From Mastodon Hunters to.
|
|
|
- Evan Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From Mastodon Hunters to.
2 Mesquakie: Celebrating the Wild Tribes of Iowa
3 From Mastodon Hunters to Mesquakie: Celebrating the Wild Tribes of Iowa Glacial Iowa Paleoindian Cultures in Iowa Archaic Culture Woodland Culture Historic Indians
4 Iowa 25,000 YBP
5 Glacial Iowa There have been four major ice ages in the earth s past million years ago million years ago (minor series) million years ago 2.5 million-10,000 years ago (Pleistocene)
6 Glacial Iowa The warmer period between colder times is called an interglacial. We are in an interglacial period now. Typical interglacial periods last ~12,000 years but can be much longer. Some estimates suggest that our current interglacial period might last 50,000 years or longer.
7 Glacial Iowa What causes ice ages? Atmospheric composition (carbon dioxide, methane) Changes in the earth s orbit (Milankovitch cycles) Milankovitch Location of the continents (continental drift) How often do ice ages come? During mya the period was 41,000 years During the past 800,000 years it has been every 100,000 years Original Milankovitch theory predicts a 41,000 year cycle.
8 Map of Glaciation in Central North America
9 Glacial Iowa What was the Iowa landscape like when the ice receded? Tundra was found along the south edge of the ice front. Taiga was found below the tundra. Savannah habitats would be found at the southern extremes.parkland forests open forests interspersed with grasslands
10 Arctic Tundra
11 Boreal Forest/Taiga
12 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) Who are the first people to arrive in Iowa? Clovis culture is the earliest well defined archeological culture known in North America. Clovis is named after the city in New Mexico where the first projectile point was found. Clovis points have a central groove (flute) along both faces and finely worked edges. The fluted nature of the point allows attachment to the spear and detachment of the point.
13 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) Typical blades are cm long by 4cm in width and are made from chert or obsidian. Clovis sites typically contain lancelolate points and butchering tools. Clovis is a big-game hunting culture that survived on the large, ice age mammals the megafauna.
14 Anzick biface (12.5" long) and Rutz point
15 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) How did the Clovis people get here? Clovis First Theory A wave of Clovis people migrated from Asia across Beringia.the land bridge exposed between modern day Bering Strait/ between Siberia and Alaska. Once Clovis people entered North America they passed through the Ice Free Corridor.a break in the continental ice sheet in western Canada. The Clovis people reached the tip of South America only 1000 years after leaving the Ice Free Corridor in Canada.
16
17 Distribution of Clovis Culture 12,000 ybp
18 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) The Blitzkrieg Hypothesis (Overkill/Wavefront) C. Vance Haynes, Jr. Clovis hunters decimated the megafaunal mammals (some 33 genera; some 70% of the existing big game animals) The Coastal Hypothesis (Pre-Clovis) Knut Fladmark Immigrants used the coastline as refugia and hopped down the coast to North America. When they reach Panama some continued south and others crossed over to the Atlantic side and moved up the Atlantic coast. Some proponents believe people may have been on the continent 30-40,000 ybp!!! A few archeologists have proposed a SE US origin of Clovis peoples based on sites in Florida.
19 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, The Solutrean/Clovis Hypothesis Dennis Stanford and Bruce Bradley/Smithsonian Solutrean flint knapping technology is identical to Clovis The Solutreans lived 22,000-16,500 ybp in northern Spain The Solutreans may have passed by sea around the north Atlantic edge of the glacier to North America.
20 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, Clovis hunters used an atlatal (also spelled atlatl) to throw spears. The atlatal is used as a lever/spring that lengthens the arm of the thrower. The atlatal allows 200 times as much power and 6 times the range of a spear thrown by the bare hand. The atlatal may have been the primary technological development that allowed hunters to kill large megafaunal mammals.
21 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, The earliest archaeological evidence of an atlatal is 25,000 ybp!
22
23 Different types of atlatls
24 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) What were the Clovis people hunting? The megafaunal mammals seem to be the primary food source of Clovis peoples. These animals include: Mastodons, Mammoths Giant Ground Sloths Giant Bison Camels Muskox Giant Beaver Western Horse Many other mammals
25
26 Mammoth Molar Mastodon Molar
27
28
29
30
31
32
33 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) The largest Clovis site in Iowa is the Rummells-Maske site west of Tipton in Cedar County. A plow-disturbed cache of Clovis points was found at this site. The oldest Clovis skeleton found carbon-dated at 10,680 ybp (Anzick site; Wilsall, north of Livingston, Montana; Park County, Montana) Please see The Voices of Bones by Doug Peacock/Outside Magazine and the papers by Dr. Larry Lahren for details.
34 Paleoindian Cultures In Iowa (12, ybp) Folsom Culture followed Clovis culture (11,000-10,000ybp). Folsom projectile points are smaller than Clovis points and indicate a shift in the animals harvested. Folsom culture arose as the glaciers receded about 10,000 ybp.
35 Clovis/Folsom Sites in Iowa
36
37 Archaic Period ( ybp) The Archaic Period is viewed as a transitional stage between cultures relying on big game and cultures with a more rounded forager adaptation. Populations depended on bison in western Iowan and on deer and elk in eastern Iowa. Climate was warming during this period (Atlantic episode or Hypsithermal) and populations gravitated to the wetter river valleys.
38 Archaic Period ( ybp) During the hypsithermal (8,000-4,000 ybp) great masses of silt filled river valleys and many Archaic sites are buried in these alluvial sediments. Toward the end of the Archaic period population densities were increasing as evidenced by the use of communal cemeteries. The end of the dry hypsithermal made many previously unsuitable areas attractive for settlement.
39 Archaic Period ( ybp) Increased exploitation of aquatic resources and nuts is indicated by the presence of bone fishhooks, net weights, nutting stones and other specialized tools for obtaining and processing these foods.
40 Woodland Period ( ybp) Developments during this period include: bow and arrow hunting pottery production plant domestication and cultivation burial mound construction Woodland peoples developed their hunter-gatherer lifestyles using fish and clams in the major rivers and continuing to harvest deer, elk and bison.
41 Woodland Period ( ybp) Woodland farmers domesticated varieties of native plants long before corn or beans became important. Early cultivated plants included gourds, sumpweed, goosefoot, sunflower, knotweed, little barley and maygrass. Woodland communities throughout the Midwest were linked by an extensive trade network referred to by archaeologists as the Hopewell Interaction Sphere.
42 Woodland Period ( ybp) Hopewell culture in Illinois and Ohio spread into Iowa from settlements along the Mississippi River and may have also come into Iowa from a Hopewellian center near Kansas City. Raw materials were traded from wide distances...knife river flint from North Dakota, obsidian from the Yellowstone area, gulf coast marine shells, Great Lakes copper, pipestones from Minnesota, Illinois and Ohio.
43 Woodland Period ( ybp) Corn was introduced around 800 ybp but did not become a staple item until later. Mound building was common in the Woodland Period. The most significant sites in Iowa are the groups of linear, effigy and conical mounds found near Harpers Ferry/Marquette...what is now Effigy Mounds National Monument.
44 Woodland Period ( ybp) The monument is 2,526 acres with 195 mounds of which 31 are effigies. The mounds are sacred burial sites that have been dated from ybp.
45 Effigy Mounds National Monument
46
47
48 Sny Magill Mounds (northern portion)
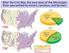
49 Little Bear Effigy Mound
50 Great Bear Mound Group
51 Marching Bear Group
52 Late Prehistoric Period ( ybp) Plains Village Cultures - characterized by a distinct adaptation to the tall grass prairie/short grass prairie ecotone of South Dakota, Nebraska, western Iowa and southern Minnesota. Improved corn varieties, garden surpluses, earthlodge houses, complex social organization were common to these communities.
53 e Late Prehistoric Period ( ybp) Bison meat was common in the diet. Bison hides were used for clothing, robes and coverings for the lodges. Bison bones were modified into a variety of tools such as scapula hoes using in gardening and digging.
54 Late Prehistoric Period ( ybp) Oneota Culture - Oneota culture dominated much of eastern Iowa as well as parts of central and northwestern Iowa. Oneota villages were large. They could be permanent or semipermanent sites. Houses varied from small dwellings to longhouses that could hold many families. The subsistence economy was based on agriculture, fishing, hunting and foraging. Oneota groups are believed to be ancestral to several midwestern tribes (Siouxan language group): Iowa, Oto, Missouri and Winnebago.
55 Historic Tribes What tribes have lived in Iowa? Siouan Speaking (Ioway, Oto, Winnebago/Ho-Chunk, Sioux, Omaha, Ponca) Algonquian Speaking (Mesquakie/Fox, Sauk, Potawatomi,Ojibway/Chippewa, Huron/Wyandot, Ottawa, Miami, Kickapoo, Menominee, Peoria, Moingwena
56 Rankin, 1997 Location of Chiwere/Siouan Tribes
57
58 Historic Tribes Almost all the tribes listed above lived in the lands to the east of Iowa and were displaced by intertribal conflicts and settlement. During the early 17 th century, the Huron were a major supplier of furs to the French. Many tribes were pushed west and sought temporary refuge in Iowa or were displaced permanently.
59 The White Cloud, Head Chief of the Iowas, 1844/45 Mahaska
60 Historic Tribes Who are the Ioway Indians? Ayuhwa is a Dakota name meaning, sleepy ones The Ioway called themselves, Paxoche which translates as, dusty noses or dusty heads. Marquette and Joliet learned of the Ioway from the Peoria in The Ioway were located on the Upper Iowa River at the time of first contact by the French traders (Perrot, 1685)
61 Historic Tribes The Ioway s story is one of almost constant relocation from the time of first contact with white people to the 20 th century. After 1685 the Ioway moved to western Iowa and eventually settled on the Missouri River in NW Iowa. In the 1760s the Ioway moved east and were located in two settlements on the Mississippi River. They settled where the Iowa River and Des Moines River enter the Mississippi. The Ioway were displaced after attack by the Sauk and Fox in 1777 to the Iowaville area on the Des Moines River.
62 Historic Tribes The Sauk, led by Chief Blackhawk, attacked the Ioway again in The Ioway ceded all their original land claims in Minnesota, Iowa and Missouri between 1824 and The Iowa were moved to the Great Nemaha River Reservation in NE Kansas/SE Nebraska
63 Historic Tribes Between a group of 14 Ioway Indians toured Great Britain with the painter, George Catlin. Catlin painted some 300 portraits of 50 different tribes between During the later half of the 19 th century a portion of the Ioway tribe moved to Oklahoma. Today there are two groups of Ioway recognized by the federal government: the Iowa Tribe of Kansas and Nebraska and the Iowa Tribe of Oklahoma.
64 Shauhaunapotinia (Man Who Killed Three Sioux) /Charles Bird King
65 Iowa Indians Who Visited London and Paris, 1861/1869
66 See-non-ty-a, an Iowa Medicine Man, 1844/1845
67 Iowa Lodges
68 Historic Tribes The Mesquakie (Fox) and Sauk The French had first contact with the Mesquakie in The tribe estimated to have 12,000 members at that time. The French called them Renard (Fox) because they met members of the Fox clan of the tribe. The Mesquakie are related linguistically/culturally to other Central Algonquian peoples, the Sauk and the Kickapoo.
69 Historic Tribes Mesquakie Origins Mesquakie oral tradition says the tribe was created by Wisaka, the Elder Brother. Wisaka created the first humans from red earth or clay. The Mesquakie are the Red Earth People. The largest clans are the Bear, Fox, Thunder and Wolf. War chiefs came from the Fox clan and peace chiefs from the Bear clan. Mesquakie tradition suggest they arose along the eastern coast of the continent. The archeological record seems to show they were most recently located around the central Great Lakes in eastern Michigan. The Mesquakie, like the Sauk, Kickapoo, Mascouten and Potawatomi, moved westward during the middle of the 17 th century.
70 Historic Tribes The Mesquakie resided in the Fox River basin in Central Wisconsin by the late 1670s. Between the French attempted to exterminate the Mesquakie because of their loyalty to the British. In 1730 the Mesquakie lost about 1000 men, women, and children as they fled the French and their allies. The Mesquakie and Sauk were forced to flee across the Mississippi into Ioway territory and successfully defended themselves against French attack. In 1737 the French government pardoned the Mesquakie and ended their pursuit. The village of Saukenuk was established in the late 1700s on the Rock River.
71 Historic Tribes Zebulon Pike described three Mesquakie villages in 1805 West Bank of the Mississippi North of the Rock River Rapids Mines of Spain area Confluence of the Turkey River and Mississippi Julien Dubuque was granted a treaty from the Mesquakie for mining lead in 1788 (Mines of Spain). The French ceded the western portion of the upper Mississippi valley to the Spanish in The land was returned back to the French in The Louisiana Purchase in 1803 allowed territorial settlement to proceed. Movement of people into Iowa proceeded quickly.
72 Historic Tribes Pressures from settlement after 1825 forced the Sauk along the Mississippi to leave western Illinois and relocate to southeast Iowa. The exception was Black Hawk s band of Sauk at Rock Island. The Black Hawk War of 1832 resulted in defeat for the Sauk. The government appointed Keokuk as the head chief of the so-called Sauk and Mesquakie nation after Black Hawk s defeat. The tribe was forced to give up 2.5 million hectares of the eastern part of Iowa (the Black Hawk Purchase) Keokuk was granted a small territory along the Iowa River (called the Keokuk Reserve)
73 Historic Tribes The Fox and Sauk remained in Iowa until 1842 when the ceded their lands for a reserve in Kansas just south of present-day Topeka. Some of the Fox left Kansas after selling their herd of horses for Iowa. In 1856 the Iowa Legislature authorized the Mesquakie to purchase 80 acres of land in Iowa near Tama ($12.50/acre; 10X what the Mesquakie were originally given; 2X the actual cost of farmland in Iowa at the time). Today Mesquakie tribal holdings are about 5,000 acres.
74 Autman, 1957 Native American Land Cessions in Iowa
75 Black Hawk /Charles Bird King
76 Keokuk
77 Appanoose
78 Ha Na Wo Wa Ta 1896
Georgia. The Land And Its Early People. and the American Experience Chapter 3: Study Presentation
 Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples? Section 1: How
Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples? Section 1: How
American Indians of the Upper Mississippi River
 American Indians of the Upper Mississippi River National Mississippi River Museum & Aquarium History Education Curriculum Target Grades: Key Words: Subject Areas: Duration: 3 rd - 8 th American Indians,
American Indians of the Upper Mississippi River National Mississippi River Museum & Aquarium History Education Curriculum Target Grades: Key Words: Subject Areas: Duration: 3 rd - 8 th American Indians,
Hunters and Gatherers 8,000 to 500 B.C.
 Archaic Tradition Page 9 Introduction Hunters and Gatherers 8,000 to 500 B.C. The Archaic tradition lasted for a very long time, the longest of any of the periods in Wisconsin. Even though it is the longest
Archaic Tradition Page 9 Introduction Hunters and Gatherers 8,000 to 500 B.C. The Archaic tradition lasted for a very long time, the longest of any of the periods in Wisconsin. Even though it is the longest
The First Americans. Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples. All images found in this PPT were found at Google.
 The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
The First Americans Lesson 1: The Search for Early Peoples All images found in this PPT were found at Google. A. Over the Land 1. During Ages a. long, hard b. skin shelters with fires inside c. summers
Unit 1: Geography of Georgia/Georgia s Beginnings Lesson 3: Prehistoric Peoples Study Presentation
 Georgia Studies Unit 1: Geography of Georgia/Georgia s Beginnings Lesson 3: Prehistoric Peoples Study Presentation Lesson 3: Prehistoric Peoples ESSENTIAL QUESTION What were the major characteristics and
Georgia Studies Unit 1: Geography of Georgia/Georgia s Beginnings Lesson 3: Prehistoric Peoples Study Presentation Lesson 3: Prehistoric Peoples ESSENTIAL QUESTION What were the major characteristics and
Student Reading 5.2: Defining Ohio s Ancient People: Paleoindian & Archaic
 Student Reading 5.2: Defining Ohio s Ancient People: Paleoindian & Archaic Paleoindian Period 13000 B.C.E. to 7000 B.C.E. Paleoindians are believed to be the first people in the Americas. They hunted large
Student Reading 5.2: Defining Ohio s Ancient People: Paleoindian & Archaic Paleoindian Period 13000 B.C.E. to 7000 B.C.E. Paleoindians are believed to be the first people in the Americas. They hunted large
7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures
 Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures Objective: I will be able to describe the growth of Native American cultures (Paleo, Archaic, Woodland, and Mississippian) prior to European contact. B.C.-A.D. or B.C.E.-C.E.?????
Georgia s Prehistoric Cultures Objective: I will be able to describe the growth of Native American cultures (Paleo, Archaic, Woodland, and Mississippian) prior to European contact. B.C.-A.D. or B.C.E.-C.E.?????
11/13/11$ The$First$Americans$ March$1,$2010$ The$world$right$about$now$ ICE$ More$ICE$
 The$First$Americans$ March$1,$2010$ The$world$right$about$now$ ICE$ More$ICE$ 1$ RUSSIA% Land$Bridge$Pic$ ALASKA% BERINGIA% Land$Bridge$Hypothesis$ H/G s$follow$migraing$ animals$(woolly$ mammoth?)$across$land$
The$First$Americans$ March$1,$2010$ The$world$right$about$now$ ICE$ More$ICE$ 1$ RUSSIA% Land$Bridge$Pic$ ALASKA% BERINGIA% Land$Bridge$Hypothesis$ H/G s$follow$migraing$ animals$(woolly$ mammoth?)$across$land$
Cultures of North America
 Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area
 Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area The Mound Builders The Mound Builders is a term used to describe First Nation's cultures that built earthen burial mounds and other earthworks
Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area The Mound Builders The Mound Builders is a term used to describe First Nation's cultures that built earthen burial mounds and other earthworks
Hunters, Gatherers, Fishers and Gardeners Southern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1200 A.D. Northern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1700 A.D.
 Woodland Tradition Page 19 Introduction Hunters, Gatherers, Fishers and Gardeners Southern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1200 A.D. Northern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1700 A.D. The Woodland tradition begins about
Woodland Tradition Page 19 Introduction Hunters, Gatherers, Fishers and Gardeners Southern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1200 A.D. Northern Wisconsin: 500 B.C. to 1700 A.D. The Woodland tradition begins about
Chapter 2 Section 1. Paleolithic Age
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
Chapter 2 Section 1 Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Age - second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC Stone Age
First Humans of Utah NOTES #1
 First Humans of Utah NOTES #1 History History is the study of the past. It deals with written records or accounts. PREHISTORIC: Term used referring to people who lived before white explorers and missionaries
First Humans of Utah NOTES #1 History History is the study of the past. It deals with written records or accounts. PREHISTORIC: Term used referring to people who lived before white explorers and missionaries
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
PREHISTORIC SETTLEMENT
 PREHISTORIC SETTLEMENT CHAPTER 2 This chapter provides an overview of prehistoric settlement in the Highland Creek watershed. Included is information about the aboriginal groups that once inhabited the
PREHISTORIC SETTLEMENT CHAPTER 2 This chapter provides an overview of prehistoric settlement in the Highland Creek watershed. Included is information about the aboriginal groups that once inhabited the
American Indians. The First Americans
 The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The first Coloradoans
 The first Coloradoans Prehistoric Indians Paleo Indians Clovis Period Folsom Period Plano Period Pueblo Farmers Overview Prehistoric Indians Indians that lived on the land before written history existed
The first Coloradoans Prehistoric Indians Paleo Indians Clovis Period Folsom Period Plano Period Pueblo Farmers Overview Prehistoric Indians Indians that lived on the land before written history existed
Graphic Organizer. Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter.
 Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Graphic Organizer THE LAND BRIDGE THEORY Early people depended on Ice Age animals for food, clothing and shelter. After a climate change, early people followed Ice Age animals over a Land Bridge into North
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago
 The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
The Stone Ages and Early Cultures 5,000,000 years ago 5,000 years ago Section 1 P. 28-34 Prehistory - the time before writing Archaeologists & anthropologists do the research Hominids - early ancestors
162 Chapter 8: Native Peoples and Explorers
 As you read, look for how archaeologists learn about early cultures, the four early Native American cultures, terms: artifacts, archaeology, culture, nomad, horticulture, palisade. Human beings have lived
As you read, look for how archaeologists learn about early cultures, the four early Native American cultures, terms: artifacts, archaeology, culture, nomad, horticulture, palisade. Human beings have lived
Georgia and the American Experience. Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People
 Slide 1 Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Slide 2 Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples?
Slide 1 Georgia and the American Experience Chapter 3: The Land And Its Early People Study Presentation Slide 2 Georgia and the American Experience Section 1: How Did We Learn About the Earliest Peoples?
TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE
 TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE Tool use did not begin with humans, but can be found among even the earliest hominin species. The primary material used for creating tools was stone, which is why the earliest period
TOOLS OF THE STONE AGE Tool use did not begin with humans, but can be found among even the earliest hominin species. The primary material used for creating tools was stone, which is why the earliest period
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell
 World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
World History I SOL WH1.2 Mr. Driskell A. Modern people are called homosapiens, meaning wise man. B. Homo-sapiens first existed in East Africa, several hundred thousand years ago. C. Home-sapiens spread
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos. Ancient Cultures of North America
 Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Ancient Cultures of North America Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders *the
Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Ancient Cultures of North America Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders *the
Introduction. This timeline shows the major traditions defined by archaeologists for Wisconsin.
 Introduction The human story of Wisconsin spans 12,000 years, from the first Native Americans to today's diverse rural and urban populations. Over the past one hundred years, archaeologists have recorded
Introduction The human story of Wisconsin spans 12,000 years, from the first Native Americans to today's diverse rural and urban populations. Over the past one hundred years, archaeologists have recorded
Unit 2: American Indians
 Unit 2: American Indians CLASS WEBSITE: https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/american-indians.html QUIZLET GAMES: https://quizlet.com/join/msfyy94t5 American Indians 1 Early People Learning about Early People
Unit 2: American Indians CLASS WEBSITE: https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/american-indians.html QUIZLET GAMES: https://quizlet.com/join/msfyy94t5 American Indians 1 Early People Learning about Early People
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1
 THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
Article by Grant Keddie, Curator of Archaeology, Royal British Columbia Museum
 The Atlatl Weapon By Grant Keddie, Curator of Archaeology. (1988) The atlatl (pronounced at-ul-at-ul) is a fascinating weapon, used long before the bow and arrow. An atlatl is made of wood or antler, often
The Atlatl Weapon By Grant Keddie, Curator of Archaeology. (1988) The atlatl (pronounced at-ul-at-ul) is a fascinating weapon, used long before the bow and arrow. An atlatl is made of wood or antler, often
Ancient Civilizations of North America. Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos
 Ancient Civilizations of North America Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders
Ancient Civilizations of North America Prof. Ruthie García Vera Historia de Estados Unidos Three groups dominate the oldest period of North American prehistory: The Hohokam The Anasazi The Mound Builders
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies?
 How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
Stone Age & Archaeology. Unit Review
 Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS. What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things?
 WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
WARM-UP: HUNTER- GATHERERS What is a hunter-gatherer? Who hunts? Who gathers? What is hunted? What is gathered? How will you get these things? PALEOLITHIC & NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION Societies Begin HOMOSAPIENS
The Woolly Mammoth. Edward I. Maxwell
 The Woolly Mammoth The Woolly Mammoth Edward I. Maxwell The closest relative of the woolly mammoth is the Asian elephant. The main difference between the two is that the mammoth had an incredible coat
The Woolly Mammoth The Woolly Mammoth Edward I. Maxwell The closest relative of the woolly mammoth is the Asian elephant. The main difference between the two is that the mammoth had an incredible coat
Chapter 2 Early Cultures in Oklahoma
 Chapter 2 Early Cultures in Oklahoma Section 1: Oklahoma s Paleo Indians The earliest people came to North America more than 12,000 years ago, during the Prehistoric Era. The Prehistoric Era (or Prehistory)
Chapter 2 Early Cultures in Oklahoma Section 1: Oklahoma s Paleo Indians The earliest people came to North America more than 12,000 years ago, during the Prehistoric Era. The Prehistoric Era (or Prehistory)
NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age. Making A Connection
 Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Mr. Curzan Roots Of Civ. NAME: DATE: PER: Paleolithic People: The Paleolithic Age Key Terms: Define each term from the readings on the next few pages prehistory - civilization - migrate bands - home territory
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The Louisiana Purchase. Chapter 9, Section 2
 The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
The Louisiana Purchase Chapter 9, Section 2 What was the importance of the purchase and exploration of the Louisiana Territory? The tide of westward settlement speeded up in the years after America s independence.
hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan
 hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan Immigrating to Texas Various theories that historians believed early people came to Texas: 1. Sailed from the Eastern Hemisphere 2. Traveled across the North Atlantic
hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan Immigrating to Texas Various theories that historians believed early people came to Texas: 1. Sailed from the Eastern Hemisphere 2. Traveled across the North Atlantic
followed animals from Asia.
 Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
The Great Bend People - A Prelude to History
 Kansas State University Libraries New Prairie Press Symphony in the Flint Hills Field Journal 2009 Discovering this Place (Marty White, Editor) The Great Bend People - A Prelude to History Follow this
Kansas State University Libraries New Prairie Press Symphony in the Flint Hills Field Journal 2009 Discovering this Place (Marty White, Editor) The Great Bend People - A Prelude to History Follow this
THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS 1. MODERN HUMANS
 THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS Modern Humans The Advent of Behavioral Modernity Advances in Technology Glacial Retreat Cave Art The Settling of Australia Settling the Americas The Peopling of the
THE ORIGIN AND SPREAD OF MODERN HUMANS Modern Humans The Advent of Behavioral Modernity Advances in Technology Glacial Retreat Cave Art The Settling of Australia Settling the Americas The Peopling of the
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples. What Makes a Culture Unique?
 Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
North American Native Americans
 North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
North American Native Americans Introduction While the civilizations of the Maya, Aztec, and Inca were flourishing in Mesoamerica and South America, distinct civilizations were also emerging in North America.
The First Americans. You didn t discover it, we were already here.
 The First Americans You didn t discover it, we were already here. 9/3/2015 Template copyright 2005 www.brainybetty.com 2 Primary and Secondary Sources Primary Source: An original, first hand account created
The First Americans You didn t discover it, we were already here. 9/3/2015 Template copyright 2005 www.brainybetty.com 2 Primary and Secondary Sources Primary Source: An original, first hand account created
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Danger Cave. Much of what we don t about Utah s prehistoric people
 Danger Cave Much of what we don t about Utah s prehistoric people comes from Danger Cave. Danger Cave is in the West Desert near Wendover. Danger Cave Artifacts such as; beetle wings, textiles, leather
Danger Cave Much of what we don t about Utah s prehistoric people comes from Danger Cave. Danger Cave is in the West Desert near Wendover. Danger Cave Artifacts such as; beetle wings, textiles, leather
Archaeology and the Saskatchewan Archaeological Society
 Archaeology and the Saskatchewan Archaeological Society 1 What is Archaeology? Archaeology is the study of the human past using a wide range of scientific methods and techniques Archaeology is not the
Archaeology and the Saskatchewan Archaeological Society 1 What is Archaeology? Archaeology is the study of the human past using a wide range of scientific methods and techniques Archaeology is not the
PLANET OF THE APES. Can you imagine a world like this? Can you imagine a world like this?
 P a l e o l I t h I c P e o p l e s PLANET OF THE APES While humans are the only ones still alive today, there were once many different hominin (formerly called hominid) species living in our world. In
P a l e o l I t h I c P e o p l e s PLANET OF THE APES While humans are the only ones still alive today, there were once many different hominin (formerly called hominid) species living in our world. In
EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins.
 EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins. Avatar Finding similarities in 1492 and 2015 Copy under
EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins. Avatar Finding similarities in 1492 and 2015 Copy under
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America?
 2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
PREHISTORY THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND
 TASK 1: How do you understand the term Prehistory? What does the prefix pre- mean? When does history start then? THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND There are three theories explaining the origins of life
TASK 1: How do you understand the term Prehistory? What does the prefix pre- mean? When does history start then? THE ORIGINS OF LIFE AND HUMANKIND There are three theories explaining the origins of life
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Historical Society SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS kshs.org
 Historical Society 6425 SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS 66615 785-272-8681 kshs.org 2014 Student Journal The Archaeology of Early Agriculture in Kansas Cali Letts Mary J. Adair Virginia A. Wulfkuhle Robert Hoard
Historical Society 6425 SW 6th Avenue Topeka KS 66615 785-272-8681 kshs.org 2014 Student Journal The Archaeology of Early Agriculture in Kansas Cali Letts Mary J. Adair Virginia A. Wulfkuhle Robert Hoard
The First Inhabitants
 The First Inhabitants As you read, look for: the various periods into which scientists divide prehistoric cultures vocabulary terms archaeologist, atlatl, pemmican, culture, ceremonial center This section
The First Inhabitants As you read, look for: the various periods into which scientists divide prehistoric cultures vocabulary terms archaeologist, atlatl, pemmican, culture, ceremonial center This section
People of the Old Stone Age
 1 People of the Old Stone Age Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period Notebook Number 2 Neanderthal People Learned Basic Skills Imagine, if you can, a muscular group of people
1 People of the Old Stone Age Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period Notebook Number 2 Neanderthal People Learned Basic Skills Imagine, if you can, a muscular group of people
Chapter 2: The First People 15,000 B.C A.D.
 Chapter 2: The First People 15,000 B.C.-1800 A.D. Origins of Native Peoples Theories of how Native Americans arrived in Pennsylvania walked from Asia over a land bridge into Alaska land bridge is buried
Chapter 2: The First People 15,000 B.C.-1800 A.D. Origins of Native Peoples Theories of how Native Americans arrived in Pennsylvania walked from Asia over a land bridge into Alaska land bridge is buried
Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac built a fort near Detroit. He invited several tribes to move there.
 The First Fox War The French slowly reopened the fur trade in the west. They built forts in outlying areas. They invited Indians to settle nearby. Indian trappers and hunters were sent out to get furs.
The First Fox War The French slowly reopened the fur trade in the west. They built forts in outlying areas. They invited Indians to settle nearby. Indian trappers and hunters were sent out to get furs.
Do Now. Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper
 Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
Do Now Take notes on the article on a separate sheet of paper Early Humans { Early Humans Historians rely on documents and written records to learn about the past Prehistory is the period before writing
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta
 Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Early People in the Central American Land Bridge Early People in the Central American Land Bridge James Folta People have been living in Central and South America for many, many years now. How did ancient
Early People. The American Indians Chapter 3
 Early People The American Indians Chapter 3 Introduction Utah s History is story of many different kinds of people. The American Indians first arrived in Utah around 12,000 B.C.E., which converts to 14,000
Early People The American Indians Chapter 3 Introduction Utah s History is story of many different kinds of people. The American Indians first arrived in Utah around 12,000 B.C.E., which converts to 14,000
KEY. Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People
 KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
KEY Chapter 2: The Stone Age and Early Cultures Section 1: The First People Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Scientists
Virginia s Indians Unit
 Virginia s Indians Unit VS.2 d-g The student will demonstrate knowledge of the physical geography and native peoples, past and present, early inhabitants of Virginia by: d) locating three American Indian
Virginia s Indians Unit VS.2 d-g The student will demonstrate knowledge of the physical geography and native peoples, past and present, early inhabitants of Virginia by: d) locating three American Indian
ROCKSHELTERS IN THE RED RIVER GORGE
 ROCKSHELTERS IN THE RED RIVER GORGE For nearly 12,000 years, people have lived in the Red River Gorge. This beautiful place has everything they need: food, shelter, other resources, and inspiration. The
ROCKSHELTERS IN THE RED RIVER GORGE For nearly 12,000 years, people have lived in the Red River Gorge. This beautiful place has everything they need: food, shelter, other resources, and inspiration. The
Unit 3. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C.
 Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
Unit 3 Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution 8000 B.C. to 2000 B.C. The Beginning of Humans http://www.becominghuman.org/node/interactivedocumentary The Stone Age Old Stone Age Paleolithic Age 2,500,000
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history
 Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history So how do we form a realistic idea about humans at the Dawn of Time? With information provided by: ARCHEOLOGISTS:
Prehistoric: the time before humans developed written languages to record their history So how do we form a realistic idea about humans at the Dawn of Time? With information provided by: ARCHEOLOGISTS:
MAYANS. The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE.
 MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
Name Class Date. Use the information from pages to complete the following.
 GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in?
 1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in? 4) What development allowed people to settle and quit constantly moving around? REGION OF TEXAS Lived between
1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in? 4) What development allowed people to settle and quit constantly moving around? REGION OF TEXAS Lived between
Chapter 1. The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C.
 Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
Chapter 1 The Peopling of the World, Prehistory 2500 B.C. Time Line 4,000,000 B.C. First hominids appear in Africa. 1,600,000 B.C. Homo erectus appears. 8000 B.C. Neolithic Age begins; first agriculture
Archeology in the Central Plains has a long and sto-
 Historical studies involve a certain type of investigative research poring over newspapers, correspondence, records, journals, and all the other written documents and oral histories that attest to life
Historical studies involve a certain type of investigative research poring over newspapers, correspondence, records, journals, and all the other written documents and oral histories that attest to life
11/13/11$ Week 11. Neanderthals/Humans Early humans
 Week 11 Neanderthals/Humans Early humans 1$ The world right about now ICE More ICE! ICE AGE series of warm and cold periods (8-10 degrees cooler on average)! Lasts from 1.9 million years ago until 10,000
Week 11 Neanderthals/Humans Early humans 1$ The world right about now ICE More ICE! ICE AGE series of warm and cold periods (8-10 degrees cooler on average)! Lasts from 1.9 million years ago until 10,000
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide
 Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Natives & Europeans Collide Study Guide 1. Locate Spain on the Map. 2. Locate France on a Map. 3. Locate England on the Map. England Spain France HINT: Elmo Fell & SPrained his ankle 4. What country did
Section1. common experiences. Anthropologists may also study artifacts and
 Section Preview As you read, look for: how archaeologists and anthropologists learn about ancient peoples, the four prehistoric Indian cultures, where Native American mounds and artifacts have been found
Section Preview As you read, look for: how archaeologists and anthropologists learn about ancient peoples, the four prehistoric Indian cultures, where Native American mounds and artifacts have been found
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880
 After the Civil War, the area west of the Mississippi River was settled by miners, ranchers, and farmers Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880 Mining was the first industry to attract settlers to the West
After the Civil War, the area west of the Mississippi River was settled by miners, ranchers, and farmers Land use in 1860 Land use in 1880 Mining was the first industry to attract settlers to the West
Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade
 Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade 1492 and Beyond In 1492, Christopher Columbus (Spain) lands in the Caribbean (San Salvador) In 1607, Captain John Smith (England) founds
Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade 1492 and Beyond In 1492, Christopher Columbus (Spain) lands in the Caribbean (San Salvador) In 1607, Captain John Smith (England) founds
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Activity 4.1: Eating off the Land
 4 : Eating off the Land The Fur Trade Era: Exploration and Exchange in Wisconsin Teacher Materials Preparation/Organization Students will work with their own copies of Student Pages 1 and 2 for this activity,
4 : Eating off the Land The Fur Trade Era: Exploration and Exchange in Wisconsin Teacher Materials Preparation/Organization Students will work with their own copies of Student Pages 1 and 2 for this activity,
Figure 15 Timeline: 10,000 B.C A.D. 10,000B.C. 8,000B.C. 6,000B.C. 4,000B.C. 2,000B.C. 0 A.D. 2,000
 Section1 Prehistoric Cultures As you read, look for: the role of archaeology in the story of prehistoric cultures, the importance of the Poverty Point site, and vocabulary terms archaeologist, midden,
Section1 Prehistoric Cultures As you read, look for: the role of archaeology in the story of prehistoric cultures, the importance of the Poverty Point site, and vocabulary terms archaeologist, midden,
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
LEQ: From what continent were the first immigrants to North America?
 LEQ: From what continent were the first immigrants to North America? This image shows the seven continents of the world. North America is on the left. This image is courtesy of pinterest. LEQ: From what
LEQ: From what continent were the first immigrants to North America? This image shows the seven continents of the world. North America is on the left. This image is courtesy of pinterest. LEQ: From what
Ancient Cultures of North America. Prof. Ruthie García Vera AP US History
 Ancient Cultures of North America Prof. Ruthie García Vera AP US History Arctic/Subarctic Peoples Inuit living in the arctic region are descendants of a prehistoric hunting society that spread across Canada
Ancient Cultures of North America Prof. Ruthie García Vera AP US History Arctic/Subarctic Peoples Inuit living in the arctic region are descendants of a prehistoric hunting society that spread across Canada
1. Introduction enabled
 1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
1. Introduction Scientists have identified and studied five important groups of hominids. Like the hominids before them, early modern humans hunted and gathered their food. In this chapter, you'll read
Vocabulary Builder. netw rks. A. Content Vocabulary. Early Humans and the Agricultural Revolution
 Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
Vocabulary Builder A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select a vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write a term in each blank Paleolithic nomad technology ice age domesticate Neolithic
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
