Honors World Cultures Unit 3: SE Asia -- Geography of China
|
|
|
- Rudolph Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Honors World Cultures Unit 3: SE Asia -- Geography of China The North China Plain Physical characteristics: As its name indicates, this is an area of gently rolling topography. It is subject to flooding, and water often stands in large pools and "lakes," as there is no place for drainage. This creates marshes and shallow, reed-filled lakes, which are good for thatching and weaving as well as migratory birds, fish, and snails. Winter and summer temperatures can be extreme, and dust storms are common. Highly variable weather means good harvests for only three out of every five years. History: The North China Plain was one of the cradles of Chinese civilization. China's earliest agricultural societies as well as dynasties formed there. People traditionally lived in dispersed communities rather than nucleated settlements because food and water were available everywhere. The primary need to nucleate was as a defense against invaders and raiders. The earliest archaeological sites of "cities" are at the foot of the Taihang Mountains, where there are minerals as well as manageable water resources for all seasons. Economic activities and resources today: Even today the North China Plain is a land of dispersed agricultural settlements. There is little or no industry other than distinctive indigenous handicrafts. Fresh water must come from wells that often are salty because of poor drainage. The lack of topographic relief means seasonal winds are strong and often destructive. The result is that many areas have planted windbreaks to protect the soil of the fields from erosion. Life on the North China Plain is one of self-sufficiency and subsistence. Wheat, cotton, tobacco, peanuts, persimmons, and other seasonal fruits and vegetables are grown there. Housing: mud-based, single-story structures with flat roofs Social organization: villages and clans Transportation: walking, bicycles, cars Food staples: wheat-based foods The Loess Plateau Physical characteristics: The overwhelming distinctive characteristic of the Loess Plateau is the wind-blown alluvium (dust) that has accumulated to depths of over 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) in some places and is known as loess. While loess is rich in calcium and thus fertile, the overall aridity of the region coupled with the fact that loess does not hold water makes traditional methods of irrigation and farming useless. Environmental conditions, including highly variable rainfall (when it does occur), means that farmers seldom expect to harvest more than two crops every three years. History: Two cultural patterns resulted from the physical environment and location of the Loess Plateau. One was human poverty and isolated communities; the other a dependency upon trade with nomadic peoples and the empires beyond the Great Wall. Economically, trade has dominated the Loess Plateau and commercial cities have flourished and died as routes and the direction of trade have shifted. It has never been a strong food-producing region.
2 Economic activities and resources today: As in the past, key cities in the Loess Plateau are those that facilitate trade and transport to and from eastern China and the North China Plain. Cities such as Xi'an and Lanzhou are trade hubs stemming from a reinvigorated economy in Xinjiang and the former Soviet countries of central Asia. Today, however, oil has replaced silk as the major economic commodity. Oil is a major resource in Gansu, Xinjiang, and the contiguous country of Kazakhstan. Housing: caves carved into the loess cliffs and mud-brick houses in rural areas, apartments in urban areas Social organization: nuclear families Transportation: walking, mule, and horse in rural areas; cars, buses, and bicycles in urban areas Food staples: wheat-noodles and sour cabbage The Southeast Coast and Shanghai Physical characteristics: This region shares the entire Yangzi Valley's dominant characteristics of water, wetlands, and hot and humid summers. However, the influence of the Pacific Ocean as well as access thereto makes the area distinctive. The ocean's warm current creates milder winter temperatures than in the interior. In addition the nearby mountains (Huangshan and Wuyi) are favorable for crops other than aquaculture (rice, shrimp, ducks, and so on), which is prominent in the lowlands. Mild climates and abundant rainfall mean farmers in this area generally expect to obtain three or more crops every year. Some form of food, whether from land or sea, is always abundant and in surplus. History: This was the first region to feel the impact of the West through the Opium War and "Treaty Ports" of the eighteenth century. It has had the greatest number of Christian missionaries, Chinese Christians, and Christian churches in China. Like so many of China's distinct physical environments, it is dominated by ethnic peoples not fully identifiable as "Han," who speak distinct languages and often have closer ties to Chinese overseas. Economic activities and resources today: Shanghai is the major city of this region. Located at the mouth of the Yangzi, it is a thriving port and a center for steel, telecommunications, automobiles, power production equipment, petrochemicals and electric appliances. Having a strong service industry, the city is also focused on finance and insurance, commerce, real estate, tourism, and information. On the coast fishing and shipping are important industries. Other cities along the coast also have been designated "special economic zones." In the interior regions rice is an important cash crop, except in the mountainous areas, where fishing and forestry take place. Other specialty crops, such as tea and citrus fruits, are grown, but the coast is subject to typhoons. Housing: plaster or brick to offset rain in rural areas, apartment buildings in urban areas Social organization: class, family, or business compounds Transportation: boats and ships on rivers and canals, cars, buses, and bicycles Food staples: rice, seafood, and tropical fruits
3 The Yangzi Valley Physical characteristics: Separated from other regions by mountains and extensive wetlands is the Yangzi (Yangtze or Changjiang-"long river"); its tributaries and lakes are the focus of life and economics in the valley. Summers tend to be hot, humid, and rainy along the river, while winters are brief but cold. History: The Yangzi Valley has traditionally been an important food producer. The river has been the center of economic life, bringing trade and influences from distant places. During the twentieth century, initiatives to dam the Yangzi have brought about drastic changes in the landscape, economy, and lives of the people living in the Yangzi Valley, forcing many to relocate. Economic activities and resources today: Fishing and boat commerce dominate life and culture. Cities, such as Chongqing (in Sichuan province), Wuhan, and Nanjiang, are driven by economies tied to water-borne transportation and commerce-not agriculture or even food processing. Major manufacturing centers exist along the river because it is a cheap means of transport. There are large numbers of people who spend their entire lives on small or medium boats, making a living moving goods and people via the numerous lakes, canals, and rivers of the entire Yangzi valley. Housing: white-plastered, multistoried houses with black tiled roofs, houseboats, apartments in cities Social organization: commercial/trade "families" Transportation: river and canal boats, trucks, cars, bicycles in cities Food staples: rice and fish The Sichuan Basin Physical characteristics: The defining physical feature of this region is the large Sichuan Basin, which is divided into two parts, Chengdu and Chongqing. High and difficult mountains surround the basin. Primary access to eastern China is via the Yangzi River, which traverses the famous Three Gorges. This geographic setting creates a mild climate. Extremely fertile soils are largely derived from old lake sediments. Farmers not only can count on several crops every year, they can depend on a diversity of food crops as well as specialties. History: It is often said "Sichuan in the first province to declare independence and the last to be reunited after there is peace." Located in a highly protected, productive setting and adjacent to virtually every major region of historic China, Sichuan is capable of being wholly independent from the rest of China. Yet, control of Sichuan and its agricultural riches provided access to every other major political and economic realm, making it the target of many outside warlords and emperors. Economic activities and resources today: Sichuan has always been known for its tea, silk, flowers, medicinal herbs, and diverse wildlife, including pandas, deer, and tigers. These resources remain a major staple of its modern economy as do the raising of sheep, pork, and grain. Tourism is also crucial to Sichuan's economy. Popular tourist sites include the Thousand- Buddha Cliff, Qingcheng Mountain, the Bamboo Forest, the Corridor of Cypresses, Woolong
4 Nature Reserve (for panda conservation), and Xiling National Forest Park. The Yangzi River is a thoroughfare of trade, meaning that Sichuan is rapidly changing with the influx of foreign investors and developers. Housing: timber, stone, or straw houses in rural areas; large apartment buildings in the cities Social organization: village clusters in rural areas Transportation: walking, mule, horses, in the mountains; bicycles and cars on the plains, boats on rivers Food staples: varied Southwest Uplands Physical characteristics: Nothing so dominates and defines southwest China as its rugged, highly eroded topography. Because it is close to the tropical cyclones of the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea it has abundant rainfall (often causing erosion or denuded slopes). This location and terrain create numerous distinctive local "niches" that often are self-sufficient, which in turn support an abundance of distinct ethnic groups, many of which also live in the neighboring countries of Laos, Vietnam, Burma, and even Thailand. History: This region first came into the Chinese sphere during the Mongol Yuan dynasty ( ). Its history reflects both its rugged topography as well as its proximity to the modern countries and peoples of Southeast Asia, such as Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and Myanmar (Burma). Trade between these countries and the Southwest Uplands often has been illegal and generally consisted of small items of great value, such as jade or opium. Economic activities and resources today: Land for grazing and the cultivation of rice, winter wheat, tea, and beans are available in the region. The tropical plateau along the border of Vietnam and Laos is ideal for cultivating rubber and bananas. The mining of tin, another major industry of this region, is the only distinctive economy that is both traditional and modern. More valuable, however, has been the cultivation and export of opium, an activity developed as a result of Britain's Opium War with China. Housing: caves carved into the loess cliffs and mud-brick houses in rural areas; apartments in urban areas Social organization: nuclear families Transportation: walking, mule, and horse in rural areas Food staples: vegetables, rice, ducks and geese Xinjiang Physical characteristics: China's largest province is a landscape of deserts, mountains, and oases. Most of the region is dominated by the Tarim Basin, which is filled mostly by the formidable Taklamakan desert and rimmed by high mountains-the Kunlun Shan to the south, the Karakorum
5 to the west, and the Tian Shan to the north. The alpine beauty of the Tian Shan separates the Tarim Basin from the smaller Junggar Basin, which is characterized by more moisture and grass. History: The inhabitants of the Junggar Basin have a long association with various Mongol peoples, but they are more pastoral than nomadic. Located between the cultural empires of China in the east and central Asia in the west, Xinjiang was an important historic link along the Silk Roads. The peoples living along oases around the rim of the Tarim Basin had closer ties to Persia and the Islamic influences of the Middle East. The Uighurs, Xinjiang's largest minority, are predominantly Muslim and Turkic in ethnicity and language. Their economic history is more closely linked to the mercantile cities and trade of the ancient Silk Road than to the irrigation practices of eastern China. The trade and traffic along this famous route integrated people and cultures and introduced distinctive styles of music and musical instruments, especially the suona and pipa, or Chinese-style lute. The beginning of the twentieth century found the British, Germans, American, Japanese, and Russians vying for control of this strategically important location. Economic activities and resources today: Xinjiang is rich in oil. The Taklamakan is too barren for agriculture but is often used as a nuclear test site. Despite the fact that the railroad does not extend very far west into the province, tourism is gaining in this remote region of spectacular scenery with a wealth of archaeological treasures, including Buddhist cave temples, ruined cities and fortresses, petrogylphs, and 4,000-year-old mummies. Housing: earth/adobe houses, two-storied with flat roofs. Nomads live in tents, while apartments are common in urban areas. Mosques and some residential architecture have Central Asian or Persian-style influences. Social organization: nuclear families in urban areas; groups of families for nomads Transportation: long-distance trucks and buses in rural areas; bicycles within cities. Mules are used in cities, and horses and camels in rural areas. Food staples: wheat noodles, flat wheat bread (nan), and mutton Northeast (Manchuria) Physical characteristics: The dominant physical feature of this region is its winter cold and ice. Equally distinctive and important are its two extensive wetlands-the northernmost associated with the Songari River and the southern with the Liao River. Nevertheless, its basic natural resources of iron ore and coal have made it economically vital to the rest of China. History: The Manchus invaded China in the seventeenth century, establishing the Qing dynasty in The lands of Manchuria, however, were not open to Han settlement until the dynasty's end in Most Chinese migrants worked in existing industry and on large commercial farms producing mostly soybeans and corn. Economic activities and resources today: Manchuria is China's most important region for heavy industry. Coal and iron mining are also central to the region's economy, and ginseng, soybeans, and timber are major products.
6 Housing: caves carved into the loess cliffs and mud-brick houses in rural areas; apartments in urban areas. Some Russian influence in the architecture. Social organization: nuclear families Transportation: walking, mule, and horse in rural areas Food staples: meat and soybean curds Qinghai and the Tibetan Plateau Physical characteristics: Altitude, which can average meters (13,000 feet), best defines the physical environment of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Except in the bright sunlight, it always is very cold. Located mostly in the rain shadow of the Himalayas, the region is arid to semi-arid. This means that despite a latitude close to the Tropic of Cancer, Qinghai and Tibet are nontropical for the most part. Still, there are areas along its southern and western boundaries, where rhododendron and banana trees grow in the shadow of active glaciers. This is attributable to the heavy rainfall and temperatures associated with the Indian monsoon. History: Because of the region's proximity to India and central Asia, China has seldom affected the people, economies, and even religion of Qinghai and Tibet in the east. Even Mongolia had closer cultural links to this region than did China proper. Animal husbandry and nomadism are traditional ways of life. Until the 1950s, one out of every five Tibetans was a Buddhist nun or monk. Monasteries have been at the center of society since at least the eighth century. Economic activities and resources today: Qinghai and Tibet remain remote and largely unpopulated. Where conditions permit, the Chinese have encouraged the westward migration of farmers from overpopulated areas to the east. Animals continue to be raised, and wool weavings are another important product. Goods are also produced from indigenous gold and turquoise. Housing: nomads live in yak-felt tents. Homes are two stories with inward-slanting mud, earthen, brick, or stone walls and earthen floors. Social organization: monasteries play a role in Buddhist communities, mosques in Islamic ones. Nomads gather in family clusters. Transportation: walking, caravans, trucks and buses, horses in rural areas; bicycles and cars in urban areas Food staples: yak butter, tea, barley, vegetables, yak, or lamb Excerpt taken from: McColl, Robert W.. "AskAsia.". Jan Asia Society. 12 Oct < from:
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Population distribution
 Land forms Population distribution Climate and water Provinces and regions Resources Regional differentiation Formation: collision of Indian subcontinent and Asian landmass China landmass tilts west to
Land forms Population distribution Climate and water Provinces and regions Resources Regional differentiation Formation: collision of Indian subcontinent and Asian landmass China landmass tilts west to
Setting the Stage - Ancient China
 Setting the Stage - Ancient China The land of ancient China is part of a vast region that today is called mainland East Asia. Mainland East Asia includes the present day countries of China, Mongolia, North
Setting the Stage - Ancient China The land of ancient China is part of a vast region that today is called mainland East Asia. Mainland East Asia includes the present day countries of China, Mongolia, North
THE COFFEE POT OF THE WORLD BRAZIL
 THE COFFEE POT OF THE WORLD BRAZIL Brazil lies in the north-eastern part of South America and occupies a little less than one-half the total area of the continent. In area, this is the fifth largest country
THE COFFEE POT OF THE WORLD BRAZIL Brazil lies in the north-eastern part of South America and occupies a little less than one-half the total area of the continent. In area, this is the fifth largest country
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Packet 7. Movement of People and Goods
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Review Questions 1. How did the Bantu migrations affect existing cultures?
 Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
Africa includes tropical rain forests, grassy plains called savannas, and deserts such as the vast Sahara. Deserts, rain forests, the interior plateau, and rivers with cataracts, or waterfalls, limited
The Fertile Crescent and the Promised Land
 Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
The Qin and Han Dynasties
 The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
The Qin and Han Dynasties Four Chinese Dynasties Section Overview This section describes the first civilizations in China and how the geography of the region, especially its rivers, mountains, and deserts,
Tuesday, February 7, 17 THE SILK ROAD
 THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
THE SILK ROAD THE SILK ROAD The Silk Road was actually a network of smaller trade routes that reached over 4,000 miles across Asia. The Silk Road reached from Louyang (China) to Antioch (Syria). The Silk
The two civilizations were isolated for years, with this they faced many challenges. They faced environmental challenges such as polar
 The two civilizations were isolated for 15000 years, with this they faced many challenges. They faced environmental challenges such as polar extremes, high mountain ranges, deserts, and prairies. These
The two civilizations were isolated for 15000 years, with this they faced many challenges. They faced environmental challenges such as polar extremes, high mountain ranges, deserts, and prairies. These
Directions for East Asia (Map #1)
 Directions for East Asia (Map #1) http://www.teacheroz.com/ap-mapreview.pdf (a site with a ton of maps that can help you locate the following) Directions: Label the map of China with the land and water
Directions for East Asia (Map #1) http://www.teacheroz.com/ap-mapreview.pdf (a site with a ton of maps that can help you locate the following) Directions: Label the map of China with the land and water
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
Where is our stuff made?
 Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
Where is our stuff made? Today s Title The Silk Road The Internet of the Past Today s Date January 24 th, 2018 Today s Page Number: 70 Today s EQ: What is cultural diffusion? How can it positively impact
Countries Of The World: China
 Countries Of The World: China By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 02.15.18 Word Count 571 Level MAX Image 1: The Great Wall of China is a popular place for tourists to visit. It is
Countries Of The World: China By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 02.15.18 Word Count 571 Level MAX Image 1: The Great Wall of China is a popular place for tourists to visit. It is
New England Middle Atlantic Region
 New England Middle Atlantic Region I. States of the New England Middle Atlantic Region: Maine - Delaware New Hampshire - New York Vermont - New Jersey Massachusetts - Pennsylvania Connecticut - Maryland
New England Middle Atlantic Region I. States of the New England Middle Atlantic Region: Maine - Delaware New Hampshire - New York Vermont - New Jersey Massachusetts - Pennsylvania Connecticut - Maryland
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Question: What crop is being discussed in the above paragraph?
 ICEBREAKER: A crop is grown in the fields, where it is harvested and put into 100- pound bags. These bags are sold by the farmer for anywhere between $70-$100. The product is then brought into another
ICEBREAKER: A crop is grown in the fields, where it is harvested and put into 100- pound bags. These bags are sold by the farmer for anywhere between $70-$100. The product is then brought into another
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD.
 SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
SSWH6 Describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before 1500 CE/AD. b. Describe the trading networks and distribution of resources by examining transsaharan trade in gold, salt, slaves;
 Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
followed animals from Asia.
 Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties
 Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties Sui Dynasty (589-618) After collapse of the Han Dynasty (220AD), no emperor strong enough to hold China together. centuries of fragmented power; who in society enjoys more
Warm-Up: Where were your shoes made?
 Warm-Up: Where were your shoes made? Where shoes are made https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/to p-shoe-manufacturing-countries.html INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK Learning
Warm-Up: Where were your shoes made? Where shoes are made https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/to p-shoe-manufacturing-countries.html INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK Learning
Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar
 Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development The land of China A glance on Chinese history Chinese
Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development ( Part I) By Dr. Ming Men Visiting Fulbright Scholar Chinese Culture and Recent Economic Development The land of China A glance on Chinese history Chinese
Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture The Cultural Landscape:
 Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Culture The combination of three things: Values Material artifacts Political institutions This chapter deals
Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Culture The combination of three things: Values Material artifacts Political institutions This chapter deals
Text One. The Silk Road
 Text One The Silk Road The Silk Road was an extensive network of overland trade routes across the Asian continent. They connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North
Text One The Silk Road The Silk Road was an extensive network of overland trade routes across the Asian continent. They connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean world, including North
China and Mongols: Significant Changes
 China and Mongols: Significant Changes Lesson 3, Unit 9 Objectives & Key Terms Describe China s accomplishments under the Tang and Song dynasties Illustrate the changes that occurred after the Mongol invasion
China and Mongols: Significant Changes Lesson 3, Unit 9 Objectives & Key Terms Describe China s accomplishments under the Tang and Song dynasties Illustrate the changes that occurred after the Mongol invasion
The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River)
 Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
controlled the southern territory around the port of Aden. They withdrew in 1967 and the area
 Yemen Background In 1918, North Yemen became independent from the Ottoman Empire. The British controlled the southern territory around the port of Aden. They withdrew in 1967 and the area became known
Yemen Background In 1918, North Yemen became independent from the Ottoman Empire. The British controlled the southern territory around the port of Aden. They withdrew in 1967 and the area became known
Physical Geography Micronesia Melanesia Polynesia
 Oceania Physical Geography How did thousands of islands appear across the Pacific Ocean? There are 3.3 million square miles of the Pacific Ocean between Australia, Indonesia, and the Hawaiian Islands.
Oceania Physical Geography How did thousands of islands appear across the Pacific Ocean? There are 3.3 million square miles of the Pacific Ocean between Australia, Indonesia, and the Hawaiian Islands.
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Chapter 5. Early Society in East Asia. Copyright 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. Permission Required for Reproduction or Display.
 Chapter 5 Early Society in East Asia 1 The Yellow River Huang He 3000 Miles: Tibet to the Yellow Sea Deposits fertile, light colored soil Periodic flooding: China s sorrow 2 Prehistoric Society: Yangshao
Chapter 5 Early Society in East Asia 1 The Yellow River Huang He 3000 Miles: Tibet to the Yellow Sea Deposits fertile, light colored soil Periodic flooding: China s sorrow 2 Prehistoric Society: Yangshao
Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia
 Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia Min Shu Waseda University 2017/11/6 1 Outline of the Lecture A brief history of colonialism in East Asia Participating in East Asian trade networks Spice
Spice, Opium, Oil and Colonialism in East Asia Min Shu Waseda University 2017/11/6 1 Outline of the Lecture A brief history of colonialism in East Asia Participating in East Asian trade networks Spice
Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia
 1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
1 Silk Roads: Exchange Across Eurasia The Growth of the Silk Roads Eurasian landmass has long been home to the majority of as well as the world s most productive, largest, and greatest concentration of
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
The Geography of the Arabian Peninsula
 This photograph of the Arabian Peninsula was taken from a satellite in space. CHAPTER The Geography of the Arabian Peninsula 7.1 Introduction Our study of Islam begins with the Arabian Peninsula, where
This photograph of the Arabian Peninsula was taken from a satellite in space. CHAPTER The Geography of the Arabian Peninsula 7.1 Introduction Our study of Islam begins with the Arabian Peninsula, where
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere
 Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
BC A
 Skara Brae Skara Brae, on the southern shore of Sandwick, Orkney, was a late Neolithic settlement that was inhabited between 3200 and 2200 BC. Eight prehistoric houses, connected by low covered passageways,
Skara Brae Skara Brae, on the southern shore of Sandwick, Orkney, was a late Neolithic settlement that was inhabited between 3200 and 2200 BC. Eight prehistoric houses, connected by low covered passageways,
Assessment: China Develops a New Economy
 Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1
 THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
New England Colonies Economy
 New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
AFRICA. Human Geography
 AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
AFRICA Human Geography A. Human Beginnings- Historically people in Africa governed themselves along lineages and family relationships. B. East Africa 1. East Africa is known as the cradle of humanity.
*China s physical geography helped keep China economically and culturally isolated throughout its early dynasties *Its mountains and deserts
 Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
The Ming and Qing Dynasties
 Preview The Ming and Qing Dynasties Main Idea / Reading Focus The Ming Dynasty The Qing Dynasty Ming and Qing Culture Map: Ming and Qing Dynasties Main Idea The Ming and Qing Dynasties During the Ming
Preview The Ming and Qing Dynasties Main Idea / Reading Focus The Ming Dynasty The Qing Dynasty Ming and Qing Culture Map: Ming and Qing Dynasties Main Idea The Ming and Qing Dynasties During the Ming
Post Classical Civs. F Block - Humanities
 Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
Post Classical Civs F Block - Humanities #1 Ghana Empire Time period: A.D.800-1076 Rise: Ghana grew from a kingdom to an empire because of the strong military the king had control over and he was able
Sea Road: Indian Ocean. By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton
 Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
Sea Road: Indian Ocean By Kaleah Ross- Leopoldo, Aidan O Shea, Johnantony Munoz, Jacquelyn Fullerton Indian Ocean Route Sea routes in the Indian Ocean were not without dangers. Pirates were a common issue
8 HOW DID THE WORLD ZONES CONNECT?
 8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
North American Native Americans
 North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
AP World History
 AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
AP World History I. The Silk Road A. Origins and Operations 1. Overland route that linked China to the Mediterranean world. 2. Trade was fostered by the Chinese need for horses and by the Parthian state
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods. Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick
 Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
Silk Roads: Exchange and Goods Alexis Ruiz, Darby Miller, Kiara Melendez, Liam Fick History Ancient road from China to Rome The Silk Road was actually a connection of several routes that lead to the main
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming
 Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Japanese Knotweed Red Winged Blackbird
 Japanese Knotweed Red Winged Blackbird Emerald Ash Borer White Ash Tree Asian Long Horned Beetle Maple Tree I am a beautiful songbird native to North America. I live in marine and freshwater wetlands and
Japanese Knotweed Red Winged Blackbird Emerald Ash Borer White Ash Tree Asian Long Horned Beetle Maple Tree I am a beautiful songbird native to North America. I live in marine and freshwater wetlands and
Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia
 Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia Imaginealifedirectlydefinedbyroughlyathirdofayearofrainandflooding.Thepeopleof ancientmesopotamia,egypt,andthekingdomofkushalllivedthatlife:theireconomies, power,andsimplesurvivaldependedontheseasonsoftheriversthatranthrougheach
Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia Imaginealifedirectlydefinedbyroughlyathirdofayearofrainandflooding.Thepeopleof ancientmesopotamia,egypt,andthekingdomofkushalllivedthatlife:theireconomies, power,andsimplesurvivaldependedontheseasonsoftheriversthatranthrougheach
HISTORY USES AND HEALTH BENEFITS. Figure 31. Nanking cherries
 nanking cherries Nanking cherries (Prunus tomentosa) are shrubs that grow from three feet up to ten feet tall with twigs that usually occupy an area twice as wide as the plant is tall. Up to 20 canes can
nanking cherries Nanking cherries (Prunus tomentosa) are shrubs that grow from three feet up to ten feet tall with twigs that usually occupy an area twice as wide as the plant is tall. Up to 20 canes can
Cultures of North America
 Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
China Before it was China. September 10, 2013
 China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
China Before it was China September 10, 2013 Review How do we define Asia? How has geography influenced Asian history? Which religion spread across most of Asia? How much linguistic diversity is there
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS. What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things?
 WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
Back to the English. HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS
 HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS Have you ever taken a close look at what kinds of plants are growing in your school garden? Have you ever tried to name some plants that you see on the street or on a mountain???
HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS Have you ever taken a close look at what kinds of plants are growing in your school garden? Have you ever tried to name some plants that you see on the street or on a mountain???
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
World History 3219 January 2017
 World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
World History 3219 January 2017 In the previous two units we investigated how the human experience changed as a result of innovation and new ideas. In this outcome your understanding of change will deepen
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Mesopotamian History. Chapter 2 Art History. Roxanna Ford 2014
 Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE. AP World History Notes Time Period:
 CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
CHAPTER 15 GLOBAL COMMERCE AP World History Notes Time Period: 1450-1750 EUROPEANS AND ASIAN COMMERCE European countries that got involved in Asian commerce = first the Portuguese, then the Spanish, French,
Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos. Ancient Cultures of North America
 Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Ancient Cultures of North America Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders *the
Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Ancient Cultures of North America Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders *the
Unit 9- Medieval Europe. Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review. Name:
 1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
1 Unit 9- Medieval Europe Lesson 4 Crusades, trade, and the Plague & Review Name: 2 The Crusades The, which began in 1095, were major military expeditions fought to win back the and protect the Byzantine
Name: QHS Social Studies Period:
 World History Quincy High Summer Reading: History of the World in 6 Glasses...Tom Standage's bright idea really is bright: "A History of the World in 6 Glasses," a book that divides world history into
World History Quincy High Summer Reading: History of the World in 6 Glasses...Tom Standage's bright idea really is bright: "A History of the World in 6 Glasses," a book that divides world history into
Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture. Unit 3
 Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture Unit 3 Culture The combination of three things: 1. Values 2. Material artifacts 3. Political institutions This chapter focuses on: Daily necessities: food, clothing,
Chapter 4: Folk and Popular Culture Unit 3 Culture The combination of three things: 1. Values 2. Material artifacts 3. Political institutions This chapter focuses on: Daily necessities: food, clothing,
Foodservice Market Prospects
 Foodservice Market Prospects Australia & South East Asia Food SA Summit 5th June 2012 BIS Foodservice 3 4 Three Available Food & Beverage Markets The Three Food & Non-Alcoholic Beverage Markets Market
Foodservice Market Prospects Australia & South East Asia Food SA Summit 5th June 2012 BIS Foodservice 3 4 Three Available Food & Beverage Markets The Three Food & Non-Alcoholic Beverage Markets Market
Big Idea. The Ming Restore Chinese Rule
 Big Idea The Ming Restore Chinese Rule Essential Question How did the Ming Dynasty gain and maintain power? Words To Know Ming Dynasty The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644 A.D., during which
Big Idea The Ming Restore Chinese Rule Essential Question How did the Ming Dynasty gain and maintain power? Words To Know Ming Dynasty The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644 A.D., during which
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
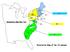 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
Monterey County Ranch Johnson Canyon Road Gonzales, CA Acres
 Monterey County Ranch 31701 Johnson Canyon Road Gonzales, CA 523.15 Acres Introduction Located in California s Central Coast in the heart of the Salinas Valley lies the Gallo family s Monterey County Ranch.
Monterey County Ranch 31701 Johnson Canyon Road Gonzales, CA 523.15 Acres Introduction Located in California s Central Coast in the heart of the Salinas Valley lies the Gallo family s Monterey County Ranch.
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
