UNITED STATES HISTORY PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF NORTH AMERICA
|
|
|
- Samantha Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.1 UNITED STATES HISTORY PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF NORTH AMERICA Skill 1.1a Demonstrate knowledge of North America s location in the world and of the continent s rivers, lakes, and important land features North America consists of Canada; the United States of America; Mexico; the Caribbean island nations of the West Indies including Cuba, Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic; and the "land bridge" of Middle America, including Panama, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Guatemala, and others. At its most northern extreme, Alaska and Canada border the Arctic Ocean. At its most southern extreme, the Isthmus of Panama borders Colombia. The west coast borders the Pacific Ocean, while the east coast borders the Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico, further southeast. The major freshwater bodies are the Great Lakes Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie and Superior which lie between Canada and the United States. The Mississippi River is the longest North American river, extending from the U.S.- Canada border to the Gulf of Mexico, draining the Ohio River from the east and the Missouri River to the west. Other significant rivers are the St. Lawrence, which connects Lake Erie to the Atlantic Ocean, and the Rio Grande, which forms most of the border between Mexico and the United States. The three most significant mountain ranges are the Appalachian Mountains, which extend from the Canadian Maritime Provinces south to Georgia in the United States along the eastern seaboard; the Rocky Mountains, which extend from west-central Canada through the United States to Mexico; and the Sierra Nevada cordillera, which extends from Alaska in the United States, through Canada, through the west coast of the United States, and through Mexico and Mesoamerica to South America.
2 Skill 1.1b Demonstrate knowledge of broad climate patterns and physiographic regions Climate is average weather or daily weather conditions for a specific region or location over a long or extended period of time. Studying the climate of an area includes information gathered on the area's monthly and yearly temperatures and its monthly and yearly amounts of precipitation. In addition, a characteristic of an area's climate is the length of its growing season. Four reasons for the different climate regions on the earth are differences in the following: Latitude, The amount of moisture, Temperatures in land and water, and The earth's land surface. The earth has many different climates. It is most unusual if a country contains just one kind of climate. Regions of climates are divided according to latitudes. 0-23½ are the "low latitudes" 23½ - 66½ are the "middle latitudes" 66½ to the Poles are the "high latitudes" The low latitudes are composed of the rainforest, savanna, and desert climates. The tropical rainforest climate is found in equatorial lowlands and is hot and wet. There is sun, extreme heat and rain every day. Although daily temperatures rarely rise above 90 F, the daily humidity is always high, leaving everything sticky and damp. North and south of the tropical rainforests are the tropical grasslands called "savannas," the "lands of two seasons" a winter dry season and a summer wet season. Further north and south of the tropical grasslands or savannas are the deserts. These areas are the hottest and driest parts of the earth, receiving less than 10 inches of annual rainfall. These areas have extreme temperatures between night and day. After the sun sets, the land cools quickly dropping the temperature as much as 50 F. The middle latitudes contain the Mediterranean, humid-subtropical, humidcontinental, marine, steppe, and desert climates. Lands containing the Mediterranean climate are considered "sunny" lands found in six areas of the world: lands bordering the Mediterranean Sea, a small portion of southwestern Africa, areas in southern and southwestern Australia, a small part of the Ukraine near the Black Sea, central Chile, and Southern California. Summers are hot and dry with mild winters. The growing season usually lasts all year and what little rain the region gets falls during the winter months. What is rather unusual is that the Mediterranean climate is located between 30 and 40 degrees north and south latitude on the western coasts of countries.
3 The humid subtropical climate is found north and south of the tropics and is moist indeed. The areas having this type of climate are found on the eastern side of their continents and include the southeastern coasts of Japan, mainland China, Australia, Africa, South America, and the United States. An interesting feature of their locations is the warm ocean currents. The winds that blow across these currents bring in warm moist air all year round. Because of the long, warm summers and short, mild winters, these regions have a long growing season, which means that different crops can be grown several times a year. All contribute to the productivity of this climate type, which supports more people than any of the other climates. The marine climate is found in Western Europe, the British Isles, the U.S. Pacific Northwest, the western coast of Canada, southern Chile, southern New Zealand and southeastern Australia. A common characteristic of these lands is their proximity to water. The ocean winds are wet and warm bringing a mild, rainy climate to these areas. In the summer, the daily temperatures average at or below 70 degrees Fahrenheit. The temperatures rarely fall below freezing during the winter because of the warming effect of the ocean waters. In northern and central United States, northern China, south central and southeastern Canada, and the western and southeastern parts of the former Soviet Union, the "climate of four seasons" is found. This humid continental climate has spring, summer, fall, and winter. Cold winters, hot summers, and enough rainfall to grow a variety of crops are the major characteristics of this climate. In areas with the humid continental climate, some of the world's best farmlands and important activities such as trading and mining are found. Differences in temperatures throughout the year are determined by the distance a place is inland, away from the coasts. The steppe or prairie climate is located in the interiors of the large continents such as Asia and North America. These dry flatlands are far from ocean breezes and are called prairies or the Great Plains in Canada and the United States and steppes in Asia. Although the summers are similar to the humid continental climate, the big difference is in annual rainfall. In the steppe climate, rainfall is light and uncertain, 10 to 20 inches a year, mainly in spring and summer, is considered normal. Where rain is more plentiful, grass grows; in areas of less rain, the steppes or prairies gradually become deserts. These are found in the Gobi Desert of Asia, central and western Australia, southwestern United States, and in the smaller deserts found in Pakistan, Argentina, and Africa south of the Equator.
4 The two major climates found in the high latitudes are tundra and taiga. The word tundra meaning marshy plain is a Russian word and aptly describes the climatic conditions in the northern areas of Russia, Europe, and Canada. Winters are extremely cold and very long. For most of the year, the ground is frozen but becomes rather mushy during the very short summer months. Surprisingly less snow falls in the area of the tundra than in the eastern part of the United States. However, because of the harshness of the extreme cold, very few people live there and no crops can be raised. Despite having a small human population, many plants and animals are found there. The taiga is the northern forest region and is located south of the tundra. The world's largest forestlands are found here along with vast mineral wealth and fur bearing animals. The climate is so extreme that very few people live here; they are not able to grow crops because of the extremely short growing season. The winter temperatures are colder and the summer temperatures are hotter than those in the tundra because the taiga climate region is farther from the waters of the Arctic Ocean. The taiga is found in the northern parts of Russia, Sweden, Norway, Finland, Canada, and Alaska with most of their lands covered with marshes and swamps. In certain areas of the earth, there exists a type of climate unique to areas with high mountains, usually different from their surroundings. This type of climate is called a "vertical climate" because the temperatures, crops, vegetation, and human activities change and become different as one ascends the different levels of elevation. At the foot of the mountain, one finds a hot and rainy climate and the cultivation of many lowland crops. As one climbs higher, the air becomes cooler, the climate changes sharply, and economic activities change to such endeavors as grazing sheep and growing corn. At the top of many mountains, snow is found year-round.
5 COMPETENCY 1.2 NATIVE AMERICAN PEOPLES Skill 1.2a Demonstrate knowledge of Native American tribes living in the various regions of North America Strong archaeological evidence supports the contention that the ancestors of today's Native Americans and Latin American Indians crossed the Bering Strait from Asia to Alaska, eventually settling in all parts of the Americas; and evidence suggests that some may have arrived from Asia and the Pacific islands via a more southerly transoceanic seafaring route. Indigenous peoples of North America have been traditionally divided by anthropologists and ethnologists into mutually unintelligible linguistic groups. Inuit In the north, from western Arctic Alaska, across Arctic Canada to the Canadian Maritimes; Dineh From interior Alaska to the Sonoran Desert in Mexico (Athapaskan, Apache, Navajo, etc.); Anishinabe (Algonquian) Eastern woodlands United States and Canada (Ojibwe, Mohican, Abenaki); Siouan Midwestern and western Great Plains of the United States and Canada (Lakota, Dakota, Nakota); Iroquoian Northeastern United States and southeastern Canada woodlands (Seneca, Oneida, Mohawk, Onondaga, Cayuga); Nahuatl Central Mexico (Aztec); Mayan Southern Mexico and Mesoamerica; and Northwest Indian Southern Alaska Panhandle through Pacific Coastal Canada to the Oregon coast (Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, Nitnat). Skill 1.2b Demonstrate understanding of the political, economic, social, and cultural life of Native American peoples Native American tribes lived throughout what we now call the United States in varying degrees of togetherness. They adopted different customs, pursued different methods of agriculture and food gathering, and made slightly different weapons. They fought among themselves and with other peoples. They had established varying degrees of culture long before Columbus or any other European explorer arrived on the scene.
6 Perhaps the most famous Native American tribe is the Algonquians. We know so much about this tribe because they were one of the first to interact with the newly arrived English settlers in Plymouth, Massachusetts, and elsewhere. The Algonquians lived in wigwams and wore clothing made from animal skins. They were proficient hunters, gatherers, and trappers who also knew quite a bit about farming. Beginning with a brave man named Squanto, they shared this agricultural knowledge with the English settlers, including how to plant and cultivate corn, pumpkins, and squash. Other famous Algonquians included Pocahontas and her father, Powhatan, both of whom are immortalized in English literature, and Tecumseh and Black Hawk, known foremost for their fierce fighting ability. To the overall Native American culture, they contributed wampum and dream catchers. Another tribe who lived in the Northeast was the fierce fighting and forward thinking Iroquois. They lived in long houses and wore clothes made of buckskin. They, too, were expert farmers, growing the Three Sisters (corn, squash, and beans). Five of the Iroquois tribes formed a Confederacy, a shared form of government. The Iroquois also formed the False Face Society, a group of medicine men who shared their medical knowledge with others but kept their identities secret while doing so. These masks are one of the enduring symbols of the Native American era. Living in the Southeast were the Seminoles and Creeks, a huge collection of people who lived in chickees (open, bark-covered houses) and wore clothes made from plant fibers. They were expert planters and hunters and were proficient at paddling dugout canoes, which they made. The bead necklaces they created were some of the most beautiful on the continent. They are best known, however, for their struggle against Spanish and English settlers, especially led by the great Osceola. The Cherokee also lived in the Southeast. They were one of the most advanced tribes, living in domed houses and wearing deerskin and rabbit fur. Accomplished hunters, farmers, and fishermen, the Cherokee were known the continent over for their intricate and beautiful basketry and clay pottery. They also played a game called lacrosse, which survives to this day in countries around the world. In the middle of the continent lived the Plains Tribes, such as the Sioux, Cheyenne, Blackfeet, Comanche, and Pawnee. These peoples lived in teepees and wore buffalo skins and feather headdresses. (It is this image of the Native American that has made its way into most American movies depicting the period.) They hunted wild animals on the Plains, especially the buffalo. They were well known for their many ceremonies including the Sun Dance and for the peace pipes that they smoked. Famous Plains people include Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull, authors of the Custer disaster; Sacagawea, leader of the Lewis and Clark expedition; and Chief Joseph, the famous Nez Perce leader.
7 Dotting the deserts of the Southwest were a handful of tribes, including the famous Pueblo, who lived in houses that bear their tribe s name. They wore clothes made of wool and woven cotton, farmed crops in the middle of desert land, created exquisite pottery and Kachina dolls, and had one of the most complex religions of all the tribes. They are perhaps best known for the challenging vista-based villages that they constructed from the sheer faces of cliffs and rocks and for their adobes, mud-brick buildings that housed their living and meeting quarters. The Pueblos chose their own chiefs. Their government was perhaps one of the oldest representative governments in the world. Another well-known Southwestern tribe was the Apache and their famous leader Geronimo. The Apache lived in homes called wickiups, which were made of bark, grass, and branches. They wore cotton clothing and were excellent hunters and gatherers. Adept at basketry, the Apache believed that everything in Nature had special powers and that they were honored just to be part of it all. The Navajo, also residents of the Southwest, lived in hogans (round homes built with forked sticks) and wore clothes of rabbit skin. Their major contributions to the overall culture of the continent were in sand painting, weapon making, silversmithing, and weaving. Navajo hands crafted some of the most beautiful woven rugs. Living in the Northwest were the Inuit, who lived in tents made from animal skins or, in some cases, igloos. They wore clothes made of animal skins, usually seals or caribou. They were excellent fishermen and hunters and crafted efficient kayaks and umiaks to take them through waterways and harpoons with which to hunt animals. The Inuit are perhaps best known for the great carvings that they left behind. Among these are ivory figures and tall totem poles.
8 COMPETENCY 1.3 EUROPEAN EXPLORATION AND COLONIZATION Skill 1.3a Identify the major explorers and the reasons for European exploration A number of individuals and events led to the time of exploration and discoveries. The Vivaldo brothers and Marco Polo wrote of their travels and experiences, which signaled the early beginnings. Survivors from the Crusades made their way home to different places in Europe. They brought new information about exotic lands, people, customs, and desired foods and goods such as spices and silks. The Renaissance ushered in a time of curiosity, learning, and incredible energy sparking the desire for trade to procure these new, exotic products and to find better, faster, cheaper trade routes to get to them. The work of geographers, astronomers and mapmakers made important contributions; many studied and applied the work of such men as Hipparchus of Greece, Ptolemy of Egypt, Tycho Brahe of Denmark, and Fra Mauro of Italy. Portugal made the start under the encouragement, support, and financing of Prince Henry the Navigator. The better known explorers who sailed under the flag of Portugal included Cabral, Diaz, and Vasco da Gama, who successfully sailed all the way from Portugal, around the southern tip of Africa, to Calcutta, India. Christopher Columbus, sailing for Spain, is credited with the discovery of America although he never set foot on its soil. Magellan is credited with the first circumnavigation of the earth. Other Spanish explorers made their marks in parts of what are now the United States, Mexico, and South America. For France, claims to various parts of North America were the result of the efforts of such men as Verrazano, Champlain, Cartier, LaSalle, Father Marquette and Joliet. Dutch claims were based on the work of one Henry Hudson. John Cabot gave England its stake in North America along with John Hawkins, Sir Francis Drake, and the half-brothers Sir Walter Raleigh and Sir Humphrey Gilbert. Actually the first Europeans in the New World were Norsemen led by Eric the Red and later, his son Leif the Lucky. However, before any of these, the ancestors of today's Native Americans and Latin American Indians crossed the Bering Strait from Asia to Alaska, eventually settling in all parts of the Americas.
9 Skill 1.3b Demonstrate understanding of the consequences of early contacts between Europeans and Native Americans The first documented contact between Europeans and Native Americans that has archaeological evidence to support it was the Viking settlement of eastern Canada in 1000 CE. Under the leadership of Leif Eriksson, the Norse immigrants first encountered hostile Inuit in what is now northeastern Quebec and ventured south to Inland, what is now L ans aux Meadows, to establish a permanent settlement. Again, their encounter with the Native Americans was hostile. Eventually the incessant warfare between the Viking immigrants and the Native Americans was fought under conditions of relative parity of weapons, compelled the Vikings to abandon the Inland settlement, never to return. The next recorded contact was in 1492 CE, when Christopher Columbus, a Genoese adventurer commanding a squadron of Spanish ships, landed in what is now believed to be the island of Hispaniola, which is now Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Although the Native American inhabitants were initially curious and welcomed the newcomers, hostilities quickly ensued as the Spaniards raided indigenous villages for gold and slaves. Unlike the Vikings of five centuries earlier, the Spaniards had an advantage in arms. They had firearms; however, many of the Native Americans perished as a result of contracting diseases for which they had no immunity. The European and African immigrants brought such diseases as smallpox, measles, shingles, cholera, and influenza. As successive Spanish expeditions established landfalls in Florida, the Gulf Coast, Mesoamerica and other locations, a similar pattern of the search for gold, the taking of native populations for slaves, and the introduction of new diseases spelled disaster for the Native Americans in their early contacts with Europeans.
10 Skill 1.3c Demonstrate knowledge of colonization by various European powers The part of North America claimed by France was called New France. It consisted of the land west of the Appalachian Mountains. This area of claim and settlement included the St. Lawrence Valley, the Great Lakes, the Mississippi Valley, and the entire region of land westward to the Rocky Mountains. They established the permanent settlements of Montreal and New Orleans, thus giving them control of the two major gateways into the heart of North America, the vast, rich interior. The St. Lawrence River, the Great Lakes, and the Mississippi River along with its tributaries made it possible for the French explorers and traders to roam at will, virtually unhindered in exploring, trapping, trading, and furthering the interests of France. Most of the French settlements were in Canada along the St. Lawrence River. Only scattered forts and trading posts were found in the upper Mississippi Valley and Great Lakes region. The rulers of France originally intended New France to have vast estates owned by nobles and worked by peasants who would live on the estates in compact farming villages the New World version of the Old World's medieval system of feudalism. However, it didn't work out that way. Each of the nobles wanted his estate to be on the river for ease of transportation. The peasants working the estates also wanted the prime waterfront location. The result of all this real estate squabbling was that New France's settled areas wound up mostly as a string of farmhouses stretching from Quebec to Montreal along the St. Lawrence and Richelieu Rivers. In the non-settled areas in the interior were the French fur traders. They made friends with the friendly tribes of Indians, spending the winters with them getting the furs needed for trade. In the spring, they would return to Montreal in time to take advantage of trading their furs for the products brought from France, which usually arrived at about the same time. Most of the wealth for New France and its "Mother Country" was from the fur trade, which provided a livelihood for many, many people. Manufacturers and workmen back in France, ship-owners and merchants, as well as the fur traders and their Indian allies all benefited. However, the freedom of roaming and trapping in the interior was a strong enticement for the younger, stronger men and resulted in the French not strengthening the areas settled along the St. Lawrence.
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson Viking Greenland Vinland first to step foot in North America
 Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Leif Eriksson Leif Eriksson was a Viking from Greenland. Vikings were combative, plundering seafarers or pirates. He sailed the northern Atlantic Ocean and settled briefly in North America which he called
Unit 2: American Indians
 Unit 2: American Indians CLASS WEBSITE: https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/american-indians.html QUIZLET GAMES: https://quizlet.com/join/msfyy94t5 American Indians 1 Early People Learning about Early People
Unit 2: American Indians CLASS WEBSITE: https://mryoungtms.weebly.com/american-indians.html QUIZLET GAMES: https://quizlet.com/join/msfyy94t5 American Indians 1 Early People Learning about Early People
followed animals from Asia.
 Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Native American Tribes Study Guide Test: JACOBS: Friday, October 1 st REYOR: Tuesday, October 5 th. Name: Date: Vocabulary Migration: moving from one region to another. Ancient Americans migrated to North
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map
 Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Land bridge Pre-European contact Development of cultural regions Language map 1 Land bridge between North America and Asia Archaeological evidence has been discovered that shows the sea levels were lower
Cultures of North America
 Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Cultures of North America Focus Question: How did geography influence the development of cultures in North America? AD Sep 7 5:50 PM Mississippian Mound Builders 12 areas in Mississippi Mississippian Mound
Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America. Chapter 20 Section 2 European Nations Settle North America 3/26/13
 Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
Spain has success and others want in on everything. 1494 Treaty of Tordessillas divided the newly discovered lands between Portugal and Spain. Other counties ignored the treaty. Want to build own empire
The Native American Experience
 The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
The Native American Experience NATIVE PEOPLE AND GROUPS The First Americans Archaeologists believe that migrants from Asia crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska sometime between 13,000 and 3,000
Native Americans Culture
 Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Native Americans Native Americans have lived in what is now the United States for thousands of years. In that time, they developed many cultures. Culture is the way of life of a group of people. View the
Research Project: American Indians in the 19th Century 4.G.iii, 4.G.v
 Name: USA Studies Weekly Date: Week 10, 2nd Quarter Research Project: American Indians in the 19th Century 4.G.iii, 4.G.v Read the article below to get some background information for the research project.
Name: USA Studies Weekly Date: Week 10, 2nd Quarter Research Project: American Indians in the 19th Century 4.G.iii, 4.G.v Read the article below to get some background information for the research project.
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples. What Makes a Culture Unique?
 Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
Lesson 3 - North American Peoples What Makes a Culture Unique? Early Native American groups of North America adapted to their environments Advanced cultures developed in parts of North America long before
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Prince Henry the Navigator
 Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
Prince Henry the Navigator 1394-1460 Portugal Sponsored voyages of exploration along west African coast; supported study of navigation Motivation: To spread Christianity; to establish trade in Africa to
7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard #7H117 Do Now Day #17 Aims: SWBAT read and analyze a map locating representative Native American populations SWBAT compare how geography
New England Middle Atlantic Region
 New England Middle Atlantic Region I. States of the New England Middle Atlantic Region: Maine - Delaware New Hampshire - New York Vermont - New Jersey Massachusetts - Pennsylvania Connecticut - Maryland
New England Middle Atlantic Region I. States of the New England Middle Atlantic Region: Maine - Delaware New Hampshire - New York Vermont - New Jersey Massachusetts - Pennsylvania Connecticut - Maryland
American Indians. The First Americans
 The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
The Buffalo Hunter by Seth Eastman (1808-1875). Horses were introduced into North America by Spanish explorers in the 16th century, but American Indians soon became expert bareback riders of horses. American
Exploration ( )
 Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Exploration (1400-1607) - For many years, people in Europe knew of a distant land to the east called Asia, or the Far East. - They wanted to explore routes to the Far East - During this unit we will learn
Native Americans and Early Explorers
 Native Americans and Early Explorers Unit focus topics: 1. Land Bridge Theory 2. Lives of Native Americans in each region of North America Specific Tribes of Interest: Eastern Woodlands Plains Native Americans
Native Americans and Early Explorers Unit focus topics: 1. Land Bridge Theory 2. Lives of Native Americans in each region of North America Specific Tribes of Interest: Eastern Woodlands Plains Native Americans
Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769
 Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Name: Date: Per. Chapter 1 Study Guide New World Beginnings: 33,000 B.C-A.D. 1769 You need to know the historical significance of the following key terms. I suggest you make flashcards. 1. Marco Polo 2.
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
List any questions that you have pertaining about the Economics Unit we just finished.
 Unit 2: Native American Cultures Do now Beringia Native American Cultures Exit slip The Arrival of Men (worksheet) I can explain the Beringia Land Theory. American Heritage: Native Americans 21:52 By:
Unit 2: Native American Cultures Do now Beringia Native American Cultures Exit slip The Arrival of Men (worksheet) I can explain the Beringia Land Theory. American Heritage: Native Americans 21:52 By:
Explorers. of the NEW WORLD. Discover the Golden Age of Exploration. Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel
 Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
Explorers of the NEW WORLD Discover the Golden Age of Exploration Carla Mooney Illustrated by Tom Casteel Timeline ~ iv Introduction Exploring in the Age of Discovery ~ 1 Chapter 1 Searching for a Water
ExplorationColonizationPart1.notebook October 09, 2018
 "a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
"a disk floating on a great ocean", only 3 continents (Europe, Asia, Africa) life was hard enough, focused on own survival religious wars led to more trade with people in Asia and Africa (the Crusades)
Competition for a Continent Why did early French and English efforts at colonization falter?
 1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
1 2 3 Worlds Apart Native American Societies before 1492 How did the precontact histories of Native Americans, especially in the centuries just before 1492, shape their encounters with Europeans? West
First Contact: The Norse
 European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
European Contact First Contact: The Norse The Vikings were the first Europeans to establish colonies in the Americas, as early as the 10 th century AD Norsemen from Iceland first settled Greenland in the
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Wrote book on his explorations that generated excitement in others to develop trade with China and India 1st European who traveled the length of Asia
 AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
AD 1271-1295 left from Venice to go to China Trip took 4 years Served Kublai Khan for 20 years Brought back spices of cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, ginger, pepper, saffron, poppy, and incense Wrote book on
Quiz Show. Chapter 2 European Explorers
 Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
Quiz Show Chapter 2 European Explorers When supply of a product increases, demand drops. The Portuguese were the first to use technological advances in their explorations. A commission was a granting of
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world
 EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
EUROPEAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 OBJECTIVE: To identify the factors that led European countries to explore the world Factors that encouraged exploration Crusades Growth of commerce Population increase Rise
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
VS.2 VIRGINA GEOGRAPHY
 VS.2 VIRGINA GEOGRAPHY 1. What two large bodies of water Atlantic Ocean border Chesapeake Bay 2. What states border 1. Maryland 2. West Virginia 3. Kentucky 4. Tennessee 5. North Carolina 3. What are some
VS.2 VIRGINA GEOGRAPHY 1. What two large bodies of water Atlantic Ocean border Chesapeake Bay 2. What states border 1. Maryland 2. West Virginia 3. Kentucky 4. Tennessee 5. North Carolina 3. What are some
The World Economy. Chapter 17
 The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
The World Economy Chapter 17 Reasons for European Expansion/exploration 1. Trade domination route to Asian markets 2. Profit motive mercantilism 3. Raw materials/natural resources 4. Markets 5. Political
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
An Age of Exploration. Chapter 1 Section 2
 An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
An Age of Exploration Chapter 1 Section 2 The World in the 1400s: The Americas The Americas were home to two powerful civilizations: the Incas and the Aztecs Pg 12 The World in the 1400s: The Americas
Native Americans & Spaniards. Two Worlds Collide. Name Date Class. The Americas Prior to Spanish Exploration
 Native Americans & Spaniards Two Worlds Collide Name Date Class The Americas Prior to Spanish Exploration Thousands of Native American groups thrived throughout North and South America before Spanish exploration.
Native Americans & Spaniards Two Worlds Collide Name Date Class The Americas Prior to Spanish Exploration Thousands of Native American groups thrived throughout North and South America before Spanish exploration.
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land. Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War
 Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Text 1: Europeans Fight over North American Land Topic 3: The Revolutionary Era Lesson 1: The French and Indian War Europeans Fight Over North American Land Mid-1700s Britain, France, Spain, and the Netherlands
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA,
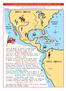 3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
3 4 SPANISH EXPLORATION AND CONQUEST OF AMERICA, 1492-1610 1492 1610 Columbus was right. The spirit of adventure brought many explorers to America. Here is an overview of Spanish explorers, who came first.
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION
 UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
UNIT 2- GEORGIA S COLONIZATION European Exploration and Settlement Essential Question: Why did European countries explore, claim, and settle the North American continent? The 3 G s During the early to
HIST-VS Echo Lake_Adams_Virginia Geography, Native Peoples Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 HIST-VS Echo Lake_Adams_Virginia Geography, Native Peoples Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1C17S7 1 Who were the first group of people to live in Virginia? A English B Scots-Irish
HIST-VS Echo Lake_Adams_Virginia Geography, Native Peoples Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1C17S7 1 Who were the first group of people to live in Virginia? A English B Scots-Irish
United States History. Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples
 Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Study Guide- Age of Exploration
 Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
Name Study Guide- Age of Exploration Binder Page Period Date (Know how.) What technology allowed the Europeans to explore? [Know what each one does] Caravel (ship) Astrolabe / Quadrant Magnetic compass
MAYANS. The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE.
 MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
MAYANS The Mayans lived on the Yucatan Peninsula (in brown, right). This civilization flourished between 300 and 900 CE. The Mayans had one of the most advanced civilizations in the Americas. They built
Creating America (Survey)
 Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Creating America (Survey) Chapter 1: The World in 1500, Beginnings to 1500 Section 1: Crossing to the Americas Main Idea: Ancient peoples came from Asia to the Americas and over time developed complex
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary
 Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
Unit 2, Activity 1, Age of Discovery Vocabulary Key Term? Example Definition Scientific Revolution Heliocentric theory Telescope Cartography Compass Caravel Astrolabe Commercial Revolution Indentured servitude
UNIT 1 COLONIAL AMERICA
 Objectives UNIT 1 COLONIAL AMERICA Discuss the migration of the first people to the Americas. Explain why Europeans wanted to develop a sea route to India in the 1400s. Describe the importance of trade
Objectives UNIT 1 COLONIAL AMERICA Discuss the migration of the first people to the Americas. Explain why Europeans wanted to develop a sea route to India in the 1400s. Describe the importance of trade
Woodlands Cultural Area Discover - Experience Connect Page 1 of 17
 Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Woodlands Culture Area Map The Woodlands Culture Area spanned west to the Mississippi River and east to the Atlantic Ocean. It stretched north into Canada and south to the Gulf of Mexico. The Great Lakes
Michigan. Copyright 2011 WorksheetWeb
 Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
Michigan Michigan is located in the northern Midwest. Michigan has a most unusual shape because it touches on four of the five Great Lakes. The western edge of Lake Erie forms the southeastern border of
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Everyday Life Southwest Desert. Indian Men
 Everyday Life Southwest Desert Invented ways to irrigate their crops, mostly by digging canals from nearby rivers farmers. Men hunted, but it wasn t important to the Desert Indians; there weren t any large
Everyday Life Southwest Desert Invented ways to irrigate their crops, mostly by digging canals from nearby rivers farmers. Men hunted, but it wasn t important to the Desert Indians; there weren t any large
hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan
 hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan Immigrating to Texas Various theories that historians believed early people came to Texas: 1. Sailed from the Eastern Hemisphere 2. Traveled across the North Atlantic
hapter 3 Lesson 1: The Earliest Texan Immigrating to Texas Various theories that historians believed early people came to Texas: 1. Sailed from the Eastern Hemisphere 2. Traveled across the North Atlantic
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1
 THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
THREE WORLDS MEET CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1: PEOPLING THE AMERICAS SECTION 2: NORTH AMERICAN SOCIETIES AROUND 1492 Mitten CSHS AMAZ History Semester 1 Peopling the Americas Three Worlds Meet Main Idea - In ancient
Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail
 Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
Name: Date: Section 2-1: Europeans Set Sail Fill in the blanks: Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. The was an epidemic disease that killed as many as 30 million people in Europe during the Middle Ages. 2. The was
1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in?
 1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in? 4) What development allowed people to settle and quit constantly moving around? REGION OF TEXAS Lived between
1) Draw an atlatl: 2) Define Nomadic: 3) What part of North America did most people settle in? 4) What development allowed people to settle and quit constantly moving around? REGION OF TEXAS Lived between
In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel
 Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
Motives and Impact In the late 1400 s scientific discoveries and the desire for wealth led to an age of exploration. New technologies allowed Europeans to travel further and discover distant lands with
CAUSES OF EXPLORATION. READING and ASSIGNMENT. Read the excerpt below. Use the reading to complete the section of the graphic organizer.
 Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Most Europeans had little knowledge of the world outside of their manor. Manors were self-sufficient. That is, people made almost everything they needed. Life for peasants was hard. They struggled to produce
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
United States History. Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples
 Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
Domain I: United States History Skill 1.1a Native American Peoples Native American tribes lived throughout North America with a variety of different customs, different avenues of agriculture and food-gathering,
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1
 BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
BRAINIAC CASE FILE #1 Portugal Begins the Age of Exploration Key Explorers The key figure in early Portuguese exploration was Prince Henry, the son of King John I. Nicknamed the Navigator, Henry was not
Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory
 Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
Unit 2 Unit 2, Notes 1 Three G s Gold Obtain bullion (gold and silver) Export raw materials (timber, fur) and/or grow cash crops (tobacco, indigo) to make a profit Glory Discover secrets of the New World
The World of the 1400s. What Was Going On?
 The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
The World of the 1400s What Was Going On? When European colonizers arrived in the Western Hemisphere, they found two continents that were certainly NOT empty of inhabitants. The Native Americans The earliest
EARLY AMERICAS. Ice age and the Olmec
 EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
EARLY AMERICAS Ice age and the Olmec LAND BRIDGE Beringia- Land bridge that connects Asia and America. Large glaciers during the Ice Age locked up water so that it was possible to walk across on land Animals
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The Age of Exploration was a time when
 Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
Unit 3: Age of Exploration Turning Points in History Age of Exploration 3:19 Vikings Who Discovered America First (worksheet) I can explain a Vikings way of life. Exploring the World The Viking Explorers
DISEASE PLANTS ANIMAL. Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes
 ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
ANIMAL PLANTS DISEASE Social Studies Name: Directions: Summarize the ideas of the readings in the chart below using point-form. Point-form Summary Notes Social Studies Name: Directions: On the map below,
Session One: Colonial America
 2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2018 AP US HISTORY Prep Webinars Session One: Colonial America 1491-1754 KEY CONCEPT 1.1 Native Amerian Cultures HUNTING&FARMING HUNTING FISHING FARMING HUNTING& FARMING Public Domain Map by Nikater AMERICAN
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America?
 2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
2.1 Why and how did humans first come to north America? Objective you are going to analyze 10 native cultures of North and South America. The Many Native groups in America had a wide variety of beliefs
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. Generations of schoolchildren have been taught that Christopher Columbus discovered the New World.
HSS-VS BnES 2d-g First Americans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 HSS-VS BnES 2d-g First Americans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1X52JT 1 Which American Indians were mostly located in the Tidewater Region? A Appalachian B Monacan C Cherokee D
HSS-VS BnES 2d-g First Americans Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1X52JT 1 Which American Indians were mostly located in the Tidewater Region? A Appalachian B Monacan C Cherokee D
of where they lived. However, the Sioux rarely stayed in one place. They were nomadic. They moved where and when the buffalo moved.
 The Plains Indians The land between the Mississippi River and the Rocky Mountains was once known as the Great Plains. In the summer, the temperature often went above 100 degrees. The area usually flooded
The Plains Indians The land between the Mississippi River and the Rocky Mountains was once known as the Great Plains. In the summer, the temperature often went above 100 degrees. The area usually flooded
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian. notes
 1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian notes Pre- Columbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration Early Human
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
European Discovery and the Conquest of America
 European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
European Discovery and the Conquest of America Native Culture Ancient land bridge and migration over centuries At time of Eur. Discovery -> perhaps 54 million?; 2000 distinct languages? Thousands of peoples
The Age of Exploration. Europe Encounters the World
 The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
The Age of Exploration Europe Encounters the World Why did explorations happen when they did? A variety of factors all came together to make the time period (1450-1700) the age of exploration Some of these
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa. Is called what??
 TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
TRADE between. England American colonies Africa Is called what?? TRIANGULAR TRADE Africa Which colonies were settled For religious reasons? MassachusettsBay Pennsylvania Plymouth were Settled for religious
UNIT 4 Native Americans
 UNIT 4 Native Americans Lesson 4-1 Native Americans of the West How did the Tlingit use their environment? I can analyze the effects of the Northwest environment on the Tlingit culture.! I can evaluate
UNIT 4 Native Americans Lesson 4-1 Native Americans of the West How did the Tlingit use their environment? I can analyze the effects of the Northwest environment on the Tlingit culture.! I can evaluate
Name Class Date. Use the information from pages to complete the following.
 GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
GUIDED READING A Place Called Mississippi Chapter 3: The European Period, 1540-1798 Section 1 Directions: Spanish Exploration Use the information from pages 72-74 to complete the following. 1. Prince Henry
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies,
 Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Chapter 2 The Planting of English America, 1500 1733 Chapter 3 Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619 1700 Characteristics of European Settlement in North America Spain: Florida, Mexico, SW Conquistadores,
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.19.17 Word Count 557 Level 560L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Wednesday, August 21
 Wednesday, August 21 1. Bellringer: Pick up Indian Chart from table and replicate it in your Spiral. 2. Discuss Why Do Historians 3. Native Americans Ppt (Powerpoint) 4. Two Views of Columbus reading for
Wednesday, August 21 1. Bellringer: Pick up Indian Chart from table and replicate it in your Spiral. 2. Discuss Why Do Historians 3. Native Americans Ppt (Powerpoint) 4. Two Views of Columbus reading for
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade
 Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade 1492 and Beyond In 1492, Christopher Columbus (Spain) lands in the Caribbean (San Salvador) In 1607, Captain John Smith (England) founds
Native and European Encounters & The Beginning of the Fur Trade 1492 and Beyond In 1492, Christopher Columbus (Spain) lands in the Caribbean (San Salvador) In 1607, Captain John Smith (England) founds
6. List 4 ways the people in New England made a living. Grain mills and sawmills, shipbuilding, trade, cod industry (fishing)
 The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
The Colonial Period Study Guide New Peoples 1. What years was the Colonial Period? 1607-1776 2. From what 8 countries did most settlers who came to America during this time travel? England, Netherlands,
EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins.
 EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins. Avatar Finding similarities in 1492 and 2015 Copy under
EQ: How did the Age of Exploration lead to the colonization of North Carolina? Warm Up: Get your NOTEBOOK and copy down the EQ before class begins. Avatar Finding similarities in 1492 and 2015 Copy under
THE COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE
 Name: Date: Directions: Read the following passage about the Columbian Exchange. Answer the questions that follow using complete sentences. Remember to give specific details from the text to support your
Name: Date: Directions: Read the following passage about the Columbian Exchange. Answer the questions that follow using complete sentences. Remember to give specific details from the text to support your
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America.
 SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. Olmecs were
Aztec and Inca Review
 Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Aztec and Inca Review Why take the risk? The Spanish took the great risk of exploring unknown land because: They wanted to obtain more gold and silver. They wanted to claim more land. They wanted to spread
Roanoke and Jamestown. Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live?
 Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Roanoke and Jamestown Essential Question: How Does Geography Affect the Way People Live? The Mystery of Roanoke Question: What problems did the Roanoke settlers encounter? The great powers of Europe were
Chapter 1 Worlds Apart
 1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
Medieval Africa Section One: The Rise of African Civilizations
 I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
I. Geography A. Sahara Desert 1. World s Largest Desert 2. Nomads a. Know where oases were 3. Swirling Winds 4. Sand Dunes 5. Little Water 6. Extreme Temperatures a. Hot During the Day b. Cold at Night
United States History. Chapter 1
 United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
United States History Chapter 1 Native Americans (Indians) North - Inuit and Alelut Northwest Coast- relied on natural resources such as salmon California- small bands fish flour from acorns- beans from
The Age of Exploration
 The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
The Age of Exploration A Resource to Accompany History Alive! The United States Through Industrialism Teachers Curriculum Institute 1 Introduction In this reading, you will learn about the Age of Exploration.
Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area
 Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area The Mound Builders The Mound Builders is a term used to describe First Nation's cultures that built earthen burial mounds and other earthworks
Religions of the Boyne City and the Charlevoix County area The Mound Builders The Mound Builders is a term used to describe First Nation's cultures that built earthen burial mounds and other earthworks
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl
 Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark Mapping the West: The Journey of Lewis and Clark By Michael Stahl The United States of America is one of the largest countries on the planet. Much of America
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA
 SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
SSWH10 THE STUDENT WILL ANALYZE THE IMPACT OF THE AGE OF DISCOVERY AND EXPANSION INTO THE AMERICAS, AFRICA, AND ASIA 10.a- Explain the roles of explorers and conquistadors; include Zheng He, Vasco da Gama,
Age of Exploration. Use the text to answer each question below.
 Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
Name Date Age of Exploration Use the text to answer each question below. 1. In the 1200s, explorer Marco Polo returned to Italy after adventuring in China. He brought back silks, teas and spices, and,
