Social Studies 6: Scott Foresman TheWorld LESSON OBJECTIVES ASSESSMENT throughout STANDARDS VOCABULARY
|
|
|
- Joseph Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 1 LESSON OBJECTIVES ASSESSMENT throughout STANDARDS VOCABULARY beginning Early Civilizations and Cultures CHAPTER 1 Digging Up The Past Lesson 1 Early Gatherers and Hunters Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Cultures Early Farmers Developing *Acquire information from primary sources individuals in prehistoric times *Analyze information by identifying the sequence of events *Define archaeologist and explain the role of an archaeologist *Explain who the Clovis people were and how we know about them *Describe how historians and archaeologists use artifacts to study the past *Explain why we still do not know who the first Americans were *Describe what Stone Age healers did and identify the tools they used *List the characteristics of the Stone Age *Define and explain domestication *Explain how the somestication of crops and animals changed the way people lived *Explain how we know what animals were domesticated during the Stone Age *Interpret information in time lines *Describe how complex cultures developed *Define and explain culture *Explain what encouraged the development of culture in the Americas Observation verbal questioning Text book website self testing Text web site lesson study guides and note creation Lesson Reviews Workbook pages Foldables Chapter Reviews Chapter Tests Unit Reviews Unit tests Performance Assessment options Various Internet Webquests, games, activities Power Point and Perzi creation archaeologist archaeology artifact glacier migrate prehistory agriculture, carbon dating, climate, domestication, excavation site, domesticate, harvest, nomad, social division, technology anthropology
2 CHAPTER 2 Early Civilizations Lesson 1 The Fertile Crescent Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Assyria Mesopotamia Babylonia and *Describe the artifacts that tell us the most about the development of culture *Explain how landforms and climate influence cultures *Explain how Mesopotamian civilization began and grew *Explain and describe where one of the first civilations arose *Describe the early agricultural techniques people used in Mesopotamia *Explain the significance of economic surplus in the rise of civilization in Mesopotamia *Explain why people in the Fertile Crescent settled in southern Mesopotamia *Describe Sumerian civilization *Explain the relationship between Sumerian religion and government *Explain how Sumerian writing changed over time *List and explain the significant achievements in technology and invention in early Mesopotamia *Explain how advances in Sumerian civilization occurred over time individuals in early societies *Explain who Hammarabi was *Explain the significance of the Code of Hammarabi culture diverse geography landform artisan, city-state, civilization, fertile, irrigation, plain, plateau, region conquer, cuneiform, dynasty, empire, polytheism, scribe, society, ziggurat,
3 Lesson 4 Hebrews, Phoenicians, and Lydians *List the similarities and differences between the Assyrian and Babylonian cultures *List and describe the contributions made by the Babylonians to civilization individuals in early societies *Describe the origin of Ancient Israel and its civilization *Describe the origin and significance of Judaism as one of the first monotheistic religions *Explain the significance of Solomon's Temple *List and explain the significance of the contributions of the Lydians *Explain how the Phoenicians helped Spread ideas *Make inferences when all the facts are not available UNIT 1 end *Identify significant examples of literature from various periods in world history *Describe how objects provide clues about a culture UNIT 2 beginning Early Civilizations in Africa and Asia CHAPTER 3 Ancient Egypt and Nubia *Acquire information from primary sources individuals in ancient Egypt, China, & India *Analyze information by summarizing conquest barter covenant descendant monotheism slavery synagogue
4 Lesson 1 the Nile The Lifeline of *Explain how often and when the Nile flooded *Describe the route of the Nile River Lesson 2 Life in Eqypt *List some of the technology the Egyptians used to adapt to the annual flooding of the Nile *List the ways the Nile was both beneficial and disastrous to Eqyptian civilization *Explain how understanding the flooding of the Nile helped Egyptian civilization thrive and last for thousands of years *Describe how map scales can show both large and small areas *Compare the relative sizes of scales of large and small areas *Describe and explain the importance of pharaohs and pyramid building *Explain who unified Upper and Lower Egypt and when this happened *Define hieroglyphics and explain how we decoded them *List and explain the similarities and differences between Egyptian and Sumerian culture *Explain why trade was so important to Egypt's economy *Summarize the accomplishments of the tomb builders *Describe the difficulty and danger of the tomb builders' job *Evaluate the loyalty and courage shown by the timb builders *Identify the contributions of Hatshepsut *Evaluate the success of Hatshepsut's reign delta cataract papyrus silt economy hieroglyphics mummy pharaoh pyramid unify
5 Lesson 3 Egypt Nubia and *Compare and contrast the geography of Egypt and Nubia *Explain how and why the Egyptians interacted with the Nubians *Explain why other groups of peoples invaded Egypt and explain how this affected Nubia independent Chapter 4 Ancient China Lesson 1 The Geography of China *Explain how the relationship between the Egyptians and Nubians changed over time *Explain how people living in China control the Huang River *Explain how the Huang River is both beneficial and distrous to the people living by it *Explain why the Huang River is also called the Yellow River *Describe how the geography in China makes it a diverse country *Explain how to use a climograph to find out the average precipitation and temperature of an area over a period of time *Compare and contrast the climates of different areas using climographs Lesson 2 China's Past *List and describe some of the major achievemnets of the Han Dynasty *Explain how Chinese culture became unified during the Han Dynasty *List and describe some inventions that were made to improve daily life in ancient China double cropping levee loess terrace ancestor civil service middleman
6 Lesson 3 Legacy of Thought Chapter 5 Ancient India and Persia Lesson 1 Geography of South Asia Lesson 2 India and Persia *Explain why Qin Shi Huangdi connected the defensive walls to make the Great Wall *Identify the contributions Qin Shi Huangdi made to China *Explain why the oppressive ruling style of *Qin Shi Huangdi led to his downfall *Explain how Confucianism, Daoism, and other ways of thought have influenced Chinese history and culture *List and explain the main principles of Confucianism *Explain what the Analects are *Explain other ways of thinking, besided Conficianism, that influenced Chines culture *List and describe the main physical features in South Asia *Define subcontinent and explain how India became one *Describe how people have farmed on the Indo-Ganges Plain *Describe how the human geography of South Asia is diverse *Identify the significance and contributions of the Mauryan Empire to Indian civilization *Explain and describe the Aryan migration *List and describe some of the ways the Persian culture influenced Indian culture and civilization oracle bone pictograph province nobility monsoon season subcontinent subsistence farming brahmin
7 *Explain the sequence of events from early civilizations in India through the growth of Indian empires *Explain how the Vedas and other literature left by the Aryans affected Indian beliefs individuals Lesson 3 Hinduism *List and explain the main beliefs of Hinduism *Explain the roots of Hinduism *Describe and explain the significance of Brahman in Hinduism *Explain why the caste system was banned in the Indian government Lesson 4 Buddhism *List and explain the main beliefs of Buddhism *Indetify the significance of the Buddha *Explain the relationship between the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path in Biddhism *Gather, organize, and summarize information for a report UNIT 2 end *Explain how songs reflect the culture about which they were written *Understand form and function of an Egytian pyramid UNIT 4 beginning *Acquire information from primary sources Mediterranean Empires individuals in ancient Greece and Rome *Analyze information by identifying the main idea and details sudra caste reincarnation enlightenment meditation
8 Chapter 9 Ancient Greece Lesson 1 The Geography of Greece *Describe the physical features of Greece Lesson 2 The Greek City- States Lesson 3 The Golden Age of Athens *Explain the importance of Minoan civilization *Name and describe the bodies of water that surround Greece *Explain how Greece's physical geography affected the lives of its people *Describe the importance of the sea in the life of the Greek people *Compare and contrast a democracy and an aristocracy *Describe the religious beliefs of the ancient Greeks *Define aristocracy *Describe the similarities and differences between civilizations in Sparta and Athens individuals in ancient Greece, including Pericles *Interpret data on maps of different scales *Identify situations in which maps of a large scale or small scale are more useful *Describe the Golden Age of Athens *Define and explain the Delian League *Explain the importance of the Battle of the Salamis *Name some of the fields of study in which the Greeks excelled during the Golden Age agora plunder aristocracy democracy immortal myth marathon mercenary philosopher plague reason
9 Lesson 4 Alexander the Great *Describe how the Greek city-states united to defeat Athens *Identify the accomplishments of significant individuals in ancient Greece *Explain how Alexander expanded the empire and spread Greek culture *Explain how Alexander became emperor *Explain and describe and explain Alexander's leadership skills *Define and describe Hellenistic culture Chapter 10 Ancient Rome *Explain how the discoveries of Hippocrates changed Greek and other people's lives Lesson 1 Rome's Beginnings Lesson 2 The Roman Republic *Explain how the Romans borrowed ideas and ways from the Etruscans *Explain the legend of Romulus and Remus and their importance to the study of ancient Roman history *Describe the importance of the Tiber River to the development of Roman civilization *Explain how Rome's physical geography helped its civilization *Explain the legend of Rome's founding Acquire information from primary and secondary sources *Describe the system of government in the Roman Republic *Define republic *Explain who Hannibal was and identify his achievements caesar consul dictator patrician patriotism
10 Lesson 3 Empire The Roman *Expalin the impact of Rome's conquests on the republic *Compare and contrast the powers that plebians and the patricians had during the Roman Republic *Describe the major achievements of the Romans *Explain who Augustus was and his significance in Roman history *Define and explain Pax Romana plebian representative republic Senate tribune Lesson 4 The Rise of Christianity Lesson 5 Rise and Fall *Explain the importance of good rulers to the growth and expansion of the Roman Empire *List examples of Rome's advanced civilizations *Identify the accomplishments of Marcus Aurelius *Explain how Marcus Aurelius cared for the people of Rome *Identify the contributions of people who devote their lives to helping and caring for others *Explain how the Christian religion spread throughout the Roman Empire *Describe the contributions of Peter and Paul to Christianity *Define persecution and explain why the Christians were persecuted *Explain why Christianity became the main religion in the Roman Empire *Expalin connections between Christianity and Judaism *Explain how barbarian invasions affected the Roman Empire emperor gladiator catacomb disciple persecute synagogue auction pillage
11 Define and explain the significance of mercenaries in the Roman Empire *Describe the impact of Constantine on the Roman Empire *Explain why the eastern half of the Roman Empire survived after the fall of the western half UNIT 4 end *Read an excerpt from literature written by Herodotus pope vandal *Explain some of Herodotus's contributions *Describe details of Greek mythology
Month/ Quarter. Topic Standards Skills Resources/Materials/ Grade Level: Key Terminology. Assessments. Activities
 Grade Level: 6th Subject/Course: Social Studies Month/ Topic Standards Skills Resources/Materials/ Activities Key Terminology Assessments 1st Early Civilizations and Cultures Ch. 1, 2 SS.IS.6-8, SS.IS.2.6-8,
Grade Level: 6th Subject/Course: Social Studies Month/ Topic Standards Skills Resources/Materials/ Activities Key Terminology Assessments 1st Early Civilizations and Cultures Ch. 1, 2 SS.IS.6-8, SS.IS.2.6-8,
Social Studies at a Glance 6 th Grade Chapter Map Artifact Worksheets Art Lesson Ideas Reading Video/Games Geography Map of
 Geography Map of * Geography test World 1 Ancient Civilization p. 65 * Cave art SKILLS p.3 Lat/Long First Footsteps p. 5-6 Time line * Archeological dig * PLAY: Piltdown Man Fire at Terra Amata Adventure
Geography Map of * Geography test World 1 Ancient Civilization p. 65 * Cave art SKILLS p.3 Lat/Long First Footsteps p. 5-6 Time line * Archeological dig * PLAY: Piltdown Man Fire at Terra Amata Adventure
SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES
 NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS
 YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
SOL Narrative Review. with questions
 SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera. 1.) Define: bipedalism, primary source and Paleolithic Age.
 Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
SC06SS Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago?
 PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
earliest recorded history to today. writing art artifacts Centuries-old written records reveal a long-lasting civilization in
 Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Mesopotamia People settled near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers around 3,500 BC Modern Day Farming in Mesopotamia Flood plains were very fertile and used for growing
Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period
 Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period Unit 2 - Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Overview: During this unit, students will explore how Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Kush
Englewood Public Scho District World History Grade 5 Second Marking Period Unit 2 - Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Overview: During this unit, students will explore how Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Kush
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers. Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent BC
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 7000-500 BC Lesson 1: Geography of the Fertile Crescent Rivers People settled near rivers because crops would grow here. Floods kept the soil fertile. The
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary
 Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
Beginning of Man Stone Age Vocabulary Paleolithic Era DEF: Old Stone Age CONNECT: Stone Age time tools were poorly made of stone Neolithic Era DEF: New Stone Age CONNECT: time tools were carefully made
*China s physical geography helped keep China economically and culturally isolated throughout its early dynasties *Its mountains and deserts
 Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Gobi Desert Taklimakan Desert Huang He Xi Jiang Label: Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Taklimakan Desert, Huang He (Yellow River), Chang Jiang (Yangtze River), Xi Jiang, Tibetan Plateau teau Copyright 2017 2017
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
The earliest written language. BCE The years before the year 0. The worship and belief in many gods. The land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
 Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Rise of Civilizations & Mesopotamia Study Guide Test: Monday, November 19 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Rise of Civilization, Uruk Civilization Organizer, Ancient Mesopotamian
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
Located in what is now partly Syria and Iraq
 The Fertile Crescent A plain with rich topsoil carried down the Tigris and Euphrates River valleys with the spring floods. Bordered by the Zagros Mountains to the East, and the Syrian and Arabian Deserts
The Fertile Crescent A plain with rich topsoil carried down the Tigris and Euphrates River valleys with the spring floods. Bordered by the Zagros Mountains to the East, and the Syrian and Arabian Deserts
Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST!
 Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST! 1. How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? Flood Control Built levees and storage basin to
Mesopotamia Study Guide Review STUDY GUIDES ARE DUE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST! 1. How did the Mesopotamians use AND control the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers? Flood Control Built levees and storage basin to
City-States in Mesopotamia
 Name CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more
Name CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY. PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
UNIT 7. OUR HISTORY PRIMARY 3 / Social Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández PREHISTORY IT IS THE TIME BEFORE THE INVENTION OF WRITING. Since this, there aren t written record of what life was like during
Table of Contents. World History Detective. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Teacher Overview... iv About the Author... vi 1. The Fertile Crescent and the Sumerians...1 2. Babylonian Empire...5 3. Hittites and Phoenicians...9 4. Religious History
Table of Contents Table of Contents Teacher Overview... iv About the Author... vi 1. The Fertile Crescent and the Sumerians...1 2. Babylonian Empire...5 3. Hittites and Phoenicians...9 4. Religious History
Chapter 3 NOTES. RPC: How did Sargon establish and rule his empire? CT: Why do you think this monument was built? What or whom does it commemorate?
 Chapter 3 NOTES Lesson 1 Comparing and Contrasting- Use a graphic organizer like the one below to compare and contrast the empires of Akkad and Babylon. RPC: How did Sargon establish and rule his empire?
Chapter 3 NOTES Lesson 1 Comparing and Contrasting- Use a graphic organizer like the one below to compare and contrast the empires of Akkad and Babylon. RPC: How did Sargon establish and rule his empire?
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE)
 AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea.
 The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
The Fertile Crescent is a region of the Middle East that stretches in a large, crescent-shaped curve from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Fertile Crescent includes Mesopotamia, a wide, flat
World History Midterm Study Guide
 World History Midterm Study Guide Primary source: eyewitness accounts of an event, laws, artifacts: reveal to historians culture, lifestyle, prejudices and biases of ancient civilizations Radiocarbon dating:
World History Midterm Study Guide Primary source: eyewitness accounts of an event, laws, artifacts: reveal to historians culture, lifestyle, prejudices and biases of ancient civilizations Radiocarbon dating:
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming
 Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
Agriculture marked a dramatic change in how people lived together. They began dwelling in larger, more organized communities, such as farming villages and towns. From some of these settlements, cities
City-States in Mesopotamia
 CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more about
CHAPTER 2 Section 1 (pages 29 34) City-States in Mesopotamia BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the earliest humans and the first civilization. In this section, you will learn more about
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION
 MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
MESOPOTAMIA THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESCENT I. Rivers support early civilizations A. Early people settled where crops would grow. B. Many civilizations began near rivers. 1.
True of most river valley civilizations.
 True of most river valley civilizations. China under the Shang Dynasty Chinese legend says that Pan Gu the first man created the universe. The first legendary dynasty was the Xia. Scholars are not sure
True of most river valley civilizations. China under the Shang Dynasty Chinese legend says that Pan Gu the first man created the universe. The first legendary dynasty was the Xia. Scholars are not sure
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere
 Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
RULING A LARGE EMPIRE
 RULING A LARGE EMPIRE The First Empire Builder: In 2,300B.C., Sargon, the ruler or Akkad, invaded and conquered the city-state of Sumer. He thus created the very first empire in known history when he spread
RULING A LARGE EMPIRE The First Empire Builder: In 2,300B.C., Sargon, the ruler or Akkad, invaded and conquered the city-state of Sumer. He thus created the very first empire in known history when he spread
5/21/14 CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO
 CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS AP World History PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting
CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS AP World History PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION -12,000 YEARS AGO The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting
Amazing Mesopotamia. Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography
 Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Amazing Mesopotamia Southwest Asia (Middle East) Geography 1. Most of Southwest Asia has an Arid climate today. An Arid climate receives less than 10 inches of precipitation (rain, sleet, or snow). Arid
Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations
 Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
Name Notes: Unit 2 Chapter 5: The Rise of River Valley Civilizations Important Ideas A. The earliest humans survived by their food. They used tools of wood, bone, and. They also learned to make. B. About,
China s First Dynasties
 Preview China s First Dynasties Main Idea / Reading Focus China s Geography The Shang Dynasty The Zhou Dynasty Map: Shang and Zhou Dynasties New Philosophies Faces of History: Chinese Philosophers Preview,
Preview China s First Dynasties Main Idea / Reading Focus China s Geography The Shang Dynasty The Zhou Dynasty Map: Shang and Zhou Dynasties New Philosophies Faces of History: Chinese Philosophers Preview,
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources
 Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers
 Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Mesopotamia - The Land Between Two Rivers Mesopotamia was a place where many ancient cities were established. The word Mesopotamia means located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River
Unit Ancient River Civilizations. Case studies
 Unit 1.3-1.4 Ancient River Civilizations Case studies Do Now: Think About It Hazlo ahora: piensa en eso... Why would most of the earliest civilizations develop near rivers??? Por qué la mayoría de las
Unit 1.3-1.4 Ancient River Civilizations Case studies Do Now: Think About It Hazlo ahora: piensa en eso... Why would most of the earliest civilizations develop near rivers??? Por qué la mayoría de las
CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS
 CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION - 12,000 BCE The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting and Gathering: over
CHAPTER 1: FROM HUMAN PREHISTORY TO THE EARLY CIVILIZATIONS PALEOLITHIC ERA OLD STONE AGE 2.5 MILLION - 12,000 BCE The human species has existed for about 2.5 million years. Hunting and Gathering: over
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Mesopotamia ancient civilization river Afterlife Ur ancient city in Mesopotamia India Hittites-empire used iron weapons
 What do you suppose life was like five thousand years ago in the first river valley civilizations for everyday people? Below is a list of terms associated with that time period. We are going to examine
What do you suppose life was like five thousand years ago in the first river valley civilizations for everyday people? Below is a list of terms associated with that time period. We are going to examine
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
Unit 1 Packet. c BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1
 Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
Unit 1 Packet c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE NAME : 1 Note: Keep this packet until the end of the year so you can study it! Timeline Dates (all dates are BCE) Event Location(s) 10,000 8,000 Agricultural Revolution
1. Where is the food?
 1. Where is the food? Before the Neolithic Revolution, humans were forced to travel from place to place in search of food as nomads. The result of the Revolution was a shift from a food gathering to food
1. Where is the food? Before the Neolithic Revolution, humans were forced to travel from place to place in search of food as nomads. The result of the Revolution was a shift from a food gathering to food
Fertile Crescent Empires
 Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
Preview Main Idea / Reading Focus The Hittites Maps: Conquering the Fertile Crescent The Assyrians and the Chaldeans Faces of History: Nebuchadnezzar II The Phoenicians Map: Phoenician Trade Quick Facts:
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT
 GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
GEOGRAPHY OF THE FERTILE CRESENT The Land Between the Rivers: The first civilization in the fertile crescent was Mesopotamia. It was located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In Sumer, as in Egypt,
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations B.C.
 Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Geography of the Fertile Crescent
 Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
Geography of the Fertile Crescent The Big Idea The valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the site of the world s first civilizations. Main Ideas The rivers of Southwest Asia supported the growth
How was life along the Yellow River both similar and different from life along the Nile River?
 As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
As in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and along the Indus River, Chinese civilization began within a major river valley. Modern China itself is a huge geographical expanse. Around 4000 BC, this huge area contained
The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River)
 Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Early China The Huang He River (a.k.a. YELLOW River) starts in the TIBETAN Plateau and flows 2,900 miles to the Yellow Sea carries LOESS - a dusty yellow soil called "China's SORROW due to devastating
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Chapter 1: Prehistoric Era. AP World History Chapter 1
 Chapter 1: Prehistoric Era AP World History Chapter 1 Paleolithic Era -- 2.5 million - 12,000 BCE Human species: existed for 2.5 million years. Hominids: members of the family of humans (includes Homo
Chapter 1: Prehistoric Era AP World History Chapter 1 Paleolithic Era -- 2.5 million - 12,000 BCE Human species: existed for 2.5 million years. Hominids: members of the family of humans (includes Homo
Human Origins in Africa
 Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
Name CHAPTER 1 Section 1 (pages 5 13) Human Origins in Africa BEFORE YOU READ In this section, you will read about the earliest humans. AS YOU READ Use the time line below to take notes on the earliest
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations
 CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia Between Rivers Iraq today Mesopotamia 1 Mesopotamia w Tigris & Euphrates River Valley w Fertile Crescent w 25 miles to 250 miles apart w Flood rich soil for agriculture
Chapter 2 Section 1 Mesopotamia Between Rivers Iraq today Mesopotamia 1 Mesopotamia w Tigris & Euphrates River Valley w Fertile Crescent w 25 miles to 250 miles apart w Flood rich soil for agriculture
World History: Patterns of Interaction. Early River Valley Civilizations, 3500 B.C. 450 B.C.
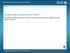 Early River Valley Civilizations, 3500 B.C. 450 B.C. Civilizations emerge and develop on fertile river plains in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley, and China. Early River Valley Civilizations, 3500
Early River Valley Civilizations, 3500 B.C. 450 B.C. Civilizations emerge and develop on fertile river plains in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley, and China. Early River Valley Civilizations, 3500
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C
 UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
UNIT ONE Reading Passages Ancient Mesopotamia 1B Ancient Sumer 1C N MESOPOTAMIA Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means between two rivers. The two rivers referred to are the Tigris and Euphrates
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Stone Age & Archaeology. Unit Review
 Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
Stone Age & Archaeology Unit Review 1. Archaeologists: What is an Archaeologist? What do they use to study the past? Archaeology is the study of the past based on what people left behind. Archaeologists
MIDDLE SCHOOL HISTORY LABORATORY 1ST SEMESTER
 Name: Date: Teacher: Miss Susana Santacruz Grade: 1 I I. The beginning of the civilization. 1.- Read the text below and answer the questions that follows 1 Who dug up artifacts like tools and pottery?
Name: Date: Teacher: Miss Susana Santacruz Grade: 1 I I. The beginning of the civilization. 1.- Read the text below and answer the questions that follows 1 Who dug up artifacts like tools and pottery?
Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest
 Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
Name Date Block Mesopotamia, Sumer and Babylon Webquest Directions: Answer the questions using www.mesopotamia.co.uk AND YOUR OWN background knowledge! Click on Mesopotamia, then Geography from the left
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade:10 B & C. Subject: Social Studies. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade:10 B & C Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Nour Al Maaref International School Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia S/Y 2017-2018 1. Geography
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade:10 B & C Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Nour Al Maaref International School Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia S/Y 2017-2018 1. Geography
Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society
 1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
1 Chapter 1 The Beginnings of Human Society Section 1 Geography and History Section 2 Prehistory Section 3 The Beginnings of Civilization Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 Now
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia What were the most important achievements of the Mesopotamian empires? In ancient Mesopotamia, rulers recorded their greatest achievements on steles. A stele (STEE-lee)
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia What were the most important achievements of the Mesopotamian empires? In ancient Mesopotamia, rulers recorded their greatest achievements on steles. A stele (STEE-lee)
Blue Print for Achievement Test. Standard : 9 th. Subject : Social Science. Unit : Ancient Civilisation. Time : 1.30 hrs. Maximum Marks : 75. Sl. No.
 Blue Print for Achievement Test Standard : 9 th Subject : Social Science Unit : Ancient Civilisation Time : 1.30 hrs. Maximum Marks : 75 Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sub-headings of the Unit Ancient Civilasation
Blue Print for Achievement Test Standard : 9 th Subject : Social Science Unit : Ancient Civilisation Time : 1.30 hrs. Maximum Marks : 75 Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sub-headings of the Unit Ancient Civilasation
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia. Miss Genovese
 Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia Miss Genovese Geography Mesopotamia is the region between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (AKA The Land Between Two Rivers) Land was mostly flat with small plants Tigris
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent 1 The Rise of Sumer The Big Idea: The Sumerians developed the first civilization in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians developed the first advanced society. 2 The Appearance
Chapter 4 Section 1- Egypt Under the Pharaohs. Titles Notes QCIPL. - The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles)
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL I) The Nile River Valley A) The World s Longest River The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles) it flows from the south in modern
Chapter 4 Section 1 Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL I) The Nile River Valley A) The World s Longest River The Nile is the worlds longest river (3500 miles) it flows from the south in modern
The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two AB The code consisted of over 200 acts and their required
The Cradle of Civilization- Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Marshall High School Mr. Cline Western Civilization I: Ancient Foundations Unit Two AB The code consisted of over 200 acts and their required
Student s Name: Subject: Social Studies
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
ADVANCED CITIES: The people who established the world's first civilization around 4000 B.C. in southern Mesopotamia were known as the Sumerians.
 ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
ADVANCED CITIES: Caption: This artifact is huge and can only be viewed if a picture of it is placed on a piece of paper like the one to the left. It is a picture of the first major city in Mesopotamia:
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
9/12/16. Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People
 9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
9/12/16 Lesson 2-1 Notes: Early People Lesson Objectives Identify possible explanations of how people came to live in the Americas. Explain how early peoples in the Americas lived, hunted, and farmed.
Chapter 5 Early Society in Mainland East Asia. pages
 Chapter 5 Early Society in Mainland East Asia pages 90-108 What is a civilization and what are defining characteristics of a civilization? How did the civilization of your chapter develop and grow more
Chapter 5 Early Society in Mainland East Asia pages 90-108 What is a civilization and what are defining characteristics of a civilization? How did the civilization of your chapter develop and grow more
Ancient China History Flow Chart
 R78 L85 Ancient China History Flow Chart First Civ. of China- Xia (Shyah) or Shang Dynasty? Pgs 280-283 Zhou Dynasty- Longest dynasty Pgs 283-285 Warring States- Chinese Philosophy develop Qin (Chin) Dynasty
R78 L85 Ancient China History Flow Chart First Civ. of China- Xia (Shyah) or Shang Dynasty? Pgs 280-283 Zhou Dynasty- Longest dynasty Pgs 283-285 Warring States- Chinese Philosophy develop Qin (Chin) Dynasty
Ch 1 and 2 Review. Ancient River Valley Civilizations
 Ch 1 and 2 Review Ancient River Valley Civilizations PREHISTORY PERIOD IN WHICH OUR ANCESTORS EXISTED ON EARTH BUT HAD NOT YET INVENTED WRITING OUR KNOWLEDGE OF THEM COMES FROM SCATTERED AND SCARCE PHYSICAL
Ch 1 and 2 Review Ancient River Valley Civilizations PREHISTORY PERIOD IN WHICH OUR ANCESTORS EXISTED ON EARTH BUT HAD NOT YET INVENTED WRITING OUR KNOWLEDGE OF THEM COMES FROM SCATTERED AND SCARCE PHYSICAL
Ancient China. Map of Ancient China
 Ancient China Map of Ancient China Name: Date: In this unit, you will learn about ancient China. Look carefully at the map. Trace the length of the Huang River in black. Put an orange star next to Anyang.
Ancient China Map of Ancient China Name: Date: In this unit, you will learn about ancient China. Look carefully at the map. Trace the length of the Huang River in black. Put an orange star next to Anyang.
