The Antebellum Economy
|
|
|
- Kimberly Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section3 The Antebellum Economy As you read, look for: the workings of the plantation system, transportation improvements in antebellum Louisiana, and vocabulary terms exports, factor, canal, internal improvements, and manifest destiny. Louisiana s economy grew in spite of the political unrest. The plantation system had already been well established by the Creoles. The American newcomers bought existing plantations or created new ones along the Mississippi River. These plantations created some of the wealthiest people in America. Below: Antebellum New Orleans was a bustling port and came to be called the Queen City of the South. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 285
2 Lagniappe The typical plantation had between ten and twenty-five slaves. Only the largest sugar plantations had hundreds of slaves. The majority of whites in antebellum Louisiana did not own slaves. Below: Houmas House in Ascension Parish was the state s largest sugar plantation. The profitable plantation economy relied on the port city of New Orleans. The only larger United States port was New York, and only three world ports had a larger export volume. (Exports are goods sent or sold to another country.) New Orleans was the state s commercial urban center. Banking New Orleans also developed as the banking center for Louisiana. The growing economy required investment capital (money that could be put into or loaned to businesses to help them grow). People needed loans to buy land. Those who operated businesses or plantations needed to borrow money to pay expenses. The factor system developed partly from the planters need for quick financial and business assistance. A factor is a commercial agent. The factor represented the planter in the sale of a crop and earned a percentage of the profit. During the year, the factor might advance money to the planter for various expenses. Some factors also represented the planter by buying needed goods and sending them to the plantation. If the planter needed a large loan, the factor often agreed to repay the loan if the planter could not. The plantation economy made many factors as wealthy as the planters. The early banks in Louisiana were sounder than those in much of the United States, but they could not avoid the national banking crisis of Many who had borrowed money to pay for land could not repay their loans. Louisiana dealt with these banking problems through new banking laws and provisions in the constitutions of 1845 and By 1860, Louisiana banks ranked among the best. Those banks supported the business interests and the plantation system. 286 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression Agriculture Cotton became a profitable southern crop when Eli Whitney designed an efficient cotton gin in The gin (short for engine) removed the cotton seeds from the cotton fibers, a time-consuming task when done by hand. Once cotton could be ginned quickly, more cotton was grown and more slaves were needed. Long grown in Louisiana, cotton soon became a major cash crop. The Plantation System Louisiana wanted a share of this wealth. Both large plantations and small farms could produce cotton. A farmer could grow a few acres of cotton, sometimes with just the help of his family. As profits increased, the farmer bought more land and planted more cotton.
3 Factories in the North and in Great Britain turned the South s cotton into cloth. Industrial progress steam engines, automatic spinning machines, and power looms made it easier and cheaper to produce cloth, which increased the demand for cotton. While not quite spinning gold from straw, growing cotton created great riches. The boom in agriculture was not limited to cotton. Sugar plantations made even more profits than cotton plantations, but they required a larger capital investment of workers and equipment. The South Louisiana climate was perfect for growing sugar cane. Sugar was the main plantation crop in the West Indies. Immigrants from that region brought their sugar-producing skills to Louisiana. An invention by Norbert Rillieux, a free man of color from New Orleans, revolutionized sugar production, just as the cotton gin increased cotton production. Rillieux invented a vacuum pan evaporator for refining sugar. This invention resulted in finer, whiter sugar with a huge reduction in costs and labor. The device made the crop even more profitable. One of the richest sugar planters was John Burnside of Houmas House in Ascension Parish. He owned over 98,000 acres of land and 1,000 slaves. His Above: St. John Plantation was a sugar plantation in St. Martin Parish. Note the factory buildings on the right. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 287
4 Spotlight Rosedown Plantation Louisiana s beautiful plantation homes have long attracted tourists to the state. For many years, the focus was on the elegance of the house and the lifestyle of the plantation owners. Today, awareness grows that plantation life has a history as layered as the soil that is studied in the archaeological digs exploring these sites. The contributions and the lives of the hundreds of slaves who lived on large plantations are being researched through archaeology, historic documents, and living history experiences. The state of Louisiana has purchased several plantation homes as part of its historic preservation and tourism program. The latest is Rosedown in St. Francisville. Rosedown was one of several large cotton plantations along the Mississippi River. The people who settled in the Feliciana parishes were mostly Anglos who came from the British colonies. The style of Rosedown shows this connection with the Atlantic Coast because it resembles the Carolina Tidewater style. The house was built from local cypress, but many of the construction materials were imported. Marble for the fireplaces and fine furniture were brought from Europe especially for this house. The gardens were as formal and elegant as the house, with many exotic imported plants. The last family members who lived in the house, four sisters who were descendants of the original owner, loved these gardens and struggled to maintain the many acres that had been planted a century earlier. Today, the gardens and the house have been restored and are visited by thousands of tourists every year. 288 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression Rosedown Plantation in St. Francisville is an Anglo-style plantation (above). The main house contains much original furniture (opposite page, top left). The kitchen has its own vegetable garden (opposite page, top right).
5 Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 289
6 Top: Laura Plantation in Vacherie is a Creole-style plantation. Bottom: The four slave cabins on the grounds were built in the 1840s. huge plantation made him very wealthy and enabled him to live the lifestyle usually associated with the plantations. For example, guests were offered portable bathtubs filled with water and blocks of ice to provide relief from the muggy Louisiana heat. At the time, ice was an expensive luxury that had to be brought from northern lakes. Steamboats carried the ice, packed in sawdust, to Burnside s landing on the Mississippi River. 290 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression
7 Slave Labor Behind this view of luxury was another scene. Slavery supported this lifestyle and economic structure. Not only did slaves provide the labor in this economy but it was their status as property that made slave owners wealthy. Slave labor produced the plantation crops. But slaves also did basic manual labor, worked in the plantation houses, and performed skilled tasks. Workers such as blacksmiths Above: The dining room at Laura Plantation. Opposite page, middle: This bedroom is less ornate but brightly decorated. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 291
8 and coopers (barrel makers) were valuable assets. These skilled slaves were often hired out; field hands too might be hired out to bring in crops. Plantation owners hired overseers to supervise work. Some slaves were selected to be drivers and were held responsible for the work of other slaves. The work day usually was from can to can t, meaning from daylight ( can see ) to dark ( can t see ). A bell or horn started their work day before dawn. Every hour was structured to produce as much work as possible and to control the slaves. They were allowed to leave the plantation only with permission and a written pass. Punishment was used to keep order in this rigid system. Slaves were disciplined when they stole, ran away, or did not work. Documents from the time show that the punishment varied from fairly mild to extremely cruel. Whipping was the most common form of punishment. But even under the best conditions, the slave system was paternalistic. A plantation owner with this attitude felt responsible for the slaves but still controlled all aspects of their lives. A journalist from the North visited Richard Taylor s Fashion Plantation in Ascension Parish and said he found the best conditions he had ever seen for slaves. But he also learned from the carriage driver that the good treatment did not lessen the slaves desire for freedom. Above: The hardest jobs were those of the field hands. Women often worked the fields. Right: Some slaves were skilled workers such as carpenters. Others worked inside the home, such as this maid. Opposite page, above: These preserved slave cabins from a Louisiana plantation are exhibits at the LSU Rural Life Museum. Opposite page, below: Slaves were considered property and were bought and sold at auctions, as seen in this engraving of the Rotunda in New Orleans. 292 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression
9 Farmers Slave-holding plantations dominated Louisiana s antebellum economy. But more than 71 percent of the white population did not own slaves. These people included merchants, skilled crafters, professionals, laborers, and small farmers. While the planters goal was profit, the small farmers were mainly concerned with feeding their families. Generally, the small farmers owned just enough land to raise crops for their own use. Sometimes the farmers had excess crops that they could sell for cash. The farmers and their families provided the labor. Farmers also raised cattle and hogs. The animals were branded or had their ears notched for identification and were allowed to roam the nearby woods. The corn crop helped feed these animals as well as the farm families. In fact, the basic farm diet was often described as hog and hominy (hominy was a dish made from corn). The small farms were basically self-sufficient. But peddlers traveled to isolated farms, bringing goods the farm could not provide. Coffee and sugar were two of the prized items purchased from these traveling salesmen. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 293
10 Above: Steamboat travel was the main method of transport along the Mississippi until the coming of the railroads in the late 1870s. Lagniappe By the 1850s, about three thousand steamboats docked at New Orleans each year. Transportation Imagine a ten-mile trip taking six days. This was not uncommon on the roads of antebellum Louisiana. Wagons pulled by teams of oxen often had to struggle through deep, muddy ruts on the wilderness roads. Rural residents urged the state government to improve roads because they needed the access to markets. But rainfall and the Louisiana soil made road-building difficult. In 1827, the first road-improvement bill funded the road from Covington through Washington Parish to Mississippi. Water travel was always easier than trying to build a road. The coming of the steamboat in the early nineteenth century made water travel faster. Water Travel The steamboat became the main transportation in Louisiana. Not only did the steamboats travel the state s rivers, but they also transported freight through canals, manmade waterways that connected Louisiana s rivers and bayous. The first canals were dug by private investors (people who risked their own money on a project) who charged users a fee. Later, banks and the government funded canals in New Orleans and outside the city. In 1831, a special bank was organized to build the New Basin Canal in New Orleans. Water-filled Louisiana required another major improvement. A levee system was needed to protect the plantation economy. From the time of the French colony, the government had required landowners to build and maintain their 294 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression
11 own levees. Now, the demand for governmentfunded levees became a major political issue. In 1832, the state created the Board of Public Works, which gave special attention to waterways, including levees. In 1856, the board developed a system of levee districts to maintain the levee by sections. These districts made some efforts, but not as much as was needed. The Civil War, however, halted further efforts for flood control. Railroads The political and economic focus on internal improvements (roads, bridges, canals, and other transportation needs) increased with the coming of the railroad. The Pontchartrain Railroad was the first railroad west of the Alleghenies. Begun in 1831, the six-mile-long track ran between New Orleans and Lake Pontchartrain. Passengers on the earliest railroads in Louisiana paid a 25-cent fare for an exciting but not always pleasant ride. The train often slipped off the unstable tracks. Getting the train going again required the passengers help. Other obstacles were common. One traveler described in graphic detail the cow that was run over by the train. Building and improving the railroads cost huge sums of money, but New Orleans needed those railroads to compete with the North. As the demand for the railroads increased, the state and the city of New Orleans helped finance the railroad building. By the 1850s, three major railroad lines had been funded in this way. One line was planned to link New Orleans with Nashville, another was to run westward from New Orleans to Texas, and the third line was to connect Shreveport and Vicksburg. The building of these railroads was slowed by the Panic of 1837 and completely stopped when the Civil War started. Check for Understanding 1. What was the only port larger than New Orleans in the antebellum United States? 2. What were the duties of a factor? 3. What effect did Norbert Rillieux have on Louisiana agriculture? 4. What was the major means of transportation in antebellum Louisiana? Map 31 Transportation in Antebellum Louisiana Map Skill: How might a traveler get from Shreveport to Vicksburg? Lagniappe Passengers jokingly complained about the Pontchartrain Railroad by calling it the Smoky Mary. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 295
12 Connecting with U.S. History The Mexican War Americans believed the entire continent waited for their arrival. This idea was labeled manifest destiny, from a column by journalist John L. O Sullivan. He wrote of the fulfillment of our manifest destiny to overspread the continent allotted by Providence for the free development of our yearly multiplying millions. This attitude led the United States into war with Mexico. Mexico had gained its independence from Spain in Texas, then a colony of Mexico, was a vast, 296 Chapter 9 Louisiana s Antebellum Era: Riches and Repression Above: The Battle of Chapultepec Castle was the last battle of the Mexican War. unpopulated area. The Mexican government offered Texas land to Americans willing to become Mexican citizens and Catholics. The plan backfired when the Americans in Texas decided they too wanted their independence. The Texas Revolution was fought in , and Louisiana volunteers joined that fight. After
13 Above: News from the Mexican War Front shows how interested people were in the war. Left: General Zachary Taylor won major victories at Monterrey and Buena Vista. In the war, New Orleans was a center of much activity as General Taylor assembled many of his forces there. gaining its independence, Texas declared itself a republic but hoped to join the United States. Southerners supported Texas s admission as a slave state. But those who opposed slavery opposed admitting Texas to the Union. The issue became part of the presidential election of Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform stressing manifest destiny. His victory convinced Congress that the country wanted Texas annexed. Texas officially became a state on December 29, Because of the annexation, Mexico broke off diplomatic relations with the United States. Relations were also strained because the boundary between Mexico and Texas was disputed. Was it south to the Rio Grande River, as the United States claimed, or was it 150 miles farther north at the Nueces River, which was Mexico s claim? Louisianian John Slidell went to Mexico to negotiate this conflict and to try to buy California and New Mexico. When Slidell s efforts failed, President Polk ordered General Zachary Taylor to move the American army from the Nueces River to the Rio Grande. The United States would either force negotiations or force war. Mexico considered Taylor s move an act of war, and Mexican troops fired on Taylor s army. The war began in April Sixteen months later, the war ended with an American victory. Zachary Taylor became a national hero and was later elected president. His victorious army included many future Civil War generals on both sides, including Ulysses S. Grant and Robert E. Lee. Section 3 The Antebellum Economy 297
The Louisiana Purchase
 The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
New England Colonies Economy
 New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
The Manor Life & The Town Life
 The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor House In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor used
The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor House In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor used
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century. By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham
 Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Slavery and Plantation Economy in Brazil and the Guyanas in the 19th Century By Mason Schrage and Wesley Eastham Brazil What is the story? Portugal s colonization of Brazil Slave population in the 19th
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo
 Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Assessment: China Develops a New Economy
 Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
The Southern Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 4
 The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
Britain the workshop of the world and france buying the goods. Brianna vanschoyck, Francesca down, daisy vazquez
 Britain the workshop of the world and france buying the goods Brianna vanschoyck, Francesca down, daisy vazquez the question compare the economic, political, and social conditions in great britain and
Britain the workshop of the world and france buying the goods Brianna vanschoyck, Francesca down, daisy vazquez the question compare the economic, political, and social conditions in great britain and
The Louisiana Purchase. Chapter 9, Section 2
 The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Westward Expansion Internet Scavenger Hunt WebQuest
 Name: Date: Westward Expansion Internet Scavenger Hunt WebQuest Directions: Click on the link below to answer the following questions. http://www.ducksters.com/history/westward_expansion/ 1. The original
Name: Date: Westward Expansion Internet Scavenger Hunt WebQuest Directions: Click on the link below to answer the following questions. http://www.ducksters.com/history/westward_expansion/ 1. The original
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon Lord Baltimore
 Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
John Smith The Starving Time
 The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
Chapter 4-1 Notes. The Economy of the Colonies
 Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Thomas Jefferson and the West.
 Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
The Middle Colonies. If YOU were there. How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? SECTION. What You Will Learn
 The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880
 After the Civil War, the area west of the Mississippi River was settled by miners, ranchers, and farmers Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880 Mining was the first industry to attract settlers to the West
After the Civil War, the area west of the Mississippi River was settled by miners, ranchers, and farmers Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880 Mining was the first industry to attract settlers to the West
Students will be assessed through answering of the questions that follow as well as with a reading quiz.
 Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
Section Preview. Economic Growth in Georgia. Section3
 Section3 Economic Growth in Georgia Section Preview As you read, look for: the impact of the cotton gin and mechanical reaper on agriculture, improvements in transportation, and vocabulary terms: depression
Section3 Economic Growth in Georgia Section Preview As you read, look for: the impact of the cotton gin and mechanical reaper on agriculture, improvements in transportation, and vocabulary terms: depression
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d. Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary
 The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The People of Antebellum Louisiana
 Section1 The People of Antebellum Louisiana As you read, look for: the ethnic and cultural groups living in antebellum Louisiana, and vocabulary terms antebellum and immigrant. White cotton and white columns
Section1 The People of Antebellum Louisiana As you read, look for: the ethnic and cultural groups living in antebellum Louisiana, and vocabulary terms antebellum and immigrant. White cotton and white columns
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
The Manor Life & The Town Life
 The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor Population In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor
The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor Population In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
The Manor Life & The Town Life
 The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor Life In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor used to
The Manor Life & The Town Life The Manor Life In Medieval Europe, more than 90% of the population lived in rural communities and worked on the land. Farming was a full-time job. The Lord's manor used to
Tobacco & Labor Saves Virginia
 Tobacco & Labor Saves Virginia As tobacco crops start to make Virginia a profitable place to live, there was a labor shortage. The crop was labor intensive; and many English men and women did not want
Tobacco & Labor Saves Virginia As tobacco crops start to make Virginia a profitable place to live, there was a labor shortage. The crop was labor intensive; and many English men and women did not want
Early British Colonies
 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
The 13 English Colonies
 The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Name Period Date. Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new ways.
 Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
Name Period Date Chapter 3: The Tigris and Euphrates Lesson 1: Civilization in Sumer Big Idea: City-states in Mesopotamia developed into one of the world s first civilizations by using resources in new
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
The California Gold Rush
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The California Gold Rush by Peggy Bresnick Kendler Genre Expository nonfiction
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The California Gold Rush by Peggy Bresnick Kendler Genre Expository nonfiction
Exploring Kings Mountain State Park. An Example of an 1850s Yeoman Farm in UpCountry South Carolina. Name
 Exploring Kings Mountain State Park An Example of an 1850s Yeoman Farm in UpCountry South Carolina Name Pre-Visit Assignment (8 th grade) After reading Chapter 12 and pages 491-483 in your book, think
Exploring Kings Mountain State Park An Example of an 1850s Yeoman Farm in UpCountry South Carolina Name Pre-Visit Assignment (8 th grade) After reading Chapter 12 and pages 491-483 in your book, think
Chapter 16 The Civil War ( ) Section 4 The Strain of War
 Chapter 16 The Civil War (1861-1865) Section 4 The Strain of War Which do you feel is the most important quality in a good leader? A. Enthusiasm B. Confidence C. Courage D. Decisiveness A. A B. B C. C
Chapter 16 The Civil War (1861-1865) Section 4 The Strain of War Which do you feel is the most important quality in a good leader? A. Enthusiasm B. Confidence C. Courage D. Decisiveness A. A B. B C. C
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
CHINESE EMPIRE. AP World History Notes Chapter 4
 CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
CHINESE EMPIRE AP World History Notes Chapter 4 From 1100 BCE until the 200s CE --> 3 great dynasties ruled China = Zhou (JOH) = Qin (CHIN) = Han (HAHN) The Enduring Zhou Ruled China for more than 800
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers
 A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root ( )
 Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Back to the English. HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS
 HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS Have you ever taken a close look at what kinds of plants are growing in your school garden? Have you ever tried to name some plants that you see on the street or on a mountain???
HISTORY'S INFLUENTIAL PLANTS Have you ever taken a close look at what kinds of plants are growing in your school garden? Have you ever tried to name some plants that you see on the street or on a mountain???
The 13 Colonies. Religious, Political and Economic Foundations
 The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Where did the Acadians settle?
 NAME: Why did the Spanish want the Acadians to move to Louisiana? HR: Excerpt from The Exile of the Acadians The Spaniards, unlike the French, were determined to populate their Louisiana. The Spaniards
NAME: Why did the Spanish want the Acadians to move to Louisiana? HR: Excerpt from The Exile of the Acadians The Spaniards, unlike the French, were determined to populate their Louisiana. The Spaniards
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Black Gold: The Movie Mini-Debates
 1. Black Gold is a recent British documentary film about the international coffee industry. It exposes a situation in which small coffee farmers in developing countries receive very little for their back-breaking
1. Black Gold is a recent British documentary film about the international coffee industry. It exposes a situation in which small coffee farmers in developing countries receive very little for their back-breaking
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Causes of the American Revolution
 Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Name Class Date. Use the information from pages to complete the following.
 GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
Big Idea. The Ming Restore Chinese Rule
 Big Idea The Ming Restore Chinese Rule Essential Question How did the Ming Dynasty gain and maintain power? Words To Know Ming Dynasty The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644 A.D., during which
Big Idea The Ming Restore Chinese Rule Essential Question How did the Ming Dynasty gain and maintain power? Words To Know Ming Dynasty The Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644 A.D., during which
The Battle for New Orleans at Chalmette Battlefield
 The Battle for New Orleans at Chalmette Battlefield New Orleans in 1814-1815 Thriving city on the Mississippi River Mississippi controlled trade up and down the river Residents were a mixture of Creoles,
The Battle for New Orleans at Chalmette Battlefield New Orleans in 1814-1815 Thriving city on the Mississippi River Mississippi controlled trade up and down the river Residents were a mixture of Creoles,
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
CAUSES OF EXPLORATION. READING and ASSIGNMENT. Read the excerpt below. Use the reading to complete the section of the graphic organizer.
 Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter
 Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies
 Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Absolute and Comparative Advantage ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does trade benefit all participating parties? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary volume amount; quantity enables made possible Content
Lesson 1 Absolute and Comparative Advantage ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does trade benefit all participating parties? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary volume amount; quantity enables made possible Content
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent BC
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
~VANIA ..- ~ ~ ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2. Land Use. Religion in the Middle Colonies, I 775
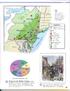 ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
APWH chapter 18.notebook January 11, 2013
 Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Information - Peanuts
 Information - Peanuts Peanuts were grown by ancient civilizations of South America at least 2,000 years ago. Peanuts, though native to South America, have been consumed as food for centuries in other places
Information - Peanuts Peanuts were grown by ancient civilizations of South America at least 2,000 years ago. Peanuts, though native to South America, have been consumed as food for centuries in other places
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Founding Economic Structure/Activities Trade Sources of Econ. Development Economic sources
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Founding Economic Structure/Activities Trade Sources of Econ. Development Economic sources
Chapter 2. Expansion of Trade
 Chapter 2 Expansion of Trade The Impact of Trade Italy and the Polo family What do you know about The infamous Marco Polo? 3 Trade & Expansion Before the Plague Europe was expanding Trade played a huge
Chapter 2 Expansion of Trade The Impact of Trade Italy and the Polo family What do you know about The infamous Marco Polo? 3 Trade & Expansion Before the Plague Europe was expanding Trade played a huge
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
LAST TIME Spanish Colonial Settlement patterns
 LAST TIME Spanish Colonial Settlement patterns TODAY Development and colonial Latin America Political Independence Neo-colonial (post independence) Extractive Economies (begin) Overview development and
LAST TIME Spanish Colonial Settlement patterns TODAY Development and colonial Latin America Political Independence Neo-colonial (post independence) Extractive Economies (begin) Overview development and
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
Topic of Discussion Colonial Economics
 I Introduction A. What does Economics mean and where did it come from? B. Economic issues have concerned human beings for millennia, ever since the early primitive hunters considered how to distribute
I Introduction A. What does Economics mean and where did it come from? B. Economic issues have concerned human beings for millennia, ever since the early primitive hunters considered how to distribute
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography
 Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
Mesopotamia Mesopotamia = the land between two rivers Geography * About 9,000 years ago, wandering tribes settled in the river valley between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. * This area, also known as
