Setting the Stage. Europe Enters the Modern Age. European Exploration and Land Claims,
|
|
|
- Noah Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 fe 1 I.* \>>
3 Setting the Stage o Europe Enters the Modern Age In the last unit, you learned about the Renaissance and the Reformation. In this unit, you'll learn about Europe during the early modern age.this period lasted from the 1400s to the 1700s. The early modern age was a time of major discoveries and new ways of thinking. It began with a series of voyages by European explorers during the 1400s, 1500s, and early 1600s. Historians call this time the Age of Exploration. Before the 1400s, Europeans had only limited knowledge of other continents. Beginning in about 1418, several countries sent explorers by sea to other parts of the world. Portugal and Spain led the way. They were followed NORTH AMERICA 1,500 3,000 miles 1,500 3,000 kilometers < Portugal's voyages of exploration F~~! Territory claimed or controlled by Portugal (1600) -< Spain's voyages of exploration ^ Territory claimed or controlled by Spatn (1600) England's voyages of exploratior France's voyages ot exploration The Netherlands'voyages of exploration European Exploration and Land Claims,
4 by England, France, and the Netherlands.Their journeys took explorers to Africa, Asia, and North and South America.Their discoveries changed Europeans' knowledge of the world forever. Countries raced to take advantage of this new knowledge.they sought riches through trade.they also claimed large parts of the world for themselves. As they competed with one another, Europeans had an enormous impact on people living in distant lands. A second great change during this period was the Scientific Revolution. Between 1500 and 1700, scientists used observations, experiments, and logic P AC 11-1C OCEAN to make dramatic discoveries. For example, Isaac Newton formulated the laws of gravity.these laws explained both the movement of physical objects on Earth and the motions of planets in the heavens.the methods used by Newton and other scientists led to rapid progress in many fields. Advances in science helped pave the way for a period called the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment began during the 1600s. It was a time of optimistic faith in progress based on reason (rational thinking). In fact, it is often called the Age of Reason. Enlightenment thinkers wanted to apply observation and reason to problems in human society.this approach led to new ideas about government, human nature, and people's rights as human beings. The far-reaching changes of the early modern age helped to shape the world we live in today. Let's begin our study of this important time with the voyages of discovery that took place during the Age of Exploration. 373
5
6 Explorer Christopher Columbus plants Spain's flag in the Americas. CHAPTER The Age of Exploration 33.1 Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about the Age of Exploration. This period of discovery lasted from about 1418 to During this time, European explorers made many daring voyages that changed world history. A major reason for these voyages was the desire to find sea routes to east Asia, which Europeans called the Indies. When Christopher Columbus sailed west across the Atlantic Ocean, he was looking for such a route. Instead, he landed in the Americas. Columbus thought he had reached the Indies. In time, Europeans would realize that he had found what they called the "New World." European nations soon rushed to claim lands in the Americas for themselves. Early explorers often suffered terrible hardships. In 1520, Ferdinand Magellan set out with three ships to cross the Pacific Ocean from South America. He had guessed, correctly, that the Indies lay on the other side of the Pacific. But Magellan hud no idea how vast the ocean really was. He thought his crew would be sailing for a few weeks at most. Instead, the crossing took three months. While the ships were still at sea, the crew ran out of food. One sailor wrote about this terrible time. "We ate biscuit... swarming with worms... We drank yellow water that had been putrid [rotten] for days... and often we ate sawdust from boards." Why did explorers brave such dangers? In this chapter, you will discover some of the reasons for the Age of Exploration. Then you will learn about the voyages of explorers from Portugal, Spain, and other European countries. You will also learn about the impact of their discoveries on Europe and on the lands they explored. The Age of Exploration 375
7 Mapmakers created better, more accurate maps by using navigational tools and information from explorers Reasons for the Age of Exploration Why did European exploration begin to flourish in the 1400s? Two main reasons stand out. First, Europeans of this time had several motives for exploring the world. Second, advances in knowledge and technology helped make voyages of discovery possible. Motives for Exploration For early explorers, one of the main motives for exploration was the desire to find new trade routes to Asia. By the 1400s, merchants and crusaders had brought many goods to Europe from Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. Demand for these goods increased the desire for trade. Europeans were especially interested in spices from Asia. They had learned to use spices lo help preserve lot id during winter and to cover up the taste of food that was no longer fresh. Trade with the East, however, was expensive and difficult. Muslims and Italians controlled the flow of trade. Muslim traders carried goods to the east coast of the Mediterranean Sea. Italian merchants then brought the goods to Europe. Problems arose when Muslim rulers sometimes closed the trade routes from Asia to Europe. Also, the goods went through many hands, and each trading party raised their price. European monarchs and merchants wanted to break the hold that Muslims and Italians had on trade. One way to do so was to find a sea route to Asia. Portuguese sailors looked for a route that went around Africa. Christopher Columbus tried to reach Asia by sailing west across the Atlantic. Other motives also came into play. Many people were excited by the opportunity for new knowledge. Explorers saw the chance to earn fame and glory as well as wealth. Some craved adventure. And as new lands were discovered, nations wanted to claim the lands" riches for themselves. A final motive for exploration was the desire to spread Christianity. As you learned in Unit 7, both Protestant and Catholic nations were eager to make new converts. Missionaries followed the path blazed by explorers, sometimes using force to bring native peoples into their faiths. 376 Chapter 33
8 Advances in Knowledge and Technology The Age of Exploration began in the midst of the Renaissance. As you have learned, the Renaissance was a time of new learning. A number of advances made it easier for explorers to venture into the unknown. One key advance was in cartography, the art and science of mapmaking. In the early 1400s, an Italian scholar translated an ancient book called Guide to Geography from Greek into Latin. The book had been written by Ptolemy in the second century O.K. Printed copies of the book inspired new interest in cartography. European mapmakers used Ptolemy's work to draw more accurate maps. Discoveries by explorers gave mapmakers new information to work with. The result was a dramatic change in Europeans' view of the world. By the 1500s, globes showed Earth as a sphere, or ball. In 1507, a German cartographer made the first map that clearly showed North and South America separated from Asia. In turn, better maps helped explorers by making navigation easier. The most important Renaissance geographer, Gerardus Mercator, created maps using improved lines of longitude and latitude. Mercator's mapmaking technique was a great help to navigators. An improved ship design also helped explorers. By the 1400s. Portuguese and Spanish shipbuilders were making caravels. These ships were small, fast, and easy to maneuver. Their shallow bottoms made it easier for explorers to travel along coastlines where the water was not deep. Caravels also used lateen (triangular) sails, an idea borrowed from Muslim ships. These sails could be positioned to take Lid\;u)Uige of the \l no matter \\liich \> it blew. Along with better ships, new navigational tools helped sailors to travel more safely on the open seas. By the end of the 15th century, the compass was much improved. Sailors used compasses to find their bearing, or direction of travel. The astrolabe, which you read about in Unit 2, helped sailors figure out their distance north or south from the equator. Finally, improved weapons gave Europeans a huge advantage over the people they met in their explorations. Sailors could fire their cannons at targets near the shore without leaving their ships. On land, the weapons of native peoples often were no match for European guns, armor, and horses. Europe's Age of Exploration produced important advances in cartography and navigation. This 15th-century map of the world is drawn according to the work of 2nd-century Greek geographer Ptolemy. cartography the art and science of mapmaking longitude a measure of how far east or west a place on Earth is from an imaginary line that runs between the North and South Poles latitude a measure of how far north or south a place on Earth is from the equator caravel a light sailing ship that is easy to maneuver and can sail in shallow water The Age of Exploration 377
9 Prince Henry the Navigator encouraged Portuguese exploration and began a school of navigation. Vascoda Gama 33.3 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration The Age of Exploration began in Portugal. This small country is located on the southwestern tip of Europe. Its rulers sent explorers first to nearby Africa and then around the world. Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed "the Navigator," Henry was not an explorer himself. Instead, he encouraged exploration and directed many important expeditions. Beginning in about 1418, Henry sent explorers to sea almost every year. He also started a school of navigation where sailors and mapmakers could learn their trades. His cartographers made new maps based on the information captains brought back. Henry's early expeditions focused on the west coast of Africa. He wanted to continue the crusades against the Muslims, find gold, and take part in trade. Gradually, Portuguese explorers made their way farther and farther south. In Bartolomeu Dias became the first European to go around the southern tip of Africa. Later, Dias died in a storm at sea. In July 1497, Vasco da Gama set sail with four ships to chart a sea route to India. Da Gama's ships rounded Africa's southern tip and then sailed up the east coast of the continent. With the help of a sailor who knew the route to India, they crossed the Indian Ocean. Da Gama arrived in the port of Calicut, India, in May There he obtained a load of cinnamon and pepper. On the return trip to Portugal, da Gama lost half of his ships. Many of his crewmembers died of hunger or disease. Still, the valuable cargo he brought back paid for the voyage many times over. His trip made the Portuguese even more eager to trade directly with Indian merchants. In 1500, Pedro Cabral set sail for India with a fleet of 13 ships. Cabral first sailed southwest to avoid calms (areas where there are no winds to fill sails). But he sailed so far west that he reached the east coast of present-day Brazil. After claiming this land for Portugal, he 378 Chapter 33
10 sailed east and rounded Africa. Routes of Portugal's Explorers Arriving in Calicut, he established a trading post and signed trading treaties. He returned to Portugal in June 1501 after battling several Muslim ships. The Impact of Portuguese Exploration Portugal's explorers changed Europeans' understanding of the world in several ways. They explored the coasts of Africa and brought back gold and slaves. They also found a sea route to India. From India, explorers brought back spices like cinnamon and pepper and goods such as porcelain, incense, jewels, and silk. After Cabral's voyage, the Portuguese took control of the eastern sea rouk's to Asia. They sei/eil the seaport ol'cioa in India and built forts there. They attacked towns on the east coast of Africa. They also set their sights on the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, in what is now Indonesia. In 1511, they attacked the main port of the islands and killed the Muslim defenders. The captain of this expedition explained what was at stake. If Portugal could take the spice trade away from Muslim traders, he wrote, then Cairo and Makkah "will be ruined." As for Italian merchants, "Venice will receive no spices unless her merchants go to buy them in Portugal." Portugal's control of the Indian Ocean broke the hold of Muslims and Italians on Asian trade. The prices of Asian goods like spices and fabrics dropped, and more people in Europe could afford to buy them. During the 1500s, Portugal also began to establish colonies in Bra/il. The native people of Bra/il suffered greatly as a result. The Portuguese tried to get the native people to give up their religion and convert to Christianity. They also forced them to work on sugar plantations. Missionaries sometimes tried to protect them from abuse, but countless numbers died from overwork and European diseases. Others fled into the interior of Brazil. The colonization of Brazil also had an impact on Africa. As the native population of Brazil decreased, the Portuguese needed more laborers. Starting in the mid 1500s, they turned to Africa. Over the next 300 years, ships brought millions of enslaved West Africans to Brazil. colony a country or an area ruled by another country plantation a large farm where crops such as sugar, rubber, or tobacco are grown Pedro Cabral The Age of Exploration 379
11 Explorer Christopher Columbus convinced King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain to support his westward voyages. strait a narrow body of water that connects two seas Christopher Columbus 33.4 Spain's Early Explorations In the late 1400s, King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain were determined to make their country a powerful force in Europe. One way to do this was to sponsor explorations and claim new lands for Spain. Key Explorers It was Ferdinand and Isabella who sponsored the voyages of Christopher Columbus. The Italian-born Columbus thought that the Indies, or eastern Asia, lay on the other side of the Atlantic Ocean. He believed sailing west would be the easiest route to the Indies. When Columbus failed to win Portuguese support for his idea, he turned to Spain. Ferdinand and Isabella agreed to pay for the risky voyage. They wanted to beat Portugal in the race to control the wealth of Asia. They also wanted to spread Christianity. In August 1492, three ships left Spain under Columbus's command. For the crew, venturing into the open ocean was frightening. As the weeks went by, some of the men began to fear they would never see Spain again. Then, on October 12, a lookout cried "Land!" Columbus went ashore on an island in the Caribbean Sea. Thinking he had reached the Indies, Columbus claimed the island for Spain. For three months, Columbus and his men explored nearby islands with the help of native islanders, whom the Spanish called Taino. Thinking they were in the Indies, the Spanish soon called all the local people "Indians." In March 1493, Columbus arrived back in Spain. He proudly reported that he had reached Asia. Over the next 10 years, he made three more voyages to what he called the West Indies. He died in Spain in 1506, still insisting that he had sailed to Asia. Many Europeans, however, believed that Columbus had actually found a land mass that lay between Europe and Asia. One of these people was Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer. Magellan believed he could sail west to the Indies if he found a strait, or channel, through South America. The strait would connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, allowing ships to continue on to Asia. Magellan won Spain's backing for a voyage to find the strait. In August 1519, he set sail with five ships and about 250 men. 380 Chapter 33
12 Magellan looked for the strait all along South America's east coast. He finally found it at the southern tip of the continent. Today it is called the Strait of Magellan. After passing through the strait, Magellan reached the Pacific Ocean in November It took another three months to cross the Pacific. During the crossing. Magellan's men ran out of food and were plagued by disease and thirst. They reached an island in the western Pacific just in time. Continuing west, Magellan visited the Philippines. There he became involved in a battle between two local chief's. In April 1521, Magellan was killed in the fighting. Magellan's crew sailed on to the Spice Islands. Three years after the expedition began, the Routes of Spain's Early Explorers NORTH, MERlCAj ^L \ JX OCI-AN SPAIN only ship to survive the expedition returned to Spain, loaded with cloves. The 18 sailors on board were the first people to circumnavigate the globe. The Impact of Early Spanish Exploration Early Spanish exploration changed Europeans' view of the world. The voyages of Columbus revealed the existence of the Americas. Magellan's expedition opened up a westward route to the Indies. It showed that it was possible to sail completely around the world. And it proved that Columbus had indeed found a "New World" one they hadn't realized was there. Columbus's voyages were the beginning of Spanish settlement in the West Indies. Spain earned great wealth from its settlements. Settlers mined for precious minerals and started sugar plantations. The Spanish also sent Europe new crops, such as sweet potatoes and pineapples. For the native people of the West Indies, Spanish settlement was devastating. Priests forced many of them to become Christians. Native people were forced to work as slaves in the mines and on the plantations. When the Spanish arrived, perhaps 1 or 2 million Taino lived on the islands. Within 50 years, fewer than 500 were left. The rest had died of starvation, overwork, or European diseases. Like Portugal, Spain looked to West Africa for new sources of laborers. From 15IS through the mid 1800s, the Spanish brought millions of enslaved Africans to work in their American colonies. circumnavigate to travel completely around something, such as Earth Ferdinand Magellan The Age of Exploration 381
13 When Spanish explorer Cortes first entered Mexico, he was welcomed by the Aztec ruler, Montezuma. Hernan Cortes 33.5 Later Spanish Exploration and Conquest After Columbia's voyages, Spain was eager to claim lands in the New World. To explore and conquer "New Spain," the Spanish turned to adventurers called conquistadors (conquerors). The conquistadors were allowed to establish settlements and seize the wealth of natives. In return, the Spanish government claimed one fifth of the treasures they found. Key Explorers In 1519, Spanish explorer Hernan Cones and a band of conquistadors set out to explore present-day Mexico. From native people, Cortes learned about the Aztecs. As you discovered in Unit 6, the Aztecs had built a large and wealthy empire in Mexico. With the help of a native woman named Malinche, Cortes and his men reached the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. The Aztec ruler, Montezuma, welcomed the Spanish with great honors. Determined to break the power of the Aztecs, Cortes took Montezuma hostage. Cortes now controlled the Aztec capital. In 1520, he left Tenochtitlan to battle a rival Spanish force. While he was gone, a group of conquistadors attacked the Aztecs in the midst of a religious celebration. In response, the Aztecs rose up against the Spanish. The soldiers had to fight their way out of the city. Many of them were killed during the escape. 382 Chapter 33
14 The following year, Cortes mounted a siege of the city, aided by thousands of native allies who resented Aztec rule. The Aztecs ran out of food and water, yet they fought desperately. After several months, the Spanish captured their leader, and Aztec resistance collapsed. The city was in ruins. The mighty Aztec Empire was no more. Four factors contributed to the defeat of the Aztec Empire. First, Aztec legend had told of the coming of a white-skinned god. When Cortes appeared, the Aztecs welcomed him because they thought he might be their god Quetzalcoatl. Second, Cortes was able to make allies of the Aztecs' native enemies. Third, their horses, armor, and superior weapons gave the Spanish an advantage in battle. The Aztecs had never seen any of these things before. Fourth, the Spanish carried diseases that caused deadly epidemics among the Aztecs. Aztec riches inspired Spanish conquistadors to continue their search for gold. In the 1520s, Francisco Pizarro received permission from Spain to conquer the Inca Empire in South America. As you learned in Unit 6, the Incas ruled an empire that ran along most of the Andes Mountains. By the time Pizarro arrived, however, a civil war had weakened the empire. In April 1532, the Inca emperor, Atahualpa, greeted the Spanish as guests. Following Cortes's example, Pizarro launched a surprise attack and kidnapped the emperor. Although the Incas paid a roomful of gold and silver for Atahualpa's ransom, the Spanish killed him the following year. Without their leader, the Incas' empire quickly fell apart. The Impact of Later Spanish Exploration and Conquest The explorations and conquests of the conquistadors transformed Spain. The Spanish rapidly expanded foreign trade and overseas colonization. For a time, wealth from the Americas made Spain one of the world's richest and most powerful countries. Besides gold and silver, ships brought corn and potatoes from the New World to Spain. These crops grew well in Europe. By increasing the food supply, they helped spur a population boom. Conquistadors also introduced Europeans to new luxury items, such as chocolate and tobacco. In the long run, gold and silver from the Americas hurt Spain's economy. Inflation, or an increase in the supply of money compared to goods, led to higher prices. Monarchs and the wealthy spent their riches wastefully instead of building up Spain's industries. The Spanish conquests had a major impact on the New World. The Spanish introduced new animals to the Americas, such as horses, cattle, sheep, and pigs. But they also destroyed two advanced civilizations. The Aztecs and Incas lost much of their culture along with their wealth. Many became laborers for the Spanish. Millions died from disease. In Mexico, for example, there were about 25 million native people in By 1605, this number had dwindled to 1 million. Routes of Spain's Later Explorers NORTH AMERICA EXICO Tenochtttlan. PACIFIC OCEAN 1, miles 2,000 kilometers ;> SOUT ^AMERICA V epidemic an outbreak of a disease that affects many people within a geographic area inflation an increase in the supply of money compared to goods, resulting in higher prices Francisco Pizarro The Age of Exploration 383
15 English explorer Henry Hudson traded with native North Americans. northwest passage a water route through North America connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans John Cabot 33.6 European Exploration of North America Spain and Portugal dominated the early years of exploration. Rulers in rival nations wanted their own share of trade and new lands in the Americas. Soon England, France, and the Netherlands all sent expeditions to North America. Key Explorers Explorers often sailed for any country that would pay for their voyages. The Italian sailor John Cabot made England's first voyage of discovery. Cabot believed he could reach the Indies by sailing northwest across the Atlantic. In 1497, he landed in what is now Canada. Believing he had reached the northeast coast of Asia, he claimed the region for England. The next year, Cabot set out on another voyage with five ships. The fate of this expedition is uncertain. Cabot may have returned to England, or he may have been lost at sea. Another Italian, Giovanni da Verrazano, sailed under the French flag. In 1524, da Verrazano explored the Atlantic coast from present-day North Carolina to Canada. His voyage gave France its first claims in the Americas. Like many explorers, however, he met an unhappy end. On a later trip to the West Indies, he was killed and eaten by native people. Sailing for the Netherlands, English explorer Henry Hudson journeyed to North America in Hudson wanted to find a northwest passage through North America to the Pacific Ocean. Such a water route would allow ships to sail from Europe to Asia without entering waters controlled by Spain. Hudson did not find a northwest passage, but he did explore what is now called the Hudson River. Twenty years later, Dutch settlers (people from the Netherlands) began arriving in the Hudson River valley. The next year Hudson tried again, this time under the flag of his native England. Searching farther north, he sailed into a large bay in Canada that is now called Hudson Bay. He spent three months looking for an outlet to the Pacific, but there was none. After a hard winter in the icy bay, some of Hudson's crew rebelled. They set him, his son, and seven loyal followers adrift in a small boat. Hudson and the other castaways were never seen again. Hudson's voyage, however, laid the basis for later English claims in Canada. 384 Chapter 33
16 Routes of European Explorers NORTH AMERICA SOUTH AMERICA The Impact of European Exploration of North America Unlike the conquistadors in the south, northern explorers did not find gold and other treasure. As a result, there was less interest at first in starting colonies. Canada's shores did offer rich resources of cod and other fish. Within a few years of Cabot's trip, fishing boats regularly visited the region. Europeans were also interested in trading with Native Americans for otter skins, whale oil, and beaver and fox furs. By the 1600s, Europeans had set up a number of trading posts in North America. English exploration also contributed to a war between England and Spain. As English ships roamed the seas, some captains, nicknamed "sea dogs," began raiding Spanish ports and ships to take their gold. Between 1577 and Francis Drake sailed around the world. He also claimed part of what is now California for England, ignoring Spain's claims to the area. The English raids added to other tensions between England and Spain. In 1588, King Philip II of Spain sent an armada, or fleet, to invade England. With 130 heavily armed vessels and about 31,000 men, the Spanish Armada seemed an unbeatable force. But the smaller English fleet was fast and well armed. Their guns had a longer range, so they could attack from a safe distance. After several battles, a number of the armada's ships had been sunk or driven ashore. The rest turned around but faced terrible storms on the way home. Fewer than half of the ships made it back to Spain. 'I IK- dclcal ol the Spanish Armada marked the start of a shift in power in Europe. By Spain no longer dominated the continent. With Spain's decline, other countries particularly England and the Netherlands took an active role in trade and colonization around the world. Giovanni da Verrazano Henry Hudson The Age of Exploration 385
17 Major European Trade Routes, About 1750 ETHERLANDS EUROPE capitalism an economic system based on investment of money (capital) for profit market economy an economy in which prices are determined by the buying and selling decisions of individuals in the marketplace 33.7 The Impact of Exploration on European Commerce and Economies The voyages of explorers had a dramatic impact on European commerce and economies. As a result of exploration, more goods, raw materials, and precious metals entered Europe. Mapmakers carefully charted trade routes and the locations of newly discovered lands. By the 1700s, European ships traveled trade routes that spanned the globe. New centers of commerce developed in the port cities of the Netherlands and England, which had colonies and trading posts in faraway lands. Exploration and trade contributed to the growth of capitalism. This economic system is based on investing money for profit. Merchants gained great wealth by trading and selling goods from around the world. Many of them used their profits to finance still more voyages and to start trading companies. Other people began investing money in these companies and shared in the profits. Soon this type of shared ownership was applied to other kinds of business. Another aspect of the capitalist economy concerned the way people exchanged goods and services. Money became more important as precious metals flowed into Europe. Instead of having a fixed price, items were sold for prices that were set by the open market. This meant that the price of an item depended on how much of the item was available and how many people wanted to buy it. Sellers could charge high prices for scarce items that many people wanted. If the supply of an item was large and few people wanted it, sellers lowered the price. This kind of system is called a market economy. Labor, too, was given a money value. Increasingly, people began working for hire instead of directly providing for their own needs. 386 Chapter 33
18 Merchants hired people to work in their own cottages, turning raw materials from overseas into finished products. This growing cottage industry was especially important in the making of textiles. Often entire families worked at home, spinning wool into thread or weaving thread into cloth. Cottage industry was a step toward the system of factories operated by capitalists in later centuries. A final result of exploration was a new economic policy called mercantilism. European rulers believed that piling up wealth was the best way to build their countries' power. For this reason, they tried to reduce the things they bought from other countries and increase the items they sold. Having colonies was a key part of this policy. Nations looked to their colonies to supply raw materials for their industries. They profited by turning the materials into finished goods that they could sell to other countries and to their own colonies. To protect the valuable trade with their colonies, rulers often forbade colonists from trading with other nations Chapter Summary In this chapter, you learned about the Age of Exploration. Beginning in the 1400s, European explorers went on great voyages of discovery. Their voyages had a major impact on Europe and on the lands they explored. European explorers sought wealth, land, knowledge, and adventure. They also wanted to spread Christianity. A number of advances in knowledge and technology made their journeys possible. The Portuguese explored Africa's coasts, charted a sea route to Asia, and claimed Brazil. The voyages of Christopher Columbus led to Spanish colonization in the Americas. England, France, and the Netherlands sent explorers to North America. Millions of people living in the Americas died as a result of European colonization and conquest. The Inca and Aztec Empires were destroyed. West Africans suffered greatly when they were brought to the Americas to work as slaves. The Age of Exploration vastly increased Europeans' knowledge of the world. In the next chapter, you will learn about another source of new knowledge: the Scientific Revolution. Weaving cloth became a growing cottage industry as families set up looms and workshops in their homes. cottage industry a smallscale business in which people work mostly at home mercantilism an economic policy by which nations try to gather as much gold and silver as possible by controlling trade and establishing colonies The Age of Exploration 387
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration
 The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations
 Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
Fall of the Aztec & Inca Civilizations Part Two Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Christopher Columbus asks
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Unit Seven Notes Bennett Warm Up! Discuss with your Elbow Buddy: 1. Describe the Incan Empire. 2. Describe the Aztec Empire. 3. How are they similar and different? Spain
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Exploration & Colonization. Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School
 Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
CAUSES OF EXPLORATION. READING and ASSIGNMENT. Read the excerpt below. Use the reading to complete the section of the graphic organizer.
 Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires
 Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
Fall of the Aztec & Incan Empires Spain Vs. Portugal Christopher Columbus asks both countries to sponsor his voyage--spain agrees. Portugal saw the wealth that Spain was gaining, and wanted to be part
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1
 Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe.
 I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas. Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain
 Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain Conquistadors Bernal Díaz del Castillo was one of the many Spanish conquistadors or conquerors, who marched
Text 1: Conquistadores Arrive in the Americas Topic 2 Lesson 1: Spanish Colonization and New Spain Conquistadors Bernal Díaz del Castillo was one of the many Spanish conquistadors or conquerors, who marched
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Bartholomeu Dias. Cape of Good Hope 1487
 Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Renaissance Economics. The Age of Discovery
 Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
New Ideas, New Nations
 New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Columbus was thrilled. In a later letter, he wrote, I write this to tell you how in thirty-three
 Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Section: 2. Spain Starts an Empire Marco Polo s book continued to be read over the next two centuries. This was a time of great change in Europe. The rediscovered writings of ancient Greeks and Romans
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
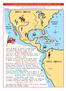 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA
 SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Spain Builds an Empire
 Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Spain Builds an Empire Spanish Conquistadors Conquistador- conqueror We came here to serve God and the king and also to get rich Bernal Diaz del Castillo 3 G s- God, Glory, Gold Spain became one of the
Wrote book on his explorations that generated excitement in others to develop trade with China and India 1st European who traveled the length of Asia
 AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? Age of Exploration and Trade Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Lesson 1 The Age of Exploration ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does technology change the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did Europeans begin to explore the world? 2. Which leaders were responsible for
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
Age of Discovery. SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
 Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
Age of Discovery SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Reasons for Exploration Marco Polo: fascinated by Marco Polo s account
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY ( )
 THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
TIP Vocabulary Chart. Exploration Vocabulary. 1. Circumnavigate: To sail around something, in this case the globe. Term Information Picture
 Exploration Vocabulary 1. Circumnavigate: To sail around something, in this case the globe. TIP Vocabulary Chart Term Information Picture 2. Conquistadors: (Con-kees-tuh-doors) Spanish Conquerors 3. Great
Exploration Vocabulary 1. Circumnavigate: To sail around something, in this case the globe. TIP Vocabulary Chart Term Information Picture 2. Conquistadors: (Con-kees-tuh-doors) Spanish Conquerors 3. Great
Conquest in the Americas. World History
 Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
Conquest in the Americas World History First Encounters in the Americas Columbus landed in the New World in 1492. He landed in the Caribbean on islands we now call the West Indies. The Native Americans
Clash of Cultures: Two Worlds Collide By UShistory.org 2017
 Name: Class: Clash of Cultures: Two Worlds Collide By UShistory.org 2017 The Aztec empire was an advanced civilization that ruled in Mexico before Spanish explorers arrived. This informational text discusses
Name: Class: Clash of Cultures: Two Worlds Collide By UShistory.org 2017 The Aztec empire was an advanced civilization that ruled in Mexico before Spanish explorers arrived. This informational text discusses
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Encounters with Europe THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) The reaction toward European exploration varied in Africa, Indian Ocean states, and in the Americas. For example, whereas some saw practical benefits
Age of Exploration. Use the text to answer each question below.
 Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
Clash of Cultures: Cortes Conquers Moctezuma and the Aztecs
 Clash of Cultures: Cortes Conquers Moctezuma and the Aztecs By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.21.17 Word Count 751 Titled "Entrance of Cortes into Mexico," this illustration shows Spain's
Clash of Cultures: Cortes Conquers Moctezuma and the Aztecs By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.21.17 Word Count 751 Titled "Entrance of Cortes into Mexico," this illustration shows Spain's
ISN 4. #2. List reasons why people migrate.
 ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
ISN 4 #2. List reasons why people migrate. 8 9 Reasons for Exploration You need a blank sheet of paper! With your partner, write as many reasons as you can think of that someone would explore/migrate to
For Review Only. Contents. The World in the Year Columbus and His Big Plan The Big Voyage Land!... 12
 Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Contents The World in the Year 1451... 4 Columbus and His Big Plan... 7 The Big Voyage... 10 Land!... 12 What Happened Next?... 15 Comprehension Questions... 18 Glossary... 19 World History Timeline...
Exploration and Settlement Unit 2
 Exploration and Settlement Unit 2 Big Idea Cooperation (act of working together) and Conflict (disagreement or fight) Cultural differences and competition for land led to conflicts among different groups
Exploration and Settlement Unit 2 Big Idea Cooperation (act of working together) and Conflict (disagreement or fight) Cultural differences and competition for land led to conflicts among different groups
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s
 European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
European Exploration and the New Global Age 1400s -1600s Global Changes Amid the 1400s in Europe, advances in technology and trade would impact world history and change the globe forever These changes
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Quiz Show. Chapter 2 European Explorers
 Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
The World of the 1400s. What Was Going On?
 The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
THE COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE
 Name: Date: Directions: Read the following passage about the Columbian Exchange. Answer the questions that follow using complete sentences. Remember to give specific details from the text to support your
Name: Date: Directions: Read the following passage about the Columbian Exchange. Answer the questions that follow using complete sentences. Remember to give specific details from the text to support your
Chapter Two. When Worlds Collide
 Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration. Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture
 Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Chapter Objectives Classify the explorers and their areas of exploration Evaluate the impact of European exploration on Native American culture Examine how technology made long sea voyages possible Explore
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02)
 American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
American History Unit 1: Age of Exploration (Part 02) Christopher Columbus I. Christopher Columbus A. Born near Genoa, Italy in 1451. 1. Expert navigator. B. Columbus had a radical idea. 1. Thought the
First Visitors From Europe
 THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
THE AGE OF EXPLORATION In the 1400s, European explorers first met Native Americans. For the next three centuries, European explorers and settlers expanded their influence across North and South America.
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
Lesson 1 European Exploration and Expansion ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the effects of political and economic expansion? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary overseas beyond or across the sea Content Vocabulary
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST
 WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
WHAT TO STUDY FOR CHAPTER 3 TEST 3. How did Columbus reach the Americas? In the late 1400 s King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, from Spain, wanted their share of the Asian spice trade. Even though he was
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Exploration and Conquest of the New World
 Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
The Aztec and the Spanish Unit Test
 The Aztec and the Spanish Unit Test 4 1 2 3 5 1) Where on the map is the Aztec Empire located? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 2) Where on the map is Spain located? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 Artifact #1 Artifact
The Aztec and the Spanish Unit Test 4 1 2 3 5 1) Where on the map is the Aztec Empire located? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 2) Where on the map is Spain located? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 Artifact #1 Artifact
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Thomas Jefferson and the West.
 Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
APWH chapter 18.notebook January 11, 2013
 Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
They built a magnificent city called Tenochtitlan (now Mexico City).
 Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico in 1100s (central Mexico, including present day Mexico City). They built a magnificent city called Tenochtitlan (now Mexico City). Diorama of Tenochtitlan This was
Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico in 1100s (central Mexico, including present day Mexico City). They built a magnificent city called Tenochtitlan (now Mexico City). Diorama of Tenochtitlan This was
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
