AP World History Summer Assignment
|
|
|
- Charity Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP World History Summer Assignment SUMMER 2017 McKinley Technology High School Instructor: Mr. Tyrone Shaw Student Name: DUE THE FIRST WEEK OF CLASS. AUGUST 25 TH (A-DAY) & 28 TH (B-DAY), 2017 Welcome to AP World History, I look forward to a great year with you. As an APWH student, you are held to a higher expectation than the average student of history. Despite the fact that you are in the 10 th grade, AP World History is a college level course; you will be given college level work. As part of the college level curriculum and expectation, there is the opportunity to earn college credit; however, this can only be achieved if you are willing to put forth college level effort. As an introduction to this course, it is required that you complete this summer assignment in an effort to become more familiar with the areas of history that are covered. Your entire packet is due the by the end of the first week of your AP class. 1
2 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017 Dear Students Welcome to your sophomore AP World History course! In preparation for our busy year, you are expected to complete the following FOUR assignments over the summer! Please review the descriptions of the activities listed below and the assessments for each assignment. We will begin our course of study in the year 8,000 B.C.E. and finish the school year looking at modern day issues. The majority of your summer assignments will require you to read, reflect and analyze a book. You will also have to complete three basic world religions charts, answer questions about the Neolithic Revolution and complete a geography assignment. Please feel free to me over the summer if you have questions. Sincerely, Mr. Shaw Tyrone.Shaw@dc.gov Assignment One WORLD RELIGIONS The influence of major religions and semi-religious philosophies on societies will provide a reoccurring theme throughout the course. It is important for you to be familiar with each religion as we proceed. Please follow the directions below: 1. Visit the following sources: BBC Religion & Ethics Website Infoplease.com World Religions PowerPoint on Edmodo. 2. Complete each of the following: Western Eurasian Religions Chart Eastern Eurasian Religions Chart Classical Eastern Semi-Religious Philosophies Chart An example of the detail expected of you can be found on the Classical Eastern Semi- Religious Philosophies Chart under Daoism (Taoism). To help you complete each section of the chart, be sure to keep the following in mind: 1. Symbol Draw in and name the appropriate symbol for each religion 2. Founder/Patriarch Name the historical founder (if any) 3. Place & Date of Origin When and where the religion began 4. Modern Extent Where most adherents live today (country, continent) 5. Holy or Sacred Texts Make sure to look at the websites or the Barron's book carefully 6. Teachings Summarize the core beliefs and teachings of each religion (i.e. Islam s 5 Pillars) 7. Role of Women Explain the accepted role of women in each religion 2
3 MONOTHEISTIC RELIGIONS OF WESTERN EURASIA Symbol JUDAISM CHRISTIANITY ISLAM Founder / Patriarch Place and Date of Origin & Modern Extent Holy or Sacred Text Teaching or Core Beliefs Role of Women 3
4 POLYTHEISTIC RELIGIONS OF EASTERN EURASIA HINDUISM BUDDHISM Symbol Founder / Patriarch Place and Date of Origin & Modern Extent Holy or Sacred Text Teaching or Core Beliefs Role of Women 4
5 CLASSICAL EASTERN SEMI-RELIGIOUS PHILOSOPHES DAOISM CONFUCIANISM Symbol Founder / Patriarch Laozi (Lao-tzu), otherwise known as the Old Master Place and Date of Origin & Modern Extent c. 500 BCE during the Zhou Dynasty; would become popularized throughout China c. 200 BCE; birth/death dates unknown (probably c.500 BCE) Holy or Sacred Text Teaching or Core Beliefs Tao-te Ching (Book of the Way) stresses the path toward wisdom through experience; I- Ching (Book of Changes) analyzes & predicts future events Mostly Practiced in China Dictates that the universe and all within are permeated by a natural order that must be felt and experienced to be understood. Temporal (worldly) matters are of little concern; seeking knowledge of the Dao (or Way) through nature, poetry, and experience is all that matters. Great emphasis on the individual and the balance with nature. (Yin-Yang) A true Taoist embraces the nature of things, and does not waste effort effecting their whim on life, but rather surrenders themselves to experience Taoist rituals permeated other ancient practices, and commonly became associated with the mystical. Co-exists within Eastern concepts of Buddhism and Confucianism. Many Mahayana Buddhist sects have elements of Daoism infused in their teachings (underscores Chinese influence on the spread of Buddhism to Korea & Japan) For Confucianism, the Taoist belief in balance accentuates the balance between benevolence and respect that superiors must show their subordinates. Role of Women Daoism makes no concrete distinction between men and women; all individuals are equal in light of the Dao 5
6 Assignment Two GEOGRAPHY Directions: Label (or number) the world map with the land and water features listed below in the color indicated in parenthesis. Several maps have been provided. Continents- (make each a different color) 1. North America 2. South America 3. Australia 4. Europe 5. Antarctica 6. Asia 7. Africa Oceans and Seas (Blue) 1. Arctic Ocean 2. Atlantic Ocean 3. Indian Ocean 4. Pacific Ocean 5. Southern Ocean 6. Adriatic Sea 7. Aegean Sea 8. Arabian Sea 9. Baltic Sea 10. Barents Sea 11. Bay of Bengal 12. Bering Sea 13. Black Sea 14. Caribbean Sea 15. Caspian Sea 16. Coral Sea 17. East China Sea 18. English Channel 19. Great Lakes 20. Gulf of Mexico 21. Mediterranean Sea 22. North Sea 23. Norwegian Sea 24. Persian Gulf 25. Red Sea 26. Sea of Japan 27. South China Sea 28. Yellow Sea Rivers (Red) 1. Amazon River 2. Congo River 3. Danube River 4. Euphrates River 5. Ganges River 6. Indus River 7. Mississippi River Mountain Ranges (Brown) 1. Alaska Range 2. Alps 3. Andes Mountains 4. Appalachian Mountains 5. Atlas Mountains 6. Himalaya Mountains 7. Hindu Kush Mountains 8. Rocky Mountains 9. Ural Mountains Deserts (Tan) 1. Atacama Desert 2. Gobi Desert 3. Great Sandy Desert 4. Kalahari Desert 5. Namib Desert 6. Sahara Desert 7. Syrian Desert 8. Niger River 9. Nile River 10. Rio Grande 11. Tigres River 12. Yangtze River 13. Yellow River Please Draw & Label the Following: Arctic Circle (@66.5 Degrees N Latitude) Equator (0 Degrees Latitude) Tropic of Cancer (@23.5 Degrees N Latitude) Tropic of Capricorn (@23.5 Degrees S Latitude) Antarctic Circle (@66.5 Degrees S Latitude) Prime Meridian (0 Degrees Longitude) International Date Line (180 Degrees Longitude) 6
7 Map #1 - Bodies of Water, Straits and Rivers 7
8 Map #2 Mountains, Deserts, Peninsulas and other Landforms 8
9 Map #3 - AP World Regions 9
10 Name: Period: Date: Assignment Three NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION SHORT ANSWER Chapter 2, First Farmers: The Revolutions of Agriculture, 10,000 B.C.E -3,000 B.C.E., Study Guide, (With Sources: pp ) CHAPTER IS AVAILABLE ON: McKinleyTech.org Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources The Agricultural Revolution in World History 1. What were the revolutionary transformations brought about by the Neolithic or Agricultural Revolution? 2. What was the importance of intensification in the Neolithic Age? Comparing Agricultural Beginnings 3. What accounts for the emergence of agriculture after countless millennia of human life without it? 4. What were the indications that the transition to a fully agricultural and domesticated new way of life took place quickly in the Fertile Crescent region? 5. Why did animal domestication precede the domestication of plants in Africa? (present day Sudan) 6. While sorghum was the first grain to be tamed in Eastern Africa, what plants were important crops in West Africa? 7. Why did the peoples of America lack sources of protein, manure, and power to pull carts? The Globalization of Agriculture 8. In what ways did agriculture spread? 9. Describe the development of agricultural societies in the southern half of he African continent beginning around 3,000 B.C.E. 10
11 10. Where was agriculture sometimes resisted? Why? 11. What was the impact on the environment from farmers and herders? Social Variations in the Age of Agriculture 12. Describe the 3 different kinds of societies that emerged out of the Agricultural Revolution. (Who were they? How were they organized? pp ) 13. After reading about Catalhuyuk in Turkey, why do you think the people designed their city the way they did? Visit these websites for more background information: This website is interactive. Second Thoughts What s the significance? Do you know the significance of these terms? Fertile Crescent Secondary production revolution Diffusion Pastoral societies Bantu migration Catalhuyuk People of Australia Agricultural villages 11
12 Stateless societies Domestication Chiefdoms Animal husbandry Big Picture Questions 1. The Agricultural Revolution marked a decisive turning point in human history. What evidence might you offer to support this claim, and how might you argue against it? 2. How did early agricultural societies differ from those of the Paleolithic era? How does the example of settled gathering and hunting peoples such as the Chumash complicate this comparison? 3. Was the Agricultural Revolution inevitable? Why did it occur so late in the story of humankind? 4. The Agricultural Revolution provides evidence for progress in human affairs. How would you evaluate this statement 12
13 Name: Period: Date: Assignment FOUR SUMMER READING FOR AP WORLD HISTORY A History of the World in Six Glasses By Tom Standage A summer reading assignment is the beginning of most Advanced Placement courses. This year`s summer reading assignment for AP World History is A History of the World in 6 Glasses by Tom Standage. This book traces the history of the world though a discussion of beverages that people drank in various time periods beer, wine, spirits, coffee, tea and Coca-Cola. Reading the book will help you develop a perspective on our yearlong study of history of world civilization in AP World History. A PDF copy of this book is available at: Standage, Tom. A History of the World in 6 Glasses ISBN-10 (for paperback edition): or ISBN-13: *** Disclaimer: The use of this book as a summer reading assignment in no way represents any endorsement by Mr. Shaw or McKinley Technology High School of the use or misuse of any of these beverages, alcoholic, caffeinated, or otherwise. The book merely offers an innovative and interesting perspective to initiate our year-long discussion of world history. *** A HISTORY OF THE WORLD IN SIX GLASSES GUIDED READING QUESTIONS: As you read, answer the attached reading questions for each chapter. Your answers need to be thorough, but do not need to be lengthy- 3 to 4 sentences should suffice. INTRODUCTION 1. What is the author`s main thesis (argument) in setting up his book? Why/how are these fluids vital? 2. Why did water get replaced by other beverages in human settlements? BEER IN MESOPOTAMIA AND EGYPT (CHAPTERS 1 AND 2) 1. What remarkable shift began happening about 12,000 years ago? Where did it happen? 2. Describe the ratchet effect which caused farming to spread beyond the Fertile Crescent. 3. How might beer have influenced the transition from hunting and gathering (Paleolithic) to agricultural based (Neolithic) societies? 13
14 4. What does the story of beer tell you about social and gender roles in ancient SW Asia and Europe? 5. How important do you think beer was in the growth and diffusion of the earliest civilizations? Would the earliest civilizations of SW Asia and Egypt have been as prosperous without the discovery of beer? 6. What sources does the author use to gather his information on the use of beer and early civilizations? 7. What is the relationship between early civilizations and writing? Civilizations and health? WINE IN GREECE AND ROME (CHAPTERS 3 AND 4) 1. Based on the story at the beginning of this chapter, DESCRIBE how rulers showed power and authority in early civilizations and empires. Then, ANALYZE why these methods were effective at that time. 2. What does the story of wine tell you about social and gender roles in the Mediterranean world? How did this change over time? 3. What effect does wine have on the development of Christianity and of Islam (separately)? 4. How and why did wine evolve into a status symbol in Greece? 5. What does the movement of wine show us about Rome and trading networks during this period of history? 14
15 6. How was the complex social hierarchy of Rome revealed by wine? 7. Describe and analyze the relationships between wine and empire, and wine and medicine and religion in Rome. SPIRITS IN THE COLONIAL PERIOD (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6) 1. In the 18th century, how did spirits change the balance of power amongst the western European nations (particularly Britain and France)? 2. Describe how spirits were first invented by Muslim scholars and then spread as a medicine to Europe. 3. Describe and analyze the links between slavery, sugar, and alcohol. Then, explain how it was used by European explorers and naval forces. 4. Why were spirits an important staple in Colonial America? 5. How did rum play a role in the American Revolution? 6. What is the connection between spirits and colonization? 15
16 COFFEE IN THE AGE OF REASON (CHAPTERS 7 AND 8) 1. Was coffee the first true global beverage? Why or why not? 2. How (and why) did coffee play a pivotal role in the Enlightenment and French Revolution? 3. What different regions of the world were connected through the coffee trade? What role did each place have in trade? 4. What important functions did coffee houses serve in the flow of information in the 1600s and 1700s? 5. How did coffee and coffeehouses impact the following: a. Scientific thought b. Business c. Political thought TEA AND THE BRITISH EMPIRE (CHAPTERS 9 AND 10) 1. Why was tea important to China`s economy, and how did it affect China`s relationships with other countries? 2. Explain the relationship between tea and the Industrial Revolution. 3. Compare and contrast how the British trade in tea affected America and India. 4. Why was the British Empire called this vast empire on which the sun never sets? 16
17 5. How did tea reach England? How did it spread from the very top of society to the drink enjoyed by coalcarters and common working people? 6. How did Britain become a drug-dealing nation, in order to retain and grow their access to tea? 7. How do the actions of Britain against China during this period show the impact of the Industrial Revolution on power relationships in the globe? COCA-COLA AND THE RISE OF AMERICA (CHAPTERS 11 AND 12) 1. How does the story of Coca-Cola relate to the rise of capitalism and entrepreneurship in the 19th and early 20th century? How does this story show a larger global economic shift? 2. How does Coca-Cola affect people`s views of the United States? Is the spread of Coca-Cola an example of Americanization around the world? 3. How did Coca-Cola successfully market its product? EXPLAIN how this example shows the development of consumer culture. 4. ANALYZE how these developments exhibit the idea of globalization. 17
18 EPILOGUE- BACK TO THE SOURCE These should be answered in 6-8 sentences. 1. Do you agree or disagree with Standage`s argument in the epilogue? Will water be the most influential beverage in shaping the global situation of the next 100+ years? Why or why not? 2. Define Developed World and Developing World. 3. What differences can you see in these two Worlds based on their issues with this beverage? 18
The assignments listed below are MANDATORY and are pledged. Reading questions are due the first day of school Maps due on the second week of class.
 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017-2018 A summer reading assignment is the beginning of most Advanced Placement courses. This year s summer reading assignment for AP World History is A History of
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017-2018 A summer reading assignment is the beginning of most Advanced Placement courses. This year s summer reading assignment for AP World History is A History of
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT,
 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT, 2015-2016 A summer reading assignment is the beginning of most Advanced Placement courses. This year s summer reading assignment for AP World History is A History of
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT, 2015-2016 A summer reading assignment is the beginning of most Advanced Placement courses. This year s summer reading assignment for AP World History is A History of
Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources
 Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Name Per. Robert W. Strayer Ways of the World: A Brief Global History Ways of the World: A Brief Global History with Sources Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. What was the first hominid species to use fire in a
Questions? or
 Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Students taking AP World History in the fall must complete the following summer reading assignment: A History of the World In Six Glasses by Tom Standage. The students will be tested on the content of
Mr. Lessard NAME
 NAME AP World History Summer Assignment 2018-2019 COMPLETE AND TURN IN ON FIRST DAY OF CLASS Future AP World Students, In preparation for AP World History, you are required to complete a THREE-part assignment
NAME AP World History Summer Assignment 2018-2019 COMPLETE AND TURN IN ON FIRST DAY OF CLASS Future AP World Students, In preparation for AP World History, you are required to complete a THREE-part assignment
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera. 1.) Define: bipedalism, primary source and Paleolithic Age.
 Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
Name AP World Summer Institute Assignment, 2015 Ms. Scalera This assignment requires the use of the text AP World History: An Essential Course book, 2 nd Edition by Ethel Wood. Directions: you will need
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2019
 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2019 About the APWH course: You have chosen to join the fastest growing AP course in America. AP World History is a rigorous yet enriching course of study. This college-level
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2019 About the APWH course: You have chosen to join the fastest growing AP course in America. AP World History is a rigorous yet enriching course of study. This college-level
Advanced Placement World History SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS
 Advanced Placement World History SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS 2018-2019 This assignment is due on the first day of school by 8am. Your document must be shared with me via Google Docs by then. If you finish
Advanced Placement World History SUMMER READING ASSIGNMENTS 2018-2019 This assignment is due on the first day of school by 8am. Your document must be shared with me via Google Docs by then. If you finish
Name: QHS Social Studies Period:
 World History Quincy High Summer Reading: History of the World in 6 Glasses...Tom Standage's bright idea really is bright: "A History of the World in 6 Glasses," a book that divides world history into
World History Quincy High Summer Reading: History of the World in 6 Glasses...Tom Standage's bright idea really is bright: "A History of the World in 6 Glasses," a book that divides world history into
SUMMER WORK 2018 AP Human Geography Ms. Sommer Mahoney 11;
 SUMMER WORK 2018 AP Human Geography Ms. Sommer Mahoney 11; smahoney@wma.us AP Human Geography 2018 Summer Work Read A History of the World in 6 Glasses by Tom Standage This book, through the lens of beverages,
SUMMER WORK 2018 AP Human Geography Ms. Sommer Mahoney 11; smahoney@wma.us AP Human Geography 2018 Summer Work Read A History of the World in 6 Glasses by Tom Standage This book, through the lens of beverages,
What was Africa like before global integration?
 What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
What was Africa like before global integration? will be establishing sea-based empires in the Americas and trading-post empires in Africa and Asia The land empires (,,,, and ) expand dramatically Gunpowder,
Prehistory Overview & Study Guide
 Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Prehistory Overview & Study Guide Big Picture: Peopling the Earth: The first big event in this course is the spread of humans across the earth. This is the story of how communities of hunters, foragers,
Name Date Period. Social Studies Midterm Review Packet. Exam Date: Room#
 Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
Name Date Period Social Studies Midterm Review Packet Exam Date: Room# Part 1: Five Themes of Geography Directions: Write the theme of geography on the line next to the correct definition or example. relative
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE)
 AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World Map Packet Part 1 (World History from the 1 million BCE to 1500 CE) Please read the directions at the top of each map. Please be sure to label everything with the proper name, and not just number
AP World History Summer Assignments
 AP World History Summer Assignments jimenezj@ivyacademia.com 1. You will need to read the first four chapters in the AP textbook: World History by William J. Duiker and Jackson J. Spielvogel: you can check
AP World History Summer Assignments jimenezj@ivyacademia.com 1. You will need to read the first four chapters in the AP textbook: World History by William J. Duiker and Jackson J. Spielvogel: you can check
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to
 SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BC to 500 BC. SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins,
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace B.C.
 CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
CIVILIZATION IN AFRICA NUBIAN Necklace 1700 1550 B.C. overview - How and why did Civilization emerge? Archaeological record demonstrates that early humans practiced nomadism for many thousands of years
Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Traveling Asia s Silk Road Use with pages 102 104. Vocabulary emperor the ruler of an empire magnetic compass a tool sailors use to see what direction they are traveling The
Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25
 Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
Due Date: I. PREHISTORY 1. Define prehistory: A. Archaeology and Anthropology 1. Define archaeology: Chapter 1 Reading Guide/Study Guide Section One Early Humans (pages 19 25 Name: 2. Define artifacts:
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies?
 How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
How did the Neolithic Revolution transform human societies? The history of the universe is greater than the history of humanity. This Cosmic History or Big History dates back to the Big Bang (around13.7
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange. Key Concept 2.3
 Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Emergence of Transregional Networks of Communication and Exchange Key Concept 2.3 Breaking down the standard With the organization of large-scale empires, the volume of long-distance trade increased dramatically
Students will be assessed through answering of the questions that follow as well as with a reading quiz.
 Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
Summer, 2017 Dear Parents: Background knowledge in the various cultures, political and economic vocabulary and geography has traditionally been among the biggest obstacles to success for our students.
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations
 CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
CHAPTER ONE From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered
Ancient Civilizations Project
 Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Ancient Civilizations Project Step One: Choose and research an early civilization with your group members. Step Two: Create a Power Point document to use during your presentation. Bibliography to be included
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads
 Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
Geography of the Middle East, an ancient and modern crossroads By WGBH Educational Foundation, adapted by Newsela staff on 01.09.18 Word Count 1,035 Level 1040L Image 1: The Nile River runs through the
The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
GUIDED READING The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade A. Analyzing Causes and Recognizing Effects As you read this section, note some cause-and-effect relationships relating to the European colonization
SC06SS Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago?
 PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
PASS Social Studies Grade 6 Test 1 SC06SS060101 1. Which innovation can be credited to hunter-gatherers who lived over 10,000 years ago? A the use of fire for cooking and heat B the use of concrete in
NAME DATE CLASS. Paleolithic Sites in Europe and Southwest Asia GREECE. Crete EGYPT
 Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during the
Lesson 1 Hunter-Gatherers ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do people adapt to their environment? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What was life like during the Paleolithic Age? 2. How did people adapt to survive during the
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires
 Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Eastern Hemisphere African Empires Eastern Hemisphere in the Middle Ages Europe Asia Africa India Background: During the Medieval Period several major trade routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere.
Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST
 SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
SECTION Note Taking Study Guide UNDERSTANDING OUR PAST Focus Question: What have scholars learned about the ancestors of humans, and how have they done so? A. As you read Studying the Historical Past and
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 1: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Exploration and the Colonial Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW Native Americans develop complex societies. Starting in 1492, Europeans
Chapter 2 NOTES. RPC: What role did the Nile River play in the development of Egyptian civilization?
 Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Chapter 2 NOTES Lesson 1 Classifying: Use the following graphic organizer to identify people's social roles in Egyptian society. Upper: pharoah, nobles, priests. Middle: merchants,artisans,scribes,tax
Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies
 Name: Date: Period: Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies Directions : Answer the questions using evidence from the documents provided. Historical Context The Neolithic revolution states
Name: Date: Period: Document Based Question Emergence of Complex Societies Directions : Answer the questions using evidence from the documents provided. Historical Context The Neolithic revolution states
River Valley Practice Test Block:
 River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
River Valley Practice Test Name: Block: 1. Subsistence farming can best be defined as A) harvesting a surplus of crops to be sold for profit B) producing just enough food for a family s survival C) domesticating
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind.
 The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
The study of past societies through an analysis of what people have left behind. Artifacts are those things that people left behind, they can include: Tools and Weapons Pottery Jewelry Art and Sculpture
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade
 World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
World History and Geography to 1500 A.D. Unit VII Eastern Hemisphere Trade During the Medieval Period (500 to 1500 A.D.), several major trading routes developed in the Eastern Hemisphere. These trading
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS
 YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
YEAR AT A GLANCE- MAJOR TOPICS First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks STUDYING GEOGRAPHY Chapter 2 Lesson 1 Maps and Globes The Six Essential Elements of Geography Geographic
WHI.02: Early Humans
 WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
WHI.02: Early Humans WHI.2 The student will demonstrate knowledge of early development of humankind from the Paleolithic Era to the agricultural revolution by a) explaining the impact of geographic environment
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet
 Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
Unit 2: Three Worlds Meet HISTORICAL OVERVIEW Time Frame: more than 14,000 years ago. Native Societies Adaptation to diverse natural environments Cultural Differences Similarities Language Shelter Labor
Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam. Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height
 Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Terms and People Muhammad the prophet and founder of Islam Mansa Musa a Muslim ruler of the Mali empire during its height Terms and People navigation the science of locating the position and plotting the
Lesson 2: China s Past. Ancient China
 Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Lesson 2: China s Past Ancient China Vocabulary ancestor - a relative who lived longer ago than a grandparent civil service - the practice of using skills and talents to work in the government middleman
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa
 Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Kingdoms & Trading States of Medieval Africa Early Societies in West Africa 500-1600 CE Table of Contents Background Africa s Four Climate Zones Africa s Four Vegetation Zones Africa s Vegetation Map Early
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Packet 7. Movement of People and Goods
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Packet 7 Movement of People and Goods Theme: MOVEMENT MIGRATION: TRADE The movement of peoples People move because: o 1) rights are being denied (Jews from Egypt,
AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
2015 AP WORLD HISTORY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT DURING THE NEXT SCHOOL YEAR, WE WILL COVER EVERYTHING THAT S EVER HAPPENED EVER. TO GET US A BIT OF HEAD START, YOUR TASK THIS SUMMER IS TO COVER THE FIRST PERIOD
SOL Narrative Review. with questions
 SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
SOL Narrative Review with questions Day 1 Early Humans Homo sapiens (humans) emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. They then migrated from Africa to Eurasia, Australia and the Americas
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy
 early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
early human history and Central & South America Jeopardy What You Need To Know Every team will be chosen by Joe with the intention of mixing girls and boys and grade levels. Teams can choose a name if
SOL Review - Geography
 SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SOL Review - Geography I. Review Reading and Interpreting Maps, Diagrams & Pictures on the SOL A. Examine any chart, graph, map or other illustrations that accompanies the question. Examine the illustration
SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES
 NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
NAME DATE PERIOD WORLD HISTORY I WINTER 2015 WHI MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1 KEY TERMS LOOK AT THE LIST OF TERMS AND HIGHLIGHT OR STAR THE ONES YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND OR KNOW. AS YOU ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11 Reading Guide The Americas on the Eve of Invasion p
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11 Reading Guide The Americas on the Eve of Invasion p.244-264 INTRODUCTION p.244 1. Where does the term Indian, as applied to Native Americans, come from? 2. Did Indians see
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 11 Reading Guide The Americas on the Eve of Invasion p.244-264 INTRODUCTION p.244 1. Where does the term Indian, as applied to Native Americans, come from? 2. Did Indians see
Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: Migration to the Americas Use with pages 54 57. Vocabulary Ice Age a long period of extreme cold glacier a thick sheet of ice migrate to move theory an explanation for something
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States
 Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Paleolithic Era to Mesopotamian City-States Before History Prehistory = the period before written records. Archaeological information Archaeology = the study of structures of past societies by analyzing
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers. Mesopotamia
 Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
Mesopotamia: Land Between the Rivers Mesopotamia The many people of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer s city-states) (3000 B.C. - 1800 B.C.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) (1800 B.C. - 1200 B.C.
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago. Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu
 The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
The First People 5 million-5,000 years ago Picture source: humanorigins.si.edu Terms to Know Prehistory Hominid Ancestor Tool Paleolithic Era Society Hunter-gatherers GROUP 1 STARTS HERE What you will
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review
 Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Unit 2 Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia Unit Test Review Mesopotamia - Fertile Crescent Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Early
Early Humans Interactive Notebook
 Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Early Humans Interactive Notebook Contents Included in this resource 1. A Note for the Teacher 2. How to use this resource 3. Photos of every page in use. You are welcome to use them as inspiration for
Medieval Trade Systems
 Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
Medieval Trade Systems Learning Goal! Analyze how the Silk Route and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and explain how the slave trade in East Africa developed. Take notes in
The Civilizations of America
 The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
The Civilizations of America advanced societies were developing in isolation in the Americas While classical civilizations were developing in the Mediterranean & Asia Text Title During the Neolithic Revolution,
8 HOW DID THE WORLD ZONES CONNECT?
 8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
8 HOW DID THE S CONNECT? The rise of agriculture ushered in an era of increasing innovation in communication and transportation that led different parts of the world to connect in meaningful new ways.
Student s Name: Subject: Social Studies
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 9 A Subject: Social Studies Teacher Signature Choose the correct answer. REVISION SHEET SOCIAL STUDIES-9A 1.)Which of the following statements
Archaeologists Archaeologists are a type of They too study the culture and societies of people, only they study people
 What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
What is Prehistory? Before we can learn history, first we have to understand Man only learned to write years ago When stuff started to get written down, that s the start of Humans, and their ancestors,
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations B.C.
 Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Unit 1-Part 1 From the Origins of Agriculture to the First River- Valley Civilizations 8000-1500 B.C. ! Civilization- 1. Cities of administrative centers 2. A political system based on defined territory
Chapter 1 Worlds Apart
 1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
1 Chapter 1 Worlds Apart Practice Test 1. Africans primarily came to early European settlements in America A) voluntarily. B) to find employment. C) as slaves. D) looking for trading partners. 2. What
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500
 The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
The World before the Opening of the Atlantic BEGINNINGS 1500 What you will Learn Buffalo graze on the plains in South Dakota. Millions of these animals used to roam lands from Canada to Texas. In this
Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand
 WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
WARM-UP: IN WHAT COUNTRY WERE YOUR SHOES MADE? Top #7 Shoe-Manufacturing Countries in 2016 China India Brazil Vietnam Indonesia Pakistan Thailand INTERNATIONAL TRADE: MING CHINA & THE INDIAN OCEAN NETWORK
The First People. The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language.
 The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
The First People The Big Idea Prehistoric people learned to adapt to their environment, to make simple tools, to use fire, and to use language. Main Ideas Scientists study the remains of early humans to
Bell Ringer: August (), 2017
 Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
Announcements: 1: Vocabulary List due at the end of the six weeks 2: Google survey due Friday, 8/31 You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Join the Neolithic Revolution! Cartoon 3: Copy of the Paleolithic/Neolithic,
Valuable AP World History Map Information (Adapted from 5 Steps to a Five)
 Valuable AP World History Map Information (Adapted from 5 Steps to a Five) Region Major Countries Major Rivers Major Landforms Historical Example(s) East Asia China, Japan, North Korea, Yalu River, Huang
Valuable AP World History Map Information (Adapted from 5 Steps to a Five) Region Major Countries Major Rivers Major Landforms Historical Example(s) East Asia China, Japan, North Korea, Yalu River, Huang
What Will You Learn In This Chapter?
 Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Chapter 2 - The Expansion of Trade Connecting Prior Knowledge: In the previous chapter, you explored some of the ways that society, religion, and a changing economy affected worldview. You saw how towns
Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: The Voyages of Columbus Use with pages 134 138. Vocabulary expedition a journey made for a special purpose colony a settlement far from the country that rules it Columbian Exchange
 Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
Document #1: Great Wall of China Throughout China s history, they often worried about the nomads that lived along the northern border. Shi Huangdi finally developed a way to end the border wars. He ordered
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse.
 I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
I. Development of Early African Civilization A. The geography of Africa is diverse (varied). This makes the cultures of Africa very diverse. 1. The geography of Africa consists of mountains, grasslands,
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 808 Level 960L Viking Leif Eriksson discovers North America
The Fertile Crescent and the Promised Land
 Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Biblical Geography Basics NT110 LESSON 05 of 10 Jack Beck, Ph.D. Experience: Author and faculty member at Jerusalem University College in Israel Introduction There is geography in my Bible, and much of
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere
 Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Guided Notes Mrs. Watts Eastern Hemisphere China covers an area of nearly 4 million square miles, about the same size as the United States. One of the physical barriers that separates China from its neighbors
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
Slide 1 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 Paleo-Indians Paleo from palaios ( ancient in Greek) Indians from Columbus mistake Beringia Ice sheet across the Bering Strait that connected
earliest recorded history to today. writing art artifacts Centuries-old written records reveal a long-lasting civilization in
 Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
Score Chapter 4: Ancient China Lesson 2: China s Past Textbook pages 106 to 112 Name: Ms. Samuels - answers Class/Period: Date: Essential Questions Notes: The culture has been continuous, or unbroken,
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013
 History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
History Department EXAMINATION-JULY 2013 Grade: 7 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 80 Examiner: E.Aposporis Moderator: V.Du Toit Instructions: 1. The question paper consists of 6 pages. Please check that your paper
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History
 The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The First Civilizations Unit 1. Ancient and Classical Civilizations AP World History Essential Question How did the first civilizations form and what were their achievements? Specific Objectives " Identify
The Age of European Explorations
 The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
The Age of European Explorations 1400-1800 By the 1400 s Europeans were in contact with Africans, Asians, and Americans. This is known as the GLOBAL AGE. Wherever Europeans went, they brought their culture
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World. The Olmec:
 Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Student Handout #4: Era 3 Societies around the World As you read about four different societies below, think about your claims related to empires from Student Handout #3. What are important features for
Unit 3: European Explorers
 Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: European Explorers http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/european-explorers.html https://quizlet.com/class/5155476/ 1 E x p l o r e r s Motivations, Obstacles, and Accomplishments of European Explorers
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class.
 Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
Unit 3: Mesopotamia Test Respond to each question with the best answer based on what we ve learned in class. 1. Why did ancient civilizations develop in Mesopotamia along the rivers of Tigris and Euphrates?
DO THIS SHEET LAST, AFTER HAVING READ CHAPTER 1. START WITH THE CHAPTER 1 READING GUIDE QUESTION PACKET 1. Where did the human species originate?
 Name: Chapter 1 Reading Guide ADDENDUM Part 1: From Hunting and Gathering to Civilizations, 2.5 Million to 1000 B.C.E.: Origins DO THIS SHEET LAST, AFTER HAVING READ CHAPTER 1. START WITH THE CHAPTER 1
Name: Chapter 1 Reading Guide ADDENDUM Part 1: From Hunting and Gathering to Civilizations, 2.5 Million to 1000 B.C.E.: Origins DO THIS SHEET LAST, AFTER HAVING READ CHAPTER 1. START WITH THE CHAPTER 1
Name Class Date. Down 1. The Maya built these buildings to. 2. The Aztec leader killed by the. 4. He and his troops conquered the
 Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Name Class Date The Early Americas BIG IDEAS 1. The Maya developed a civilization that thrived in Mesoamerica from about 250 until the 900s. 2. The strong Aztec Empire, founded in central Mexico in 1325,
Areas of Heavy Rainfall around 7000 B.C. present
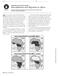 CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
CHAPTE 8 EOAPHY APPLICATION: EION Desertification and Migration in Africa Directions: ead the paragraphs below and study the maps carefully. Then answer the questions that follow. Human migration usually
Ancient Civilizations
 Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1 - The Neolithic Revolution Aim: How did the Neolithic Revolution change society? Do Now: What do you know about cavemen? Jot down up to three bullet points under the title
Unit Objectives. Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations. Analyze the development of Egypt s empire
 Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
Unit Objectives Describe the impact of farming on the development of early civilizations Analyze the development of Egypt s empire Describe the important events in the history of Israel Chapter 1 Test
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization?
 CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
CIVILIZATION (part 1) 1. What is Civilization? 2. How the city of UR exemplifies early civilization? Geography Historians believed that one of the first civilizations arose in Sumer, a region that is now
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. Humans migrate throughout much of the world and begin to develop tools, art, agriculture and cities. The Peopling of the World Prehistory 2500 B.C. SECTION
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia
 Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia What were the most important achievements of the Mesopotamian empires? In ancient Mesopotamia, rulers recorded their greatest achievements on steles. A stele (STEE-lee)
Exploring Four Empires of Mesopotamia What were the most important achievements of the Mesopotamian empires? In ancient Mesopotamia, rulers recorded their greatest achievements on steles. A stele (STEE-lee)
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe?
 EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
EQ: What was the impact of exploration and colonization on Europe? Reasons for Exploration God spread of Christianity Goods to trade and become wealthy (gold and spices) Glory explorers were seen as heroes
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it
 Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Christopher Columbus Didn't Discover the New World; he Rediscovered it By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.20.17 Word Count 941 Level 1050L Viking Leif Erikson discovers North America
Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers
 Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Name Date Assessment: From Hunters and Gatherers to Farmers Mastering the Content Select the letter next to the best answer. 1. What change began the Neolithic Age, about 8000 B.C.E.? A. trading B. hunting
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK
 Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
Score / Name: P: CHAPTER 1 BELLWORK Lesson 1 The First Americans: Migration to the Americas (Pages 1-4 in the Red Book) Reminder: Rephrase the question to form your answer. By the end of this lesson you
the scientific name for us as a species Homo sapiens
 Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
Stone Age Test Study Guide Test: Tuesday, October 23 Format: Matching, Multiple Choice, Free Response Notes: Early Humans, Evolution, Lower Paleolithic Era, Human Migration, Upper Paleolithic Era, Agricultural
Mesopotamian History. Chapter 2 Art History. Roxanna Ford 2014
 Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Mesopotamian History Chapter 2 Art History Roxanna Ford 2014 Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape Is the location of Mesopotamia significant to history? YES! Mesopotamia is located on the alluvial
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1
 Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
Geography Boot Camp Quiz 1 5 minutes to study, then we begin! You ll have 15 minutes to complete the quiz. Remain seated and quiet until I collect the quiz. There is absolutely NO talking during the quiz,
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO
 Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Plain Local 5 th Grade Social Studies SLO Early Civilizations of Western Hemisphere 1. Short Answer: Describe two reasons why the Mayans designed their cities using this layout. Use the picture below to
Ms. Lederer: A.P. Human Geography (APHG) Summer Assignment
 Ms. Lederer: A.P. Human Geography (APHG) Summer Assignment Welcome to one of the most relevant learning experiences of your high school career! Many students take this course without any real understanding
Ms. Lederer: A.P. Human Geography (APHG) Summer Assignment Welcome to one of the most relevant learning experiences of your high school career! Many students take this course without any real understanding
Human Origins Unit Test
 Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
Human Origins Unit Test The following test is over information we have studied from the Human Origins Unit. It assesses student knowledge on the Paleolithic and Neolithic time periods, as well as how we
