Double fertilization in angiosperms
|
|
|
- Elinor Alyson Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Double fertilization in angiosperms
2 Pollen tube development and vs: vegetative cell gs: generative cell sp: sperm cell pt: pollen tube POLLEN ovary pollen ovary egg + synergids central veg. nucleus antipodal cells PISTIL stigma style pollen tube sperm cell veg. cell embryo sack integument chalaza funicle
3 Structre of embryo sac egg cell central vegetative nucleus (polar nuclei) integument antipodal cells Papaver rhoeas embryo sac
4 Pollen tube on pistil surface
5 Double fertilization (diploid vegetative cell)
6 Double fertilization 2nd sperm cell 1st sperm cell
7 Development of embryo 1st sperm cell + egg cell zygote embryo 2nd sperm cell + dipl. veg. cell triploid nucleus nutritive tissue (endosperm)
8 Ovule maturation into seed fertilized egg cell germ / embryo fertilized veg. nucleus inner nutritive tissue / endosperm nucellus outer nourishing tissue / perisperm integument seed coat / testa ovary fruit wall of ovary fruit wall / pericarp seed germination: embryo seedling
9 Seeds: seed coat endosperm cotyledon 1: castor plant radicle embryo fruit wall seed coat cotyledon 2: pepper endosperm perisperm germ 4: almond 3 rye
10 Seeds and appendages A. poppy m: seed coat e: endosperm cs: germ B. greater celandine el: elaiosome C. common yew ar: arille (seed envelope) mh: seed coat
11 SEEDS Heuchera sp. seed coat (testa) Campanula sp. seed coat (testa)
12 THE FRUIT
13 Fruit types Number of carpels: monocarpellary/unicarpellary polycarpellary monocarpous follicle polycarpous capsule Degree of carpel fusion: choricarpous / apocarpous (a) a b c coenocarpous - syncarpous (b) Hypericum Lilium - paracarpous (c) /Flowers/Flower%20parts.pdf paracarpous syncarpous
14 Classification of Fruits Other aspects: position of ovary true or false fruit dry or fleshy opens or remains closed Fruit types: I. DRY DEHISCENT FRUITS II. DRY INDEHISCENT FRUITS III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS IV. COMPOUND FRUITS false fruits of rosehip (Rosa canina) true fruits of cherry (Cerasus avium)
15 I. DRY, DEHISCENT FRUITS (4 types) 1. Follicle - monocarpous, superior ovary - 1 opening (suture), multiple seeds e.g. milkweed (Asclepias syriaca), forking larkspur (Consolida regalis) Legume - monocarpous, superior ovary - 2 sutures (ventral + dorsal), many seeds e.g. bean family (Fabaceae) loment e.g. Sophora spiral e.g. clover one-seeded e.g. sainfoin indehiscent e.g. peanut
16 I. DRY, DEHISCENT FRUITS oilseed rape (Brassica napus) 3. Silique mustard family (Brassicaceae) 2 carpels superior ovary opens by 2 sutures false carpellary wall/ replum Silicle: as long as broad min. 3x longer than broad e.g. black mustard (Brassica nigra) e.g. shepherd s purse (Capsella bursa-pastoris)
17 I. DRY, DEHISCENT FRUITS 4. Capsule 2 or more carpels, inferior or superior ovary septicidal opens along the fusion of carpels e.g. thorn apple (Datura), Colchicum loculicidal opens along the main vein of carpel e.g. onion (Allium cepa) septifragil opens along the line of carpel fusion AND along the main carpel vein e.g. castor plant (Ricinus) transverse upper part separating like lid of box e.g. henbane (Hyoscyamus) toothed e.g. primrose (Primula) poricidal releases seeds through pores e.g. poppy (Papaver)
18 poppy (Papaver) Capsule Types thorn apple Datura stramonium onion (Allium cepa) henbane (Hyoscyamus) primrose (Primula) poricidal toothed loculicidal transverse septicidal
19 II. DRY, INDEHISCENT FRUITS (8 types) 1. Grain / Caryopsis - unicarpellate, superior ovary - 1-seeded, fruit wall fuses with seed coat e.g. grass family (Poaceae) 2. Achene - 1 carpel, superior, unilocular ovary - 1-seeded - usually in fruit aggregates e.g. buttercup family (Ranunculaceae) 1. achenes of Clematis vitalba Double achene / schizocarp - 2 carpels, inferior ovary - mericarps held together by carpophor e.g. carrot family (Apiaceae) 3. achenes of Carum carvi
20 II. DRY, INDEHISCENT FRUITS 4. Acorn / Nut - 2 or more carpels, superior or inferior ovary - bony (sclerenchymatous) pericarp - fruit sits in cupule: formed from bracts or receptacle e.g. hazelnut, oak, beech, sweet chestnut Nutlet - smaller form of nut, 2 or more carpels - sclerified exocarp protects the seeds (usually 4) e.g. mint family (Lamiaceae) borage family (Boraginaceae) acorns of sessile oak (Quercus petraea)
21 II. DRY, INDEHISCENT FRUITS (8 types) 6. Cypsela - 2 carpels, inferior ovary - achene-like fruit - derived from florets of capitulum - calyx often modified (e.g. pappus) seed dispersal e.g. aster family (Asteraceae) 1 pappus 6. dandelion (Taraxacum officinale)
22 II. DRY, INDEHISCENT FRUITS 7. Samara - 2 carpels, superior ovary - type of achene - pericarp membrane-like wing e.g. elms (Ulmus), ashes (Fraxinus) 8. Double samara - schizocarp with wings - fork-like carpophor e.g. maples (Acer) double samara of Acer campestre
23 III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS (6 types) 1. Berry - outer pericarp (exocarp): thin, leather-like - middle layer (mesocarp) and inner layer (endocarp) of fruit wall: fleshy, juicy - 1 or more seeds e.g. grapes (Vitis) 2. Pepper fruit - inflated berry, pericarp may dry e.g. paprika (Capsicum annuum) berries of tomato
24 III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS 3. Hesperidium - many carpels, superior, multilocular ovary exocarp: vivid color (yellow, orange), with essential oil cavities mesocarp: white, sponge-like parenchyma endocarp: fluid-filled vesicles (hairs/trichomes) e.g. orange, lemon (Citrus sp.) grapefruit (Citrus paradisi)
25 III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS 4. Pepo - usually from 3 carpels, inferior ovary - hard-rind pericarp e.g. cucurbit family (Cucurbitaceae) exocarp: leather-like mesocarp: collenchyma, juicy parenchyma endocarp: fleshy partition walls and seeds pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo)
26 III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS 5. Stone fruit / Drupe 1 or 2 carpels, superior or half-superior ovary exocarp / skin: leather-like, colored mesocarp / flesh: juicy, fleshy endocarp = shell/stone: stone cells (sclereids), seed within endocarp e.g. plum, sweet cherry, sour cherry, peach (Prunoideae), walnut (Juglans), olive (Olea europaea) plum (Prunus domestica)
27 III. SIMPLE FLESHY FRUITS 6. Pome - false fruit (receptacle, sepals take part in fruit formation) - many carpels, inferior ovary, apocarpous - cartilage-like endocarp around seedcavities, surrounded by fleshy mesocarp e.g. apple (Malus), pear (Pyrus) apple (Malus domestica) seeds quince (Cydonia oblonga) original fruit wall around seeds (endocarp in false fruit)
28 IV. COMPOUND FRUITS (6 types) AGGREGATE FRUITS 1 FLOWER: 1. Aggregate of follicles -apocarpous, superior ovary e.g. hellebore (Helleborus) 2. Aggregate of drupelets 1. - apocarpous ovary e.g. raspberry, blackberry (Rubus sp.) Helleborus odorus 2.
29 IV. COMPOUND FRUITS 3. Aggregate of achenes - apocarpous ovary - fleshy receptacle with achenes on its outer surface e.g. strawberry (Fragaria) -fleshy, cup-like receptacle with achenes inside e.g. rose hip (Rosa canina) achenes receptacle Fragaria vesca receptacle
30 IV. COMPOUND FRUITS MULTIPLE FRUITS INFLORESCENCE 1. Multiple of nutlets nutlets covered by fleshy tepals e.g. mulberry (Morus) 2. Multiple of achenes single achene fruits surrounded by fleshy inflorescence axis e.g. fig (Ficus carica) Multiple of berries fleshy fruits (berries) surrounded by fleshy bracts e.g. pineapple (Ananas comosus) 3.
Chapter 23b-Angiosperms. Double Fertilization The ovule is the site of meiosis and ultimately the formation of the seed.
 Chapter 23b-Angiosperms Double Fertilization The ovule is the site of meiosis and ultimately the formation of the seed. The ovule develops one or more layers of sterile tissue, the integuments along with
Chapter 23b-Angiosperms Double Fertilization The ovule is the site of meiosis and ultimately the formation of the seed. The ovule develops one or more layers of sterile tissue, the integuments along with
College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology
 College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology Academic year: 2014-2015 Subject: Plant taxonomy Class: Third Grade Lecturer:Dr.Hadeel R.,Dr.Rana A.,Dr.Aseel M.,Dr.Zena K. Lecture: 6 ***Fruits:
College of Science Al-Mustanseiriyah University Dep.: Biology Academic year: 2014-2015 Subject: Plant taxonomy Class: Third Grade Lecturer:Dr.Hadeel R.,Dr.Rana A.,Dr.Aseel M.,Dr.Zena K. Lecture: 6 ***Fruits:
The fruits and the seeds.
 The fruits and the seeds. The Flower- Fruit Relation Double Fertilization Double fertilization occurs: One sperm nucleus (1n) fertilizes the egg, producing a zygote (2n) which becomes the plant embryo
The fruits and the seeds. The Flower- Fruit Relation Double Fertilization Double fertilization occurs: One sperm nucleus (1n) fertilizes the egg, producing a zygote (2n) which becomes the plant embryo
Lecture Fruits. Topics. Fruit Types. Formation of fruits Basic Fruit Types
 Lecture 27-28. Fruits Topics Formation of fruits Basic Fruit Types Formation of fruits Basic Fruit Types The two principal Fruit Types are Fleshy & Dry Caution: A Legume is a dry fruit. We eat unripe legumes
Lecture 27-28. Fruits Topics Formation of fruits Basic Fruit Types Formation of fruits Basic Fruit Types The two principal Fruit Types are Fleshy & Dry Caution: A Legume is a dry fruit. We eat unripe legumes
(Inflorescence: Is a.k.a. the infructescence when the flowers have set fruit)
 INFLORESCENCE MORPHOLOGY (Inflorescence: Is a.k.a. the infructescence when the flowers have set fruit) Definition: Inflorescence is the reproductive shoot system (a shoot system bearing flowers) But note:
INFLORESCENCE MORPHOLOGY (Inflorescence: Is a.k.a. the infructescence when the flowers have set fruit) Definition: Inflorescence is the reproductive shoot system (a shoot system bearing flowers) But note:
What actually is a fruit? What is a seed?
 Fruit Morphology What actually is a fruit? A fruit is a ripened ovary (=a mature ovary) of a flower along with any adnate parts. What is a seed? - A seed is a baby in a box with its lunch. - Specifically,
Fruit Morphology What actually is a fruit? A fruit is a ripened ovary (=a mature ovary) of a flower along with any adnate parts. What is a seed? - A seed is a baby in a box with its lunch. - Specifically,
Unit B: Plant Anatomy. Lesson 4: Understanding Fruit Anatomy
 Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 4: Understanding Fruit Anatomy 1 Terms achene aggregate fruits berry capsule caryopsis cytokinins dehiscent fruits disseminated drupe endocarp exocarp follicle fruit gibberellins
Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 4: Understanding Fruit Anatomy 1 Terms achene aggregate fruits berry capsule caryopsis cytokinins dehiscent fruits disseminated drupe endocarp exocarp follicle fruit gibberellins
Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal.
 Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal. Seed dispersal syndromes: characteristics of the fruit ex. anemochory FRUIT
Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal. Seed dispersal syndromes: characteristics of the fruit ex. anemochory FRUIT
FRUITS: KINDS AND TERMS THE IMPORTANT PART OF THE LIFE CYCLE OFTEN IGNORED
 FRUITS: KINDS AND TERMS THE IMPORTANT PART OF THE LIFE CYCLE OFTEN IGNORED Technically, fruits are the mature ovaries of plants that contain ripe seeds ready for dispersal Of the many kinds of fruits,
FRUITS: KINDS AND TERMS THE IMPORTANT PART OF THE LIFE CYCLE OFTEN IGNORED Technically, fruits are the mature ovaries of plants that contain ripe seeds ready for dispersal Of the many kinds of fruits,
Angiosperms. Figure 38.4 Development of angiosperm gametophytes. Life cycle, fruits, seeds
 Angiosperms Figure 38.4 Development of angiosperm gametophytes Life cycle, fruits, seeds 1 Angiosperm seeds consist of diploid and triploid tissues Embryo: Diploid (from fertilized egg) Food Supply: Triploid
Angiosperms Figure 38.4 Development of angiosperm gametophytes Life cycle, fruits, seeds 1 Angiosperm seeds consist of diploid and triploid tissues Embryo: Diploid (from fertilized egg) Food Supply: Triploid
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany (Spring 2008) Topic 13: Angiosperms: Flowers, Inflorescences, and Fruits
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany (Spring 2008) Topic 13: Angiosperms: Flowers, Inflorescences, and Fruits A. Flower and Inflorescence Structure Angiosperms are also known as the Flowering Plants. They have
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany (Spring 2008) Topic 13: Angiosperms: Flowers, Inflorescences, and Fruits A. Flower and Inflorescence Structure Angiosperms are also known as the Flowering Plants. They have
Part I: Floral morphology
 OEB 59 Plants and Human Affairs Plant Anatomy Lab 1: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of this lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development
OEB 59 Plants and Human Affairs Plant Anatomy Lab 1: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of this lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development
BIOL 305L Laboratory Three
 Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Laboratory Three Fruit structure and its link to the mechanism of seed dispersal Introduction In this lab we will:consider the structure, function, and dispersal
Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Laboratory Three Fruit structure and its link to the mechanism of seed dispersal Introduction In this lab we will:consider the structure, function, and dispersal
Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal.
 Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal. Seed dispersal syndromes: characteristics of the fruit ex. anemochory FRUIT
Fruit develops from the ovary wall (pericarp) or accessory tissue, surrounds and protects the seeds, and aids in seed dispersal. Seed dispersal syndromes: characteristics of the fruit ex. anemochory FRUIT
BIOLOGY 103 LABORATORY EXERCISE. Day & Time of Assigned Lab: Seat Number: Fruit Lab
 6 Name: BIOLOGY 103 LABORATORY EXERCISE Day & Time of Assigned Lab: Seat Number: Learning Outcomes: Fruit Lab After completing this laboratory, you should be able to: 1. Learn terminology used to describe
6 Name: BIOLOGY 103 LABORATORY EXERCISE Day & Time of Assigned Lab: Seat Number: Learning Outcomes: Fruit Lab After completing this laboratory, you should be able to: 1. Learn terminology used to describe
FRUITS. A fruit is any ovary that has developed and matured.
 FRUITS A fruit is any ovary that has developed and matured. Fruit regions: Exocarp: the skin. Endocarp: the inner boundary around the seed(s). Mesocarp: the name is given to everything between the exocarp
FRUITS A fruit is any ovary that has developed and matured. Fruit regions: Exocarp: the skin. Endocarp: the inner boundary around the seed(s). Mesocarp: the name is given to everything between the exocarp
Fruits aid angiosperm seed dispersal by wind or by animals. Fruit development
 Fruits aid angiosperm seed dispersal by wind or by animals Fruit development Ovule àseed Entire ovary including ovules à fruit Ovary wall à pericarp The pericarp usually has three layers The exocarp is
Fruits aid angiosperm seed dispersal by wind or by animals Fruit development Ovule àseed Entire ovary including ovules à fruit Ovary wall à pericarp The pericarp usually has three layers The exocarp is
Fruits can be dry of fleshy
 Fruits aid angiosperm seed dispersal by wind or by animals Fruit development Ovule àseed Entire ovary including ovules à fruit Ovary wall à pericarp The pericarp usually has three layers The exocarp is
Fruits aid angiosperm seed dispersal by wind or by animals Fruit development Ovule àseed Entire ovary including ovules à fruit Ovary wall à pericarp The pericarp usually has three layers The exocarp is
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 4: Understanding Fruit Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe the functions
Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 4: Understanding Fruit Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe the functions
Dendrology FOR 219. Tree Life Cycle. Floral Anatomy. How Is It All Arranged? 8/27/2018
 Dendrology FOR 219 Instructor: Dr. Jeremy Stovall Lecture 4: 09.06.2018 Anatomy II: Flower, Fruit, & Cone Morphology Tree Life Cycle Seed Production Seed Germination Reproductive Tree Seedling Flowering
Dendrology FOR 219 Instructor: Dr. Jeremy Stovall Lecture 4: 09.06.2018 Anatomy II: Flower, Fruit, & Cone Morphology Tree Life Cycle Seed Production Seed Germination Reproductive Tree Seedling Flowering
Stages of Vertebrate Development
 Cleavage Stages of Vertebrate Development rapid cell division into a larger number of smaller cells no overall increase in size of the embryo ball of cells = the morula pattern is dependent on the amount
Cleavage Stages of Vertebrate Development rapid cell division into a larger number of smaller cells no overall increase in size of the embryo ball of cells = the morula pattern is dependent on the amount
Examining Flowers and Fruits. Terms. Terms. Interest Approach. Student Learning Objectives. What are the major parts of flowers?
 Student Learning Objectives Examining Flowers and Fruits Basic Principles of Agricultural/Horticultural Science Problem Area 4. Identifying Basic Principles of Plant Science Identify the major parts of
Student Learning Objectives Examining Flowers and Fruits Basic Principles of Agricultural/Horticultural Science Problem Area 4. Identifying Basic Principles of Plant Science Identify the major parts of
Botanically Speaking: Getting to Know the Food We Eat Everyday
 Bill Dowie, BA, MCPM, LEED-AP O+M Botanically Speaking: Getting to Know the Food We Eat Everyday Food is a wondrous life-giving thing. However, you may be surprised about how many parts of a plant we humans
Bill Dowie, BA, MCPM, LEED-AP O+M Botanically Speaking: Getting to Know the Food We Eat Everyday Food is a wondrous life-giving thing. However, you may be surprised about how many parts of a plant we humans
The Story of Flowering Plants: flowers, fruits and seeds and seedlings. Matthaei Botanical Gardens and Nichols Arboretum, University of Michigan
 The Story of Flowering Plants: flowers, fruits and seeds and seedlings Matthaei Botanical Gardens and Nichols Arboretum, University of Michigan And now; SEEDS and PLANT PARTS for 2 nd & 3 rd graders! When
The Story of Flowering Plants: flowers, fruits and seeds and seedlings Matthaei Botanical Gardens and Nichols Arboretum, University of Michigan And now; SEEDS and PLANT PARTS for 2 nd & 3 rd graders! When
CET Questions on Angiosperms Part - II
 CET Questions on Angiosperms Part - II 1) The enclosed seed bearing plants are called a) Angiosperms b) Gymnosperms c) Bryophytes d) Pteridophytes 2) The following groups of plants come under Angiosperms
CET Questions on Angiosperms Part - II 1) The enclosed seed bearing plants are called a) Angiosperms b) Gymnosperms c) Bryophytes d) Pteridophytes 2) The following groups of plants come under Angiosperms
Figure #1 Within the ovary, the ovules may have different arrangements within chambers called locules.
 Name: Date: Per: Botany 322: Fruit Dissection What Am I Eating? Objectives: To become familiar with the ways that flower and fruit structures vary from species to species To learn the floral origin of
Name: Date: Per: Botany 322: Fruit Dissection What Am I Eating? Objectives: To become familiar with the ways that flower and fruit structures vary from species to species To learn the floral origin of
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry. Lesson 4: Recognizing the Steps to Identifying Tree Species
 Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 4: Recognizing the Steps to Identifying Tree Species 1 Terms Angiosperms Dehiscent fruits Dichotomous venation Dioecious Gymnosperms Hardiness Indehiscent fruits
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 4: Recognizing the Steps to Identifying Tree Species 1 Terms Angiosperms Dehiscent fruits Dichotomous venation Dioecious Gymnosperms Hardiness Indehiscent fruits
Flowers of Asteraceae
 Flowers of Asteraceae The 'flower' that you see is actually a head composed of many small florets. The head (capitulum) is an inflorescence and a number of capitula are often aggregated together to form
Flowers of Asteraceae The 'flower' that you see is actually a head composed of many small florets. The head (capitulum) is an inflorescence and a number of capitula are often aggregated together to form
Earth s Birthday Project
 Earth s Birthday Project Seeds, Flowers, Fruits, Buds: Background for Teachers 1 Word Wall Seeds Grades K 6 Cotyledon (caw-duh-lee-dun) a part of the seed that stores nutrients (food) and will become a
Earth s Birthday Project Seeds, Flowers, Fruits, Buds: Background for Teachers 1 Word Wall Seeds Grades K 6 Cotyledon (caw-duh-lee-dun) a part of the seed that stores nutrients (food) and will become a
FRUITS OF ANGIOSPERMS
 FRUITS OF ANGIOSPERMS by Prof. Dr. INGRID ROTH Universidad Central de Venezuela, Caracas With 232 figures 1977 GEBRUDER BORNTRAEGER BERLIN STUTTGART Contents A. General part 1 1 The concept "fruit" 1 1.1
FRUITS OF ANGIOSPERMS by Prof. Dr. INGRID ROTH Universidad Central de Venezuela, Caracas With 232 figures 1977 GEBRUDER BORNTRAEGER BERLIN STUTTGART Contents A. General part 1 1 The concept "fruit" 1 1.1
40 Sexual Reproduction in Plants
 40 Sexual Reproduction in Plants Mr. C Biology 1 Mitosis Keeps the number of chromosomes 20 (40) Meiosis Halves the number of chromosomes 20 (40) 20 20 10 10 10 10 Mr. C Biology 2 Male Pollen Development
40 Sexual Reproduction in Plants Mr. C Biology 1 Mitosis Keeps the number of chromosomes 20 (40) Meiosis Halves the number of chromosomes 20 (40) 20 20 10 10 10 10 Mr. C Biology 2 Male Pollen Development
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 8: FLOWERS, FRUITS, AND SEEDS
 BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 8: FLOWERS, FRUITS, AND SEEDS READING: Please read pages 316-327 in your text. INTRODUCTION: In seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms), pollination (note spelling) is the mechanism
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 8: FLOWERS, FRUITS, AND SEEDS READING: Please read pages 316-327 in your text. INTRODUCTION: In seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms), pollination (note spelling) is the mechanism
THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT
 THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT Adrienne La Favre, Ph.D. Jeffrey La Favre, Ph.D. In this lesson we will begin to learn about the Solanaceae. We will spend most of our effort over the next year on the potato.
THE SOLANACEAE LESSON ONE FRUIT Adrienne La Favre, Ph.D. Jeffrey La Favre, Ph.D. In this lesson we will begin to learn about the Solanaceae. We will spend most of our effort over the next year on the potato.
Six Plant Families of Economic Importance
 Six Plant Families of Economic Importance Six Top Agricultural Crop Families Grass family (Poaceae) rice, wheat, corn, etc. Bean family (Fabaceae) soybeans, peas, beans Tomato family (Solanaceae) tomatos,
Six Plant Families of Economic Importance Six Top Agricultural Crop Families Grass family (Poaceae) rice, wheat, corn, etc. Bean family (Fabaceae) soybeans, peas, beans Tomato family (Solanaceae) tomatos,
Introduction. What is plant propagation? Can be done in one of two ways. The reproduction or increasing in number of plants. Sexual. Asexual.
 Plant Propagation Introduction What is plant propagation? The reproduction or increasing in number of plants. Can be done in one of two ways. Sexual. Asexual. Sexual Propagation The propagation or reproducing
Plant Propagation Introduction What is plant propagation? The reproduction or increasing in number of plants. Can be done in one of two ways. Sexual. Asexual. Sexual Propagation The propagation or reproducing
Describing The Fruits
 Describing The Fruits Group activity: Each member of the group must select 5 cards and describe each of them, focusing the card on the camera of the mobile device with the application Aprender Es Divertido
Describing The Fruits Group activity: Each member of the group must select 5 cards and describe each of them, focusing the card on the camera of the mobile device with the application Aprender Es Divertido
Core Eudicots. Vitales (tentatively placed in the Rosids) -Vitaceae grape family
 Core Eudicots Vitales (tentatively placed in the Rosids) -Vitaceae grape family Eudicots Rosids -Vitaceae grape family Parthenocissus quinquefolia Virginia creeper Eudicots Rosids -Vitaceae grape family
Core Eudicots Vitales (tentatively placed in the Rosids) -Vitaceae grape family Eudicots Rosids -Vitaceae grape family Parthenocissus quinquefolia Virginia creeper Eudicots Rosids -Vitaceae grape family
Field Characteristics of Common Plant Families in New Mexico
 Field Characteristics of Common Plant Families in New Mexico Introduction Major classification, the Angiosperms Monocots vs. Dicots What is a plant Family? Floral morphology and ovary position Fruit morphology
Field Characteristics of Common Plant Families in New Mexico Introduction Major classification, the Angiosperms Monocots vs. Dicots What is a plant Family? Floral morphology and ovary position Fruit morphology
Unit B: Plant Anatomy. Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy
 Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy 1 Burs Cotyledon Embryo Epicotyl (plumule) Hypocotyl Radicle Seed Seed coat Vocabulary 2 What Are the Major Parts of a Seed & Where Are They Located?
Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy 1 Burs Cotyledon Embryo Epicotyl (plumule) Hypocotyl Radicle Seed Seed coat Vocabulary 2 What Are the Major Parts of a Seed & Where Are They Located?
Tree bearing habits. Tree reproductive types. Location of flowers 2/25/ _Tree_bearing_habits_DeJong 1
 Tree bearing habits Tree reproductive types Perfect flowers male and female flower parts in the same flower. Separate male and female flowers Dioecious male and female flowers on different plants (pistachio)
Tree bearing habits Tree reproductive types Perfect flowers male and female flower parts in the same flower. Separate male and female flowers Dioecious male and female flowers on different plants (pistachio)
KEY TO THE FRUITS OF THE GENERA OF TREES OF THE NORTHERN UNITED STATES.
 506 The Ohio Naturalist. [Vol. XII, No. 6, KEY TO THE FRUITS OF THE GENERA OF TREES OF THE NORTHERN UNITED STATES. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER. The complete fruit at maturity, including the peduncle, is required
506 The Ohio Naturalist. [Vol. XII, No. 6, KEY TO THE FRUITS OF THE GENERA OF TREES OF THE NORTHERN UNITED STATES. JOHN H. SCHAFFNER. The complete fruit at maturity, including the peduncle, is required
The Primitive Flowering Plants
 The Primitive Flowering Plants Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants Early Diverging Angiosperms We will begin our survey of Great Lakes flowering plants by examining the primitive angiosperms - those groups
The Primitive Flowering Plants Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants Early Diverging Angiosperms We will begin our survey of Great Lakes flowering plants by examining the primitive angiosperms - those groups
Biological background of fruit growing
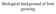 Biological background of fruit growing Practical groups of fruits Pome fruits Stone fruits Nuts Soft fruits apple pear quince medlar Cherry Sour cherry apricot peach plum walnut hazelnut chestnut almond
Biological background of fruit growing Practical groups of fruits Pome fruits Stone fruits Nuts Soft fruits apple pear quince medlar Cherry Sour cherry apricot peach plum walnut hazelnut chestnut almond
Activity Kit 3-6. Plants Galore. Grouping Plants by Name and Shape. 1 of 10
 3-6 Plants Galore Grouping Plants by Name and Shape 1 of 10 There are huge numbers of plants in the world. Botanic Gardens are designed to collect, grow and display many different plants from all over
3-6 Plants Galore Grouping Plants by Name and Shape 1 of 10 There are huge numbers of plants in the world. Botanic Gardens are designed to collect, grow and display many different plants from all over
The Beauty of the Trees & Shrubs in Farndon
 The Beauty of the Trees & Shrubs in Farndon Photographed, and compiled by John Dodson March 2010 Part 3 Conifers, Compound & Opposite Leaves 1 Definitions Leaves 1 of 2 Alternate Leaves, first on one side
The Beauty of the Trees & Shrubs in Farndon Photographed, and compiled by John Dodson March 2010 Part 3 Conifers, Compound & Opposite Leaves 1 Definitions Leaves 1 of 2 Alternate Leaves, first on one side
Phylogeny of Eudicots (or Tricolpates) Eudicots (or Tricolpates)
 Phylogeny of Eudicots (or Tricolpates) Basal eudicots Ranunculales Proteales Buxales Eudicots (or Tricolpates) Rosids Caryophyllales Asterids After Jansen et al., 2007, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:
Phylogeny of Eudicots (or Tricolpates) Basal eudicots Ranunculales Proteales Buxales Eudicots (or Tricolpates) Rosids Caryophyllales Asterids After Jansen et al., 2007, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:
Plant Biology Practical part Prepared by Shorouq S. Jaradat
 Plant Biology Practical part Prepared by Shorouq S. Jaradat 2010-2011 0 Lab 1 Wet- mount Preparation 1 Tomato cells Cell wall Nucleus Chromoplast Onion epidermal cells Potato cells 2 Lab 2 Simple Tissues
Plant Biology Practical part Prepared by Shorouq S. Jaradat 2010-2011 0 Lab 1 Wet- mount Preparation 1 Tomato cells Cell wall Nucleus Chromoplast Onion epidermal cells Potato cells 2 Lab 2 Simple Tissues
Diversity And Classification of Flowering Plants:
 Diversity And Classification of Flowering Plants: Eudicots: Rosids Michael G. Simpson ROSIDS Very large, monophyletic group of Eudicots Linked by no clear non-molecular apomorphies Ovules bitegmic (2 integuments)
Diversity And Classification of Flowering Plants: Eudicots: Rosids Michael G. Simpson ROSIDS Very large, monophyletic group of Eudicots Linked by no clear non-molecular apomorphies Ovules bitegmic (2 integuments)
Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!... milkweeds, nightshades, and morning glories...!
 Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!... milkweeds, nightshades, and morning glories...! Asterids! (1) fused petals (2) stamens = or less than number of petals (3) stamens fused to petals (4) pistil of
Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!... milkweeds, nightshades, and morning glories...! Asterids! (1) fused petals (2) stamens = or less than number of petals (3) stamens fused to petals (4) pistil of
FLOWER ANATOMY [V. Max Brown]
![FLOWER ANATOMY [V. Max Brown] FLOWER ANATOMY [V. Max Brown]](/thumbs/76/74307238.jpg) PLANT TERMINOLOGY Plant terminology for the identification of plants is a necessary evil in order to be more exact, to cut down on lengthy descriptions, and of course to use the more professional texts.
PLANT TERMINOLOGY Plant terminology for the identification of plants is a necessary evil in order to be more exact, to cut down on lengthy descriptions, and of course to use the more professional texts.
Analysis of Vegetables and Fruit Juices
 Analysis of Vegetables and Fruit Juices http://www.boardguess.com AIM INTRODUCTION MATERIAL REQUIRED CHEMICAL REQUIREMENTS PROCEDURE TEST, OBSERVATION, INFERENCE CONCLUSION AIM To analyse some fruits &
Analysis of Vegetables and Fruit Juices http://www.boardguess.com AIM INTRODUCTION MATERIAL REQUIRED CHEMICAL REQUIREMENTS PROCEDURE TEST, OBSERVATION, INFERENCE CONCLUSION AIM To analyse some fruits &
Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!
 Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!... milkweeds, nightshades, and morning glories...! Asterids! (1) fused petals (2) stamens = or less than number of petals (3) stamens fused to petals (4) pistil of
Diversity and Evolution of Asterids!... milkweeds, nightshades, and morning glories...! Asterids! (1) fused petals (2) stamens = or less than number of petals (3) stamens fused to petals (4) pistil of
Biology 2010 Lab at MUN Botanical Garden Grocery Store Botany Itinerary and Discussion Guide
 Biology 2010 Lab at MUN Botanical Garden Grocery Store Botany Itinerary and Discussion Guide PART 1. WELCOME Introductions, Safety, Housekeeping, Itinerary Anne Madden, MUNBG Education Coordinator Location:
Biology 2010 Lab at MUN Botanical Garden Grocery Store Botany Itinerary and Discussion Guide PART 1. WELCOME Introductions, Safety, Housekeeping, Itinerary Anne Madden, MUNBG Education Coordinator Location:
A new petrified unilocular hydrophytic fruit Aerocarpon gen. Nov from the Deccan Intertrappean Beds of Singpur, MP, India
 Bioscience Discovery, 9(1): 66-75, Jan - 2018 RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research
Bioscience Discovery, 9(1): 66-75, Jan - 2018 RUT Printer and Publisher Print & Online, Open Access, Research Journal Available on http://jbsd.in ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print); ISSN: 2231-024X (Online) Research
Pomegranates, Punica granatum (Puniaceae) are subtropicalfruits native to the region from Iran to the Himalayas.
 Chapter 5c-Fruits and Nuts of Warm Regions Tree Fruits from Semi Tropical Regions Pomegranates, Punica granatum (Puniaceae) are subtropicalfruits native to the region from Iran to the Himalayas. Pomegranates
Chapter 5c-Fruits and Nuts of Warm Regions Tree Fruits from Semi Tropical Regions Pomegranates, Punica granatum (Puniaceae) are subtropicalfruits native to the region from Iran to the Himalayas. Pomegranates
Lesson requires that students make daily observations of their germination chambers to determine if their predictions are true.
 Science Unit: Lesson 1: Growing Plants Plant Reproduction School Year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Charles Dickens Elementary School, Vancouver School
Science Unit: Lesson 1: Growing Plants Plant Reproduction School Year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Charles Dickens Elementary School, Vancouver School
Glossary ( 1-Jan-2001 )
 In: A Guide to Plant Poisoning of Animals in North America, A. P. Knight and R. G. Walter (Eds.) Publisher: Teton NewMedia, Jackson WY (www.veterinarywire.com) Internet Publisher: International Veterinary
In: A Guide to Plant Poisoning of Animals in North America, A. P. Knight and R. G. Walter (Eds.) Publisher: Teton NewMedia, Jackson WY (www.veterinarywire.com) Internet Publisher: International Veterinary
Garden Terms: Reproductive Plant Morphology Seeds, Flowers, and Fruits. Anne Streich, Horticulture Educator
 EXTENSION Garden Terms: Reprodutive Plant Morphology Seeds, Flowers, and Fruits EC1257 Anne Streih, Hortiulture Eduator Seeds Seeds are a plant reprodutive struture, ontaining a fertilized emryo in an
EXTENSION Garden Terms: Reprodutive Plant Morphology Seeds, Flowers, and Fruits EC1257 Anne Streih, Hortiulture Eduator Seeds Seeds are a plant reprodutive struture, ontaining a fertilized emryo in an
Basal Eudicot seeds and fruits
 Basal Eudicot seeds and fruits DQ Fuller 8.2.2006. Institute of Archaeology, UCL. MG101 Archaeobotany Practical The Eudicots are an important phylogenetic grouping within flowering plants. Although they
Basal Eudicot seeds and fruits DQ Fuller 8.2.2006. Institute of Archaeology, UCL. MG101 Archaeobotany Practical The Eudicots are an important phylogenetic grouping within flowering plants. Although they
Morphology of Flowering Plants
 65 Morphology of Flowering Plants 1. Fruit of Groundnut is [1988] (a) Legume (b) Caryopsis (c) Berry (d) Nut Legume is a dehiscent dry fruit produced from a monocarpellary superior ovary. Caryopsis is
65 Morphology of Flowering Plants 1. Fruit of Groundnut is [1988] (a) Legume (b) Caryopsis (c) Berry (d) Nut Legume is a dehiscent dry fruit produced from a monocarpellary superior ovary. Caryopsis is
HOW MANY tree species are there? When
 Recognizing Important Tree Species and Their Products HOW MANY tree species are there? When asked, most people respond by saying they don t know or they never really thought about trees being different.
Recognizing Important Tree Species and Their Products HOW MANY tree species are there? When asked, most people respond by saying they don t know or they never really thought about trees being different.
Phylogeny of Asterids. Asterids
 Phylogeny of Asterids Asterids Cornales Ericales Lamiids Campanulids Cornales Ericales Lamiids: Garryales Gentianales Lamiales Solanales Campanulids: Aquifoliales Apiales Dipsacales Asterales After APG,
Phylogeny of Asterids Asterids Cornales Ericales Lamiids Campanulids Cornales Ericales Lamiids: Garryales Gentianales Lamiales Solanales Campanulids: Aquifoliales Apiales Dipsacales Asterales After APG,
Key to the Genera of the Cichorieae Tribe of the Asteraceae Family of the New York New England Region. Introduction
 Introduction The Cichorieae Tribe: The Asteraceae family of plants is one of the largest plant families in the world, conservatively estimated to include over 23,000 species, with some estimates as high
Introduction The Cichorieae Tribe: The Asteraceae family of plants is one of the largest plant families in the world, conservatively estimated to include over 23,000 species, with some estimates as high
Leaves Flowers Fruit Other Alternate, looks whorled in 2 layers Obovate to elliptic 1-3 long Finely serrate Under: Brown & hairy on veins
 Enkianthus campanulatus (ERICACEAE) Japan Alternate, looks whorled in 2 layers Obovate to elliptic 1-3 long Finely serrate Under: Brown & hairy on veins Hydrangea anomala subsp. petiolaris (HYDRANGEACEAE)
Enkianthus campanulatus (ERICACEAE) Japan Alternate, looks whorled in 2 layers Obovate to elliptic 1-3 long Finely serrate Under: Brown & hairy on veins Hydrangea anomala subsp. petiolaris (HYDRANGEACEAE)
BIOLOGY 343 PLANTS AND PEOPLE SUMMER 2010
 BIOLOGY 343 PLANTS AND PEOPLE SUMMER 2010 July 5 July 7 Date Labs and Field Trips Field Trip: Pacific Spirit Park Lab #1: Plant Structure I July 8 Lab #1: Plant Structure I (Quiz #1) July 9 Library Orientation:
BIOLOGY 343 PLANTS AND PEOPLE SUMMER 2010 July 5 July 7 Date Labs and Field Trips Field Trip: Pacific Spirit Park Lab #1: Plant Structure I July 8 Lab #1: Plant Structure I (Quiz #1) July 9 Library Orientation:
BIOL 301 Plant Systematics Summary of Family Traits 1. Anacardiaceae (Cashew Family) (pp )
 BIOL 301 Plant Systematics Summary of Family Traits 1. Anacardiaceae (Cashew Family) (pp. 482-485) Perennial trees, shrubs, or vines Resin ducts; sometimes with milky (toxic!) sap Leaves trifoliate or
BIOL 301 Plant Systematics Summary of Family Traits 1. Anacardiaceae (Cashew Family) (pp. 482-485) Perennial trees, shrubs, or vines Resin ducts; sometimes with milky (toxic!) sap Leaves trifoliate or
3/4/10. Gentianaceae - gentian family!
 Gentianaceae - gentian family! Cosmopolitan family of 80 genera and nearly 900 species. Herbs to small trees (in the tropics) with opposite leaves. CA (4-5) CO (4-5) A 4-5 G (2) Flowers 4 or 5 merous;
Gentianaceae - gentian family! Cosmopolitan family of 80 genera and nearly 900 species. Herbs to small trees (in the tropics) with opposite leaves. CA (4-5) CO (4-5) A 4-5 G (2) Flowers 4 or 5 merous;
A new petrified pentalocular capsular fruit from the deccan intertrappean beds of Mohgaonkalan, M.P., India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 483-487 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.057
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 4 (2016) pp. 483-487 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.057
3/8/2010. Taxus : The yews. Native to Maryland: Taxus canadensis (American Yew) Taxaceae. Low growing, spreading, evergreen shrub
 Taxaceae ~5 Genera 17-20 species Trees and shrubs. Needles mostly alternate. Often spirally arranged but twisted so they appear two-ranked. Needles flattened and elongate, often linear. Needle bases extend
Taxaceae ~5 Genera 17-20 species Trees and shrubs. Needles mostly alternate. Often spirally arranged but twisted so they appear two-ranked. Needles flattened and elongate, often linear. Needle bases extend
Alder. Ash WINTER TREE ID
 Alder Alnus glutinosa Twig: Rich purple with raised orange warty marks Buds: Purple buds on short stalks and arranged spirally around the twig, buds with 2 or 3 bud scales Bark: Purple brown to dark grey-brown
Alder Alnus glutinosa Twig: Rich purple with raised orange warty marks Buds: Purple buds on short stalks and arranged spirally around the twig, buds with 2 or 3 bud scales Bark: Purple brown to dark grey-brown
Systematic Botany. Lectures 27 29
 Systematic Botany. Lectures 27 29 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Shipunov (MSU) Systematic Botany. Lectures 27 29 1 / 69 Outline Fabales: Leguminosae, or Fabaceae legume family Fagales: Fagaceae
Systematic Botany. Lectures 27 29 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Shipunov (MSU) Systematic Botany. Lectures 27 29 1 / 69 Outline Fabales: Leguminosae, or Fabaceae legume family Fagales: Fagaceae
ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE NEOTROPICAL GENERA OF ANNONACEAE
 ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE NEOTROPICAL GENERA OF ANNONACEAE by Paul J.M. Maas 1a. Leaves spirally arranged; flowers 4(-6)-merous; indument composed of stellate hairs. The Amazon region and French Guiana in
ILLUSTRATED KEY TO THE NEOTROPICAL GENERA OF ANNONACEAE by Paul J.M. Maas 1a. Leaves spirally arranged; flowers 4(-6)-merous; indument composed of stellate hairs. The Amazon region and French Guiana in
Information on Xylella fastidiosa in Germany (update) Xylella fastidiosa in Germany, information PAFF,
 Information on Xylella fastidiosa in Germany (update) Xylella fastidiosa in Germany, information PAFF, 2016-07-15 1 Surveillance Survey on specified plants in 100m radius Survey and record keeping on specified
Information on Xylella fastidiosa in Germany (update) Xylella fastidiosa in Germany, information PAFF, 2016-07-15 1 Surveillance Survey on specified plants in 100m radius Survey and record keeping on specified
Leaves Cones Other No markings on underside of leaves. Leaves on main axis conspicuously glandular Usually dull green above
 Thuja occidentalis (CUPRESSACEAE) American arborvitae E. North America Leaves Cones Other No markings on underside of leaves. Leaves on main axis conspicuously glandular Usually dull green above Very small
Thuja occidentalis (CUPRESSACEAE) American arborvitae E. North America Leaves Cones Other No markings on underside of leaves. Leaves on main axis conspicuously glandular Usually dull green above Very small
THE GROWTH OF THE CHERRY OF ROBUSTA COFFEE
 THE GROWTH OF THE CHERRY OF ROBUSTA COFFEE L WEIGHT CHANGES CORRELATED WITH WATER AVAILABILITY DURING DEVELOPMENT BY J. DANCER Department of Agriculture, Kawanda Research Station, Kampala, Uganda {Received
THE GROWTH OF THE CHERRY OF ROBUSTA COFFEE L WEIGHT CHANGES CORRELATED WITH WATER AVAILABILITY DURING DEVELOPMENT BY J. DANCER Department of Agriculture, Kawanda Research Station, Kampala, Uganda {Received
High School Gardening Curriculum Outline:
 High School Gardening Curriculum Outline: Part One: Preparing for a Garden Lesson 1: MyPlate and Plant Basics Lesson 2: Where, What, and When of Planning a Garden Part Two: Making Your Garden a Reality
High School Gardening Curriculum Outline: Part One: Preparing for a Garden Lesson 1: MyPlate and Plant Basics Lesson 2: Where, What, and When of Planning a Garden Part Two: Making Your Garden a Reality
Fall Schedule. Nov. 4, Medicinal Plants of Newfoundland A talk by Dr. John Crellin about the ethnobotanical value of some of our native plants.
 Newsletter of the Canadian Wildflower Society Newfoundland Chapter Volume 3, Number Fall 992 Fall Schedule Oct. 4, 992- Fall Fruits- rescheduled from Oct. 7, due to the storm. An informal talk with slides
Newsletter of the Canadian Wildflower Society Newfoundland Chapter Volume 3, Number Fall 992 Fall Schedule Oct. 4, 992- Fall Fruits- rescheduled from Oct. 7, due to the storm. An informal talk with slides
The genus Citrus arose from Southeast Asia, but cultivated citrus fruits are derived from species native to India, China and Myanmar (Burma).
 Citrus fruits Orange trees produce more than any other perennial fruit tree crop in the U.S. All of these fruits are in the genus Citrus (Rutaceae). All citrus species grow on trees with shiny, evergreen
Citrus fruits Orange trees produce more than any other perennial fruit tree crop in the U.S. All of these fruits are in the genus Citrus (Rutaceae). All citrus species grow on trees with shiny, evergreen
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids
 Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids Large, complex family of mustard oil producing species (broccoli, brussel sprouts, cauliflower, kale, cabbage)... mustards, mallows, maples... CA 4 CO 4 A 4+2 G (2) CA 4 CO
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids Large, complex family of mustard oil producing species (broccoli, brussel sprouts, cauliflower, kale, cabbage)... mustards, mallows, maples... CA 4 CO 4 A 4+2 G (2) CA 4 CO
BIOL 317: Plant Identification and Classification Summer Notes
 BIOL 317: Plant Identification and Classification Summer 2015 - Notes Week 6 Tuesday Plant reproduction and breeding systems(cont.) Advantages of different breeding systems asexual reproduction and selfing
BIOL 317: Plant Identification and Classification Summer 2015 - Notes Week 6 Tuesday Plant reproduction and breeding systems(cont.) Advantages of different breeding systems asexual reproduction and selfing
Boraginaceae Anacardiaceae Solanaceae Brassicaceae. Today 4 families
 Boraginaceae Anacardiaceae Solanaceae Brassicaceae Today 4 families *Remember!* Key characteristics marked with a yellow asterisk!! Boraginaceae (borage/waterleaf family) Overview World: 120 genera, 2,300
Boraginaceae Anacardiaceae Solanaceae Brassicaceae Today 4 families *Remember!* Key characteristics marked with a yellow asterisk!! Boraginaceae (borage/waterleaf family) Overview World: 120 genera, 2,300
DOWNLOAD PDF COLLAGE FROM SEEDS LEAVES AND FLOWERS FULL
 COLLAGE FROM SEEDS LEAVES PDF DOWNLOAD PDF FULL DOWNLOAD 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 collage from seeds leaves pdf How to make ribbon leaves,diy ribbon flowers leaves,green leaves tutorial Download PDF Collage from
COLLAGE FROM SEEDS LEAVES PDF DOWNLOAD PDF FULL DOWNLOAD 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 collage from seeds leaves pdf How to make ribbon leaves,diy ribbon flowers leaves,green leaves tutorial Download PDF Collage from
Weeds. Wheat and Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide 5
 Weeds www.lsuagcenter.com/wheatoats Wheat and Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide 5 Weeds 6 Annual bluegrass Latin name: Poa annua General information: Prolific weed with typical emergence from September
Weeds www.lsuagcenter.com/wheatoats Wheat and Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide 5 Weeds 6 Annual bluegrass Latin name: Poa annua General information: Prolific weed with typical emergence from September
Tree Identification Book. Tree ID Workshop Partners and Supporters
 Tree Identification Book For the Long Sault Conservation Area Clarington Ontario Created by: Kevin Church, Andrew McDonough & Ryan Handy from Sir Sandford Fleming College Tree ID Workshop Partners and
Tree Identification Book For the Long Sault Conservation Area Clarington Ontario Created by: Kevin Church, Andrew McDonough & Ryan Handy from Sir Sandford Fleming College Tree ID Workshop Partners and
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids
 Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids... elms, mulberries, legumes... Rhamnaceae - buckthorn family A large family of trees and shrubs in the tropics and temperate areas. In Wisconsin we have 2 genera (Rhamnus
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids... elms, mulberries, legumes... Rhamnaceae - buckthorn family A large family of trees and shrubs in the tropics and temperate areas. In Wisconsin we have 2 genera (Rhamnus
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids
 Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids... elms, mulberries, legumes... we will be seeing, in the next few lectures, many of the woody plants (trees/shrubs) present at your sites Rhamnaceae - buckthorn family A
Diversity of Wisconsin Rosids... elms, mulberries, legumes... we will be seeing, in the next few lectures, many of the woody plants (trees/shrubs) present at your sites Rhamnaceae - buckthorn family A
 1 Draft Notification of Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives Re : Specification of plants from certain sources as prohibited articles, of exceptions and conditions under the Plant Quarantine Act B.E.
1 Draft Notification of Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives Re : Specification of plants from certain sources as prohibited articles, of exceptions and conditions under the Plant Quarantine Act B.E.
NR Study-note 120a AN OUTLINE OF TREE SEED BIOLOGY
 NR Study-note 120a Based on the text and graphics in: With special reference to seed handling in Nepal. Technical Note no. 6 HMG/EEC/ODA National Tree Seed Project by A.M.J.Robbins (1987) Revised July
NR Study-note 120a Based on the text and graphics in: With special reference to seed handling in Nepal. Technical Note no. 6 HMG/EEC/ODA National Tree Seed Project by A.M.J.Robbins (1987) Revised July
GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS
 GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS ANACARDIACEAEAE By Pedro Acevedo-Rodríguez (5 Jun 2017) A predominantly pantropical family, extending to temperate regions, mostly of
GUIDE TO THE GENERA OF LIANAS AND CLIMBING PLANTS IN THE NEOTROPICS ANACARDIACEAEAE By Pedro Acevedo-Rodríguez (5 Jun 2017) A predominantly pantropical family, extending to temperate regions, mostly of
LESSON 6: PLANT REPRODUCTION
 LESSON 6: PLANT REPRODUCTION LEVEL ONE Like every living thing on earth, plants need to make more of themselves. Biological structures wear out over time and need to be replaced with new ones. We ve already
LESSON 6: PLANT REPRODUCTION LEVEL ONE Like every living thing on earth, plants need to make more of themselves. Biological structures wear out over time and need to be replaced with new ones. We ve already
December 2015 Number 2
 Calochortiana December 2015 Number 2 December 2015 Number 2 CONTENTS Flora of Zion National Park Walter Fertig................... 3 Introduction.................... 3 I. Key to Plant Families of Zion National
Calochortiana December 2015 Number 2 December 2015 Number 2 CONTENTS Flora of Zion National Park Walter Fertig................... 3 Introduction.................... 3 I. Key to Plant Families of Zion National
Diversity and Evolution of Rosids
 Diversity and Evolution of Rosids... hemp, figs, and legumes... N 2 fixing clade *Rosales the rest Rosaceae is sister to all other families of the order tendencies in rest of the order to loss of petals
Diversity and Evolution of Rosids... hemp, figs, and legumes... N 2 fixing clade *Rosales the rest Rosaceae is sister to all other families of the order tendencies in rest of the order to loss of petals
Major Angiosperm Clades
 Major Angiosperm Clades Basal Angiosperms The Eudicots Basal Angiosperms The eudicots are separated from all other angiosperms by a special pollen form. The Eudicots The eudicots are separated from all
Major Angiosperm Clades Basal Angiosperms The Eudicots Basal Angiosperms The eudicots are separated from all other angiosperms by a special pollen form. The Eudicots The eudicots are separated from all
A TWIN SEEDLING IN ZEA MAYS L. TWINNING IN THE GRAMINEAE
 125 A TWIN SEEDLING IN ZEA MAYS L. TWINNING IN THE GRAMINEAE i BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With Plate i and i figure in the text) Amongst some maize seedlings grown for
125 A TWIN SEEDLING IN ZEA MAYS L. TWINNING IN THE GRAMINEAE i BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, University of Leeds (With Plate i and i figure in the text) Amongst some maize seedlings grown for
FRUIT GROWTH IN THE ORIENTAL PERSIMMON
 California Avocado Society 1960 Yearbook 44: 130-133 FRUIT GROWTH IN THE ORIENTAL PERSIMMON C. A. Schroeder Associated Professor of Subtropical Horticulture, University of California at Los Angeles. The
California Avocado Society 1960 Yearbook 44: 130-133 FRUIT GROWTH IN THE ORIENTAL PERSIMMON C. A. Schroeder Associated Professor of Subtropical Horticulture, University of California at Los Angeles. The
Identifying Broadleaved Trees in Winter
 Identifying Broadleaved Trees in Winter Photo Suzanne Sancisi-Frey, Forest Research Suzanne Sancisi-Frey, Forest Research Identifying winter trees Some features that can be used to identify winter trees
Identifying Broadleaved Trees in Winter Photo Suzanne Sancisi-Frey, Forest Research Suzanne Sancisi-Frey, Forest Research Identifying winter trees Some features that can be used to identify winter trees
tulip poplar Creating Canopy 2018 Liriodendron tulipifera large shade tree height at maturity: feet spread at maturity: feet
 large shade tree height at maturity: 70-90 feet spread at maturity: 35-50 feet growth rate: fast light requirement: full/partial sun soil: moist characteristics: uniquely shaped leaves and orange/cream
large shade tree height at maturity: 70-90 feet spread at maturity: 35-50 feet growth rate: fast light requirement: full/partial sun soil: moist characteristics: uniquely shaped leaves and orange/cream
New Certification Scheme for Raspberries. Alison Dolan
 New Certification Scheme for Raspberries Alison Dolan Industry benefits from a Certification Scheme Provide fruit producers and propagators with planting material of a known health standard, vigour and
New Certification Scheme for Raspberries Alison Dolan Industry benefits from a Certification Scheme Provide fruit producers and propagators with planting material of a known health standard, vigour and
Florida 4-H Horticulture Identification and Judging Study Manual: Fruits and Nuts 1
 Circular 4HEHL 22 Florida 4-H Horticulture Identification and Judging Study Manual: Fruits and Nuts 1 J. G. Williamson 2 There are 45 fruits and nuts in the 4 H Horticulture Contest. Most of them can be
Circular 4HEHL 22 Florida 4-H Horticulture Identification and Judging Study Manual: Fruits and Nuts 1 J. G. Williamson 2 There are 45 fruits and nuts in the 4 H Horticulture Contest. Most of them can be
