ì<(sk$m)=beijdg< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
|
|
|
- Cornelia Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fascinating Facts England gave land in the Ohio River valley to a group of Virginia colonists. George Washington, one of those colonists, was sent by the British to make the French leave the area. Some Mohawks, who were part of the Iroquois League, left the league to join the French in their war against the British and other Iroquois. After the French and Indian War, the only part of mainland on the Atlantic coast that did not belong to England was Florida, which was still controlled by Spain. Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Nonfiction Compare and Contrast Maps Captions Scott Foresman Social Studies ì<(sk$m)=beijdg< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U ISBN
2 In this book you will read about the growth and development of the Thirteen English Colonies in North America. From the time of the first European settlements, the colonists experienced a complicated relationship with the American Indians. This relationship included agreements and conflicts that led to the French and Indian War. Vocabulary alliance self-sufficient backcountry trading post tributary ISBN: Copyright Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in the United States of America. This publication is protected by Copyright, and permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s), write to: Permissions Department, Scott Foresman, 1900 East Lake Avenue, Glenview, Illinois Editorial Offices: Glenview, Illinois Parsippany, New Jersey New York, New York Sales Offices: Needham, Massachusetts Duluth, Georgia Glenview, Illinois Coppell, Texas Sacramento, California Mesa, Arizona V0G
3 New Beginnings When the European settlers arrived in North America, they had to adapt to a new land with its own geography, history, and culture. There were already people living in this new land who had for centuries adapted their lives to the environment in which they lived. These people were the American Indians, or Native Americans. The settlers and the American Indians had a very complicated relationship. At different points throughout early American history, the settlers and American Indians fought wars against each other, formed trade and military alliances, and shared farming techniques. Two key factors that profoundly impacted the way of life and the interactions between the settlers and American Indians were geography and climate. The geography and climate varied greatly along the east coast of North America. The Thirteen Colonies The colonists lived along the Atlantic coast of North America. There were thirteen colonies, and each colony had distinctive characteristics. However, colonies that were geographically close to one another shared similar climates. As a result, three distinct colonial regions emerged. The regions were called the New England, the Middle, and the Southern Colonies. The Thirteen English Colonies 2 3
4 The New England Colonies The colonists who settled in the New England Colonies found rocky soil, cold winters, and short summers to be characteristic of the region s geography and climate. Because of this, most farmers in New England learned to be self-sufficient. They learned important farming techniques, such as how to grow corn, from the American Indians. Fishing, boat building, and trading were not only popular ways of earning a living, they were also important industries that helped shape the growth of the New England economy. The dense New England forests supplied plenty of timber to build ships. Other natural resources found in New England were iron and animal furs. One way the colonists obtained furs was by trading with American Indians. In 1633 Dutch colonists expanded their fur trade from the Hudson River valley in present-day New York to present-day Hartford, Connecticut. The English colonists in Massachusetts wanted to compete with the Dutch for the fur trade. The Pequot, a powerful American Indian group, saw the English as more of a threat because there were more English colonists. In 1637 conflicts over land and the fur trade sparked a war between the English and the Pequot. This was known as the Pequot War. In this war, the English colonists were assisted by the Narragansett and the Mohegan rivals of the Pequot. By the fall of 1638, English colonists and their American Indian allies defeated the Pequot, and hundreds of Pequot were killed. For nearly forty years after the end of the Pequot War, New England did not experience any major conflicts with American Indians. In 1675 King Philip s War became the most costly conflict between American Indians and the colonists. Twelve out of ninety New England towns were destroyed and 5 percent of the colonists were killed. Almost 40 percent of the American Indian population were killed or fled the region. After the war, the American Indians who stayed in New England survived in small, scattered communities. The American Indians no longer had the strength to use armed resistance to oppose the colonists. They lost control of their land, and by the early 1700s English colonists had expanded across the region. Metacom, Sachem of the Wampanoag, was known to colonists as King Philip. 4 5
5 The Middle Colonies Between the New England Colonies and the Southern Colonies lay the Middle Colonies. Unlike the colonies in the North, the Middle Colonies had very fertile soil and a more moderate climate. As a result, the Middle Colonies were often called the breadbasket colonies because they supplied the New England and the Southern Colonies with grains, such as wheat, barley, and oats. Unlike New England, there were fewer towns in the Middle Colonies because of the large amount of space required for farming. Rather than use land for a town square as in New England, farmers in the Middle Colonies needed large areas of land to grow crops and raise livestock. In addition, the Middle Colonies had excellent iron and coal resources and a strong fur industry. All of these items were traded in the bustling coastal cities of the Middle Colonies. Because many of the colonists who lived in Massachusetts were Puritans from England, people who practiced other religious beliefs were persecuted. In contrast, the Middle Colonies were much more diverse and enjoyed more religious freedom. Quakers, Presbyterians, Mennonites, and Catholics all lived in the Middle Colonies. The Quakers, many of whom lived in Pennsylvania, were known for their tolerance, especially toward African Americans and American Indians. William Penn and colonial leaders met with the Delaware in In 1682 William Penn founded the Pennsylvania colony as a place where his Quaker beliefs could be practiced. In the same year, he made a treaty with the Lenni Lenape group. In the treaty, Penn promised to pay them a fair price for most of the land that King Charles II had given him. Compared to many other colonies, Pennsylvania had no major conflicts with American Indians at least until Penn s death in The Lenape, or Delaware, lived in a region that consisted of much of the Middle Colonies. In 1600 there were about twenty thousand Delaware. By 1700 war and disease had reduced their population to about four thousand. One cause of war was the fur trade between American Indians and the colonists. The demand from Europe for fur was so great that several American Indian groups competed for the same hunting territories. This competition led to war among the groups. 6 7
6 The Southern Colonies The Southern Colonies had winters that were shorter and milder than the winters in either New England or the Middle Colonies. The geography was also different. The land close to the Atlantic coast was a mixture of bays, swamps, and rivers. This land was fertile and often wet, making it very good for growing cash crops, such as tobacco, indigo, and rice. Many cash crops were grown on plantations. Large plantations often had their own blacksmiths and dressmakers. In some cases large plantations in the South had bigger populations than some towns in New England. Southern plantations brought much wealth and prestige to the South. However, the majority of southerners did not own plantations. Like farmers in New England, many southerners were self-sufficient. These southerners lived in the backcountry, surrounded by dense woods and hills. People living in the backcountry had a complicated relationship with the American Indians of that region, on whose hunting and fishing areas they settled. The Tuscarora, an American Indian group, went to war against the North Carolina colonists in Two years later, the colonists defeated the Tuscarora with the help of the Yamasee, a rival American Indian group. In 1715 the Yamasee made an alliance with part of the Creek group in their own fight against the colonists. The colonists defeated this alliance with the help of the Cherokee and other American Indians. By the end of the war the next year, the American Indians were defeated. Many of the survivors were driven from their homes and fled to Spanishcontrolled Florida. More than a million animal furs were shipped from the port city of Charleston, South Carolina between 1700 and The fur trade forced the Cherokee to hunt farther from their homes. Competition with the colonists for hunting grounds, wars with other American Indian groups, and disease were some of the challenges faced by the Cherokee. Between 1773 and 1792, the Cherokee signed a number of treaties with colonists by which the Cherokee gave up a great deal of their land in the South. 8 9
7 The Ohio River Valley Much of the conflict that occurred between people in early North America was about land. English colonists, French traders, and many different American Indian groups were involved. By the early 1700s the Atlantic Coast was becoming too densely populated. Some English colonists began to cross the Appalachian Mountains and move further west. They moved to the Ohio River valley, which had very fertile land. By the mid-1700s, the French already had trading posts in this region, where they met American Indians and traded goods. This area was important because the Ohio River was a tributary of the Mississippi River. France had already claimed the Mississippi River and all of its tributaries as part of New France. Both the French and the English wanted to control the Ohio River valley because it offered access to the Mississippi River, fertile lands, and a central location for trade. In addition, American Indians wanted to protect this region from being settled by the English. Some American Indians depended on trade with both the French and the British in manufactured goods, especially weapons. The French and the English relied on the American Indians for fur trade and military support. All three groups wanted to have control of the Ohio River valley, and war seemed inevitable. European Land Claims,
8 The French and Indian War In the 1740s England granted land in the Ohio River valley to a group of Virginia colonists. These colonists thought the land could be sold as farmland to other colonists. This land grant increased tension between the French and the English. In the early 1750s the French built forts in the Ohio River valley to secure what they felt was their territory. The British did not want to lose their claim and demanded that the French dismantle their forts. The French refused the demand, and war soon broke out. George Washington s attempt to capture Fort Duquesne in 1754 is known as the Battle of Great Meadows. The battle took place near present-day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Washington s battle with French forces marked the beginning of the French and Indian War. A number of battles between the British, the French, and their American Indian allies followed. George Washington General Edward Braddock, Washington s commander, was mortally wounded near Fort Duquesne. The struggle for power in North America was not the only source of conflict between Britain and France. In 1756 Britain formally declared war on France and the Seven Years War began. Most of the fighting between the two countries and their allies took place in Europe. In North America the British began the war by losing battles to the French. One reason the French were winning was their alliance with American Indians. Even though American Indians traded with both the British and the French, many American Indians feared that the English colonists would drive them from their land. To help gain an advantage, both the French and British made alliances with different American Indian groups. In general, the French had a better relationship with the American Indians because they were traders and did not take the American Indians land as the English colonists did. The two major American Indian groups involved were the Algonquians and the Iroquois. These two groups were made up of different nations that shared the same language and culture. During the French and Indian War, the French formed alliances with the Algonquians and the English formed alliances with the Iroquois League. The Iroquois allied themselves with the English because the Iroquois and the Algonquians had been enemies for a long time. 13
9 In November 1756 the war changed direction when former Prime Minister William Pitt became Secretary of State. Pitt was a very forceful man, and from London, he seized control of British forces. He appointed new, young generals to lead the British and Colonial troops. As a result, the British began winning battles against the French. In 1758, British forces were able to capture Fort Duquesne, the fort George Washington had failed to capture in In this victory, four years later, Washington was able to take part in the fort s capture. The Iroquois joined the British during the war. The Iroquois hoped that this alliance would help them keep control of their land. The British captured Quebec, the French capital city in New France, in When the British gained control of Montreal in 1760, most of France s territory in North America fell under British control. In 1760 the war between Britain and France for North America largely ended. However, the two countries and their allies continued to fight in Europe for the next three years. British Control After seven years of fighting, the British won the French and Indian War. The two sides signed the Treaty of Paris in 1763, and France gave much of its land in North America to Britain, including most of Canada and all of its territory east of the Mississippi River. After the French and Indian War, England controlled much of North America. However, the British forts and troops needed to secure this vast territory were too few and too far apart. Because the French had been defeated and were no longer a threat, the colonists began to move west to settle. Many American Indians feared that the growing number of settlers would force them off their lands. This movement by the colonists would soon affect the lives of the American Indians living in the West. William Pitt became British secretary of state in
10 Glossary alliance an agreement between two groups or nations to defend each other backcountry the rugged area of land near the Appalachian Mountains self-sufficient able to rely on oneself for most of what one needs trading post a place where settlers and American Indians met to trade goods tributary a stream or river that flows into a larger river Write to It! Suppose that you are a reporter for a colonial newspaper covering the French and Indian War. Write a three- or four-paragraph article summarizing the events of the war. Write your article on a separate sheet of paper. 16 Maps 11 Mapquest.com, Inc. Photographs Every effort has been made to secure permission and provide appropriate credit for photographic material. The publisher deeply regrets any omission and pledges to correct errors called to its attention in subsequent editions. Unless otherwise acknowledged, all photographs are the property of Scott Foresman, a division of Pearson Education. Photo locators denoted as follows: Top (T), Center (C), Bottom (B), Left (L), Right (R) Background (Bkgd) Opener: Francis G. Meyer/Corbis 3 Bettmann/Corbis 4 Getty Images 7 Peter Gridley/Getty Images 12 Getty Images 13 State Historical Society of Wisconsin, Madison, USA/Bridgeman Art Library 14 Bettmann/Corbis
ì<(sk$m)=beibch< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Can We Get Fun Facts Strawberries are in the rose family. Each person in the United States eats about 103 pounds of citrus fruit a year. Thomas Jefferson introduced French fries to the United States. That
Can We Get Fun Facts Strawberries are in the rose family. Each person in the United States eats about 103 pounds of citrus fruit a year. Thomas Jefferson introduced French fries to the United States. That
ì<(sk$m)=bebiah< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Reader The Story of Pizza by Roberto Manti Illustrated by Peter Church Genre Build Background Access Content Extend Language Narrative Nonfiction Food History Pizza Map Definitions Pizza Words World Cultures
Reader The Story of Pizza by Roberto Manti Illustrated by Peter Church Genre Build Background Access Content Extend Language Narrative Nonfiction Food History Pizza Map Definitions Pizza Words World Cultures
ì<(sk$m)=bdhedf< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Put Things in Order Captions Diagrams Labels Glossary Life Cycles Scott Foresman Science 1.4 ì
Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Put Things in Order Captions Diagrams Labels Glossary Life Cycles Scott Foresman Science 1.4 ì
Name: Date: Period: VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution. Filled In. Notes VUS.4 (pt. 1): The Road to Revolution 1
 Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
Name: Date: Period: VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution Filled In Notes VUS4 (pt 1): The Road to Revolution 1 Objectives about The Road to Revolution The student will demonstrate knowledge of events and
ì<(sk$m)=bdbjhg< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Special Days, Special Food Genre Nonfiction Expository Fiction nonfiction
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Special Days, Special Food Genre Nonfiction Expository Fiction nonfiction
ì<(sk$m)=bdbjhg< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Special Days, Special Food Genre Nonfiction Expository Fiction nonfiction
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. Special Days, Special Food Genre Nonfiction Expository Fiction nonfiction
ì<(sk$m)=bddjbi< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The World of Bread! by Patricia West Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The World of Bread! by Patricia West Genre Expository nonfiction Comprehension
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Presenting... The 13 Colonies
 Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root ( )
 Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Unit 8. The English Establish 13 Colonies
 Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
The Middle Colonies. If YOU were there. How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? SECTION. What You Will Learn
 The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Chapter 4-1 Notes. The Economy of the Colonies
 Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
The 13 Colonies. Religious, Political and Economic Foundations
 The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
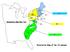 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon Lord Baltimore
 Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Early British Colonies
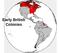 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
The Southern Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 4
 The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies
 The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
Monday, September 11
 th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
Wealth and resources. ! New beginning. ! Get out of debt. ! Escape political & religious persecution
 Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
13 Colonies New England Colonies
 13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
The Thirteen Colonies
 The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
New England Colonies Economy
 New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
13 Colonies and Regions
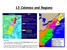 1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
John Smith The Starving Time
 The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
ì<(sk$m)=bdchdh< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The Tortilla Factory by Eve Beck illustrated by Michael Rex Genre Realistic
Suggested levels for Guided Reading, DRA, Lexile, and Reading Recovery are provided in the Pearson Scott Foresman Leveling Guide. The Tortilla Factory by Eve Beck illustrated by Michael Rex Genre Realistic
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages
 Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
MIDDLE COLONIES GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES. MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) IMPORTANT DEMOCRATIC PRINCIPALS ESTABLISHED HERE
 NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
Colonial Jeopardy. Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100. Puritans 200 Quakers 200 Native Americans 200
 Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d. Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary
 The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
~VANIA ..- ~ ~ ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2. Land Use. Religion in the Middle Colonies, I 775
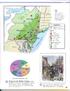 ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac built a fort near Detroit. He invited several tribes to move there.
 The First Fox War The French slowly reopened the fur trade in the west. They built forts in outlying areas. They invited Indians to settle nearby. Indian trappers and hunters were sent out to get furs.
The First Fox War The French slowly reopened the fur trade in the west. They built forts in outlying areas. They invited Indians to settle nearby. Indian trappers and hunters were sent out to get furs.
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
A Brief History of the Northwest Territory to and through the American Revolution
 A Brief History of the Northwest Territory to and through the American Revolution Presented by James S. Swift, PS February 9, 2016 Montgomery County Genealogy Club Crawfordsville, Indiana Source: Ohio
A Brief History of the Northwest Territory to and through the American Revolution Presented by James S. Swift, PS February 9, 2016 Montgomery County Genealogy Club Crawfordsville, Indiana Source: Ohio
The Louisiana Purchase
 The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
The Louisiana Purchase How did the United States gain the Louisiana Territory? Why would they want it? Do Now: 1.) Why would the United States want to expand to the West? Read the story below and answer
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies
 Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory
 Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution
 S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism. Key Concept 2.2.I C&D
 Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Name Class Date. Use the information from pages to complete the following.
 GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
American Indians. The First Americans
 The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
I want YOU to have a great summer and so does Uncle Sam:
 Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Military Geography. MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York. Landforms and Elevations. Strategic Passages 10/28/2014.
 Military Geography MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Optional Exercise 6 (graded or extra credit) explores the interrelationship between the physical
Military Geography MILITARY GEOGRAPHY and the Strategic Nature of New York Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Optional Exercise 6 (graded or extra credit) explores the interrelationship between the physical
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Causes of the American Revolution
 Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Causes of the American Revolution The Ohio River Valley Around 1750, the British and the French were competing for land beyond the Ohio River Valley. British colonists were going beyond Britain's territory
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo
 Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
Thomas Jefferson: Expansion & Embargo New Orleans & The Mississippi I. The port city of New Orleans and the Mississippi River were important economic locations for the USA A. The Mississippi River connects
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Objectives Analyze the results of the first encounters between the Spanish and Native Americans. Explain how Cortés and Pizarro gained control of the Aztec and Inca empires. Understand the short-term and
Chapter 16 The Civil War ( ) Section 4 The Strain of War
 Chapter 16 The Civil War (1861-1865) Section 4 The Strain of War Which do you feel is the most important quality in a good leader? A. Enthusiasm B. Confidence C. Courage D. Decisiveness A. A B. B C. C
Chapter 16 The Civil War (1861-1865) Section 4 The Strain of War Which do you feel is the most important quality in a good leader? A. Enthusiasm B. Confidence C. Courage D. Decisiveness A. A B. B C. C
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
The Louisiana Purchase. Chapter 9, Section 2
 The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
DISEASE PLANTS ANIMAL. Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes
 ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
The British in North America
 The British in North America hue you and your classmates are at the gym, the students in grade 7 come into your classroom. They sit at your desks and begin to use your school supplies. Soon, some grade
The British in North America hue you and your classmates are at the gym, the students in grade 7 come into your classroom. They sit at your desks and begin to use your school supplies. Soon, some grade
Roanoke 9/21/2017. The First English Colonies in North America. Roanoke & Jamestown. Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585
 The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania
 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Two: Transplantations and Borderlands
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
The 13 English Colonies
 The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
Name Period Test Date September Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East Asia? (page 122)
 Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
Name Period Test Date September 20. Review Sheet Exploration and Colonization (Chapters 5 and 6) Chapter 5 Early Explorers of Texas 1. Why did Europeans want to find new trade routes to India and East
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
APWH chapter 18.notebook January 11, 2013
 Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
