United States History. Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples
|
|
|
- Isabella Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering, and variations in weapons. Their cultures were established long before European explorers arrived. One of the first to interact with newly arrived English settlers in Plymouth, Massachusetts were the Algonquians. The name now refers to the Algonquianspeaking people from Virginia north to Hudson Bay and west to the Rocky Mountains. The language is known as Anishinaabe or Ojibwe and became the language used for trade around the Great Lakes. The French were heavily involved in the fur trade with them. The Algonquians, in what is now Canada in the Upper St. Lawrence Valley, lived in wigwams and wore clothing made from animal skins. They were proficient hunters, gatherers, and trappers. They mostly lived too far north for agriculture although who lived south developed corn and other crops. Conflicts with the Iroquois had driven them out of the Adirondack Mountains and the upper Hudson Valley. Squanto, an Algonquian who had been taken captive and sent to England, returned and shared his knowledge of agriculture with the English settlers, including how to plant and cultivate corn, pumpkins, and squash. Other famous Algonquians included Pocahontas and her father, Powhatan, both of whom are immortalized in English literature, and Tecumseh and Black Hawk, known foremost for their fierce fighting ability. The French, Dutch, and British supplied the Algonquian with firearms. Algonquins contributed wampum (made into belts to keep records) to the Native American culture, and they celebrated the first harvest with the Pilgrims, creating the first Thanksgiving.
2 Another group of tribes who lived in the Northeast were the Iroquois, who were fierce fighters and forward thinkers. They lived in longhouses and wore clothes made of buckskin. They, too, were expert farmers, growing the Three Sisters (corn, squash, and beans). Five of the Iroquois tribes formed a Confederacy which was a shared form of government. The False Face Society was composed of a group of medicine men who shared their medical knowledge with others but kept their identities secret while doing so. Their wooden masks are an enduring symbol of the Native American era. Living in the Southeast were the Seminoles and Creeks, a huge collection of people who lived in chickees (open, bark-covered houses) and wore clothes made from plant fibers. They were expert planters and hunters and were proficient at paddling dugout canoes, which they made. The bead necklaces they created were some of the most beautiful on the continent. They are best known, however, for their struggle against Spanish and English settlers, especially led by the great Osceola. The Cherokee also lived in the Southeast. One of the most advanced tribes, they lived in domed houses and wore deerskin and rabbit fur. Accomplished hunters, farmers, and fishermen, the Cherokee were known for their intricate and beautiful basketry and clay pottery. They also played a game called lacrosse, which survives to this day in countries around the world. After the Indian Removal Act was passed by Congress in 1830, the ultimate consequence was the Trail of Tears as the Cherokee were forced to march a thousand miles to Oklahoma Territory.
3 Between the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains, on the Great Plains lived the Plains tribes, including the Sioux, Cheyenne, Blackfeet, Comanche, and Pawnee. When traveling, they lived in east-facing teepees made of buffalo hides, but in their villages near the streams, their homes were earth lodges. Clothing was made from buffalo skins and deerskin. They hunted for elk, deer, and especially the buffalo. They were well known for many ceremonies including the Sun Dance, and for war pipes and peace pipes. Famous Plains people include Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull, authors of the Little Bighorn and the defeat of Custer; Sacagawea, guide for the Lewis and Clark expedition. Dotting the deserts of the Southwest were (and still are) a handful of tribes, including the Acoma, Hopi, Zuni, and Taos, all of whom are Pueblo. Their homes were made of stone or adobe. Clothing was woven from wool and cotton. Agriculture included growing beans and domesticating turkeys and, over time, other livestock. Kachina dolls are still given to children; the Kachina are spirits that bring rain and social good. In 1680 a Pueblo revolt drove the Spanish out of their territories, but the Spanish re-conquered them several years later, and Mexican domination lasted until the close of the Mexican War, when the U.S. took over--and then created reservations. Pueblos are perhaps best known for the challenging vista-based villages constructed from the sheer faces of cliffs and rocks and for their adobes, mud-brick buildings that housed (and continue to house) living and meeting quarters. Another well-known southwestern tribe was the Apache, with their famous leader Geronimo. The Apache lived in homes called wickiups, which were made of bark, grass, and branches. They wore cotton clothing and were excellent hunters and gatherers. Adept at basketry, the Apache believed that everything in Nature had special powers and that they were honored just to be part of it all. The Navajo, also residents of the Southwest, lived (and continue to live) in hogans (round homes built with forked sticks) and wore clothes of rabbit skins. Their major contribution to the overall culture of the continent was in sand painting, weapon-making, silver-smithing, and weaving. Some of the most beautiful woven rugs ever were and continue to be--crafted by Navajo hands.
4 The Northwest Coastal tribes lived in what is now Alaska, down the coast of the Pacific Ocean to Northern California. They lived in rectangular houses constructed of cedar planks, which would be home to 30 or more people. Clothing included rain capes made from cedar. Totem poles were a mode of communication. Chief Joseph, the famous Nez Perce leader, tried to lead his people to Canada when they d been ordered to a reservation, and he is famous for his moving speech of surrender when the still-living among his people were trapped by the U.S. Army. Alaska and Arctic Canada continue to be populated by the Inuit. Oftentimes, their homes were tents made from animal skins or igloos. Clothes were made of animal skins, usually seals or caribou. They were excellent fishermen and hunters, they crafted efficient kayaks and umiaks to take them through waterways, and they crafted harpoons with which to hunt animals. Inuit art includes carvings from stone, whalebone, and walrus tusk, a craft extended from the creation of tools, weapons, and utensils. Skill 1.1b European exploration and colonization The Age of Exploration had its beginnings centuries before exploration actually took place. However, it is defined as beginning in the early fifteenth century and continuing into the seventeenth century. It is also known as the Age of Discovery, and it refers to European world exploration, derived from technologies for navigation, mapmaking, and advanced shipbuilding. Prior to this period, the rise and spread of Islam in the seventh century and its subsequent control over Jerusalem led to Pope Urban II deciding upon the First Crusade in 1095 CE. The First Crusade resulted in Christian control of Jerusalem and other areas in the region for about two hundred years the first western control of the region since the fall of the Roman Empire. The First Crusade marks the first organized violence against Jews. The Crusaders believed that Jews and Muslims ideally would be converted to Christianity. The Crusades, as they continued, were a political extension of Christendom. The Byzantium Empire declined, and Italy s city-states of Florence, Genoa, and Venice became wealthy from trade with Asia spices, salt, and other luxurious items. Merchant-bankers became a new rising social group who encouraged learning. A result of the decline of the Byzantium Empire was the immigration of merchants, scholars, and priests to western Europe along with a good many of the Byzantium artistic and literary treasures. One consequence was intellectual stimulation that led to the Renaissance which began in Italy about 1300 CE.
5 During the ninth century to the twelfth century CE, Venice was the naval and commercial power of Europe. By the late 1200s, Venice was the most prosperous city in Europe, and it held the most valuable trade with the Muslim world. The Genoese Vivaldo brothers and the Venetian Marco Polo wrote about their travels and experiences in the East. Survivors of the Crusades had made their way home from the Middle East bringing with them fascinating information about exotic lands, people, and customs, and desired foods and goods such as spices and silks. Between sea voyages on the Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea and the camel caravans in central Asia and the Arabian Desert, the trade was controlled by the Italian merchants in Genoa and Venice. And--the trade routes between Europe and Asia were slow, difficult, dangerous, and very expensive. In the mid-1300s, two-thirds of the nomad Mongol population along the western trade routes came down with the black plague. It spread eastward to China and killed two-thirds of the Chinese population. Merchants from Genoa travelled in 1346 to the Black Sea ports, caught the plague, and brought it home to Europe in Sixty percent of the population of Venice died. Approximately 25 million Europeans from a population of 40 million died. By 1349, one-third of the people of the Islamic world were also dead from the black plague. The Mongol deaths contributed to the fall of the Mongol Empire. The Ottoman Turks, meanwhile, were not as affected by the plague, and so the Ottoman Empire began to grow while in Europe, government, trade, and commerce pretty much came to a stop. While Jews were scapegoated for the plague, the Roman Catholic Church was also tested when people prayed in their churches and made donations, yet still lost their families to the plague. Thousands of priest and monks also died, and it seemed to many people that God was punishing the Church. The literate survivors in Italy began to look backward to classic (and pagan) Rome and Greece, and there became a revival of interest in classical Greek art, architecture, literature, science, astronomy, and medicine. The chaos that resulted from the plague was a contributor to the beginning of the Renaissance. Gutenberg s invention of the printing press in 1440 CE meant that by 1499, fifteen million books with thirty thousand different titles had been published. Among those books was Ptolemy s Geography which Ptolemy had first published in Egypt back in 2 CE. Now with the printing press, in 1477 numerous new maps were included in the book. Maps thus began to reach the populace.
6 Just as Ptolemy had been influenced by Hipparchus of Greece ( BCE) who had invented latitude and longitude, geographers, astronomers and mapmakers of the Renaissance including the astronomer Tycho Brahe of Denmark and the Venetian mapmaker Fra Mauro studied and applied the works of Hipparchus and Ptolemy. For many centuries, maps and charts had stimulated curiosity in the West. At the same time, the Chinese were using the magnetic compass in their ships; Pacific islanders were going from island to island covering thousands of miles in open canoes navigating by sun and stars; and Arab traders were sailing all over the Indian Ocean in their dhows. Now it was time for the Age of Exploration to begin in earnest. By 1415, Prince Henry of Portugal (also called the Navigator) encouraged, supported, and financed the Portuguese seamen who led in the search for an all-water route to Asia. A shipyard was built along with a school for teaching navigation. New types of sailing ships were built which would carry the seamen safely through the ocean waters. Experiments were conducted with newer maps, newer navigational methods, and newer instruments. These included the astrolabe and the compass enabling sailors to determine direction, as well as latitude and longitude for exact location. Although Prince Henry died in 1460, the Portuguese kept on sailing and exploring Africa's west coastline. In 1488, Bartholomew Diaz and his men sailed around Africa's southern tip and headed toward Asia. Diaz wanted to push on but turned back because his men were discouraged and weary from the long months at sea, extremely fearful of the unknown, they refused to travel any further. However, the Portuguese were finally successful ten years later in 1498 when Vasco da Gama and his men, continuing the route of Diaz, rounded Africa's Cape of Good Hope, sailing across the Indian Ocean, reaching India's port of Calicut (Calcutta). Just six years after Christopher Columbus had sailed on his first transatlantic voyage to try to prove his theory that Asia could be reached by sailing west and had reached the New World and an entire hemisphere, da Gama proved Asia could be reached from Europe by sea and began the 450 years of Portuguese colonization in India, Asia, and Africa. Long after Spain had dispatched explorers and her famed conquistadors to gather the wealth for the Spanish monarchs and their coffers, the British were searching valiantly for the "Northwest Passage," a land-sea route across North America and to the open sea that would lead to the wealth of Asia. It wasn't until after the Lewis and Clark Expedition when Captains Meriwether Lewis and William Clark proved conclusively that there simply was no Northwest Passage. It did not exist.
7 However, this did not deter exploration and settlement. Spain, France, and England, along with some participation by the Dutch, led the way in taking Western European civilization to the New World. These three nations had strong monarchial governments and were struggling for dominance and power in Europe. Between its privateers and its defeat of Spain's mighty Armada in 1588, England became the undisputed mistress of the seas. Spain lost its power and influence in Europe, and it was left to France and England to carry on their rivalry. This search for passage to Asia led to eventual British control in Asia in what is now India, Pakistan, Kashmir, Sri Lanka and Myanmar (formerly called Burma), the southern part of Yemen (formerly called Aden), the Malay Peninsula, Singapore, Hong Kong, and Kuwait. Columbus, a Genoan sailing for Spain, is credited with the discovery of America although he never set foot on its soil. Magellan, a Portuguese sailing for Spain, is credited with the first circumnavigation of the earth. Amerigo Vespucci, from Florence and sailing for Spain and Portugal, recognized, unlike Columbus, that he was not in Asia when he came upon Brazil, and the Americas were named after him. Other Spanish explorers made their marks in parts of what are now the United States, Mexico, and Central and South America including Pizarro, Cortez, Ponce de Leon, Balboa, de Soto, and Coronado. For France, claims to various parts of North America were the result of the efforts of such men as Champlain, Cartier, LaSalle, Father Marquette and Joliet. Dutch claims were based on the work of Henry Hudson. John Cabot gave England its stake in North America along with John Hawkins, Sir Francis Drake, and the half-brothers Sir Walter Raleigh and Sir Humphrey Gilbert. Colonists from England, France, Holland, Sweden, and Spain all settled in North America, on lands populated by Native Americans. Spanish colonies were mainly in the south; French colonies, in the extreme north and in the middle of the continent; and the rest of the European colonies, in the northeast and along the Atlantic coast.
8 The colonies were divided generally into three regions: New England, Middle Atlantic, and Southern. The culture of each was distinct and affected attitudes, ideas towards politics, religion, and economic activities. The geography of each region also contributed to its unique characteristics. The New England colonies consisted of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire. The vast majority of the settlers shared similar origins, coming from England and Scotland. Life in these colonies was centered on the towns because town boundaries would be drawn up as soon as some residents arranged to incorporate. The form of government was the town meeting where all adult males met to make the laws, and a board of selectmen had executive authority. The legislative body, the General Court, consisted of an upper and lower house. The meadows where pilgrims first farmed in New England were actually the farms of Native Americans who died of smallpox and measles, introduced by the colonists. In addition to using these meadows, the colonists had to cut down forest and clear the land for farming. Short summers made for short growing seasons. Additionally, the soil was generally not superior for farming, and an average farm had 20 acres, and corn was the leading crop. Fish was a dietary mainstay, and groundfishing became a New England industry. In addition, New Englanders exported furs and lumber, developed granite quarries, and ultimately developed a textile industry. The Middle or Middle Atlantic colonies included New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland. New York and New Jersey were at one time the Dutch colony of New Netherland, and Delaware at one time was named New Sweden.
9 These five colonies, from their beginnings were "melting pots" with settlers from many different nations and backgrounds. The main economic activity was farming with the settlers scattered over the countryside cultivating rather large farms. The Indians did not threaten the colonists as much as in New England. The soil was very fertile, the land was gently rolling, and a milder climate provided a longer growing season. The farms produced a large surplus of food, not only for the colonists themselves but also for export. This colonial region became known as the "breadbasket" of the New World, and the New York and Philadelphia seaports were constantly filled with ships being loaded with dried meat, wheat, flour, corn, beans, butter, and sheep and hogs for the West Indies in particular. At least half of all ships sailed to the Indies to feed the population whose crop in many cases was solely sugar. The sugar was grown to make molasses, which was made into rum in the colonists rum distilleries in Rhode Island and Massachusetts. Other economic activities included shipbuilding, iron mines, and the production of items such as paper, glass, textiles, kettles, pots, pans, wrought iron, stove plates, nails, and wire so that these items did not need to be imported. In all colonies, there was a standard government structure, including a royal governor, a governor s council, and a colonial legislature. The legislative body in Pennsylvania was unicameral, consisting of one house. In the other four colonies, the legislative body had two houses. Unlike the New England colonies, church and government were separate. The Southern colonies were Virginia, North and South Carolina, and Georgia. Virginia was the first permanent successful English colony, and Georgia was the last. The year 1619 was a very important year in the history of Virginia and the United States with three significant events: 1) Sixty women were sent to Virginia to marry and establish families; 2) Twenty Africans, the first of thousands, arrived to be slaves; and 3) Virginia colonists were granted the right to self-government, and they began electing their own representatives to the House of Burgesses, their own legislative body.
10 Skill 1.1c American Revolution The American Revolution, or War for Independence was largely due to economic and political changes. After 1750 when England defeated its Armada, Spain was no longer the most powerful nation in Europe. The remaining rivalry was between Britain and France. They did not know how to co-exist peacefully together. War was their answer. For nearly 25 years, between 1689 and 1748, these two powers had engaged in a series of armed conflicts. Those conflicts ended up being fought in North America and are known here as French and Indian Wars. The War of the League of Augsburg in Europe, 1689 to 1697, also called King William's War and the Nine Years War, took place mostly in Flanders, but became the first French and Indian War. The War of the Spanish Succession, 1702 to 1713, also called Queen Anne's War, became the second French and Indian War. The War of the Austrian Succession, 1740 to 1748, also called King George's War, was the third French and Indian War. Britain and France fought for possession of colonies--especially in Asia, the Caribbean, and North America--and for control of the seas. But none of these conflicts was decisive. The final conflict, which decided once and for all who was the most powerful, was the fourth French and Indian War. In Europe where it began, it is known as the Seven Years War and in Canada the War of the Conquest. No matter what name is used, this war caused over a million deaths, and in the twentieth century Winston Churchill called it a world war since it took place in Europe, Asia, and North America. The result was the end of France's being a major colonial power in North America--and Great Britain becoming the dominant power in the world. In America, both sides had advantages and disadvantages. The British colonies were well-established and consolidated in a smaller area than the French settlements that were scattered over roughly half of the continent. Yet British colonists outnumbered French colonists 23 to 1. But the French settlements were united under one government and were quick to act and cooperate when necessary while the British colonies had separate, individual governments and seldom cooperated. In Europe, France was the more powerful of the two nations. In addition, the French had many more Indian allies than did the British.
United States History. Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples
 Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
New Ideas, New Nations
 New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
New Ideas, New Nations Why Did Spanish Explorers Want to Find America? The year is 1492 a good year for Queen Isabella. After centuries of struggle, Catholic forces have driven the Muslim invaders from
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
CAUSES OF EXPLORATION. READING and ASSIGNMENT. Read the excerpt below. Use the reading to complete the section of the graphic organizer.
 Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
American Indians. The First Americans
 The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
10/16/14. Age of Exploration. Contact and Conflict
 10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
10/16/14 Age of Exploration Contact and Conflict 1450-1700 2 Guiding Questions How and why did Europeans undertake ambitious voyages of expansion? What was the impact (long term/short term) on colonized
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP
 Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Social Studies 7 Civics Ch 2.2 : Settlement, Culture, and Government of the Colonies PP. 48-53 I. Settling the English Colonies (pp. 48-49) Settling the English Colonies A. Most of the colonists that settled
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
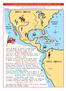 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration
 The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
The Beginning of the Age of Exploration The Impact of the Renaissance on Exploration: Inspired a new sense of adventure & curiosity New scientific advances made expanding exploration possible Increased
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE
 Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
First Permanent English Settlement
 First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
First Permanent English Settlement Name: Section 1 Section 2 STUDY GUIDE SECTION: Why did the English want to establish a colony in America? What did the English think they would find in America? What
Quiz Show. Chapter 2 European Explorers
 Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Spain in North America. 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit
 Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
Spain in North America 1580s: Franciscan Missionaries were working in the Southwest New Mexico became a missionary colony No gold to exploit New France Samuel de Champlain founded Quebec in 1608 to consolidate
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies
 Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
Geographic diversity and the political, economic, social life of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies New England Colonies New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island New England Colonies
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES
 THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
THE FIRST NORTH AMERICAN COLONIES The first Europeans to establish colonies in North America were the Spanish. In 1526 a Spaniard called Lucas Vasquez de Allyon attempted to found a colony in Carolina.
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Hard Times in Virginia Use with pages 156 162. Vocabulary charter a document that permitted colonists to settle on land stock a share in a company cash crop a crop grown for
Native Americans and Early Explorers
 Native Americans and Early Explorers Unit focus topics: 1. Land Bridge Theory 2. Lives of Native Americans in each region of North America Specific Tribes of Interest: Eastern Woodlands Plains Native Americans
Native Americans and Early Explorers Unit focus topics: 1. Land Bridge Theory 2. Lives of Native Americans in each region of North America Specific Tribes of Interest: Eastern Woodlands Plains Native Americans
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
Early British Colonies
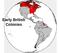 Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Early British Colonies 1607: Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement in North America Funded by Joint-stock companies Joint-stock companies allowed several investors to pool their wealth in support
Wrote book on his explorations that generated excitement in others to develop trade with China and India 1st European who traveled the length of Asia
 AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
followed animals from Asia.
 Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires
 Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
Cortes and Pizarro, Columbian Exchange, and Colonial Empires Arrival of Spanish to Mexico Cortes came in 1519 Claimed land for Spain s king and queen He took 11 ships, 100 sailors, 500 soldiers, cannons,
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
Colonial Vocabulary. Huguenots- French people who settled in New Paltz. Palantines- German settlers that came to America and settled in Newburgh
 Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Colonial Vocabulary colony- place that is settled at a distance from the country that governs (rules) it colonist- a person who lives in a colony Patroon System- the way the Dutch tried to get more people
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
Cultures of North America
 Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018
 Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Welcome back to World History! Thursday, January 18, 2018 Sit with the groups you ve been working with the past few days- be ready to present about your country! You need your notes out and something to
Exploration and Conquest of the New World
 Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Name Date Document Based Question (D.B.Q.) Exploration and Conquest of the New World HISTORICAL BACKGROUND: The first Europeans to explore the United States, Canada, and Latin America were looking for
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Exploration & Colonization. Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School
 Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
Exploration & Colonization Mr. Wilson AP World History Wren High School Motives for European Exploration Desire to gain direct access to Asian luxuries Collapse of Mongols increased price of goods Avoid
MAYANS. The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE.
 MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
UNITED STATES HISTORY
 D O M A I N I UNITED STATES HISTORY Available for purchase at www.xamonline.com eflashcards: a digital representation of a card represented with words, numbers or symbols or any combination of each and
D O M A I N I UNITED STATES HISTORY Available for purchase at www.xamonline.com eflashcards: a digital representation of a card represented with words, numbers or symbols or any combination of each and
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Renaissance Economics. The Age of Discovery
 Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Renaissance Economics The Age of Discovery Commercial Revolution Price Revolution Rising populations demanded more goods = higher prices New sources of gold & silver stimulate inflation Inflation stimulated
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World
 Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
Chapter 4: How and Why Europeans Came to the New World Section 4.3 - Ocean Crossing When sailors cross the ocean, they need a way to stay on course. They have no landmarks to guide them in the open sea.
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
The Age of Exploration During the 1400s European countries competed to find a sea route to the Indies New technology helped make long distance navigation possible Trade Route A path used by a society to
Chapter Two. When Worlds Collide
 Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Chapter Two When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 Part One Introduction When Worlds Collide 1492-1590 How does this drawing illustrate the idea of worlds colliding in the Americas? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples. What Makes a Culture Unique?
 Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
The World of the 1400s. What Was Going On?
 The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas
 The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
The Beginnings of Our Global Age: Europe and the Americas Conquest in the Americas 1492 Columbus meets the Taino in the West Indies He claims their land for Spain; takes several back to Spain Conquistadors
Transplantation and Adaptation Transplantation and Adaptation Video Series: Key Topics in U.S. History
 1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
1 2 3 Transplantation and Adaptation 1600 1685 The French in North America How did the French use Indian alliances to create their North American empire? The Dutch Overseas Empire How significant was New
Interactive Map of the 13 colonies
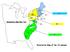 NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
NH NY MA PA NJ Conn RI Interactive Map Part Two VA MD DEL SC GA Interactive Map of the 13 colonies Rhode Island Connecticut Massachusetts New Hampshire New York Founders- Samuel de Champlain, Henry Hudson
The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe.
 I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
I. What led to the Age of Exploration? The Crusades led to a market for Asian goods in Europe. Marco Polo was a 13 th century Italian who travelled through Asia to China. This sparked interest in Asia.
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1
 Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
Europe & the Age of Exploration Part 1 World Review European connections to Asia The writings of Marco Polo had increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
Chapter 1 Worlds Apart
 1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America?
 2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
Bartholomeu Dias. Cape of Good Hope 1487
 Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Bartholomeu Dias Cape of Good Hope 1487 Vasco da Gama India 1498 Pedro Alvares Cabral Brazil Christopher Columbus! Pirates in the Mediterranean! Cut out the middle man in trade! Wealth and riches King
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide. The Colonies Take Root
 Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
Chapter 3 Discussion Guide The Colonies Take Root Section 1: The First English Settlements Why did England want to set up the colonies? What type of government existed in England during the Age of Exploration?
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY ( )
 THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
THE AGE OF DISCOVERY (1350-1750) AGE OF DISCOVERY The writings of Marco Polo increased European interest in trade with Asia. Goods, especially spices and silks, were carried overland through Constantinople
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Unit 8. The English Establish 13 Colonies
 Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
Unit 8 The English Establish 13 Colonies Lesson 8-1: The New England Colonies I can describe the Puritans' plan for Massachusetts Bay colony. I can analyze the Puritans' internal conflict and their problems
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies
 The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
The Settlement of the Original 13 English Colonies Americans: Who are we and how did we get here? From Great Britain (England) to eastern shore of North America Great Britain (England) Who financed the
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
The Middle Colonies. Chapter 3, Section 3
 The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
The Middle Colonies Chapter 3, Section 3 The diverse Middle Colonies develop and thrive. Colonists settled in the Middle Colonies for freedom of religion or to profit from trade, farming, or other occupations.
WARM UP. 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday. 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment
 WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
WARM UP 1 Continue working on the 13 colonies packet from yesterday 2 You will have 30 minutes to complete this assignment 3 If you do not use your time, you will lose your time... I WILL COLLECT THE ASSIGNMENT
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
Wealth and resources. ! New beginning. ! Get out of debt. ! Escape political & religious persecution
 Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Wealth and resources New beginning Get out of debt Escape political & religious persecution Each colony was unique in its characteristics. They are grouped together based on location, reasons they were
Jamestown Colony. First Successful English Colony in the New World
 Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
Jamestown Colony First Successful English Colony in the New World Reasons for English Colonization England wanted to establish an American colony to increase her wealth and power. By finding silver and
