Critical Reading of History Text
|
|
|
- April Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Critical Reading of History Text 20 minutes Materials Text: A Nasty Triangle Student Materials book Before Reading Determine the grouping structure for text reading. Facilitate movement into groups or pairs as needed. Refer students to the passage in their Student Materials books. Introduce the map and concept of triangular trade. There was more than one trade triangle, as you can see. Guide students in tracing two or three different triangular trade routes on the map and discuss what products were traded along each side of each triangle. Introduce the reading. During Reading The New England colonies traded lumber, fish, and furs; the southern colonies traded tobacco, rice, and indigo. Britain, a mercantilist power, turned the colonies raw materials into more expensive manufactured goods and sold them right back to the colonies for a profit. Some of these British manufactured good (guns and cloth) were shipped to Africa, where they were traded for men, women, and children. As you read, pay attention to the different way that each colonial region contributed (or didn t contribute) to triangle trade. What was sold and what was bought in each region? As we read, we ll stop to answer questions and take notes about what we ve read. As needed, clarify vocabulary. Point out connections to essential words where applicable. At each stopping point (including the final one), facilitate student note-taking in response to the provided questions. Provide corrective feedback if students misunderstand the material. After Reading Facilitate student note-taking in response to the final questions. Have students write connections to any essential words in their word logs. 20
2 1 of 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 (1) A Nasty Triangle You may be getting the idea that the United States began as a collection of settlements that were not much alike. And you are right. (2) South Carolina wasn t like Pennsylvania, and Maryland wasn t like Connecticut. The people who founded the colonies had a lot to do with those differences and so did the conditions of the land.
3 A Nasty Triangle 2 of 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 (3) Massachusetts had a special problem because of its rocky soil and cold climate. It was tough being a farmer in New England, but New Englanders were tough people who liked challenges. So they did farm, although for many it was subsistence farming. That meant that they grew enough for themselves; they didn t usually have extra crops to sell. New England s land wasn t right for large farms or plantations like those in the South. How were the New England colonies different from the southern colonies? (4) And when it came to industry, the British made things difficult. They wouldn t let the colonists manufacture goods that competed with English goods. You can understand why these mercantilist policies caused some grumbling. (5) New Englanders had to find ways to earn a living. Fishing was one way. Cod became New England s gold, just as tobacco was Virginia s. The Puritan settlers caught cod and then sold the fish in Europe or the Caribbean islands. To do that, they needed ships. So they became shipbuilders. To make ships, they needed lumber. So they harvested timber and began selling wood and wood products. And soon, Yankees were trading all kinds of things. (6) Picture a triangle a long one. Now stretch the triangle across the Atlantic Ocean. Put one point on the New England coast, another in Africa, and the third in South Carolina. Now imagine a boat sailing along that triangle, from New England to Africa to South Carolina, and back to New England. (7) Let s pretend a triangle is starting in New England, where a ship is loaded with rum and guns. The ship heads for Africa, where the rum and guns will be traded for African people. The Africans have been captured by enemy tribesmen and sold to African slave traders. The slave traders bargain with the New England boat captain, who buys as many people as he can squeeze on his ship. Some of the captives are children, kidnapped from their parents.
4 A Nasty Triangle 3 of 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 Why is the triangle trade referred to as nasty in this passage? What is nasty about it? (8) Olaudah Equiano (Oh-lawd-ah Eh-kwi-ah-no) was one of those children. He was 11 in 1756, when he was captured in Benin: (9) One day, when all our people were gone out to their works as usual, and only I and my sister were left to mind the house, two men and a woman got over our walls and in a moment seized us both; and without giving us time to cry out or to make any resistance, they stopped our mouths and ran off with us into the nearest woods. Olaudah and his sister are taken on a long journey, separated, and sold. He tries to run away but is unsuccessful. Then he sees the ocean and a slaveship waiting for its cargo. He is carried aboard and immediately handled, and tossed up to see if I was sound, by some of the crew, then tossed below deck, where the smell is so bad he becomes sick and cannot eat. When he refuses food, he is tied down and beaten. He learns that he is being taken to the white men s country to work. (10) I was then a little revived and thought that if it were no worse than working, my situation was not so desperate. Still I feared I should be put to death, for the white people looked and acted in so savage a manner. I had never seen such instances of brutal cruelty; and this is not only shown toward us blacks, but also to some of the whites themselves. One man was flogged so unmercifully that he died, and they tossed him over the side as they would have done a brute. This made me more afraid, and I expected nothing less than to be treated in the same manner. Olaudah describes the scene belowdecks, where people are packed so closely they can hardly turn over. The smells, he says, are loathsome. Women shriek, the dying groan, all is a scene of horror. One day, when we had a smooth sea and moderate wind, two of my wearied countrymen, who were chained together, preferring death to such a life of misery, jumped into the sea.
5 A Nasty Triangle 4 of 4 Colonial America Lesson 4 What is your reaction to Olaudah s experience? (11) Many Africans are sent to Virginia, where they are traded for tobacco. Some are exchanged for sugar and molasses in the West Indies. Others are traded for rice in South Carolina. Then the ships head back to their home ports. In New England, where we started our voyage, the sugar and molasses are turned into rum and the triangle begins again. That is the way the terrible triangular trade works. Every colony is a part of it. English ships carry the greatest numbers of Africans into slavery. Adapted from Hakim, J. (2005). A history of US: Making thirteen colonies. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. How was the triangle trade important to the economy of the southern colonies? Contrast the role of the New England colonies with the role of the southern colonies in the triangle trade.
6 Warm-Up Colonial America Lesson 5 mercantilism The idea that if a country imports cheap raw materials and exports finished products, it will become rich Look over the illustration of how mercantilism makes some people rich. 1. Colonists cut down trees and ship the lumber to the mother country. The colonists are paid very little. 2. The mother country uses the cheap lumber to create expensive furniture. 3. The furniture is exported to other countries and colonies and sold at a high price. The mother country becomes rich. Briefly answer the following questions: 1. Who benefits least in this process? 2. Why does this group benefit the least? 3. Is mercantilism fair?
7 Warm-Up Colonial America Lesson 6 colony Land and communities controlled by a distant country Below are pictures of colonists in the New England and southern colonies working to grow their economies. New England Colonies Southern Colonies In the sentences below, fill in the blank with one of the words or phrases in the box. The first one has been done for you. Each word or phrase will be used only once. whereas on the contrary similarly just as likewise however 1. In New England, the geography was hilly and full of forests, whereas the geography of the southern colonies was flat, with open fields that were good for growing crops. 2. In the southern colonies, slave labor was important to the economy., in New England, slave labor was not used frequently. 3. In New England, the land was an important resource that was used to make money., in the southern colonies, the land was an important resource that could be used to gain wealth.
8 TBL Knowledge Application 45 minutes Introductory Reading Activity 10 minutes Before class, identify student teams. Each team should include at least three students; consider using doubled pairs for easy grouping. Facilitate student movement into teams. Have students take their Student Materials books, textbooks, and other relevant content resources with them. Hand out a Colonial Regions map and a set of Passage cards to each team. Hang one copy of the map in view for demonstration. Introduce the activity. Today you will work in teams to discuss what made the colonial regions different from one another. You have three separate passages on large cards. As a team, read each passage aloud and discuss which colonial region that passage describes. Take turns reading the paragraphs, so everyone on your team has a chance to read. After everyone on your team agrees, place each of the passages in the region on your map that the passage describes. You have 5 minutes to complete this activity. If you finish early, discuss what you remember learning about each region. This discussion will help you in your next activity. Any questions? Set the timer for 5 minutes. As students work, monitor for understanding. Encourage dialogue within groups. Have teams share their answers. Confirm that all teams have placed the passages correctly. Colony Characteristics Sorting Activity Hand out a set of Colony Characteristic cards to each team. 20 minutes Use the hanging map to demonstrate as you preview the next activity. Hold up the William Penn card. Our three colonial regions are the New England colonies, the middle colonies, and the southern colonies. These colonies developed different ways of living, and different religions, foods, and other customs. Each team has a stack of cards. Your task is to place each card in the colonial region in which it belongs. Let me show you how this works. Here is a card with a picture of William Penn. I remember that William Penn was a Quaker. I can t remember much else about him, but if I look in my textbook, it tells me that he founded Pennsylvania. So I know that William Penn was a Quaker who founded Pennsylvania. So this card 52
9 Colonial America Lesson 9 belongs in the middle colonies area of my map. That s where the Quakers lived, and Pennsylvania is in that area. I ll put him there now. Demonstrate placing the card in the middle colonies on your hanging map. Hold out the Ports card from the pack. Let s consider another example: ports. Hmm, I know that ports are important in all three regions, for different reasons. But when I think about it, the New England colonies did a lot of shipbuilding, fishing, and trading. Ports are important for those things. So I will put the Ports card in the New England region. Demonstrate placing the card in the New England colonies on your hanging map. Hold out the Tobacco card from the pack. Take volunteers until someone answers correctly. However, if I could make a good argument for the Ports card to go in another region, I could put it there instead. The main thing is that I must have a good reason. Here is a card that has a picture of tobacco on it. Who can tell me which colonial region comes to mind when we think of tobacco? That s right! Growing and selling tobacco was a huge part of the economy of the southern colonies. So for this activity, I would discuss with my team where we think tobacco should be placed on the map. Once we all agree, we would put it there. Demonstrate placing the card in the southern colonies on your hanging map. Set the timer for 15 minutes. Monitor the teams. If my team couldn t agree or didn t know the answer, we would need to look it up in our textbook, our notes, or somewhere else. Remember to work as a team, placing one card at a time. Take turns reading a card aloud and then discuss with the group where you want to place it. I will walk around to help you if you get stuck, but I won t give you the answers. You have 54 cards to place in 15 minutes. 53
10 Students will likely struggle a bit with this activity. Do the following to help students: Point students in the right direction without giving away answers. Remind students to use their resources (e.g., textbook, notes). Encourage teams to keep conversations going and on point. Give frequent time warnings (10 minutes, halfway, 5 minutes, 1 minute). Stop the activity to reteach the class when you notice common misconceptions. After 15 minutes, pass out one copy of the key to each team and have teams self-check. Spot-check team answers aloud and correct any misunderstandings. Narrow Your Choices Activity 15 minutes Pass out one Narrow Your Choices sheet to each team. Introduce the activity. Set the timer for 7 minutes. Now your team will choose one colonial region to live in. You ll then pick four cards that best represent the region and rank them in importance. Choose wisely you will justify your choices to the class afterward. You will place your four cards on the Narrow Your Choices sheet and complete the sentence stems as a group, with one person writing your answers. You have 7 minutes for this activity. Any questions? Monitor teams. To encourage dialogue, challenge teams to their defend their choices. After 7 minutes, have each team share which region and cards they chose. Review the content by calling on students to justify their answers; consider using the following questions: Why did you choose to keep? What does tell us about the colonies? How is connected to? How are the colonies different from the colonies? During and after each team shares, discuss the following questions with the whole class: Does anyone agree or disagree with these choices? Why? Were some cards hard to place in a region? Why? How did you make your decisions? Were some cards easy to place? Why? 54
11 Colonial America Lesson 9 After all teams have shared, remind the class of the comprehension question and discuss its connection to this activity. How did the colonial regions develop differently? How did today s lesson help you better answer that question? Optional Extension Activity: Narrow Your Choices AMERICA Activity Use the same procedure as the Narrow Your Choices activity, but have students choose the four cards that best represent America. Have students write their answers on the Narrow Your Choices AMERICA sheet. Use the same follow-up questions. Passage Cards (3 per set) Descriptive Passage Card #3 This colonial region enjoyed a warm climate with hot summers and mild winters. The geography Descriptive of this area Passage included Card large, flat #2 plains and rolling hills, which provided good land for crops that required a lot of space to grow. Farmers in this colonial region could grow crops during most months, which is different from the other colonial regions. Hot summers in this region made This colonial region had warm summers disease and a cool major winters. problem, The and geography many colonists, included including many rivers those in Jamestown, died from these near the coast, good soil for growing diseases. crops along the rivers, and mountains farther away from the Descriptive Passage Card #1 coast. This colonial region had good, The safe colony harbors farthest that were north used in for this shipping. colonial The region climate was founded and by someone who was seeking a land of this region were good for farming place and where raising his religious livestock. group The colonies could freely in this practice. region Other were colonists in this region practiced known as a breadbasket because of a the different large form amount of Christianity. of bread grains Overall, that were though, grown religion and Colonists in this region experienced very cold winters and mild summers. The land was flat close was less a part of everyday life in this processed there. to the coastline, but it became hilly with many mountains as you moved inland. colonial The region soil in because this people often lived very far apart from one another, unlike in other region was rocky, which made farming Colonists difficult. in Farms this region often provided practiced just a variety regions. enough of food religions. to feed The freedom to practice religion made a single family. Many colonists in this this region region did not attractive survive to the people cold who winters, Almost were but told all for colonists to those leave who other in this colonial region were regions somehow because involved of their with farming the large plots of land found a way to stay warm, disease was religious less of beliefs. threat Colonists in this region in this than region in that the also men other tended owned. colonial to Land have owners better grew relationships rich by selling with the their Native agricultural products to other colonies regions. Americans and were less likely to own and slaves. to countries in Europe. The farmers in this colonial region purchased slaves to do the hard This colonial region had one dominant The religion economy that in most this colonial people practiced. region work also Colonists was of farming, diverse. followed including Farms in during this region the hot grew summer. different kinds of strict religious rules, and they were intolerant crops, and of businesses other religions. based there Life in turned this region raw materials centered on into finished products. Big cities in this the church, and there were severe punishments colonial region for were those places who failed where to trade attend occurred church or between who the colonies and countries across spoke out against the church. Singing the and ocean. celebrating Many craftsmen holidays were lived not in these allowed large in this cities colonial and grew wealthy by making high-quality region. products to sell. The economy in this region centered on the ocean and forests. People in this region made a lot of money selling food from the ocean and building vessels to transport goods across the ocean. The colonists cut trees and used the wood for construction or sold the wood to other countries. The colonists also hunted animals in the forests and sold their skins to make money. Colony Characteristic Cards (54 per set) William Bradford Pocahontas Thomas Hooker Ann Hutchinson Catholics City Upon a Hill Corn Dutch and German Immigrants Fertile Soil 55
12 Colonial Regions Map NEW ENGLAND COLONIES Claimed by NH and NY Massachusetts MIDDLE COLONIES New York CT Rhode Island Pennsylvania MD NJ Delaware SOUTHERN COLONIES Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia ATLANTIC OCEAN The Colonial Regions 56
13 Colonial America Lesson 9 Colonial Regions Map KEY (on Materials CD) Words with an asterisk (*) may appear in more than one category. New England Colonies Ann Hutchinson* City Upon a Hill Fishing Forests Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Great Awakening Guns John Winthrop Jonathan Edwards King George III* Loyal to British King* Lumber Mayflower Compact Mercantilism* Native Americans* Pilgrims Ports* Puritans Religious dissenter* Representative government* Rocky soil Shipbuilding Small farms Snowy winters Thomas Hooker Trapping William Bradford Middle Colonies Ann Hutchinson* Catholics Fertile soil* German and Dutch immigrants Gristmills King George III* Larger farms Livestock Loyal to British king* Mercantilism* Mild climate Native Americans* Ports* Quakers Religious dissenter* Religious tolerance Representative government* Rice* Rivers and streams Roger Williams Wheat* William Penn Southern Colonies Corn Fertile soil* House of Burgesses Indigo John Rolfe King George III* Lord Baltimore Loyal to British King* Mercantilism* Native Americans* Plantation Pocahontas Representative government* Rice* Rich plantation owners Sir Walter Raleigh Slaves Tobacco Warm climate Wheat* 57
14 Narrow Your Choices Sheet (on Materials CD) TBL Knowledge Application Narrow Your Choices Colonial America Road to Revolution Lesson 2 My team s chosen colonial region is the. #1 #2 is/are the most important part of life in our region because: is/are also an especially important part of life in our region because: In our group s opinion, Finally, #3 #4 is/are also an important part of life in our region because: is/are also an important part of life in our region because: 58
15 Colonial America Lesson 9 Narrow Your Choices AMERICA Sheet (Optional; on Materials CD) TBL Knowledge Application Narrow Your Choices AMERICA Colonial America Road to Revolution Lesson 2 #1 #2 is/are the most important part of life in America because: is/are also an especially important part of life in America because: In our group s opinion, Finally, #3 #4 is/are also an important part of life in America because: is/are also an important part of life in America because: 59
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies
 The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
Chapter 4-1 Notes. The Economy of the Colonies
 Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Chapter 4-1 Notes The Economy of the Colonies 1. What do most colonists do to make a living? FARMING! Most colonists left Europe for the opportunity to have their own farm Plenty of land in American If
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
13 Colonies and Regions
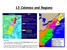 1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
1 13 Colonies and Regions Directions: 1. Use these maps to complete your 13 Colonies Map handout and to help you prepare for the upcoming quiz. 2. Read and use the documents below to help you complete
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
13 Colonies New England Colonies
 13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
13 Colonies New England Colonies Massachusetts --people who wanted religious freedom from King George and his Anglican church --Puritans Protestants --Separatists Set up their own church (Pilgrims) --1620
Number of Indentured Servants in Virginia ,456 4,122 1,
 PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
PART I 1. New England was settled by. A. German-speaking immigrants seeking economic opportunity B. Puritans seeking economic opportunity C. Dutch seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe D.
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
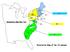 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Settled by the English and Puritans Reason for the settlement --- to escape religious persecution Established in 1620 The economy consisted of small
Unit 8. The English Establish 13 Colonies
 Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
MIDDLE COLONIES GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES. MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) IMPORTANT DEMOCRATIC PRINCIPALS ESTABLISHED HERE
 NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
NEW ENGLAND MIDDLE SOUTHERN NAMES OF GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES INDUSTRIES SETTLEMENT PATTERNS (How does it look from the sky?) MAIN LABOR FORCES (Who is doing the work?) RELIGION NATIONALITIES THAT SETTLED HERE
The 13 Colonies. Religious, Political and Economic Foundations
 The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
The 13 Colonies Religious, Political and Economic Foundations Objectives TLW explain how religion played a role in the founding of the 13 colonies TLW compare religious freedom and tolerance in different
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages
 Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
Thirteen Colonies Comprehension Passages New England Colonies The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. Massachusetts Bay was founded in 1630
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
The Thirteen Colonies
 The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies The Thirteen Colonies Geographic Regions The Colonies Economies Climate Natural Resources Population Religion Three Geographic Regions The New England Colonies The Middle Colonies
John Smith The Starving Time
 The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
The Colonies Southern Colonies Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in North America. A lack of preparation cost a lot of the colonist their lives. Most men who came to James town were adventurers
Early British Colonies
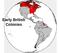 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Presenting... The 13 Colonies
 Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Presenting... The 13 Colonies Featuring... the New England Colonies Massachusetts Founded as two colonies Plymouth colony founded in 1620 by pilgrims Massachusetts Bay colony founded in 1630 by Puritans
Wealth and resources. ! New beginning. ! Get out of debt. ! Escape political & religious persecution
 Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date
 Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
Binder Page B Name Period Review of Colonies- Spain, French, Dutch & English Date New Spain 1. What year did Columbus sail to the New World? What was he trying to do? 2. Define conquistador 3. Why was
The Middle Colonies. If YOU were there. How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? SECTION. What You Will Learn
 The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
The Middle Colonies SECTION 3 If YOU were there How would you feel about moving to a country full of strangers? The middle section of the Atlantic coast offered good land and a moderate climate. Several
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape Chapter 6 The British Colonies Take Shape A NEW ENGLAND SHIPBUILDING TOWN New England Life There were considerable
Colonial Jeopardy. Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100. Puritans 200 Quakers 200 Native Americans 200
 Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Colonial Jeopardy Jamestown Pilgrims & Puritans Quakers Native American Conflicts Middle Colonies Pot Luck Jamestown 100 Puritans 100 Quakers 100 Native Americans 100 Middle Colonies 100 Pot Luck 100 Jamestown
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies
 Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
Unit 3 Lesson 3: The Development of the Southern Colonies 1 Jamestown Review 1. About what year was it founded? 2. Who founded it? 3. Why was it founded? 4. Where was it located? 5. What were two problems
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
New England Colonies Economy
 New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
New England Colonies Economy Subsistence farming/living. New England farmers often depended on their children for labor. Everyone in the family worked spinning yarn, milking cows, fencing fields, and sowing
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon Lord Baltimore
 Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Terms and People Nathaniel Bacon the leader of the frontier settlers who fought Bacon s Rebellion, an attack against Native Americans who were trying to defend their land from colonists Lord Baltimore
Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution
 S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
S- ACTUAL AND ALTERNATE HISTORIES Colonial America from Settlement to the Revolution Rodney P. Carlisle and J. Geoffrey Golson, Editors ABC CLIO Santa Barbara, California Denver, Colorado Oxford, England
~VANIA ..- ~ ~ ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2. Land Use. Religion in the Middle Colonies, I 775
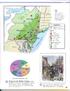 ~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
~=====================================================-"""""""" Un;t2 ~ ~ New France (Fr. ) Lake..- Wheat farm ers sold large amounts of grain to people in the cities. Which two port cities in the Middle
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d. Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary
 The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
The Virginia Colony: Growth & Changes SOL VS 4a 4d Jennifer Amores-Kalich / Sugarland Elementary Vocabulary pre-view and Review Agriculture - the business of farming, includes raising animals and growing
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary
 Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
Below are summaries of the THREE colonial regions Read & Answer the Questions in your notes! New England: A Summary New England was a rough region to settle. Consisting of Massachusetts (1620), Connecticut
The Southern Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 4
 The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
The Southern Colonies Chapter 3, Section 4 Factors that influenced the development of the Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were Southern Colonies. Factors
Monday, September 11
 th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
th Monday, September 11 Warm Up! Explain why Georgia was considered a buffer colony? YOU NEED YOUR TEXTBOOK! LEARNING INTENTION: Life in the Colonies SUCCESS CRITERIA: qi can compare the different colonial
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
The 13 English Colonies
 The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
The 13 English Colonies Name: Class: Today, you live in the United States of America which is a country located on the continent of North America. The people who first lived in what is today the United
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root ( )
 Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Section 3 The Middle Colonies IN Academic Standards: 8.1.2, 8.3.1, 8.3.2, 8.3.3, 8.3.6 Key Terms and People Proprietary Colony Royal Colony William Penn Backcountry 1. What was the geography and climate
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
U.S. History Project
 U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
U.S. History Project U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 U.S. History Project Chapter 3, Section 1: Objectives 3& 4 By: Yasmeen E, Stephen C, and Danielle P. U.S. History Project
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
Necessary Components
 Mercantilism Introduction Dominated European thought promoted economic regulation by governments Increase power of state at the expense of other nations Favorable climate for the growth of capitalism Objectives
Mercantilism Introduction Dominated European thought promoted economic regulation by governments Increase power of state at the expense of other nations Favorable climate for the growth of capitalism Objectives
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter
 Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
Peleg Folger New England Whale Hunter Tyrant-a harsh ruler, like King George III of England Backcountry-neighbored the colonies on the west and ran along the Appalachian Mountains Fall Line- the place
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION VOL. 1 Stamp Act No one likes being told what to do. The British tried to control the American colonists. It did not go well. First, they tried to make the colonists pay special taxes.
Settling Virginia VS. 4
 WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
WHAT IS AGRICULTURE? Settling Virginia VS. 4 Farming: It includes growing crops and/or raising livestock. growing crops raising animals The economy of colonial Virginia was based on agriculture. Most Virginians
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #3 Peter Allen Econ120 1 Formative Years of Colonial Economies Agriculture, dominant activity Land, resources plentiful Labor, capital scarce
English Establish 13 Colonies Unit 2 Answers Elosuk
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with english establish 13
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Unit 4: Colonies. https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html. https://quizlet.com/class/ / Colonial America 1
 Unit 4: Colonies https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ Colonial America 1 Colonization of America As the European explorers claimed the vast lands of North
Unit 4: Colonies https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/colonial-america.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ Colonial America 1 Colonization of America As the European explorers claimed the vast lands of North
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
learning about cocoa farmers
 A LESSON FOR THE CLASSROOM Adapted from a lesson by Global Connections. learning about cocoa farmers MATERIALS NEEDED Cocoa beans (if available), an Equal Exchange chocolate bar, a lot of scrap paper,
A LESSON FOR THE CLASSROOM Adapted from a lesson by Global Connections. learning about cocoa farmers MATERIALS NEEDED Cocoa beans (if available), an Equal Exchange chocolate bar, a lot of scrap paper,
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy Today you re going to explore the economics of the colonies. 1 5-U2.1.1: Describe significant developments in the southern colonies, including development
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD ( )
 Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Plantations in the Americas THE EARLY MODERN WORLD (1450 1750) Shortly after 1600 Europeans were beginning to prosper from growing tobacco in the West Indies. This product became very popular and some
Commerce and Religion
 1 New England: Commerce and Religion TERMS & NAMES Backcountry subsistence farming triangular trade Navigation Acts smuggling MAIN IDEA Fishing and trade contributed to the growth and prosperity of the
1 New England: Commerce and Religion TERMS & NAMES Backcountry subsistence farming triangular trade Navigation Acts smuggling MAIN IDEA Fishing and trade contributed to the growth and prosperity of the
Tea and Wars. Summary. Contents. Rob Waring. Level 3-8. Before Reading Think Ahead During Reading Comprehension... 5
 Level 3-8 Tea and Wars Rob Waring Summary This book is about wars that were caused by the import and export of tea by the British. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During Reading
Level 3-8 Tea and Wars Rob Waring Summary This book is about wars that were caused by the import and export of tea by the British. Contents Before Reading Think Ahead... 2 Vocabulary... 3 During Reading
A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers
 A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
A Very Messy Tea Party A Very Messy Tea Party W.M. Akers If you know anything about English people, you probably know that many of them love tea. Ever since tea was first imported to Great Britain from
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Black Gold: The Movie Mini-Debates
 1. Black Gold is a recent British documentary film about the international coffee industry. It exposes a situation in which small coffee farmers in developing countries receive very little for their back-breaking
1. Black Gold is a recent British documentary film about the international coffee industry. It exposes a situation in which small coffee farmers in developing countries receive very little for their back-breaking
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Two: Transplantations and Borderlands
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Transplantations and Borderlands The Early Chesapeake The Founding of Jamestown Jamestown Settlement with Ships (S. Solum/ PhotoLink/ Getty Images ) Early Problems
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Roanoke 9/21/2017. The First English Colonies in North America. Roanoke & Jamestown. Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585
 The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
The First English Colonies in North America Roanoke & Roanoke Established by Sir Walter Raleigh in North Carolina in 1585 Newcomers are more interested in looking for gold than fishing or growing food
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 2 : Life in the Middle Colonies SMALL GROUP ACTIVITY: The Middle Colonies What do we already know? Histo ry Geog raph y Civic s/ Gove rnme nt Econ omic s Cultu re SMALL GROUP
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Thomas Jefferson and the West.
 Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
Traveling Off the Map: The Lewis and Clark Expedition Chapter One Thomas Jefferson and the West. Questions this chapter will answer:. How would the West make the United States stronger and safer? How would
I want YOU to have a great summer and so does Uncle Sam:
 Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Summer Work for APUSH Overview: This is work that is to be completed before the first day of school. The AP US History course has a lot of ground to cover in order to prepare for the May exam. It is meant
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania
 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Thirteen Colonies Pennsylvania The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group
Assessment: China Develops a New Economy
 Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
Name Date Mastering the Content Assessment: China Develops a New Economy Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. What caused Chinese farmers to move from northern to southern China during the Tang
JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT
 JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT 1. Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? for wealth and power 2. What did the English think they would find in America? silver and
JAMESTOWN THE FIRST PERMANENT ENGLISH SETTLEMENT 1. Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? for wealth and power 2. What did the English think they would find in America? silver and
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism. Key Concept 2.2.I C&D
 Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
Salutary Neglect and Mercantilism Key Concept 2.2.I C&D Key Concept Thesis 2.2.I.C The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical,
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #53 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the causes of the Boston Tea Party DO NOW 1. Which taxes were levied, or raised by
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
EVIDENCE SCAVENGER HUNT
 NAME: DATE: EVIDENCE SCAVENGER HUNT Directions: Students will race to find textual evidence and analyze how the text supports their claim. Each team will receive: 1 point for completing each round 2 points
NAME: DATE: EVIDENCE SCAVENGER HUNT Directions: Students will race to find textual evidence and analyze how the text supports their claim. Each team will receive: 1 point for completing each round 2 points
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
The First English Settlements in America
 The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
The First English Settlements in America Roanoke The Lost Colony Atlantic Coast circa 1584 Outer Banks (Virginia / N. Carolina Border) Roanoke: Then and Now Roanoke Timeline 1584 The Queen sends scouts
Chapter 16: The First Global Age ( ) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in
 Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
Chapter 16: The First Global Age (1492-1750) First Encounters: Columbus landed in the islands that are now called the West Indies Tainos lived in villages and grew corn, yams, and cotton, which they wove
APWH chapter 18.notebook January 11, 2013
 Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Chapter 18 Plantation Agriculture in the Colonial Americas The first cash crop in the Caribbean was tobacco. By the 17th century, the Lesser Antilles were under Dutch, English, and French rule, and their
Factors Leading to The American Revolution. Part III
 Factors Leading to The American Revolution Part III BELLWORK How is the push and pull of the relationship between Parliament and the colonies establishing colonial independence rather that loyalty to England?
Factors Leading to The American Revolution Part III BELLWORK How is the push and pull of the relationship between Parliament and the colonies establishing colonial independence rather that loyalty to England?
WARM UP. 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday
 WARM UP 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday 2 Today you should do KEY EVENTS, TIME/DATE/ LOCATION, KEY EFFECTS (WHY) What are Push-Pull Factors? I. Push II.
WARM UP 1 With the people around you con2nue working on the episode map from yesterday 2 Today you should do KEY EVENTS, TIME/DATE/ LOCATION, KEY EFFECTS (WHY) What are Push-Pull Factors? I. Push II.
Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES
 Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES Objectives: o We will examine the colonial economies of the various colonies by their geographic region. o We will examine the technology that the various colonists developed.
Chapter 3: THE COLONIAL ECONOMIES Objectives: o We will examine the colonial economies of the various colonies by their geographic region. o We will examine the technology that the various colonists developed.
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Grade 3-5. Pam Olivieri - Curriculum Designer
 Grade 3-5 Pam Olivieri - Curriculum Designer 1 Columbian Exchange and European Settlement Vocabulary colonies migrate compelled missionaries cash crops Viceroy fertile Royal Colony Proprietary Colony alliances
Grade 3-5 Pam Olivieri - Curriculum Designer 1 Columbian Exchange and European Settlement Vocabulary colonies migrate compelled missionaries cash crops Viceroy fertile Royal Colony Proprietary Colony alliances
Which of these two causes do you think seems like the most convincing? Defend Thyself!
 What Worked Well? The Roanoke colony nor the initial attempt at the Jamestown colony were successful. We are going to examine what worked well for the two colonies, and what did not work well. WORKED WELL
What Worked Well? The Roanoke colony nor the initial attempt at the Jamestown colony were successful. We are going to examine what worked well for the two colonies, and what did not work well. WORKED WELL
Unit 4: Colonial Life. Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy
 Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy g a t i o n A c t s The Colonies Raw Materials Manufactured Goods Every society has RESOURCES. NATURAL RESOURCES HUMAN RESOURCES CAPITAL RESOURCES which
Unit 4: Colonial Life Lesson 7: The Colonial Economy g a t i o n A c t s The Colonies Raw Materials Manufactured Goods Every society has RESOURCES. NATURAL RESOURCES HUMAN RESOURCES CAPITAL RESOURCES which
