (HECK Finding Main Ideas What are some of West Africa's major resources? SU"IURY AND PREVIEW You have read about the physical geography of Africa. Next you will learn how physical features had an impact on culture and trade in early West Africa. FOCUS ON WRITING,7 4. Taking Notes on West Africa's Geography Review this section and take notes on the geography of West Africa. Remember that part of this land is your character's daily environment. What does he or she see every day? What challenges does the environment present? EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES
11 Main Ideas 1. Family and religion influenced daily life in early West African society. 2. Iron technology changed life in West Africa. 3. Traqe shaped the history of West Africa. + The Big Idea Family ties, religion, iron technology, and trade all contributed to the growth of West African societies. Key Terms extended family, p. 116 animism, p. 117 If YOU were there... You and your family are farmers in West Africa in about 400 BC. Farming is hard work. You use a sharp, wooden stick to dig the soil and put seeds in the ground. One day a trader brings farm tools made of a dark metal you've never seen before. These f1ne tools are so strong you can't break them! They have clean, sharp edges. How will these new tools change your life? "'11 BUILDING BACKGROUND The different climate regions of West Africa provided people with a variety of rich resources. Rivers provided water to grow crops in drier areas. The land was also a rich source of minerals, especially gold and iron. These two resources ~ played a large role in the development of African cultures..~._ ~~~~~~ Families, Religion, and Daily Life Thousands of years ago, West Africa had a damp climate. About 5,000 years ago the climate changed, though, and the area became drier. As more land became desert, people had to leave areas where they could no longer survive. People who had once roamed freely began to live closer together. Over time they settled in villages. At the heart of village life was the family. fim Analyze the importance of family, labor specialization, and regional commerce in the development of states and cities in West Africa. Families, Villages, and Loyalties A typical West African family was an extended family. Usually the extended family included the father, mother, children, and close relatives in one household. West African society expected each person to be loyal to his or her extended family. In some areas people took part in another type of group. In these groups-called age-sets-men who had been born within the same two or three years formed special bonds. Men in the same age-set had a duty to help each other. Women, too, sometimes formed age-sets. 116 CHAPTERS~
12 Families were the basic group of village society. Extended Families Extended families induded grandparents, aunts, undes, cousins, and their families. Village Chiefs Extended families often had a male leader who served as a village chief. Village Life Families were an important part of West African village society. Here a family gathers in a Nigerian village. Council of Elders Sometimes, village chiefs formed a council of elders that led the village. Loyalty to family and age-sets helped the people of a village work together. Everyone had specific duties. The men hunted and farmed. Among the crops that men tended were millet and sorghum. These hardy grains grew well in the savannah in spite of the poor soil there. After being harvested, the grain could be made into a thick paste or ground into flour to make bread. Cattle could eat the grain. Farmers also raised goats and sheep. Like the men, West African women worked very hard. They farmed, collected firewood, ground grain, and carried water. Women also cared for children. Even the very young and the very old had their own tasks. For example, the elders, or old people, taught the family's traditions to younger generations. Through songs, dances, and stories, elders passed on the community's history and values. Among the values that children learned was the need for hard work. Children began working beside older family members as soon as they were able. Religion and Culture Another central feature of village life was religion. Some religious practices were similar from village to village. A traditional belief showed the importance of families. Many West Africans believed that the unseen spirits of their ancestors stayed nearby. To honor these spi~ts, families marked places as sacred spaces by putting specially carved statues there. Family members gathered in these places to share news and problems with the ancestors. Families also offered food to the ancestors' spirits. Through these practices they hoped to keep the spirits happy. In return, they believed, these spirits would protect the village from harm. Another common West African belief had to do with nature. We call it animismthe belief that bodies of water, animals, trees, and other natural objects have spirits. Animism reflected West Africans' dependence on the natural world for survival. READING (HECK Generalizing What role did families play in traditional West African culture? ACADEMIC VOCABULARY traditional customary, time-honored EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES 1:17
13 focus ON READING What structural pattern is used to. organize information in the second column on this page? Technology and Change As time passed, the people of We~t Africa developed advanced a;nd diverse cultures. Changes in technology helped some early communities grow.. Som~time around 500 BC West Africans made a discovery that would change their region forever. They foun<;l that they could heat certain kinds of rock to get a hard metal. This metal was iron. By heating the iron again, they COl;lld shape it into useful things. Stronger than other metals, iron was good for making tools.. One of the earliest peoples to use this new technology was the Nok. Living in present-day Nigeria, the Nok made iron farm tools. One iron tool, the hoe, allowed farmers to clear the land more quickly and easily than they could with earlier tools. As a result, they could grow more food. The Nok also used iron tips for arrows and spears. Iron weapons provided a better defense against invaders and helped in hunting. As better-equipped farmers, hunters, and warriors, the Nok gained power. They also became known for fine sculptures of animals and human heads they made from clay. Iron tools also provided another benefit. They helped West Africans live in places where they couldn't live before. Iron blades allowed people to cut down trees to clear land for farms. Because they had more places to live and more farms for growing food, the population of West Africa grew. Finding Main Ideas How did technology change life in West Africa?
14 Trade and West Africa As the people of West Africa grew more food, communities had more than they needed to survive. West African~ began to trade the area's resources with buyers who lived thousands of miles away. Desert Trade For a long time, West Africans had ventured into the desert for trade. However, those early travelers could only make short trips from oasis to oasis. Their horses couldn't go far without water. In the AD ZOOs, the situation changed. At about that time, Romans started to use camels to carry goods throughout northern Africa. These long-legged animals could store water and energy in their bodies for long periods of time. They could also carry heavy loads. With camels people could cross the Sahara in two months. Traders formed caravans to make the trip. A North African people called the Berbers used their knowledge of the desert to lead the caravans. Even with camels and the Berbers' skills, crossing the Sahara was dangerous. Supplies could run out, thieves could attack, and caravans could lose their way. Trade in Gold and Salt Despite these dangers, West Africa's gold and salt mines became a source of great wealth. Camels carried salt from the mines of the Sahara to the south to trade for gold. Traders then took the gold north, to Europe and the Islamic world. Along with gold and salt, traders carried cloth, copper, silver, and other items. They also bought and sold human beings as slaves. Some of the places where people gathered to trade grew into towns. Timbuktu (tim-buk-too), for example, began as a camp for traders in about Within two centuries,,i~ would become a.l?':jstling city and a center of culture and learning. It would lie at the center of great empires that rose to power through the riches of the trans-sahara trade. Generalizing What trade goods were a source of West Africa's wealth? SUMMARY AND PREVIEW Families and religion were central to early West African cultures. When West Africans developed iron technology, communities grew. Trade in gold and salt expanded. into a wider area. ln. the next chapter, you will read about the West African empires based on this trade. Reviewing Ideas, Terms, and People lim a. Identify What are two groups to which a person in early West Africa may have owed loyalty? b. Analyze How did animism reflect what was important to early West African peoples?. 2. a. Describe How did the use of iron change farming? b. Make Inferences What evidence do you think historians have for how the Nok people lived? 3. a. Identify What animal made trade across the Sahara easier? b. Summarize In what directions did the main trade items of West Africa move? Critical Thinking 4. Identifying Cause and Effect Draw a diagram like the one below. Use it to identify two reasons towns grew. ~ ~- o. J Effect: growth of towns I ~ FOCUS ON WRITING z 5. Taking Notes on West Africa's Early Culture Review this section and take notes on the early West Africans' way of life. This section covers more than one time period and location, so be sure to note when and wh~re particular activities took place. EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES
15 Crossing the Sahara has never been easy. Bigger than the entire continent of Australia, the Sahara is one of the hottest, driest, and most barren places on earth. Yet for centuries, people have crossed the Sahara's gravel-covered plains and vast seas of sand. Long ago, West Africans crossed the desert regularly to carry on a rich trade. Salt, used to preserve and flavor food, was available in the Sahara. Traders from the north took salt south. Camel caravans carried huge slabs of salt weighing hundreds of pounds. APRICA In exchange for salt, people in West Africa offered other valuable trade goods, especially gold. Gold dust was measured with special spoons and stored in boxes. Ivory, from the tusks of elephants, was carved into jewelry. Glllr- Of Gl/in ''eci CHAPTER 5
16 ATLANTIC OCEAN aope n~ Temperature Temperatures soared to well over looof during the day and below freezing at night. Dying of heat or cold was a real danger. Water Most areas of the Sahara get less than one inch of rain per year. Travelers had to bring lots of water or they could die of thirst. Distance The Sahara is huge, and the trade routes were not well marked. Travelers could easily get lost. Bandits Valuable trade goods were a tempting target for bandits. For protection, merchants traveled in caravans. - Trade route e Settlement Scale varies on this map.
17 Making Group Decisions Making decisions as a group is a complicated and difficult skill to learn. However, it is an important skill at all levels of society-from governing a nation to choosing a movie to see with friends. At every level, success is based on the ability of group members to work together in effective and cooperative ways. In Chapter 5 you learned about the cultures of the early peoples of West Africa. In some of these cultures, group decision making was central to the government. For example, the Yoruba of presentday Nigeria, Benin, and Togo lived in independent towns in which all decisions were made by a town council. The council met daily, and each of the town's families had one member on it. This system of government worked well, largely because it forced council members to overcome their differences, compromise on goals and actions, and accept group decisions they might not have agreed with personally. Like the members of those Yoruba town councils, being part of an effective group requires certain behaviors. 0 Be an active member. Take part in setting the group's goals and in making its decisions. f) Take a position. State your views and work to persuade other members to accept them. However, also be open to negotiating and compromising to settle differences within the group. 8 Be willing to take charge if leadership is needed. But also be willing to follow the leadership of other members. Imagine you are a part of a Yoruba town council. An invader is threatening the area. You are representing your town at a meeting of representatives of nearby towns-your classmates. Together, you must decide what to do about the threat. Remember that your town is very independent. If you agree to something that upsets the people, they may not support it. When your group has finished, answer the following questions. 1. Did your group create a plan for completing its task? Did it discuss what to do about the problem? What did you contribute toward the plan? 2. How well did your group work together? What role did you play in that? 3. Was your group able to make a decision? If not, why? If so, was compromise involved? Do you support the decision? Explain why or why not. 1 ]] CHAPTER 5
18 Standards ev1ew Use the visual summary below to help you review the main ideas of the chapter. Africa's geography influenced people's way of life. The family was the basic unit of society in West Africa. Reviewing Vocabulary, Terms, and People Choose the letter of the answer that best completes each statement below. 1. An area near the equator that has many trees and heavy rainfall may be called a a. tropical area. c. savannah. b. rain forest. d. woodland. 2. The belief that natural objects have spirits is called a. animism. c. animalism. b. vegetism. d. naturalism. 3. The entire region south of a large North African desert is called a. Drakensberg. c. sub-saharan Africa. b. extended Africa. d. the sub-savannah. 4. Between the Sahara and the savannah lies the a. rain forest. c. Zambezi. b. inland delta. d. Sahel. 5. Long, deep valleys formed by the movement of the earth's crust are called a. chasms. c. volcanoes. b. rifts. d. earth'quake zones. 6. A grassland with few trees where grazing animals may live is a a. savannah. c. desert. b. Sahara. d. meadow. 7. If aunts, uncles, parents, grandparents, children, and cousins live together in the same household, these people are members of a. a group household. c. an age-set. b. a kinship home. d. an extended family. 8. If a group of people has followed a certain custom for a long time, we may say that the custom is a. timely. c. traditional. b. in an age-set. d. based on animism. EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES 1 23
19 Comprehension and.critical Thinking SECTION 1 (Pages ) 1J:m a. Identify Along what river did great civilizations develop in early West Africa? b. Analyze How does Africa's climate affect vegetation? c. Elaborate Today salt is not nearly as valuable as gold. Why do you think salt was so important in West Africa? SECTION 2 (Pages 116~119) 1J:m a. Describe What effect did the growth of trade have on some West African towns? b. Analyze What hard metal changed daily life in West Africa? How did this metal change farming? How did it change hunting? c. Evaluate Which role in the extended family do you think was the most important? Explain your answer. Reviewing Themes 11. Geography What are the four main geographic regions of West Africa? In which regions were West Africa's two main resources found?" 12. Technology How did the development of iron technology affect life in West Africa? Using the Internet 15. Activity: Writing Newspaper Articles Your group of reporters is assigned to write about West Africa. Enter the activity keyword. Then research the land, people, languages, and cultures of West Africa. Write two newspaper articles to present your research. Social Studies Skills 16. Solving Problems Imagine you are a member of an extended family of West Africa. Consider the tasks and responsibilities of each family member, and then decide what role you will play-mother, father, elder, teenager, or young child. Then imagine a challenge that your family must face, such as a dangerous wild animal, crop failure, or loss of hunting grounds. With a partner, discuss how your family will face the problem by using decision-making and planning skills. Then, on your own, write 4-5 sentences explaining the problem and how you and your partner decided to deal with it. You may want to use a chart like the one below to help you organize your thoughts. I Problem Possible Action I Result 1 Reading Skills Understanding Structural Patterns of Text Read the passage below and use it to answer the questions that follow. 11 Because people who live mainly on plant foods must add salt to their diets, salt was a valuable mineral in West Africa. The Sahara was a source of salt. Therefore, traders crossed the Sahara to get salt. Another mineral resource was gold. Gold is beautiful but soft. As a result, people used it to make jewelry and coins but not tools or weapons Writing Your Journal Entry Review your notes and choose an imaginary character. You might choose, for example, a Berber caravan leader, someone who trades goods with a nearby village, or a woman or man of the Nok culture. Then match that person with a place. Finally, write S-6 sentences as your journal entry. Include details on what the character sees, feels, and does on a typical day. 13. What structural pattern did the writer use to organize the information in the passage? 14. What signal words helped you determine the structural pattern of the information? 124 CHAPTER 5
20 I Sta a 55 5 t ~ "M' C ilbft ~ ' _ _- - %_ DIRECTIONS: Read each question, and write the letter of the best response. II Use the map to answer the following question. II How were social groups defined in traditional West African cultures? A by family and age-set B by religion and family C by age-set, family, and religion D by extended family only D West Africans supplied all of the follow~ ing trade goods to Europe and the Islamic world except A salt. B gold. C marble. D copper. Which letter on the map indicates the Sahara? AW B X c y D Z D The region of open grasslands where most grazing of cattle and other livestock takes place is the A rain forest. B Sahara. C savannah. D Sahel. D Life in early West Africa was changed by all of the following events except A the use of camels in trade. B the discovery of how to make iron tools and weapons. C the development of trade with people to the north. D the damming of rivers to control flooding and allow farming. Connecting with Past learnings D In Grade 6 you learned about early civiliza-, tions that developed along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers and along the Huang He in ancient China. Such developments can be compared to changes along which river in West Africa? A the Congo B the Niger C the Nile D the Sahel D Which East African civilization that you learned about in Grade 6 was similar to the Nok in their discovery and use of iron to make tools? A the Kushite civilization B the Mesolithic civilization C the Paleolithic civilization D the Sumerian civilization EARLY WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES 1 ]5
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1
 Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
Geography of WEST AFRICA 7.4.1 Look at this satellite photo. What is shown? Where might people be most likely to live? Why there? What resources might come from each region of this place? How do you think
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions
 Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Ms. Lincoln History Chapter 5 and 6 Study Questions Name Period 5.1 Geography of Africa What does sub-saharan Africa mean? p.112 What did the Niger River provide people living in the region? p.112 Describe
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago
 The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD.
 SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age. Making A Connection
 Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Golden kingdoms of Africa *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
OpenStax-CNX module: m22711 1 Golden kingdoms of Africa * Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 1 SOCIAL SCIENCES: History
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Journal What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa
 Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
Journal A Journal 11-03-17 What trade goods did West Africa supply to North Africa Journal B A. metal goods, salt, and cloth B. gold, cloth, and salt C. gold, slaves, and crops D. cloth, cattle hides,
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources.
 Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Did you know? Africa is one of the earth s seven continents. It is the second largest continent. Africa is a land of great beauty and resources. The earliest evidence of human beings comes from Africa.
Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society
 1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Stone Age & Archaeology. Unit Review
 Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
African History. Return
 Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Kingdoms of Africa African History Africa produced many great civilizations. During the time of the Middle Ages of Europe, the African kingdoms of Mali, Ghana and Songhai were places of advanced learning
Chapter 2 Section 1. Paleolithic Age
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Name Period Date. Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new ways.
 Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet
 Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
Journal Journal A. Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire?
 Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
Journal 10-29-18 Journal A Which is a reason for Timbuktu s importance to the Mali empire? A. It was a center for Christianity. B. It was a center for scholarship and learning. C. It was a center of agriculture.
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
African Kingdoms and Salt
 African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
African Kingdoms and Salt 1 While it may look like snow, it is not. This precious commodity is salt! 2 And you may not believe this but the human body needs salt. 3 Salt is needed by the human body to
The First Americans. Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples. All images found in this PPT were found at Google.
 The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia. Miss Genovese
 Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Government city-states
 Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
Government All Maya people shared the same religious beliefs, had the same social structure, and used the same written language. However, they lived in different city-states (a Maya city and the land it
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
Vocabulary Builder. netw rks. A. Content Vocabulary. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution
 Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Review Questions 1. How did the Bantu migrations affect existing cultures?
 Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
9/21/14. Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda. Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram. Take notes on Songhai
 Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
Bell Work Fill in the blanks. Agenda Complete vocabulary quiz. Finish Mansa Musa Instagram Take notes on Songhai 1 Vocabulary Quiz When you finish, complete your Mansa Musa instagram. Songhai I can analyze
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell
 World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
1. Introduction enabled
 1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest
 Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK
 Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Medieval Adventures. Travel Brochure. 9/27/2017 Medieval Africa Time Travel Guide - Diego Soto - Google Docs
 Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
Medieval Adventures Travel Brochure https://docs.google.com/document/d/1avfekc KS0gjWSXo3RZzix3yXh27RFZARPxf8Fy-jc/edit 1/8 2 The Wealth and Trade By Diego Soto The vast riches that you could encounter
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent BC
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Before reading. Archaeology. Preparation task. Magazine Archaeology. Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise.
 Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Before reading Do the preparation task first. Then read the article and do the exercise. Magazine Archaeology Preparation task Match the definitions (a h) with the vocabulary (1 8). Vocabulary 1. decompose
Social Studies Homework: None. Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad?
 Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
Social Studies Homework: None Social Studies Warm Up 8: -Write? And answer 1. What is prehistory? 2. What is life like for a nomad? Mankind the Story of All of Us Fire: https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=ygpzm0s_rpq
AFRICA. Human Geography
 AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
World History 3219 January 2017
 World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
Note Taking Study Guide EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA
 SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
SECTION 1 EARLY CIVILIZATIONS OF AFRICA Focus Question: How did geography and natural resources affect the development of early societies throughout Africa? As you read this section in your textbook, complete
Ancient Civilizations
 Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
earliest recorded history to today. writing art artifacts Centuries-old written records reveal a long-lasting civilization in
 Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
the scientific name for us as a species Homo sapiens
 Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
 Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS. What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things?
 WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
KEY. Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People
 KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl
 Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
Bell Ringer: August (), 2017
 Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Graphic Organizer. Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter.
 Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
The Earliest Americans. Chapter 1 Section 1
 The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
The Earliest Americans Chapter 1 Section 1 Terms to Know Migration a movement of people or animals from one region to another Environments--climates and landscapes that surround living things Culture--
